Urogynecology
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Pelvic facia, ligaments, and muscle become attenuated, increased intra-abdominal pressure, or atrophy
Pathophys for Pelvic organ prolapse
Multiparity, Age, macrosomic infant, prolonged 2nd stage of labor, mother under 25, AMA+, obesity, hysterectomy, elevated internal abdominal pressure (constipation, COPD), collagen abnormality, fam hx
Risk factors for prolapse
Cystocele (bladder prolapse, anterior)
A herniation of the anterior vaginal wall associated with descent of the bladder
Heaviness, sensation of a bulge, or fullness in the pelvis; sensation of something falling out, symptoms worsen with standing, Relieved when lying down, associated symptoms of frequency, urgency, incontinence or retention
Symptoms of Cystocele (anterior)/ apical (uterine/vaginal vault)
Rectocele (rectal prolapse, posterior)
Herniation of the posterior vaginal segment associated with descent of the rectum
Perineal pressure, obstructive defecation (digital reduction), genital looseness, palpable bulge
Symptoms of rectocele (posterior)
Stage 1
Which stage of prolapse am I describing - in the upper half of the vagina?
Stage 2
Which stage of prolapse am I describing - descending nearly to the vaginal opening?
Stage 3
Which stage of prolapse am I describing - protrudes out of the vagina on valsalva
Stage 4 (procidentia)
Which stage of prolapse am I describing - completely outta the vagina

Normal external genitalia, generalized atrophic changes, visualization of a cystocele and rectocele, cervix descends to the introitus, uterus is normal in size, rectal sphincter tone is decreased, EMB or U/S to evaluate bleeding
Pelvic exam findings for prolapse
cardinal ligaments blend with utero-sacral ligaments (attach to upper vagina, cervix, LUS)
Level I (that girl - major) support is made up of
Paravaginal attachment (keeps it midline and over the rectum) at the level of the ischial spine
Level II supports
Perineal body and membrane, superficial and deep perineal muscles, and endopelvic fascia
Level III (last line - normal position of the distal 1/3) supports are made up of
Baden-Walker System (out), POP-Q (IN)
Staging systems of Prolapse
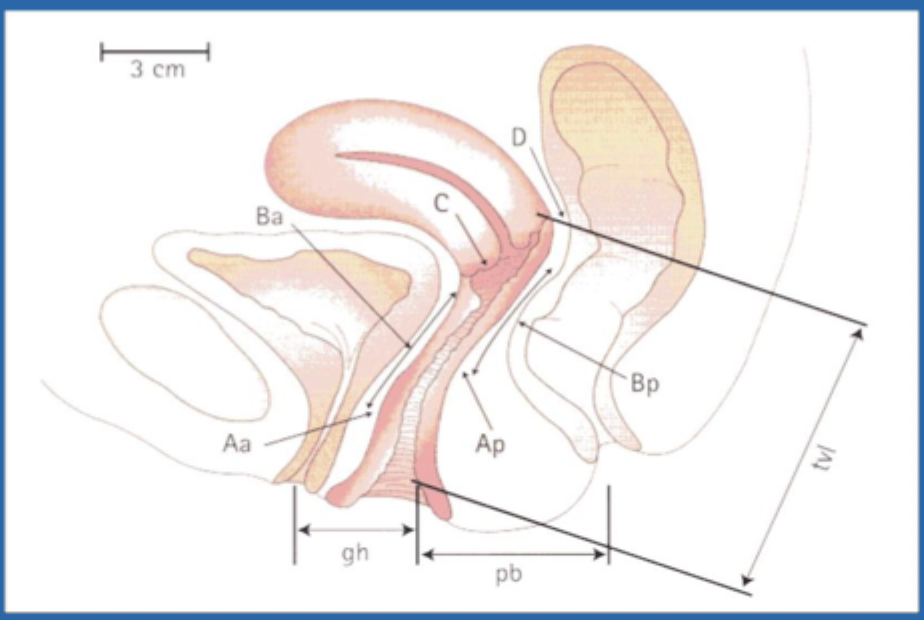
Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification (measure vaginal length and the compartments)
Staging is based on position of vaginal walls relative to the hymen (stage II is -1 - + 1)
Conservative Therapy (pessary, kegels), surgical treatment is indicated with symptomatic or failure of conservative
Treatment of a Prolapse - based on QoL and Associated Symptoms
Prolapse with symptoms and they don’t want surgery or aren't current candidates
Indications for Pessaries
vaginal or abdominal route, Sacrocolpopexy (ASC) 🏆, fixation via sacrospinous, uterosacral ligament or iliococcygeus
Surgeries for Level 1s at the vaginal apex
Midline or lateral (determined by exam), anterior colporrhaphy, paravaginal defect repair (PVDR)
Surgical management of the Anterior Compartment - level II
Posterior colporrhaphy (PR), site specific vs. repair of entire area
Surgical management of the Posterior Compartment - level III
Colpocleisis
A surgical repair of prolapse that is only used in women who no longer desire sexual activity because the vaginal vault is closed off - more durable and lower risk

filling and Storage
Which function of the badder is due to the sympathetic innervation?
Voiding (Pee)
Which function of the bladder is due to the parasympathetic innervation?
Stress Incontinence
Involuntary leakage of urine that occurs if abdominal pressure exceeds urethral pressure or resistance or urine flow (most common in those under 45)
Urethral hyperactivity, laxity of pelvic floor muscles
Etiologies of Stress Incontinence
urine leakage during laughing, cough, sneezing, lifting etc, NO URGE TO PEE
Clinical findings of Stress Incontinence
Kegels (initial 1st line), topical estrogens if postmenopausal, pessaries, Midurethral sling, alpha agonists (midodrine and pseudoephedrine)
Management of Stress Incontinence
Urge incontinence
Involuntary urinary leakage preceded by or accompanied by a sudden urge to urinate (most common in older women)
detrusor muscle OVERactivity leads to uninhibited contractions during filling
Pathophys for Urge incontinence
Increased age, idiopathic, bladder infection, stones or tumor
Etiologies for Urge incontinence
increased urgency, frequency, small volume voids, nocturia - wants to pee can’t make it to the bathroom on time → get a UA to r/o UTI
Clinical findings for Urge incontinence
Bladder training, Lifestyle mods (stop spicy foods, citrus, chocolate, EtOH, and caffeine), Kegels, Antimuscarinics (oxybutynin, tolterodine), Beta-3 agonists (mirabegron), TCAs (imipramine), Botox injections, bladder augmentation
Management of Urge incontinence
Overflow Incontinence
Urinary retention and incomplete bladder emptying leads to involuntary urine leakage once the bladder is full (least common)
Bladder detrusor UNDERactivity or bladder outlet obstruction
Pathophys for Overflow Incontinence
Neurological disorders/autonomic dysfunction (DM, MS, spinal injuries, spinal stenosis, peripheral neuropathy), BPH, uterine fibroids, prolapse, overcorrection of urethra
Etiology for Overflow Incontinence
Loss of urine w/o warning or triggers; leakage/dribbling in the setting of incomplete emptying, weak or intermittent urinary stream, hesitancy, frequency, nocturia
Clinical findings for Overflow Incontinence
Post void residual over 200 mLs, urodynamic testing to r/o urethral obstruction
Diagnostics for Overflow Incontinence
Intermittent/indwelling cath (1st line), Cholinergics (Bethanechol - increases detrusor activity)
Management of bladder atony in Overflow Incontinence
Activates Beta 3 receptors in the detrusor muscle in the bladder, leads to muscle relaxation and increase in bladder capacity - WATCH FOR CARDIAC
MOA for beta 3 agonist

anticholinergics and antispasmodics increase bladder capacity
MOA for Antimuscarinics (oxybutynin, tolterodine)

Stress + urge
Mixed incontinence is made up of