MCAT - Bio/Bchm - Glycolysis
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is the first stage of glycolysis called
investment stage
(1) Glucose → Enzyme? Products?
Hexokinase, Glucose-6-phosphate, ATP → ADP, H+
What is the point of adding the initial phosphate onto Glucose?
It traps Glu in the cell and makes it more reactive while preparing it for the rest of glycolysis
(2) Glucose 6-phosphate → Enzyme? Products?
Phosphoglucose isomerase, Fructose-6-phosphate
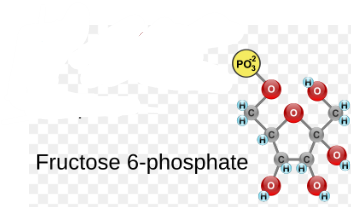
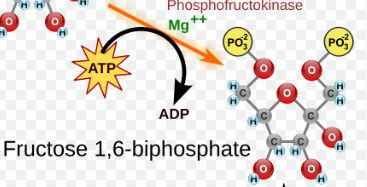
(3) Fructose 6-phosphate → Enzyme? Product?
Phosphofructokinase, Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, ATP → ADP, H+
What is the second stage of Glycolysis Called?
The Cleavage Stage
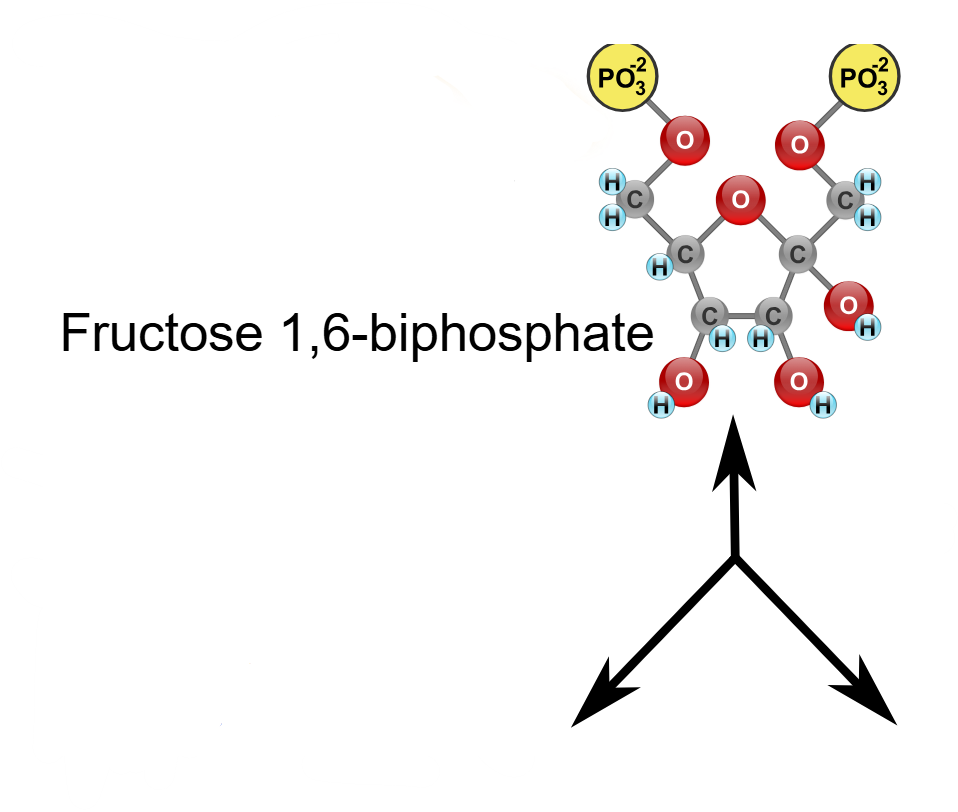
(4) Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate → Enzyme? Products?
Aldolase, Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GAP) and Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)
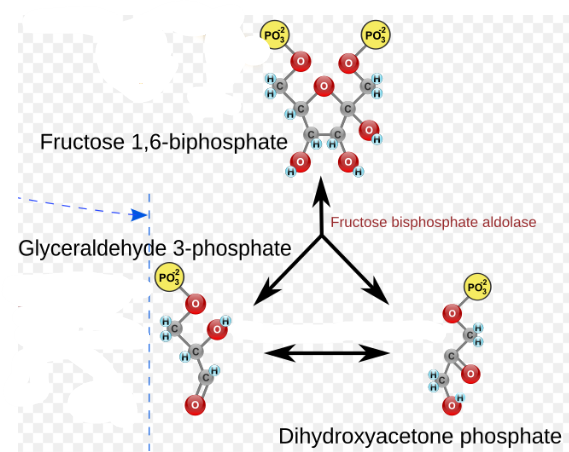
Which isomer do we need to continue with glycolysis? GAP or DHAP?
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GAP) is needed to continue with glycolysis, as it is directly involved in subsequent reactions. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) can be converted to GAP, but it is GAP that is required for the next steps.
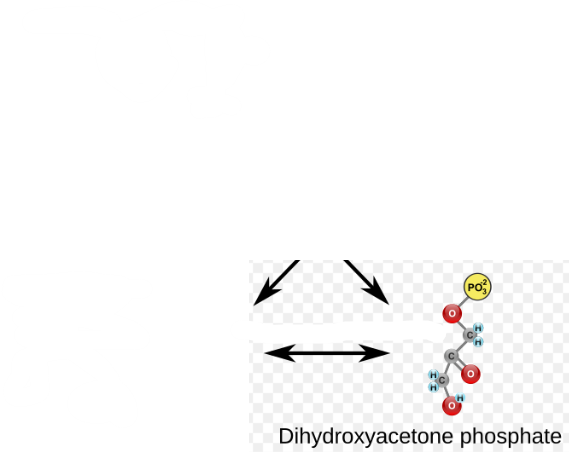
(5) DHAP → Enzyme? Products?
Triosephosphate Isomerase (TPI/TIM), and Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GAP)

What is the use of Stage 3?
The production of ATP, Pyruvate, and NADH

(6) GAP → Enzyme? Products?
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG), along with the reduction of NAD+ to NADH.
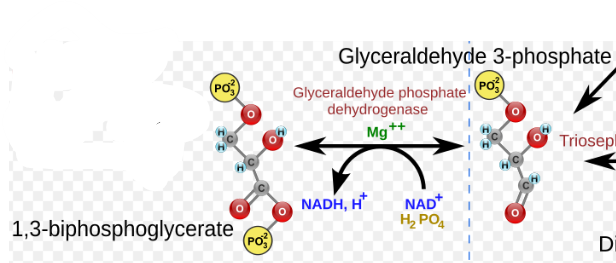
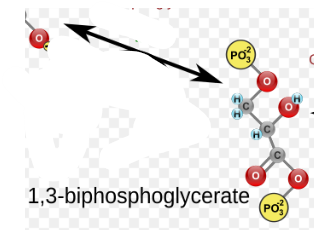
(7) 1,3-BPG → Enzyme? Products?
Phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK), 3-Phosphoglycerate (3-PG) and the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP.
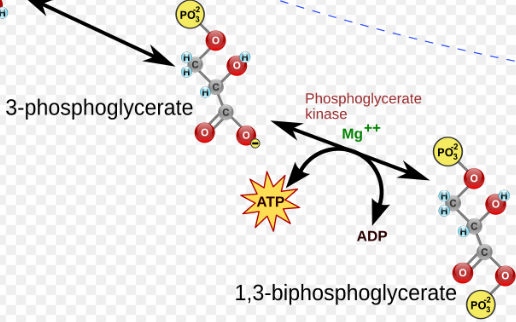
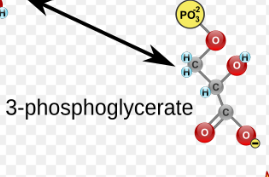
(8) 3-PG → Enzymes? Products?
Phosphoglycerate mutase (PGM), 2-Phosphoglycerate (2-PG).
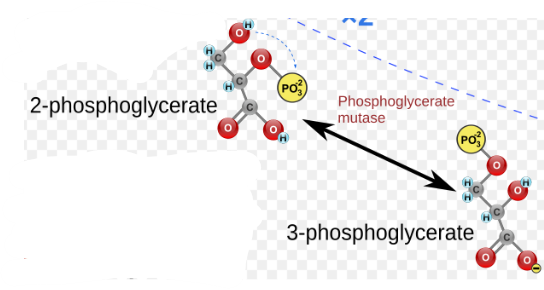
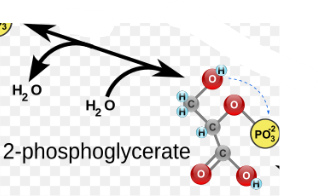
(9) 2-PG → Enzyme? Products?
Enolase (ENO), Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and the release of water.
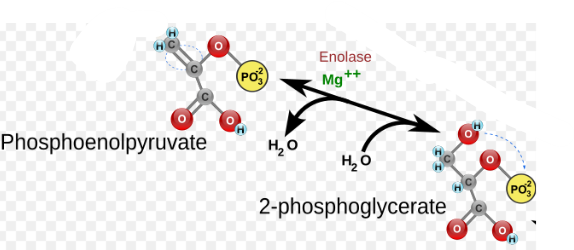
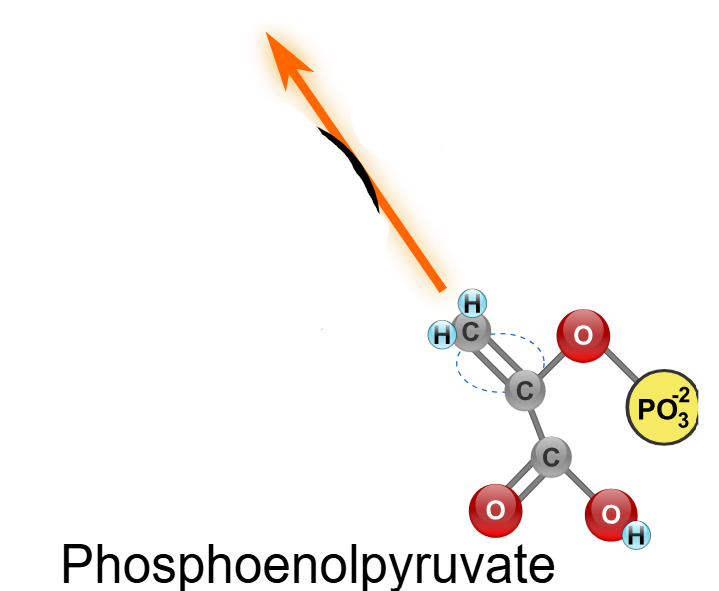
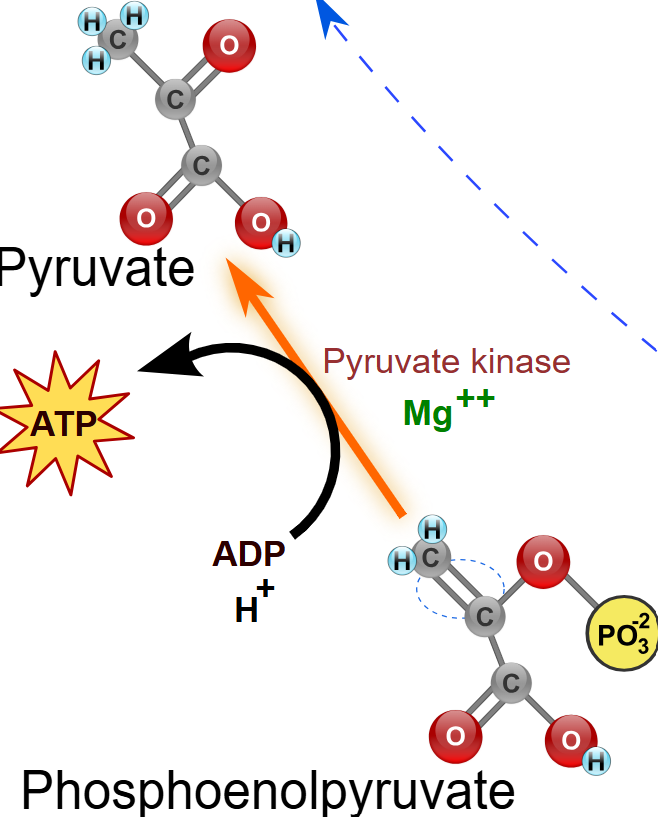
(10) PEP → Enzyme? Products?
Pyruvate kinase (PK), Pyruvate and the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP.
What are the overall net reactants?
Glucose (1), ADP (2), NAD+ (2), Pi (inorganic phosphate) (2)
What are the net overall products?
Pyruvate (2), ATP (2), NADH (2), H+ (2), H2O (2)
Why must Glu be converted to Fructose?
This allows the sugar to be symmetrical, allowing cleavage with equal carbons
Why is the second phosphate added to Fructose 6-phosphate?
It increases the energy of the molecule, making it more reactive for subsequent steps in glycolysis.
It completes the symmetry of the sugar
How many GAP sugars progress to Stage 3?
Two GAP sugars progress to Stage 3.
Why is GAP transformed into 1,3 BPG?
1,3 BPG has a higher potential for phosphoryl transfer
Why is 1,3 BPG Converted to 3-PG
This conversion allows the release of energy by facilitating the transfer of a phosphate group to ADP, forming ATP. Additionally, it prepares the molecule for further metabolism in glycolysis.
Why is 3-PG converted to 2-PG?
The phosphate is brought closer to the negatively charged oxygen, making it less stable and more reactive, which facilitates further transformation in glycolysis and optimizes the energy yield.
This is an endergonic rxn, which requires an input of energy to proceed, making it less stable.
Why is 2-PG converted to PEP?
This is a dehydration rxn that trap it in an enol state, raising phosphoryl transfer potential
What state is pyruvate in?
Ketone state
GLUT 2
GLUT 2 is a glucose transporter primarily found in hepatocytes and pancreatic β-cells, responsible for the facilitated diffusion of glucose from the duodenum.
Excess glucose is taken up by GLUT 2 after a meal
GLUT 4
GLUT 4 is a glucose transporter found in adipose tissues and muscle cells, responsible for insulin-mediated glucose uptake after meals.
Responds to Glu conc. in peripheral blood and the rate is increased by insulin.