NSC 837 - Lecture 5 - chromatic aberrations, 3d reconstructions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
how does light travels
light travels in all directions, in straight lines, from a single source
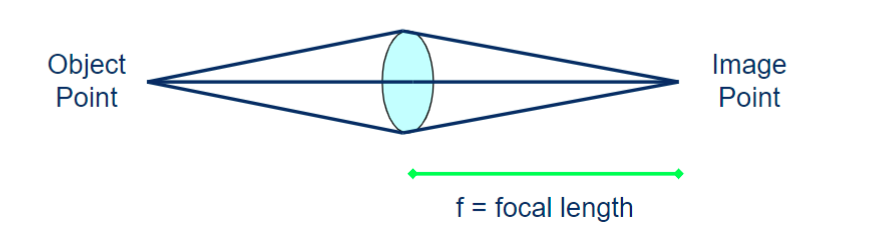
curved lenses (Biconvex)
collect the light and refocus the light rays to the image point
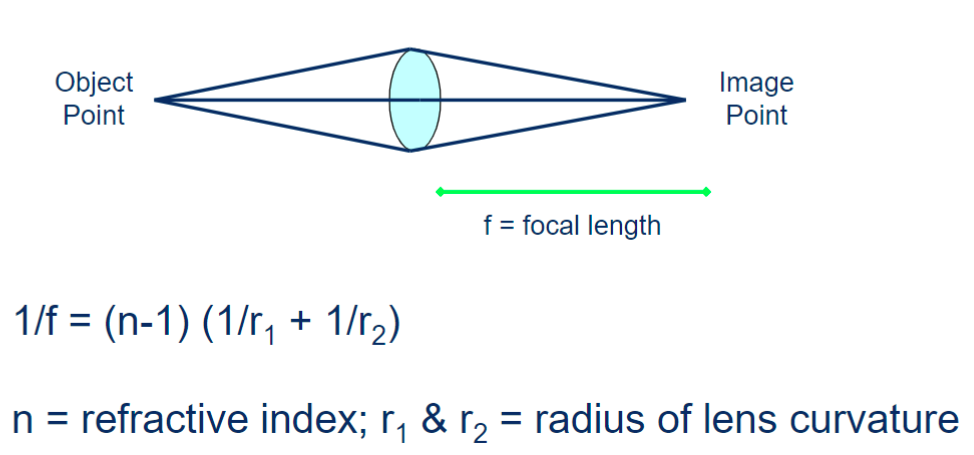
for optical lenses the focus point will depend on…
curvature of the entry and exit sides of lens
refractive index of the lens
what determines the power of the lens…
focal length
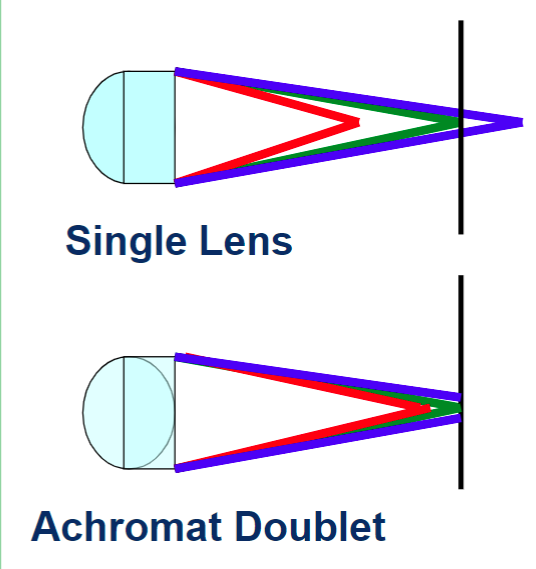
lens aberrations
1st: green and red at different depths, which makes it look like it is coming from different point
2nd: solution (not perfect but BGR much closer to same focal point)
spherical aberrations (optical aberrations)
out of focus light should appear the same above and below the focal point. Spherical abberations affect the focus of light
aplanatic lenses correct aberration
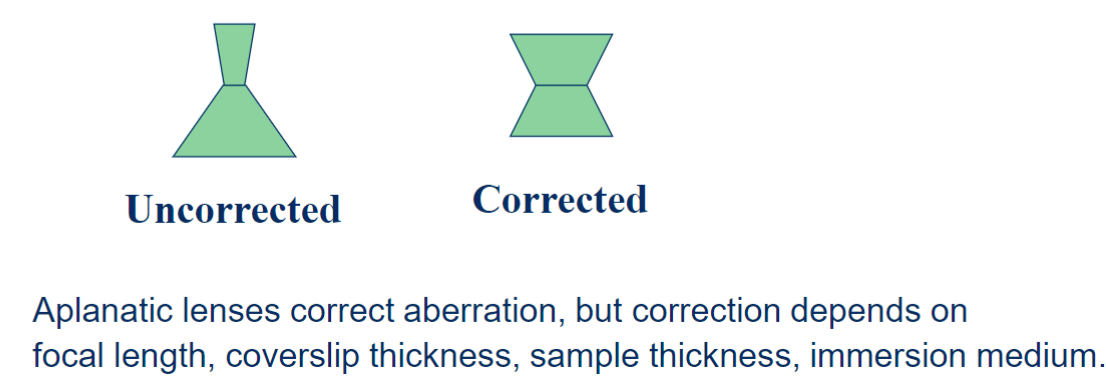
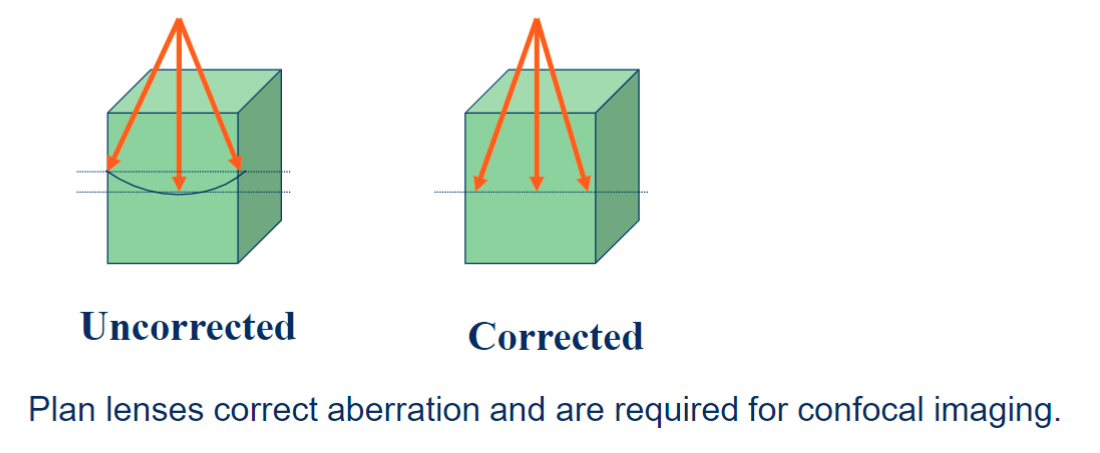
field curvature (optical aberrations)
image plane is not flat axially within fiel
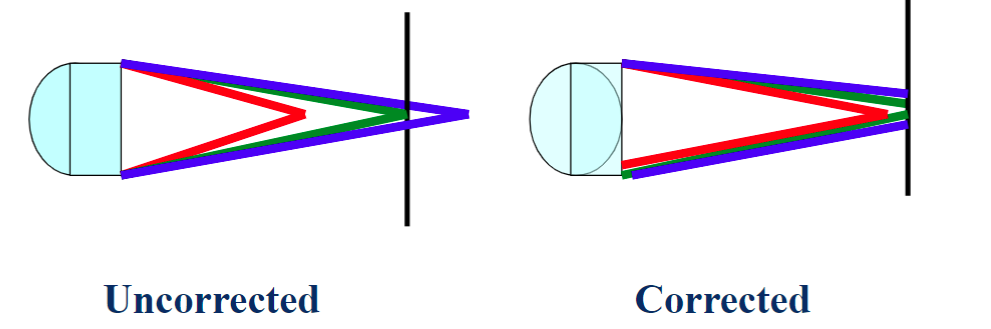
chromatic aberrations (optical aberrations)
different colors may not focus to same point. Especially in Z direction
refraction of light through the lens is wavelength dependent
achromatic corrects B/R apochromat correct B/G/R
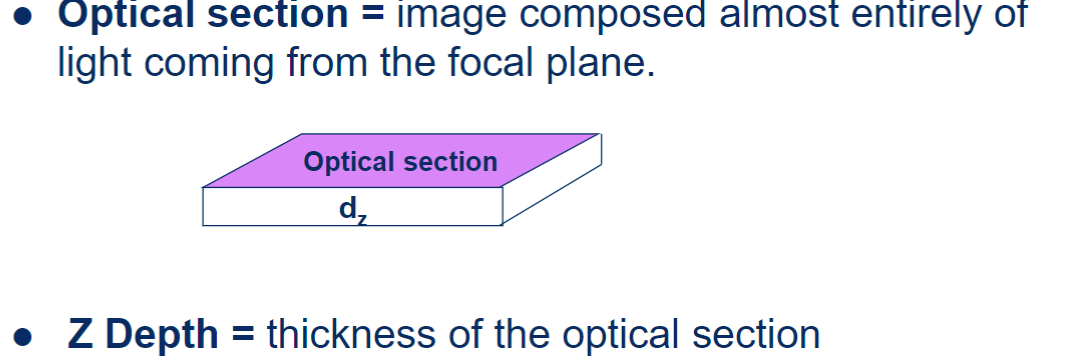
optical section
image composed almost entirely of light coming from the focal plane
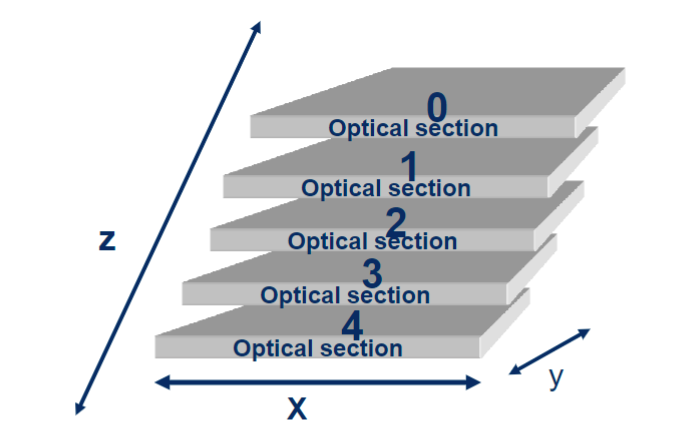
z series
automatic collection of a series of optical sections at defined intervals along z axis
z interval (step size)
distance between the top of one optical section to the top of the next optical section. controlled by the physical movement of the microscope focus (Z-stepper motor). The z inerval is defined by the user
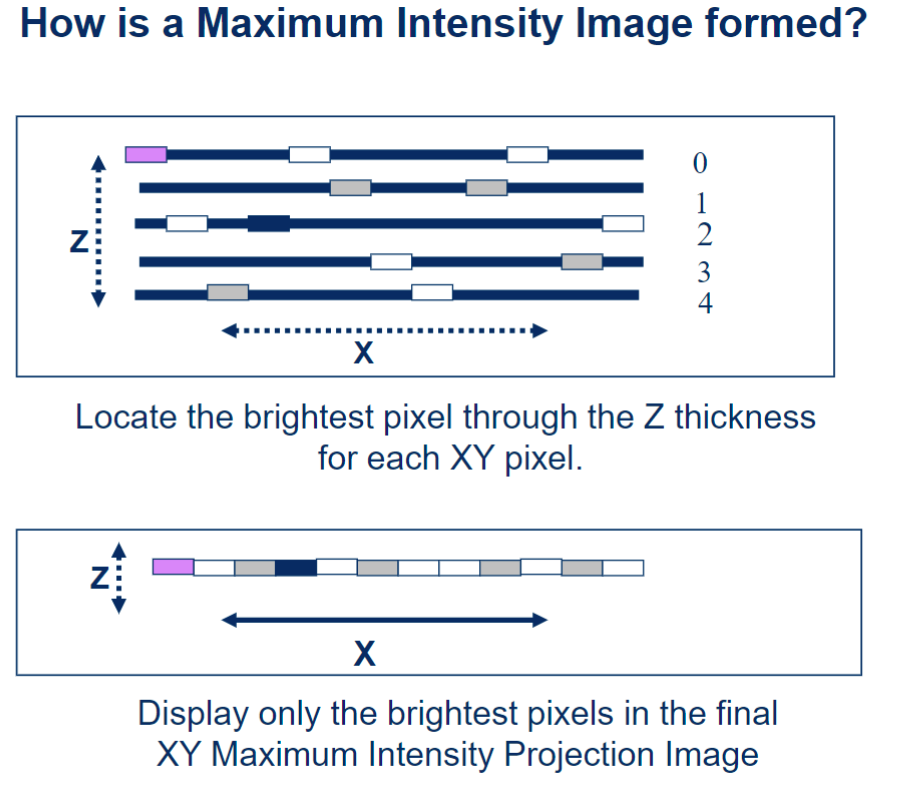
maximum intensity projection (MIP) image (3d rendering)
at each XY pixel, only the most intense pixel is used, regarless of which optical section the pixel comes from