Staining principles
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Define immunohistochemistry (IHC).
→ Immunohistochemistry is a technique that uses antigen–antibody interactions to detect specific cellular or tissue antigens within a histological section.
What principle does IHC rely on?
→ The specific binding of an antibody to its corresponding antigen in tissue, visualized using labelled detection systems.
What types of forces hold the antibody and antigen together?
→ Van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonds, and electrostatic interactions.
Why is antigen retrieval necessary before IHC staining?
→ To expose hidden or masked antigenic sites that have been cross-linked by formalin fixation, ensuring antibody binding.
Name the two main types of antigen retrieval techniques.
HIER (Heat-Induced Epitope Retrieval)
PIER (Proteolytic-Induced Epitope Retrieval)
What are common methods used in heat-induced epitope retrieval (HIER)?
→ Microwave, pressure cooker, or autoclave.
What enzyme is commonly used in proteolytic-induced epitope retrieval (PIER)?
→ Digestive enzymes such as trypsin, pepsin, or proteinase K.
What is a limitation of enzyme digestion in antigen retrieval?
→ It can destroy some epitopes and tissue morphology, leading to false negative results.
What colour indicates positive antigen detection in IHC using DAB?
→ Brown.
What is the Luxol Fast Blue stain used for?
→ Luxol Fast Blue (LFB) is used to demonstrate myelin and myelinated axons in the brain and spinal cord tissue.
What type of tissue sections can Luxol Fast Blue be applied to?
→ It can be applied to formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded or frozen sections.
What does the Luxol Fast Blue stain detect in the nervous system?
→ It detects myelin phospholipids to assess myelin integrity and visualize neuronal architecture.
What is the staining reaction of Luxol Fast Blue?
Myelin (phospholipids): Blue to green
Neurons and Nissl substance: Violet
What is the principle of Luxol Fast Blue staining?
→ Luxol Fast Blue binds to the lipoproteins of myelin sheaths via acid-base interactions, staining them blue.
What are the main reagents used in the Luxol Fast Blue method?

What colours represent different structures in LFB stain?

What is the clinical application of Luxol Fast Blue staining?
→ It is used to evaluate demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis and to assess neuronal loss in CNS pathology.
What is the Cresyl Fast Violet stain used to demonstrate?
→ It is used to demonstrate Nissl substance in neurons, which represents rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and ribosomes within the soma and dendrites.
What are Nissl substances composed of?
→ Nissl substances are composed of granular endoplasmic reticulum rich in ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Why does Nissl substance stain strongly with Cresyl Fast Violet?
→ Due to the high RNA content, which makes it strongly basophilic, allowing it to stain intensely with basic aniline dyes such as Cresyl Fast Violet.
What is the primary stain and differentiator used in the Cresyl Fast Violet method?

How can you selectively demonstrate either Nissl substance alone or both Nissl substance and nuclei?
→ By adjusting the pH and differentiation time, one can selectively stain either Nissl substance and nuclei, or only Nissl substance.
What is the diagnostic application of Cresyl Fast Violet staining?
→ It is used to evaluate neuronal structure, cell body integrity, and neuronal loss in brain and spinal cord tissue, such as in neurodegenerative diseases or CNS injuries.
What is the Ziel-Neelsen stain used for?
→ It is used to detect acid-fast organisms, primarily Mycobacterium spp., which have waxy, lipid-rich cell walls containing mycolic acids.
Why are Mycobacteria called “acid-fast”?
→ Because the carbolfuchsin–lipid complex in their cell walls resists decolourization by acid-alcohol, retaining the red stain.
What is the principle of Ziel-Neelsen staining?
→ Carbolfuchsin penetrates the waxy mycobacterial cell wall with the help of phenol and heat, binding to mycolic acids. Acid-fast cells resist decolourization; non-acid-fast cells lose the stain and take up the counterstain.
List the reagents used in Ziel-Neelsen staining
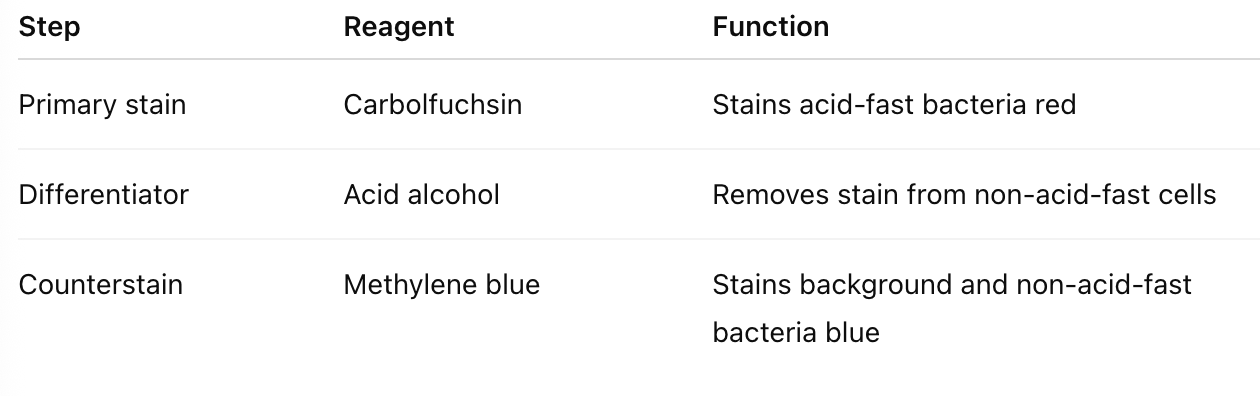
What are the results of the Ziel-Neelsen stain?

What is the purpose of the Grocott’s Methenamine Silver stain?
→ It is used to demonstrate fungal organisms in tissue sections.
Describe the principle of GMS staining.
→ Chromic acid oxidizes fungal cell wall polysaccharides to aldehydes, which reduce a methenamine–silver complex, depositing black metallic silver at fungal sites.
List the main reagents used in GMS staining.
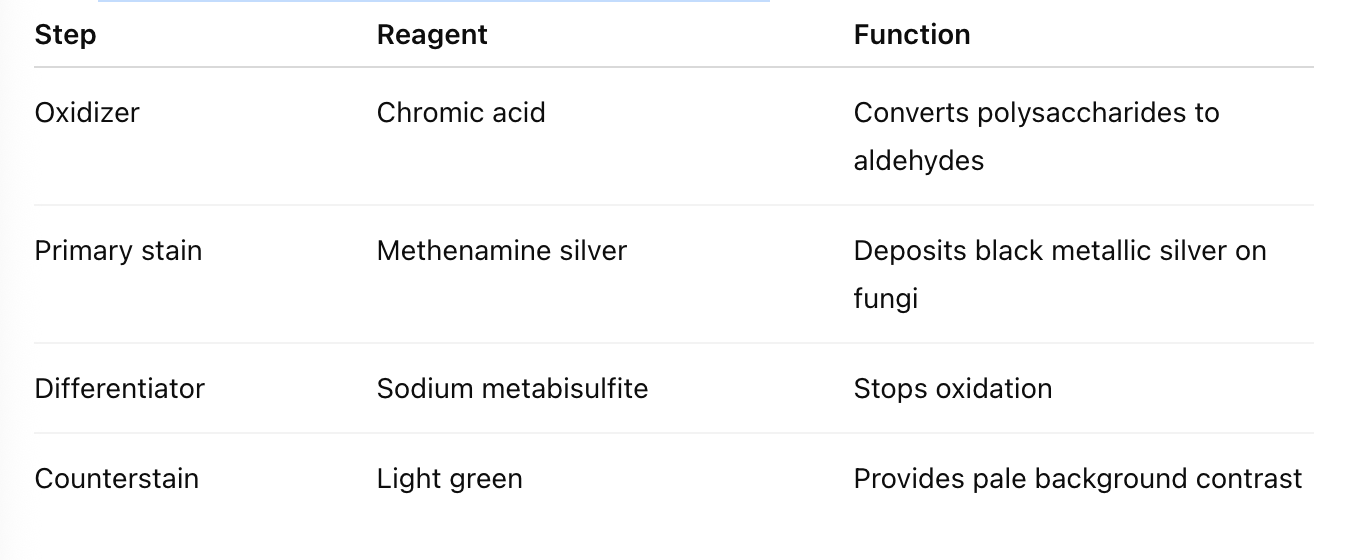
What are the results of GMS staining?

Which other histochemical stain works on a similar principle to GMS?
→ Periodic Acid–Schiff (PAS) stain — both rely on oxidation to form aldehydes.
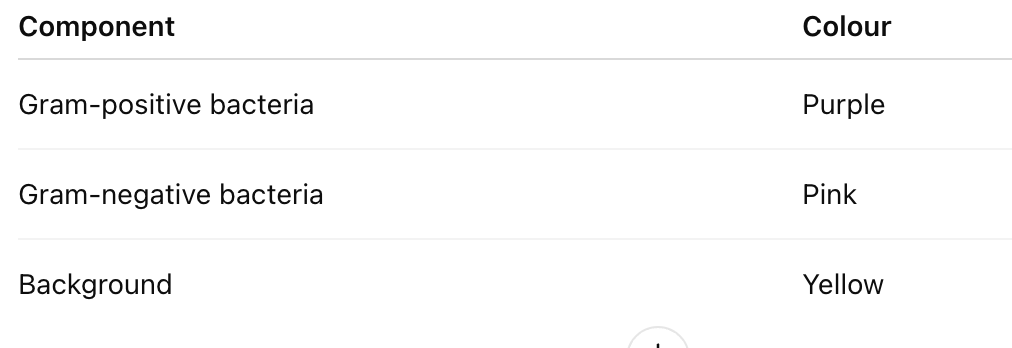
What is the purpose of Gram staining?
→ To differentiate bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram-negative based on cell wall composition and dye retention.
Explain why Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain.
→ They have thick peptidoglycan layers and low lipid content; solvent causes dehydration, trapping the crystal violet–iodine complex within the cell wall.
Why do Gram-negative bacteria lose the crystal violet stain?
→ They have thin peptidoglycan layers and high lipid content; solvent dissolves the lipids, allowing dye to wash out.
List the reagents used in Gram staining.
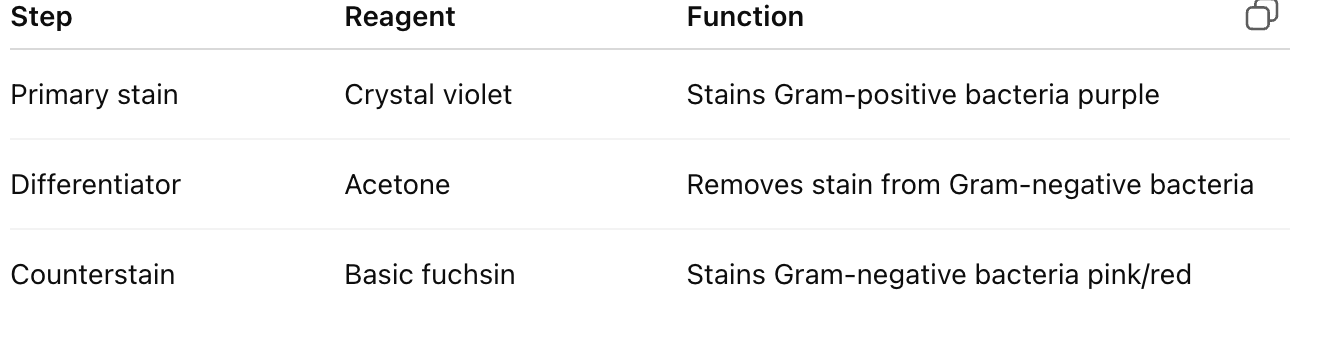
What are the results of Gram staining?
What is the main purpose of the Gordon and Sweet’s stain in histopathology?
To demonstrate reticulin fibres (type III collagen) in tissue sections.
Which type of collagen is specifically highlighted by the Gordon and Sweet’s stain?
Type III collagen (reticulin fibres).
Explain the principle of the Gordon and Sweet’s stain.
An unstable salt, ammoniacal silver nitrate, is applied to the tissue. A reducing agent, formalin, converts the silver salt into black metallic silver, which deposits selectively on reticulin fibres.
What is the purpose of the gold chloride step in the Gordon and Sweet’s stain?
Toning with gold chloride converts metallic silver to metallic gold, enhancing stability, contrast, and clarity of the reticulin fibres.
Which chemical is used to remove unreduced silver and excess gold in this staining procedure?
Sodium thiosulphate (5%).
What are the primary stain and counterstain used in Gordon and Sweet’s method, and what do they stain?
Primary stain: Silver solution – stains reticulin fibres black.
Counterstain: Nuclear fast red or light green – stains nuclei and other tissue elements red/pink for contrast.
How do reticulin fibres and other tissue elements appear after staining with Gordon and Sweet’s method?
Reticulin fibres appear black, while nuclei and other elements appear in shades of red/pink if counterstained.
What is the main purpose of the haemoatoxylin-Van Gieson stain?
To differentiate between collagen from smooth muscle in tissue samples
Explain the principle behind Haematoxylin–Van Gieson staining.
HVG uses two dyes of different molecular sizes. Picric acid (small molecule) penetrates all tissues and stains them yellow. Acid fuchsin (larger molecule) can only stain the loose, fibrous collagen, giving it a red colour.
Identify the primary stain, counterstain, and third stain used in HVG and their targets.
Primary stain: Acid fuchsin → collagen red
Counterstain: Weigert’s haematoxylin → nuclei blue/black
Third stain: Picric acid → muscle yellow
What are the expected results after HVG staining?
Nuclei = blue/black
Collagen = red
Muscle = yellow
What is the purpose of Masson’s Trichrome stain?
To distinguish collagen from muscle and other tissue components.
Explain the principle of Masson’s Trichrome stain.
Acid fuchsin initially stains all tissue. A heteropolyacid (phosphomolybdic or phosphotungstic acid) differentiates by displacing the dye from collagen. Then, a larger dye (aniline blue) selectively stains collagen blue, leaving muscle red.
List the primary stain, counterstain, third stain, and differentiator in Masson’s Trichrome method.
Primary stain: Aniline blue → collagen blue
Counterstain: Weigert’s haematoxylin → nuclei black
Third stain: Biebrich red → stains all tissue components
Differentiator: Phosphomolybdic acid / phosphotungstic acid (PMA/PTA)
What are the expected results after Masson’s Trichrome staining?
Nuclei = black
Collagen = blue
Muscle = red
What is the principle of Oil Red O staining?
Oil Red O is more soluble in neutral fats than in alcohol. When applied, the dye moves from the alcohol solution into tissue fat. Only frozen sections can be stained because paraffin processing removes tissue fat.
What are the primary stain and counterstain used in Oil Red O?
Primary stain: Oil Red O → lipids red
Counterstain: Mayer’s haematoxylin → nuclei blue
What are the expected results after Oil Red O staining?
Nuclei = blue; Lipids = red
Explain the principle of Verhoeff’s Van Gieson stain.
Haematoxylin combined with ferric chloride and iodine stains elastic fibres black. Ferric chloride acts as a mordant and differentiator, removing the dye from weaker binding tissues while elastic fibres retain it longer, giving high contrast.
List the primary stain and counterstain used in VVG.
Primary stain: Haematoxylin (with ferric chloride and iodine) → elastic fibres black
Counterstain: Van Gieson → nuclei blue/black, collagen red, other tissue yellow
What are the expected results after VVG staining?
Nuclei = blue/black
Collagen = red
Elastic fibres = black
Other tissue components = yellow
What is metachromasia and how is it demonstrated in mast cells with toluidine blue?
Metachromasia is when tissue elements stain a different colour from the dye solution. Mast cell granules (heparin, histamine) stain red-purple, while background tissue stains blue (orthochromatic).
What is the primary stain used to visualize mast cells?
Toluidine blue → mast cells violet/red-purple
What are the expected results after toluidine blue staining?
Mast cells = violet/red-purple; Background = blue
What is the principle of Congo red staining?
Congo red binds via hydrogen bonding to amyloid fibrils. Under polarized light, amyloid shows green birefringence.
What are the primary stain and counterstain in Congo red staining?
Primary stain: Congo red → amyloid red
Counterstain: Mayer’s haematoxylin → nuclei blue
What are the results of Congo red staining?
Amyloid, elastic fibres, eosinophil granules = red; Nuclei = blue; Green birefringence under polarized light for amyloid
What is demonstrated by Perl’s Prussian blue stain?
Ferric ions (Fe³⁺) in hemosiderin, forming ferric ferrocyanide (blue pigment).
What are the primary stain and counterstain for Perl’s Prussian blue?
Primary stain: Acid ferrocyanide → ferric iron blue
Counterstain: Nuclear fast red → nuclei red
What are the results of Perl’s Prussian blue staining?
Ferric iron = blue; Nuclei = red
What is the principle of Schmorl’s stain?
Melanin reduces ferric ferricyanide to ferrous ferricyanide, forming an insoluble blue compound.
What are the primary stain and counterstain in Schmorl’s method?
Primary stain: Ferric cyanide/ferric chloride → melanin, lipofuscin, argentaffin granules dark blue
Counterstain: Nuclear fast red → nuclei red, other tissue red/pink
What are the expected results of Schmorl’s staining?
Melanin, lipofuscin, argentaffin granules = dark blue; Nuclei = red; Other tissue elements = red/pink