A&P EXAM 3 Immune system and Lymphatic system
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
The lymphatic system functions to:
•Drain interstitial fluid
•Carry out immune responses
•Transport dietary fats
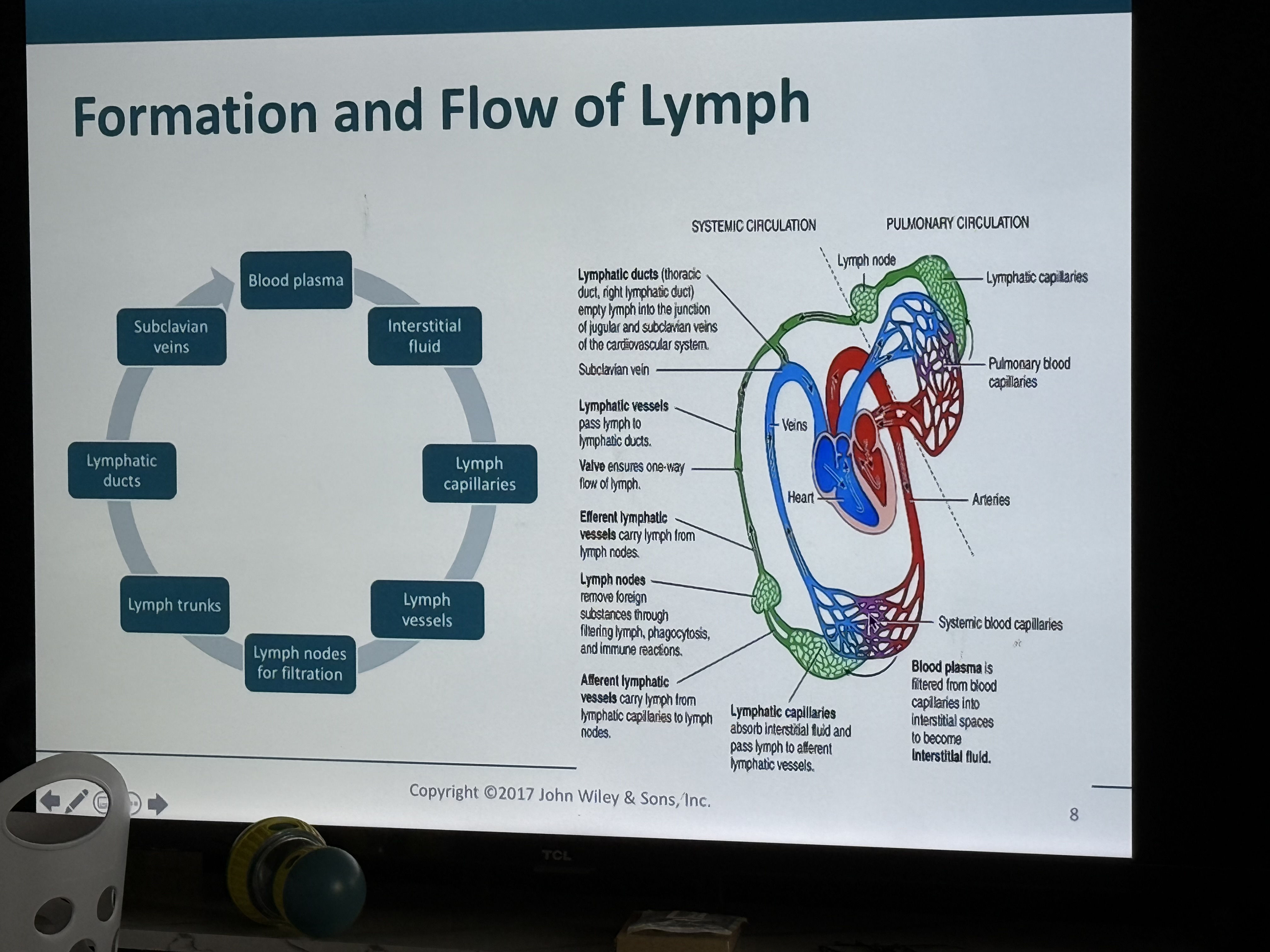
Flow of lymph photo
Hydrostatic pressure (BP) in capillary beds
Forces or pushes fluid and some plasma proteins out
Most reabsorbed at venous end
Remaining fluid becomes part of interstitial fluid between cells
Fluid and plasma proteins must be returned to keep blood volume/blood pressure maintained and to prevent
Edema which is swelling of body tissues
The lymphatic system consists of
several structures and organs that contain lymphatic tissue, bone marrow, thymus, and a fluid called lymph that flows within lymphatic vessels
Lymphatic Vessels transport
filtered fluids back to the blood
Organs & tissues house
The immune cells
•Phagocytic cells and lymphocytes
•“wastewater treatment system”
Components of the Lymphatic System
•Blind lymphatic capillaries
• Lymphatic vessels
•Lymph nodes
• Lymphatic trunks
• Lymphatic ducts
-Thoracic duct
-Right lymphatic duct
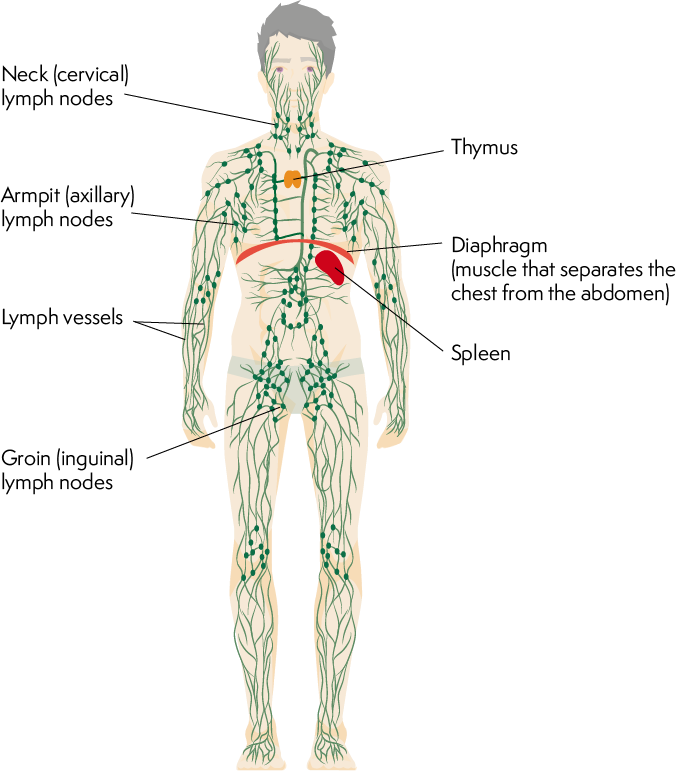
Lymphatic organ photo
Lymphatic capillaries, which are
blind; closed on one end, are located between cells of many tissues
Lymphatic capillaries merge to form lymphatic vessels, which have
thin walls and many valves to prevent backflow since there are no pumps
Lymph vessels pass through
lymph nodes and then merge into lymph trunks
Lymph trunks merge to form the
thoracic duct or the right lymphatic duct
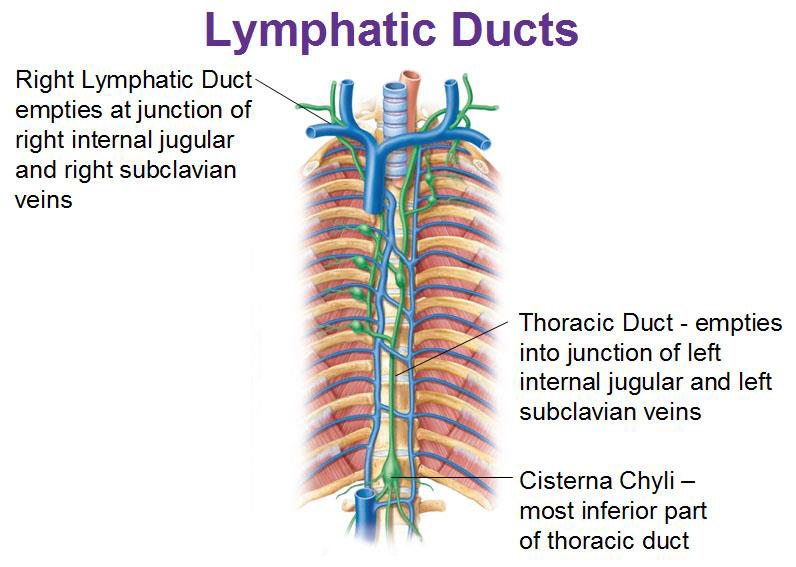
Routes of drainage
Right lymphatic Duct
Empties at junction of right internal jugular and right subclavian veins
Routes of drainage
Thoracic Duct
Empties into the junction of left internal jugular and left subclavian veins
Most inferior part of thoracic duct
Cisterna chyli
Lymphatic duct photo
Primary lymphatic organs are organs
where immune cells become immunocompetent (Cells are able to deal immune reactions properly)
•Red bone marrow
•Thymus
Lymphoid organs photo
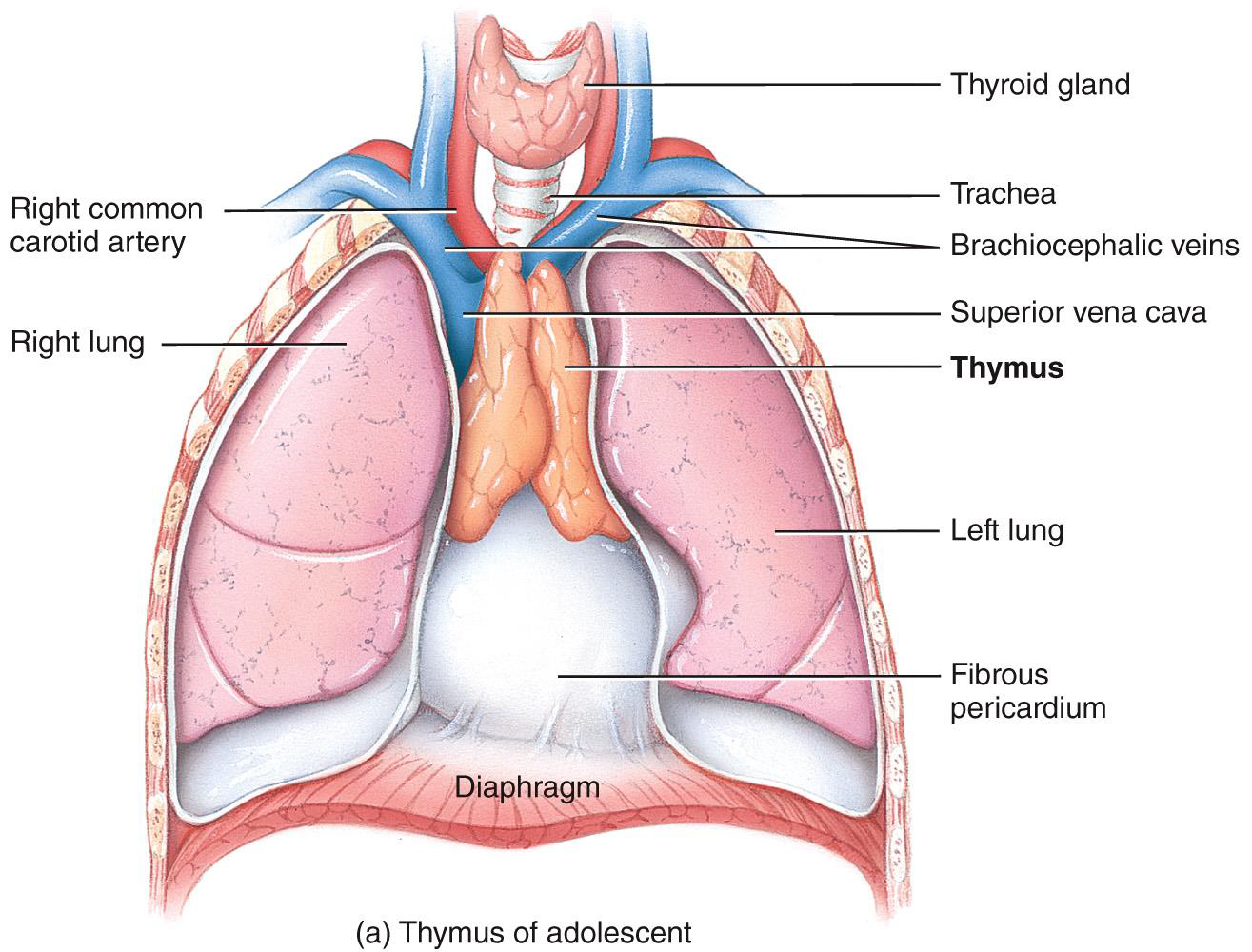
Thymus gland
•Peak function during childhood
•Produces thymosin and thymopoietins that functions to program lymphocytes (T cells)
•Site of T cell maturation
Secondary lymphatic organs are
the sites where most immune responses occur.
Secondary lymphatic organs and tissues include:
•Lymph nodes
•Spleen
•Lymphatic nodules
Structure of a lymph node photo
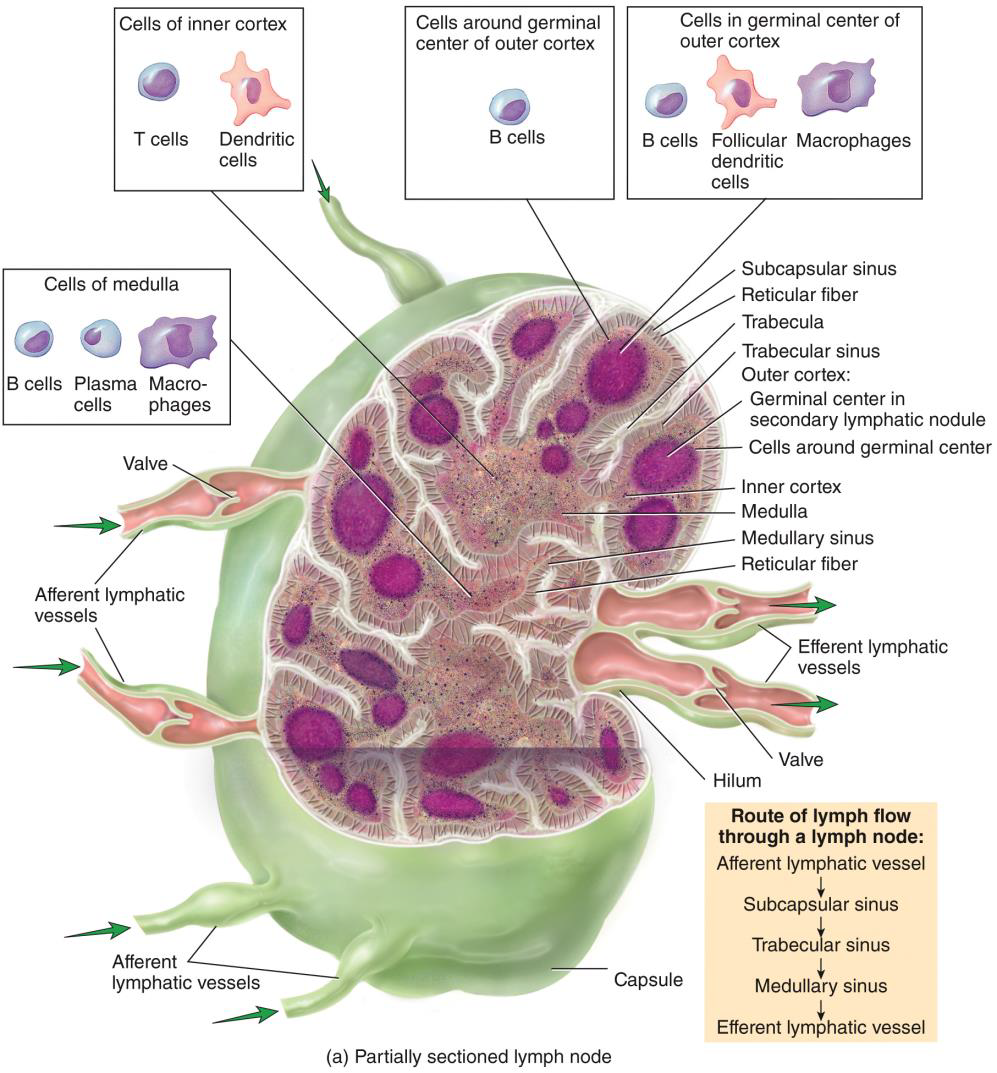
Lymph enters through
afferent lymphatic vessels--flows through node--exits at hilusby efferent lymphatic vessels
Slow flow through node
•More afferent vessels than efferent
•Allows lymphocytes and macrophages to do their job
Lymph flows through several nodes before
cleaning is complete and fluid re-enters cardiovascular system
clustered along lymphatic vessels that filter lymph
Large clusters in inguinal, axillary, and cervical regions
“Filter” lymph
Macrophages remove foreign material
Immune System Activation
Lymphocytes encounter foreign antigens and become activated
Lymph Nodes summary
• Surrounded by Connective Tissue capsule
• Contain lymphatic nodules made up of B cells
• More afferent vessels than efferent vessels –slows flow
• All lymph flows through more than one lymph node
• Contain reticular fibers that act as a filter
Swollen Lymph nodes
Buboes
Secondary cancer sites
Buboes-
overwhelmed lymph nodes, large numbers of bacteria and viruses
•Causes inflammation and tenderness
•Swelling during infection is a trapping function
Secondary cancer sites
•Some cancers use lymphatic system to spread
•Swollen glands are usually painless making them distinguishable from inflamed glands
Lymphoid Organs PHOTO
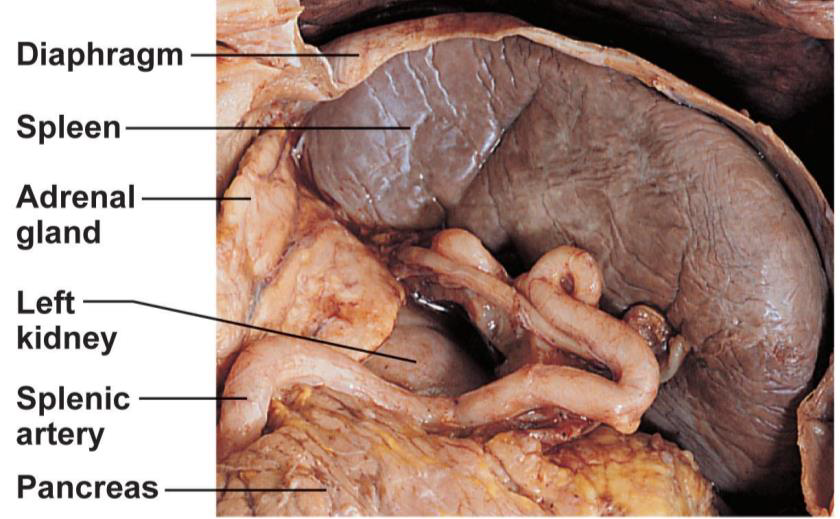
Lymphoid Organs
Spleen
•Lymphocytes check blood (not lymph) for bacteria, viruses, and debris
•Left side of abdomen
•Other functions
•Destroys and stores breakdown products of old RBCs
•Acts as blood reservoir, stores 1/3 of platelets and monocytes
•May produce RBCs in fetus
Splenectomy-
removal of spleen when hemorrhaging
•Less common today, found to heal itself and regenerate in children
Lymphatic nodules are
masses of lymphatic tissue that are not surrounded by a capsule
Lymphatic nodules are masses of lymphatic tissue that are not surrounded by a capsule. They are
scattered throughout the lamina propria of mucous membranes lining the gastrointestinal, urinary, and reproductive tracts and the respiratory airways
Lymphatic nodules in these areas are also referred to as
mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT)
Tonsils
•5 Small masses of tissue, ring the throat
•Trap foreign pathogens entering throat
•Tonsillitis - red and swollen due to excess bacteria or any foreign pathogen
•Peyer’s patches
•Wall of small intestines - ilium
•Prevent foreign substances from entering intestinal wall
Elephantiasis
Tropical disease where lymphatics are clogged with parasitic round worms resulting in edema of enormous proportions. Transmitted by mosquitos and common in India
Lymphoma
Benign or malignant tumor of lymphoid tissue
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
All cancers of lymphoid tissue except Hodgkins lymphoma, due to lymphocytes, 7thmost common cancer, often occurs in young people
Hodgkin Disease
•Malignant lymphoid tissue, malignant B cells, non-painful swollen lymph nodes, genetic and mononucleosis predisposing factors Mostly affects people between 15- 35 years old and 65+ cure rate of 90-95%
Sentinel node
First node that receives lymph drainage from a suspected cancerous area, biopsied to determine if cancer has metastasized into lymph tissue
Which of the following filter lymph?
lymph nodes
Filtered lymph is returned to the blood at the
subclavian veins
Immunology-
study of the immune system (specific defense)
Antigen-
protein (self or foreign) substance, recognized by immune system. On the surface of a cell, cell identity markers
Nonself-
foreign, threat
Pathogen-
disease causing microorganism helminth, virus, protozoan, bacteria
Antibody-
protein that tags a foreign substance
Self-
not seen as a threat
Functions to protect body can either be
•Direct
•Indirect
Functions to protect body can either be
Direct
Cell attack
Functions to protect body can either be
indirect
Mobilizing chemicals and antibodies
Two defense system
•Innate (nonspecific) system
First and Second line of defense, always ready, we are born with this
Two defense system
Adaptive (specific) system
•Third line of defense, must be primed
•Attacks particular foreign substances
uses specific antibodies that bind to antigens
Nonspecific Resistance (Innate Immunity)
Present at birth and includes defense mechanisms that provide general protection against invasion by a wide range of pathogens
Immunity (Adaptive Immunity)
Involves activation of specific lymphocytes that combat a particular pathogen or other foreign substance
The body system that carries out immune responses is
the lymphatic system
NON-SPECIFIC Innate Immunity
refers to a wide variety of body responses that serve to protect us against invasion by a wide variety of pathogens and their toxins
NON-SPECIFIC Innate Immunity
We are
born with this kind of immunity
Two lines of NON-SPECIFIC Innate Immunity
•Skin and mucous membranes
•Internal defenses = 5
Nonspecific Defenses
Surface Membrane barriers (external)
1st line of defense, skin and mucous membranes
Physical and chemical barriers
•Acidic pH of skin secretions and sebum inhibits bacteria growth
•Hydrochloric acid and digestion enzymes of the stomach
•Saliva and lacrimal fluid (lysozymes)
•Sticky mucus traps pathogens in respiratory and digestive tracts and cilia work to move the substance out
Nonspecific Defenses
2nd line of defense
1. Phagocytes
Phagocytes
•Engulf foreign substances
•Digest particles with enzymes in lysosomes
Types of phagocytes
Macrophages
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Macrophages-
derived from monocytes found in tissues
Eosinophils-
weak phagocytes, defend against parasitic worms
Neutrophils-
Become phagocytic upon encountering foreign substance
Phagocyte Mobilization
Leukocytosis > Margination > Diapedesis > Chemotaxis
Chemotaxis
•Inflammatory chemicals recruit neutrophils to precise location
•Monocytes follow Neutrophils and develop into Macrophages
Stimulate cell growth and maturity
Diapedesis
Neutrophils squeeze through capillary wall
Margination
Neutrophils travel to inflamed site, stick to capillary wall
Leukocytosis
•Injured cells produce leukocytosis-inducing factors, causes neutrophil release from bone marrow
Phagocytosis 5 stages
•Chemotaxis
•Adherence
•Ingestion
•Digestion
•Killing
During ingestion of a microbe during phagocytosis, the phagocyte releases
Pseudopods Which are cell surface projections that wraps around microbe and form a vesicle containing the microbe
Nonspecific Defenses
Natural killer (NK) cells
•Type of lymphocyte, found in blood and lymph
•Lyse and kill a variety of cancer cells and virus-infected cells
•(not specific)
•Release chemicals called perforins that cause the target cell to disintegrate
•Secrete chemicals that enhance inflammatory response
Nonspecific Defenses
Inflammatory response
Response to tissue damage, includes pain, redness, immobility, swelling, and heat (PRISH)
Inflammatory response
Injured cells release these chemicals
Histamines, kinins, prostaglandins, complement, and cytokines
Inflammatory response
Chemical effects
•Blood vessels dilate causing hyperemia-redness and heat
•Exudate seeps out of capillaries-fluid with clotting factors and antibodies, swelling and pain
•Chemotaxis - attract phagocytes and WBCs
Nonspecific Defenses
3.Inflammatory response effects
a)Prevents spread of damage (clotting factors)
b)Disposes of cell debris and pathogens
•Neutrophils and Monocytes squeeze through blood vessels (diapedesis) to damaged area to clean debris
c)Sets stage for repair (fibrin mesh)
Inflammatory Responses
•Pus
•Acute inflammation
•Chronic inflammation
•Abscesses and Ulcers
Nonspecific Defenses
4. Antimicrobial Chemicals
Interferon (IFN) proteins
Proteins produced by virus-infected cells
•diffuse to nearby cells to induce synthesis of antiviral proteins –prevent replication
Genetically engineered IFNs used to combat Hepatitis C, herpes, and viral infections in organ transplants
Antimicrobial Chemicals
Interferon (IFN) proteins effects
•Cause uninfected cells to produce the enzyme PKR protein that interferes with virus replication
•Activate Macrophages and NK cells
Antimicrobial Chemicals
Complement proteins
•20-30 plasma proteins in blood
•Amplify inflammatory response, cause cell lysis, promote phagocytosis
Complement fixation-
attachment of protein to foreign body, activates the protein
Membrane Attack Complexes-
formed by complement fixation, proteins form holes in cell membrane for lysis. Non cellular means of poking holes into a cell
Opsonization
(coating of microbe)-causes membranes to become sticky, easier for adherence (phagocytosis)
Nonspecific Defenses
Fever
•Abnormally high body temp.
•Pyrogens-chemicals secreted by WBCs and macrophages, cause body temp. to increase
•Mild to moderate fever
•Liver and spleen gather iron and zinc, bacteria need these nutrients to multiply
•Increases metabolic rates to
High fever-
dangerous due to denaturation-proteins (enzymes) break down
Innate vs adaptive defense photo
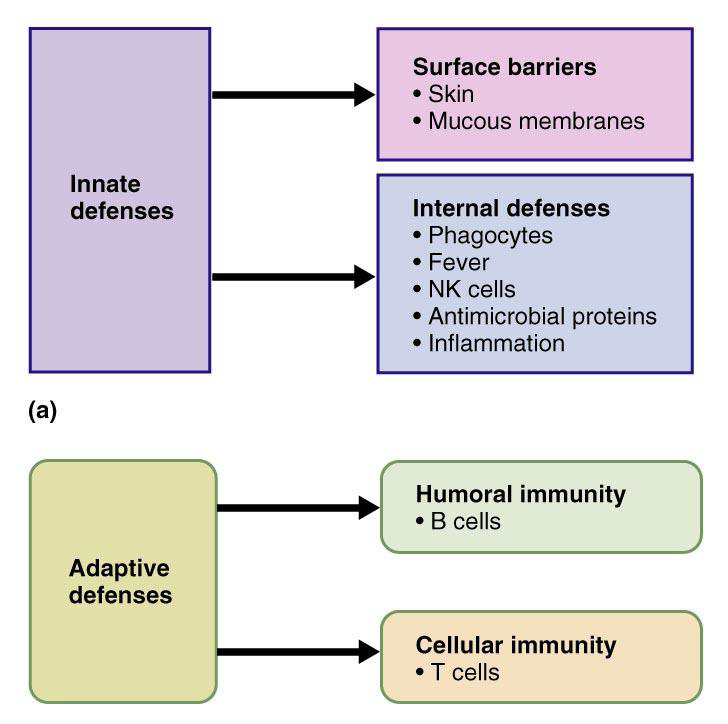
3rd line of defense-Immune Response to Antigens - Characteristics
•Antigen specific
•Systemic-not restricted to initial infection site
•Memory-mounts stronger attacks on previously encountered pathogens
Adaptive Immunity (SPECIFIC)
refers to the body’s ability to defend itself against specific invading agents (bacteria, viruses, transplants, self-cells that have mutated)
Antigens are substances recognized as foreign that provoke immune responses (ANTIbody GENerating)
Adaptive immunity has both specificity and memory and is divided into 2 types
Cell-mediated; T cells mature in the thymus produced in bone marrow
Antibody-mediated: B cells mature in the bone marrow humorous
Self-antigens-
proteins found on our cells, don’t usually activate immune response
Self-antigens-proteins found on our cells, don’t usually activate immune response
•Major histocompatibility complex
•Human leukocyte antigens
•May be antigenic to other people (transplants)