Chem II Midterm 1
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
“Normal” ___ Point
Means atmospheric pressure is equal to 1 atm
Vapor Pressure Definition (P^o)
The partial pressure of the vapor phase in dynamic equilibrium w/ a condensed phase
Dynamic Equilibrium Definition
The rate or speed of the forward rxn is the same as the rate of the reverse rxn
aka for every water that evaporates, another condenses so they cancel out
Relationship Between Vapor Pressure and Temperature
Direct relationship
Relative Humidity Formula
PH2O = partial pressure of water
P^oH2O = vapor pressure of water
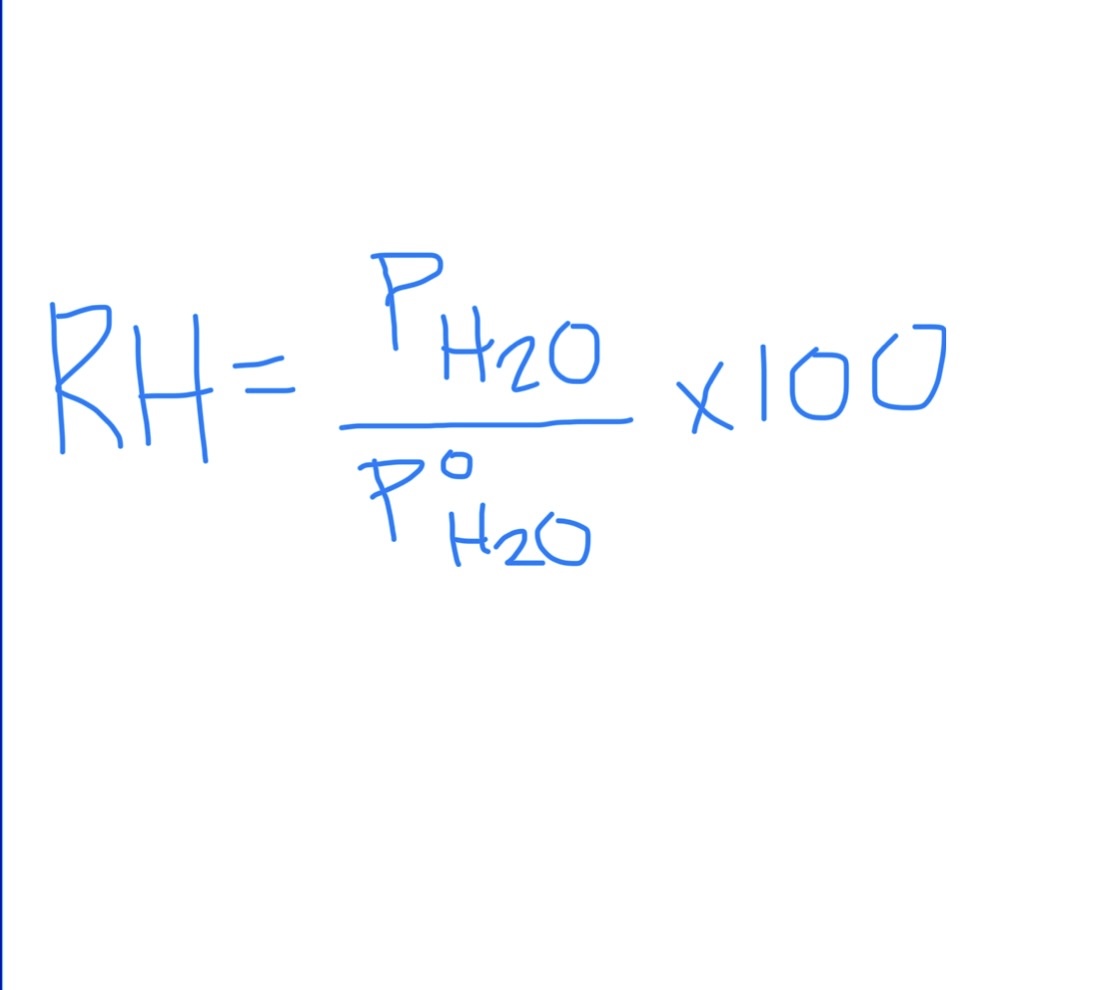
RH is 100% when…
… when partial pressure = vapor pressure
Boiling Point Definition
The temperature at which the vapor pressure is equal to the atmospheric pressure
Relationship Between Boiling Point and Vapor Pressure
Inverse Relationship
Clausius-Clapeyron Equation
Always make P2^o the unknown of solving for it
Temperature = Kelvin
R = 8.314 × 10^-3 kJ/mol*K
At 25 C, ΔHvap = 44 kJ/mol
At 100 C, ΔHvap = 40.65 kJ/mol
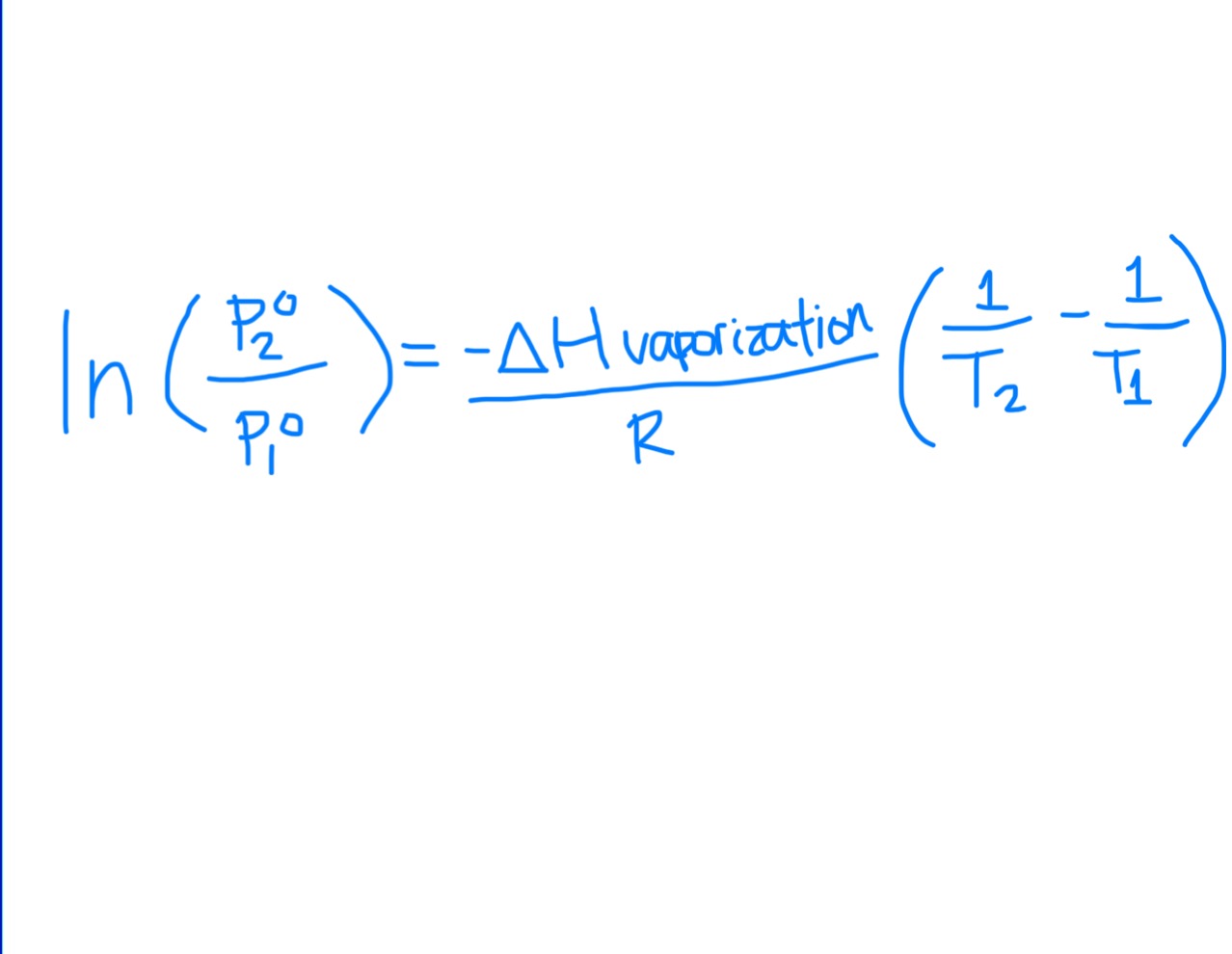
At 25 C, ΔHvap is …
44 kJ/mol
At 100 C, ΔHvap is …
40.65 kJ/mol
Phase Diagram
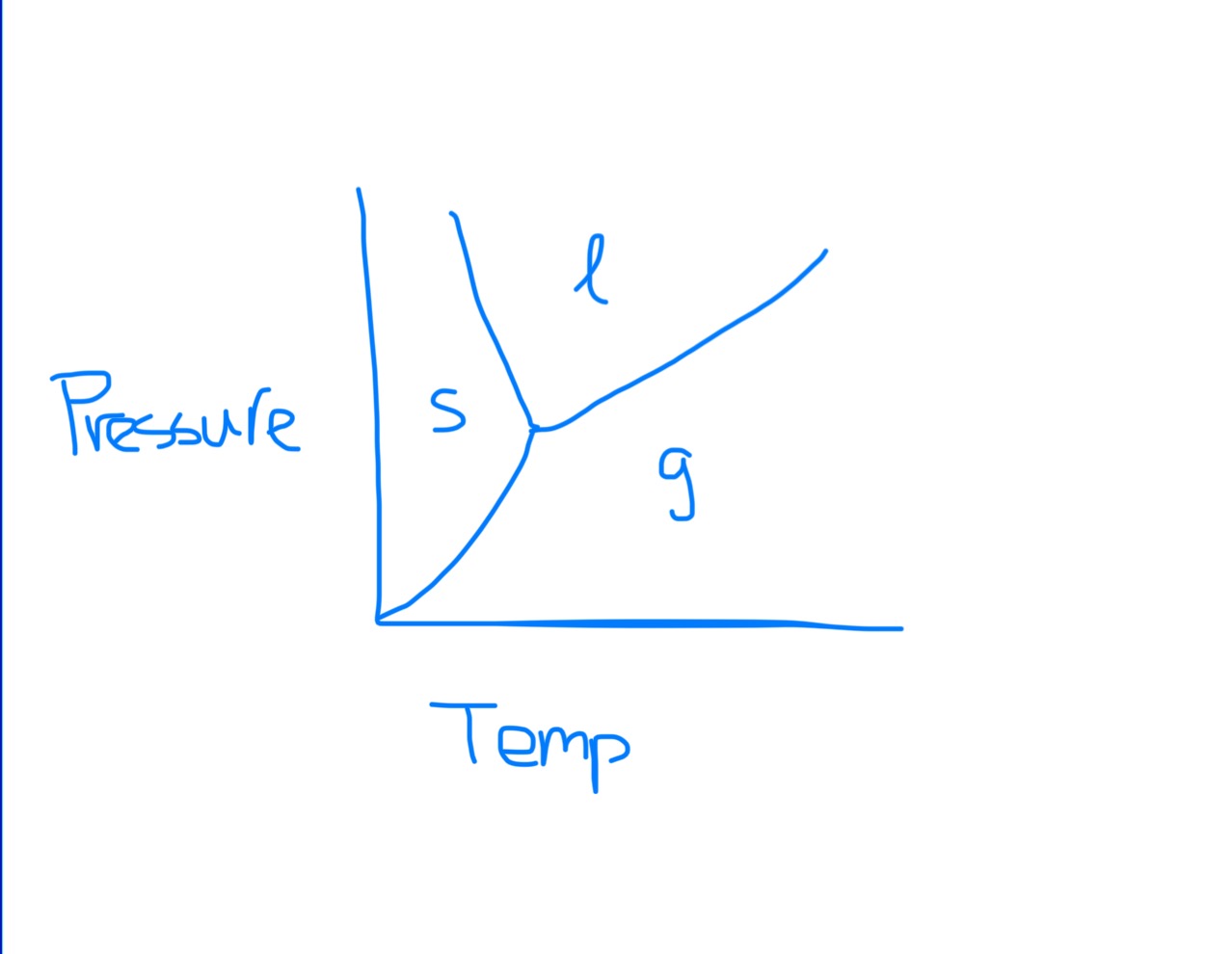
Normal Melting/Freezing Point on Phase Diagram
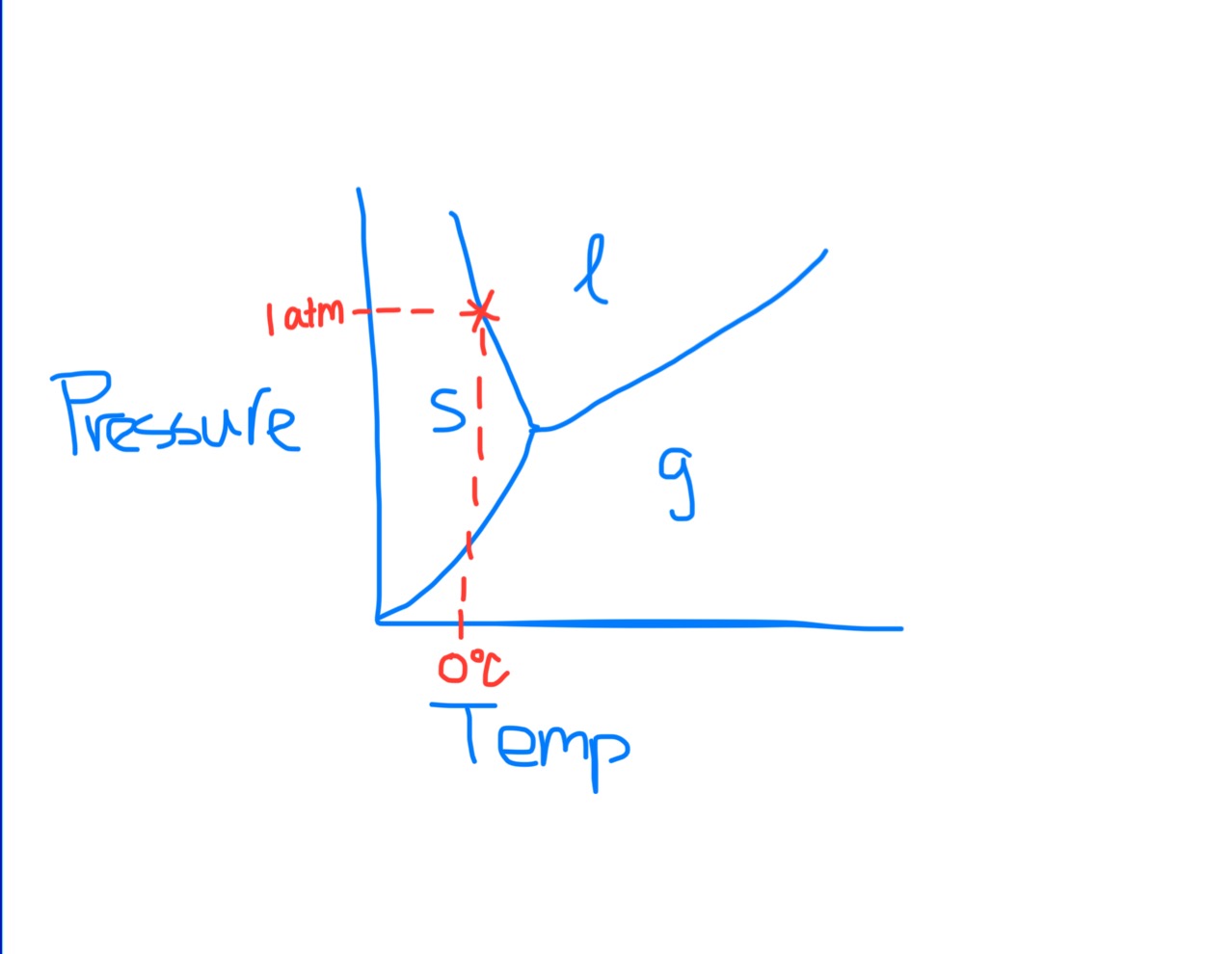
Normal Boiling Point on Phase Diagram
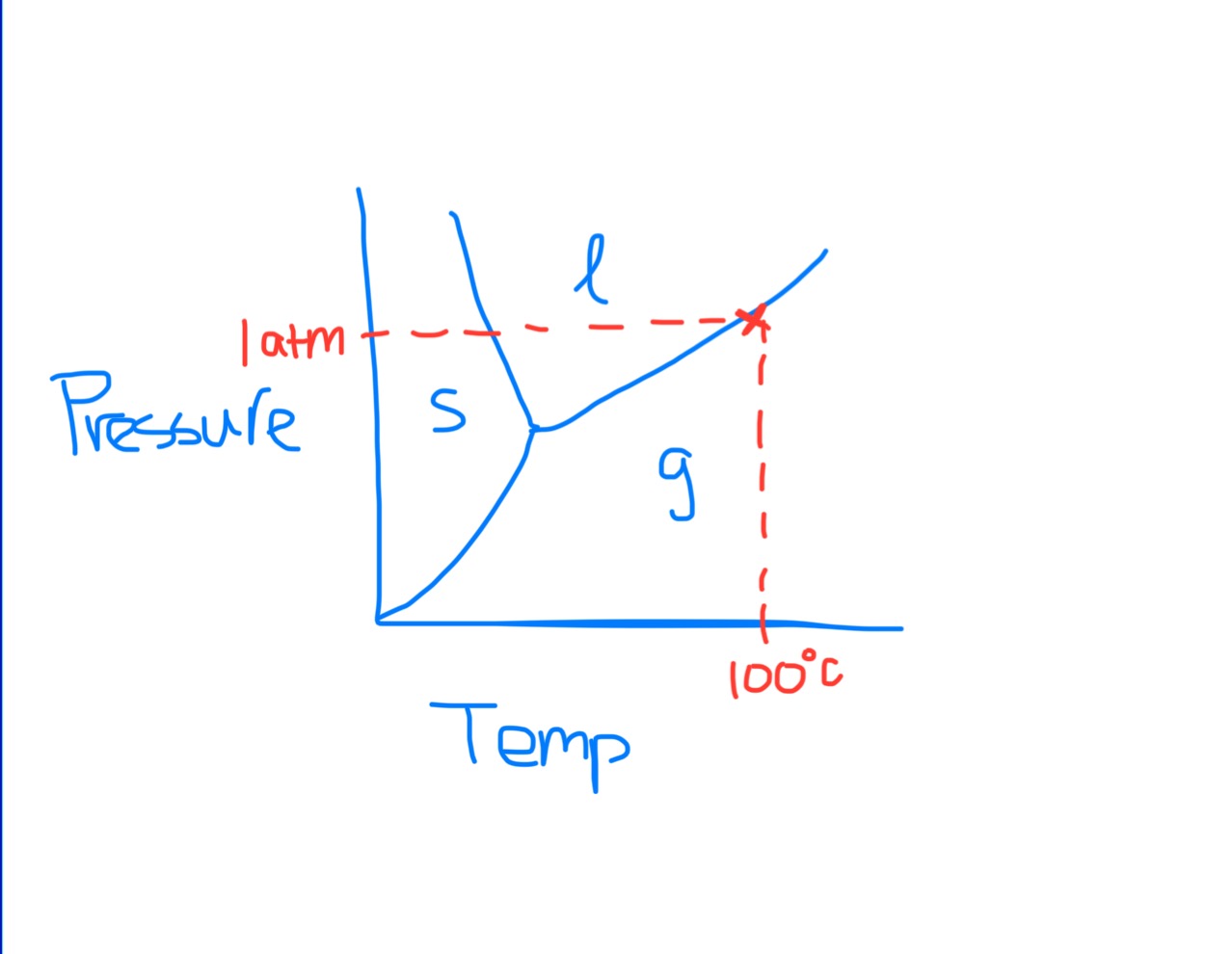
Low pressure + high temp is what phase?
Gas phase
Colligative Properties Definition
Physical properties that depend on the number of solute particles in solution
interested in concentration of solute
Molarity (M) Formula

Osmotic Pressure (π) Formula
π has to be in atm
T has to be in Kelvin

What R do you use to find osmotic pressure?
0.08206 L*atm/mol*K
Mass Percent
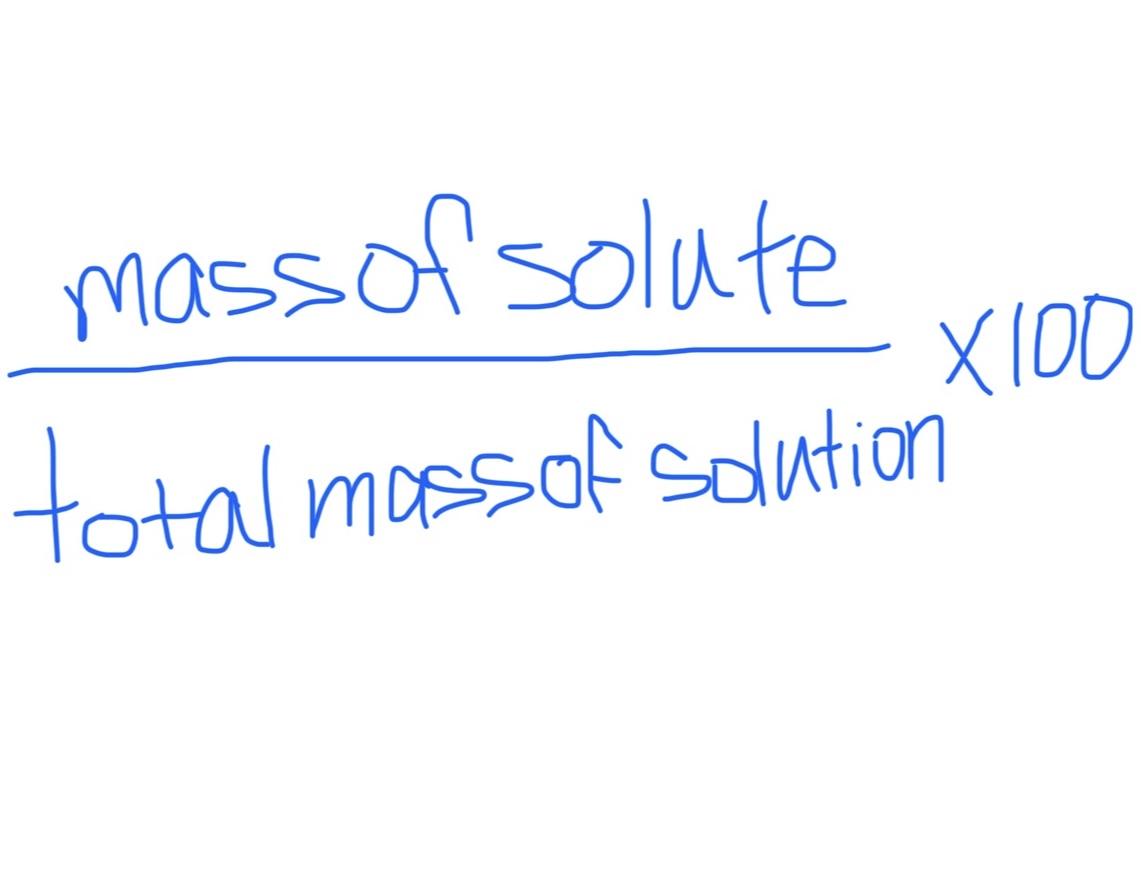
Molality
Temp dependent concentration
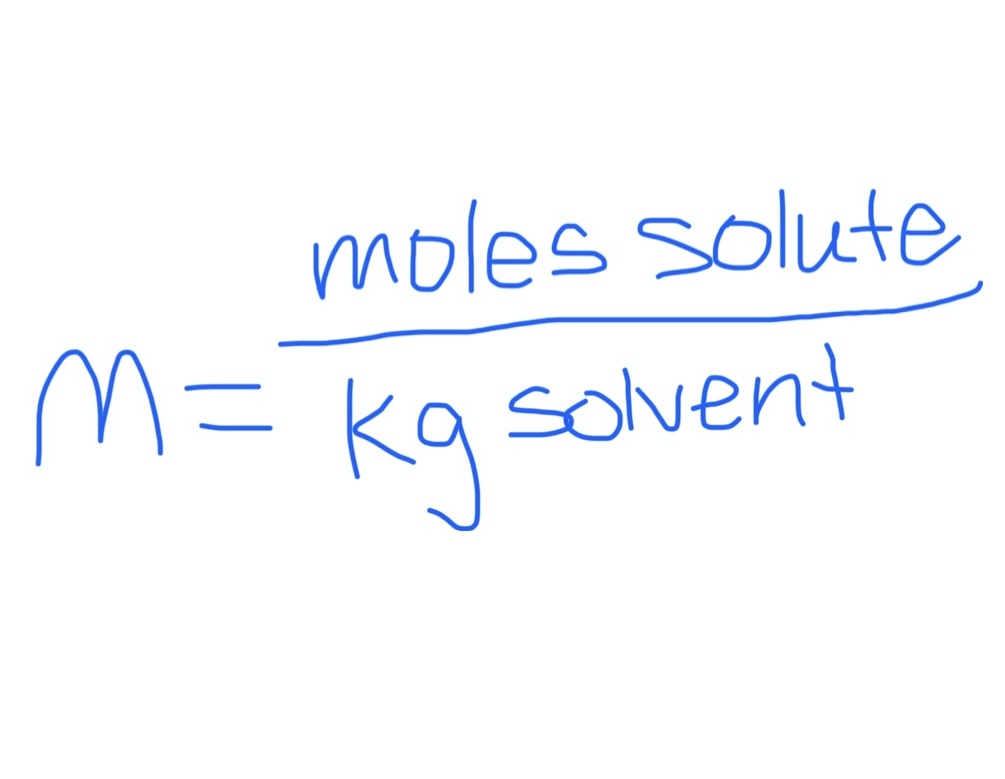
Mole Fraction
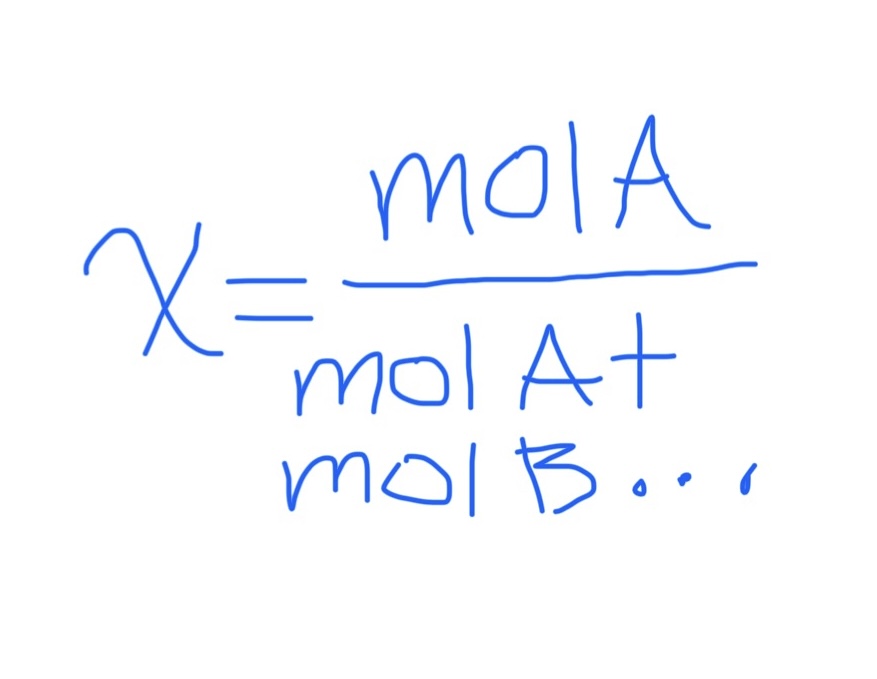
Relationship Between Two Mole Fractions
Can be used if there’s two unknowns
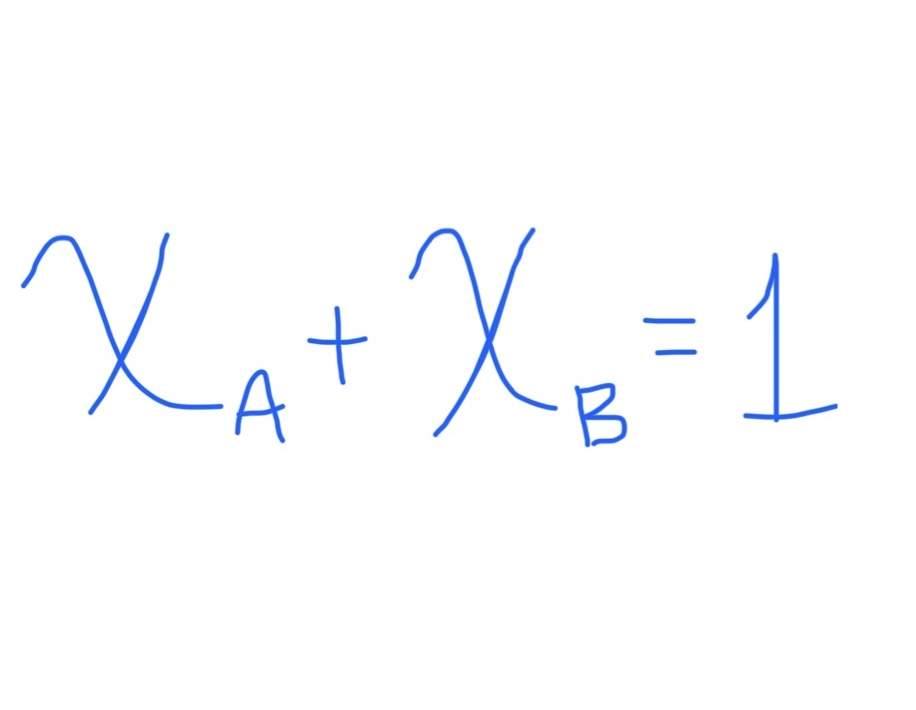
The Four Colligative Properties
Vapor Pressure Lowering
Boiling Point Elevation
Freezing Point Depression
Osmosis
Vapor Pressure Lowering Definition
Adding a nonvolatile solute lowers vapor pressure of solvent
Raoult’s Law:
a) Equation for Reduced Vapor Pressure of Solvent in Solution
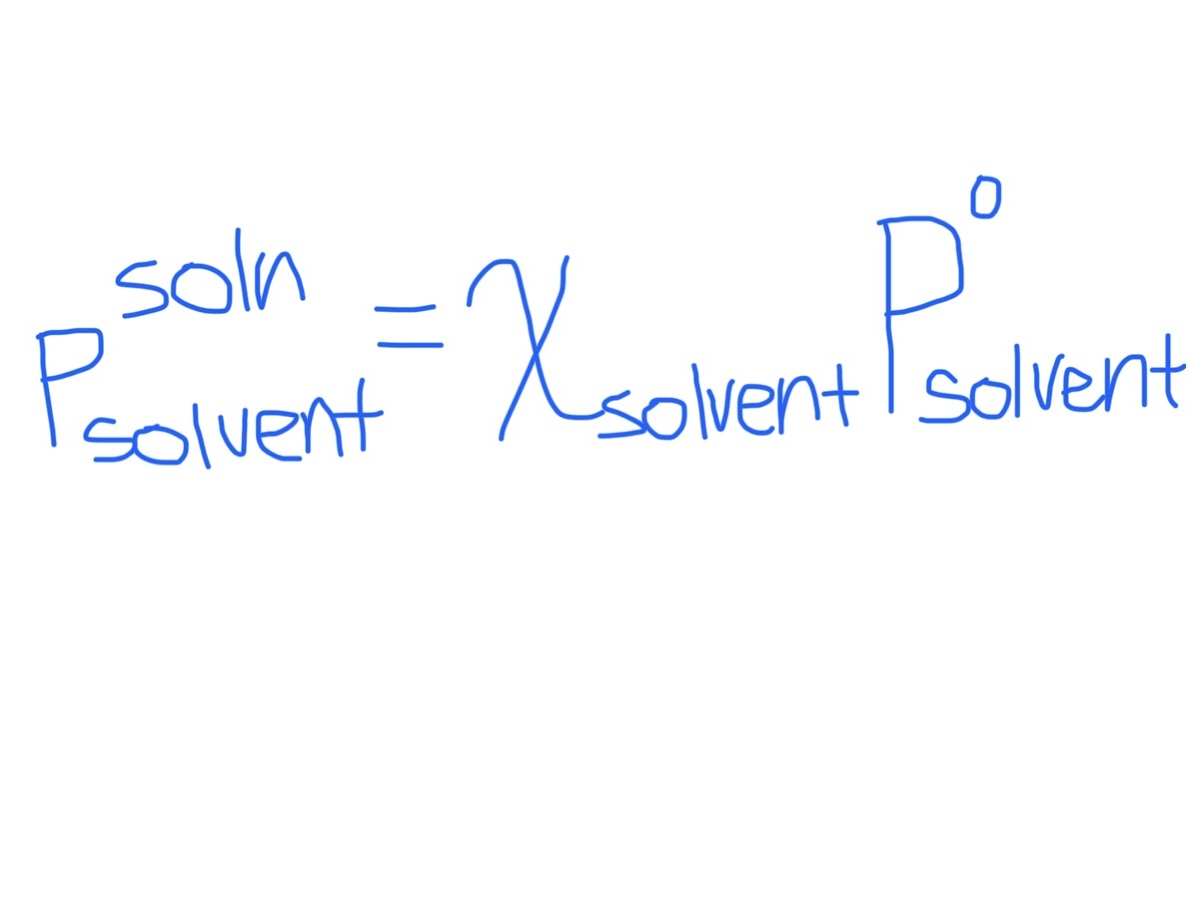
Raoult’s Law:
a) Equation for Reduced Vapor Pressure of Solute in Solution
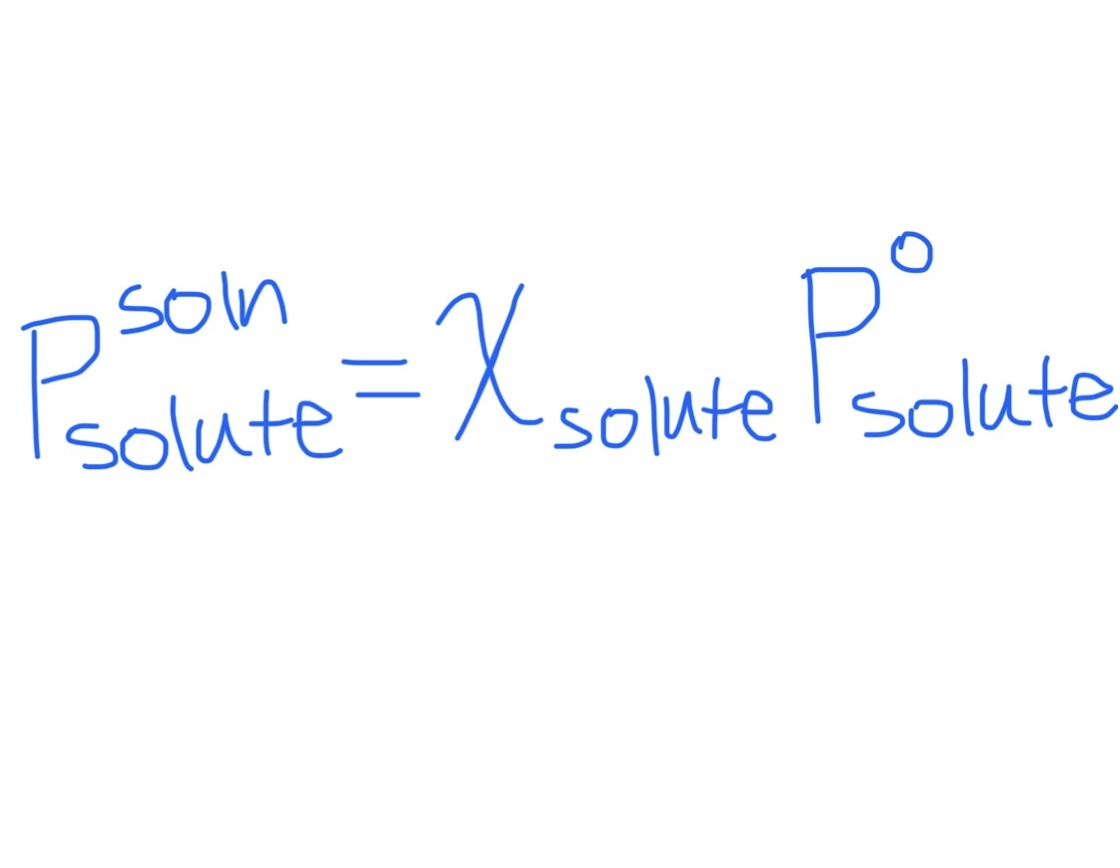
Formula for Total Vapor Pressure in Solution
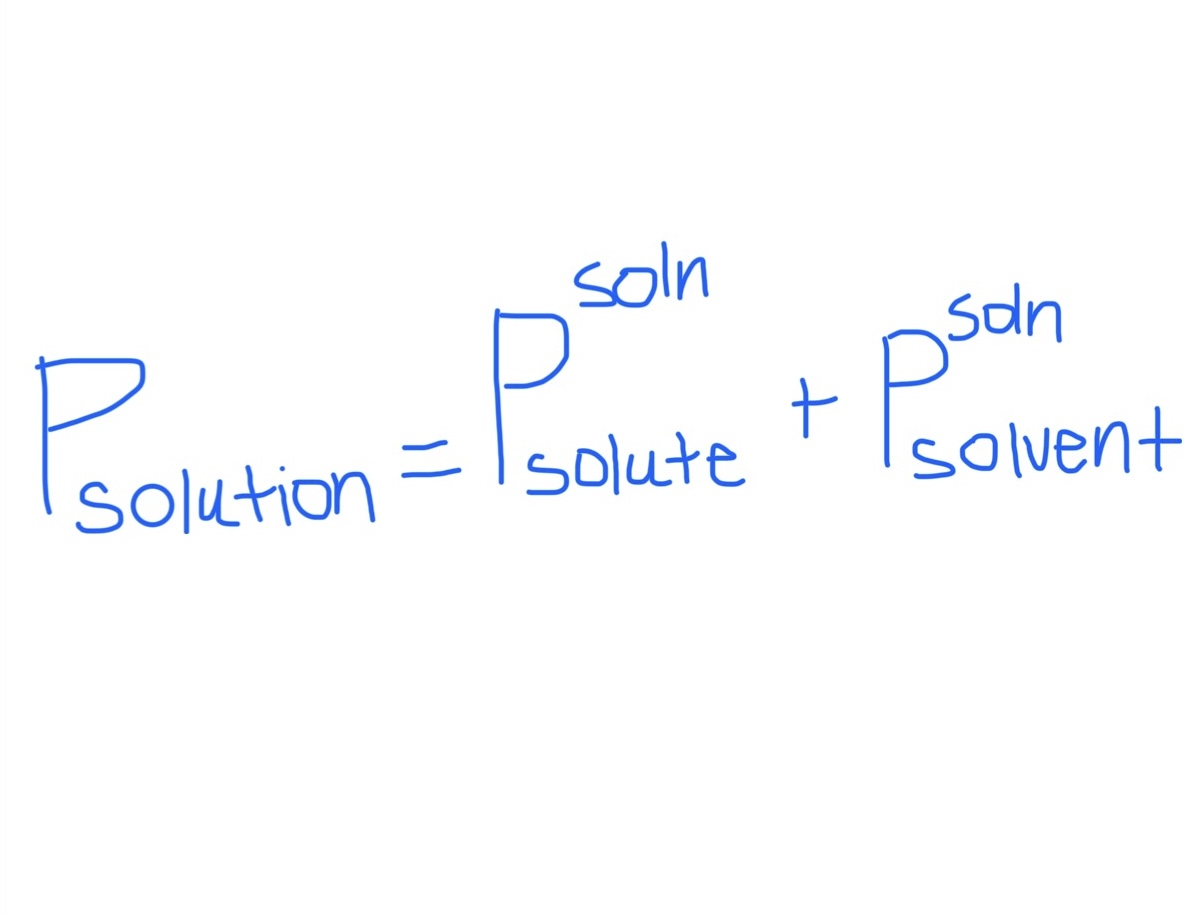
Relating Mole Fraction of Solvent and Solute
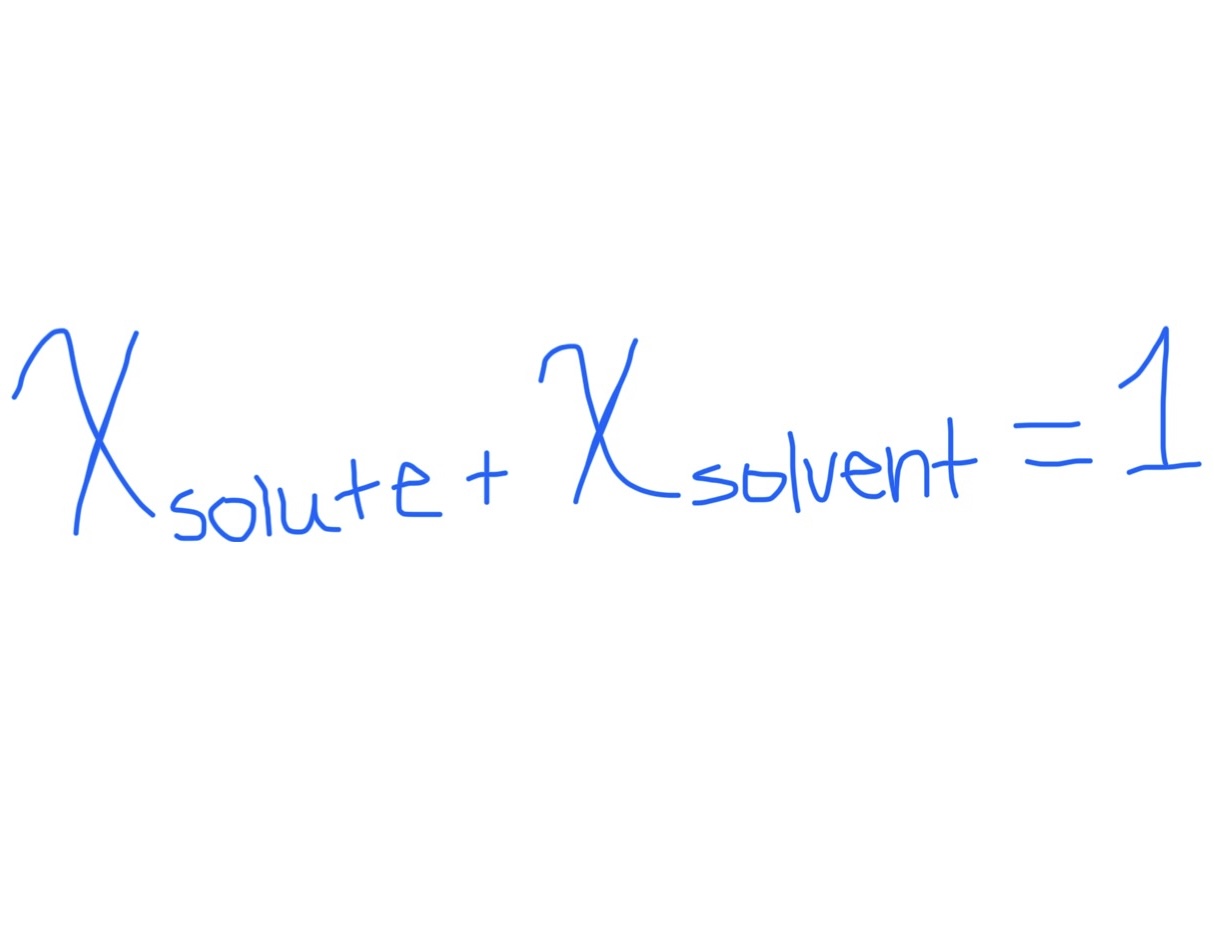
Ideal Solutions Definition
Solutions where solute-solvent intermolecular forces are the same strength as solvent-solvent intermolecular forces
If solute-solvent intramolecular forces are STRONGER than solvent-solvent …
You get negative deviation
Boiling Point is higher than ideal solution’s to reach 1 atm
Raoult’s Law = overestimation
If solute-solvent intramolecular forces are WEAKER than solvent-solvent …
You get positive deviation
Boiling Point is lower than ideal solution’s to reach 1 atm
Raoult’s Law = underestimation
Boiling Point Elevation Definition
Adding a solute raises the boiling point of the solvent b/c it lowers vapor pressure
Equation for Change in Boiling Point
Kb is specific to the solvent
For nonelectrolytes, i = 1
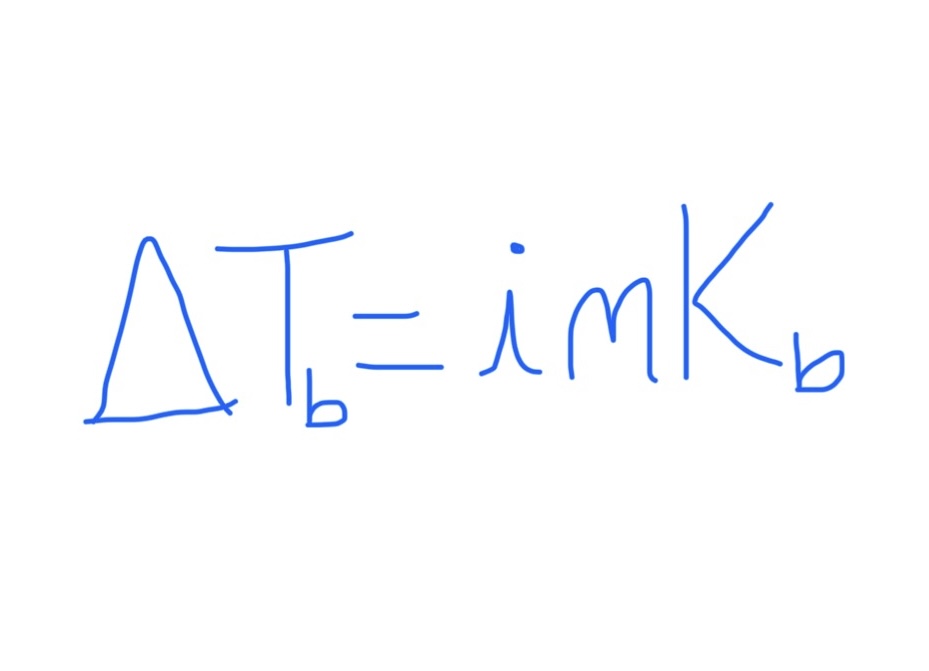
Freezing Point Depression Definition
Adding a solute lowers the freezing point of the solvent
Equation for Freezing Point of Solution
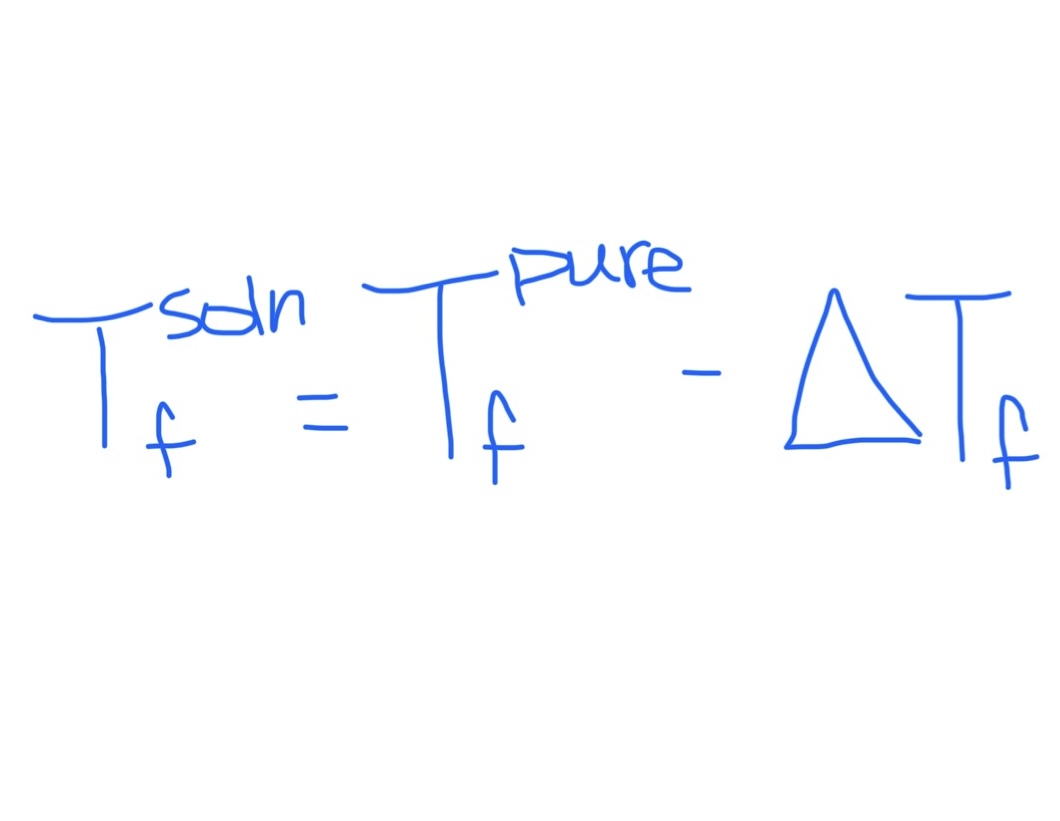
Equation for Change in Freezing Point
Kf is dependent on solvent
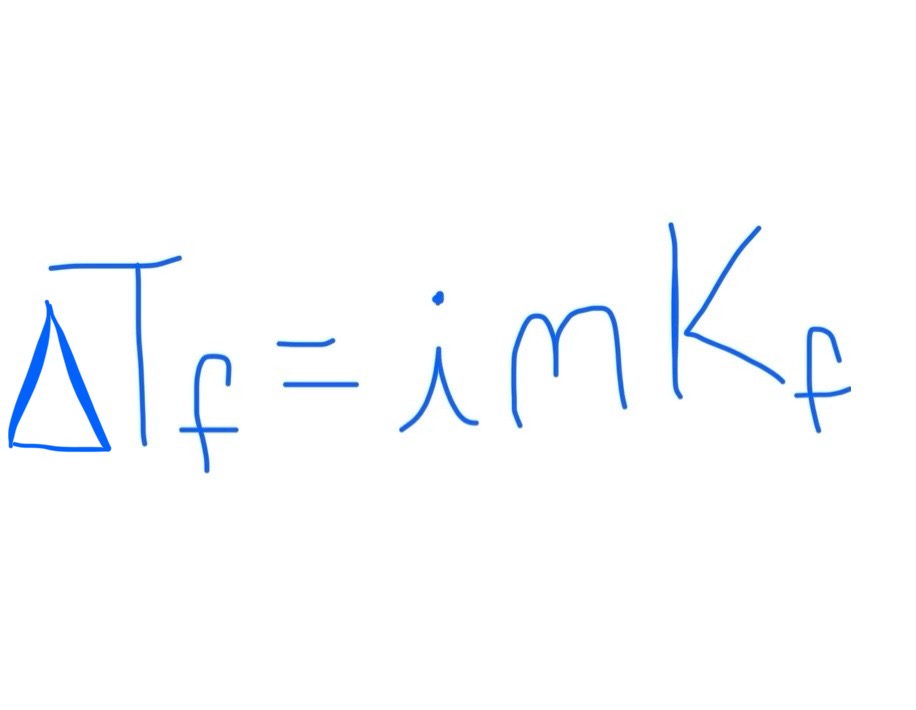
Equation for Boiling Point of Solution
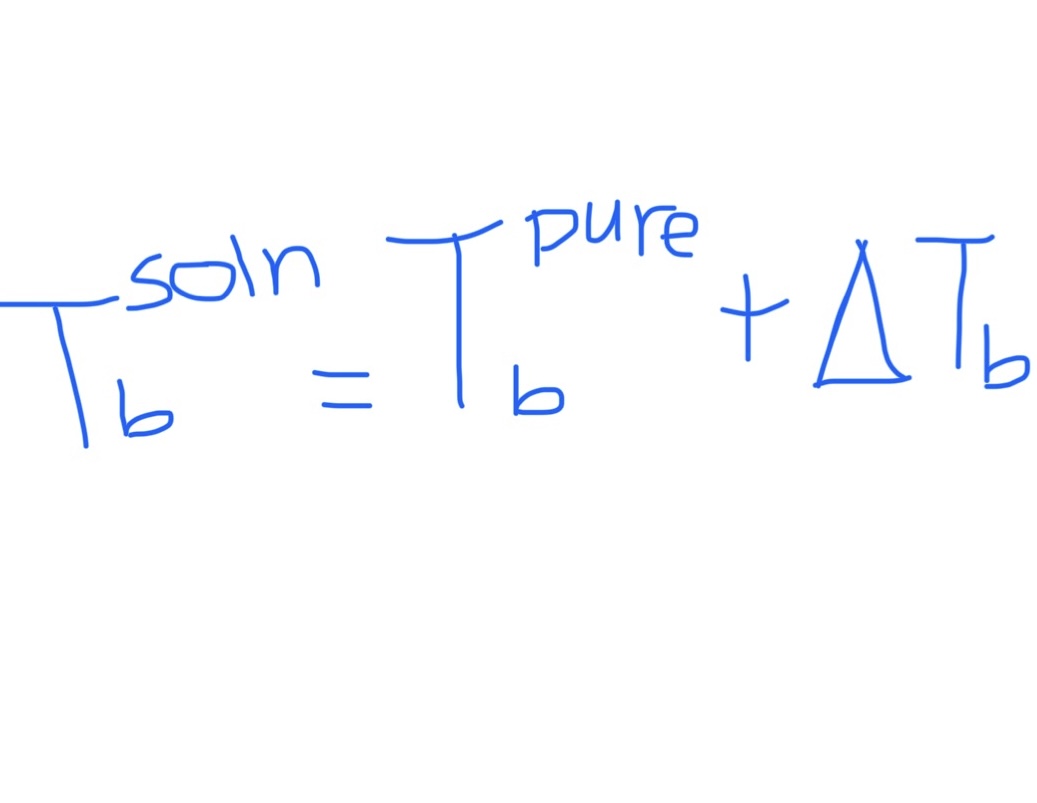
Osmosis Definition
The flow of solvent through a semi-permeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to one of high solute concentration
Osmotic Pressure Definition
The pressure to reverse osmosis
Kinetics Definition
The study of the rate (speed) of reactions and why
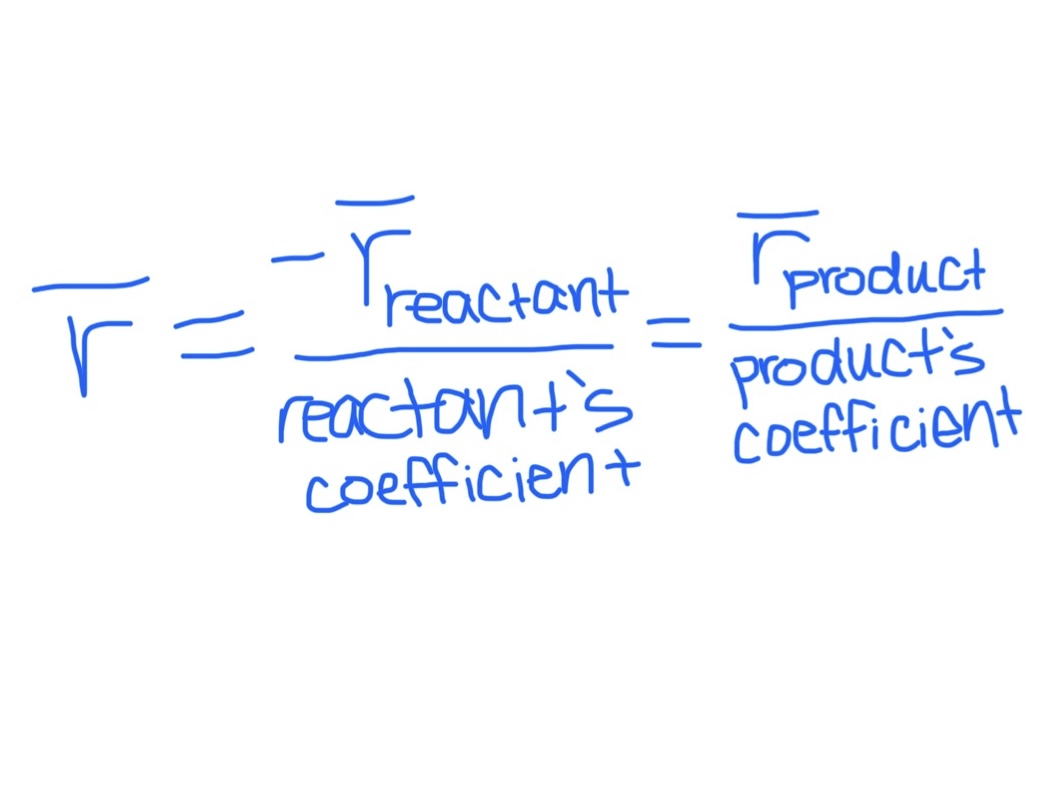
Equation Relating Average Rate of a Reaction, Reactant, & Product
Instantaneous Rate Definition
How fast a reaction goes
Relation Between Concentration and Speed of Reaction
They are directly related
high concentration = faster rxn
Rate Law: Relates Rate of Reaction to Concentration
x and y = individual rxn orders
if = 1, don’t write out 1
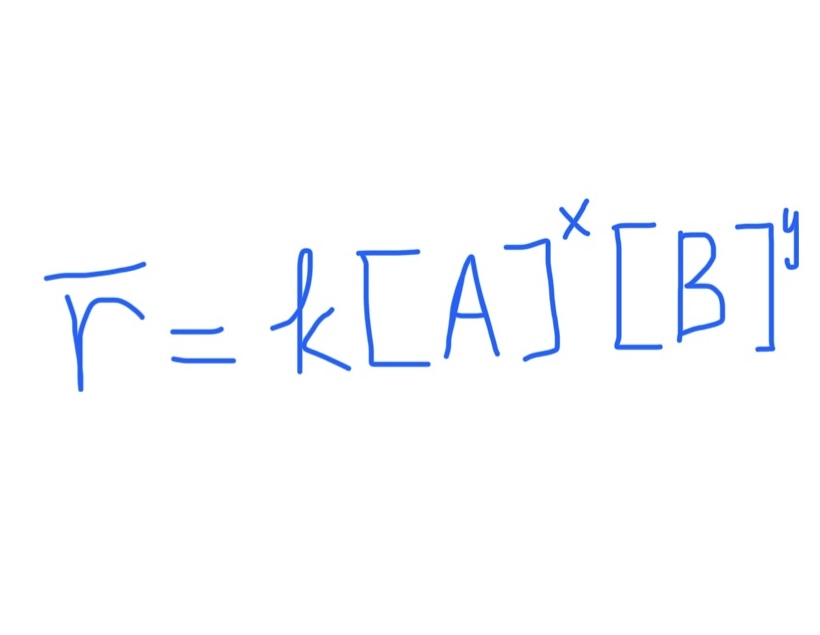
Formula for Units of k
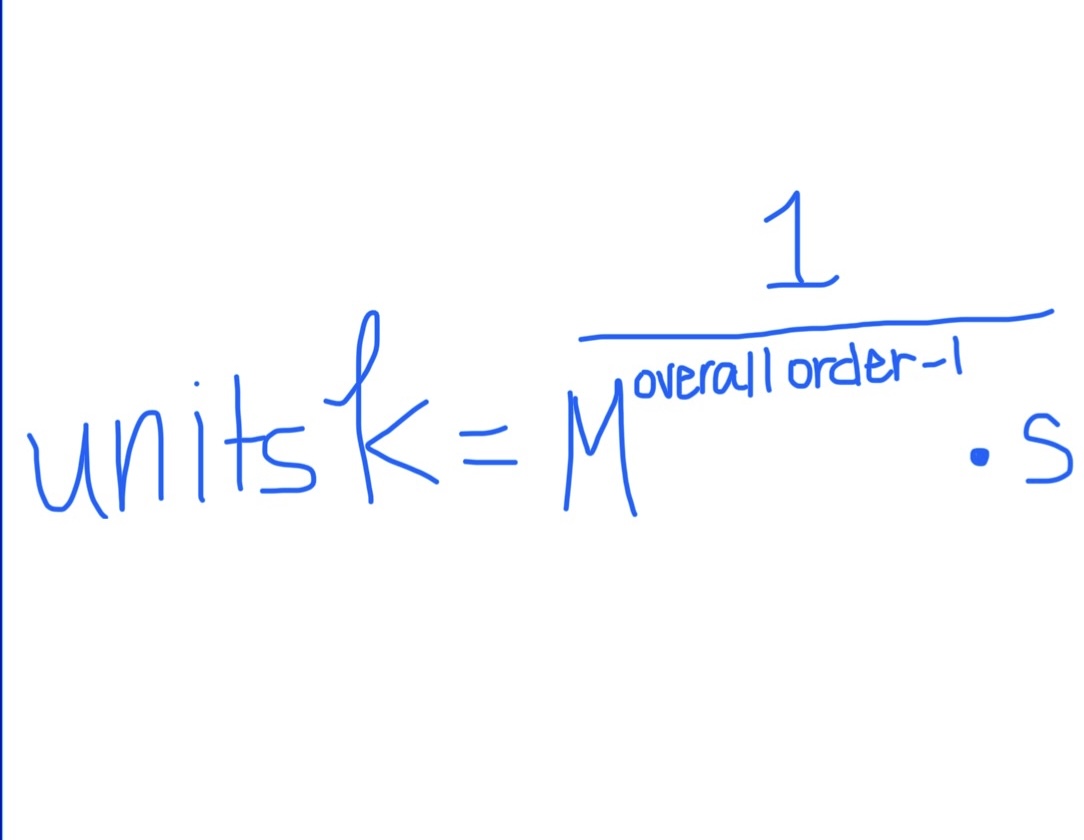
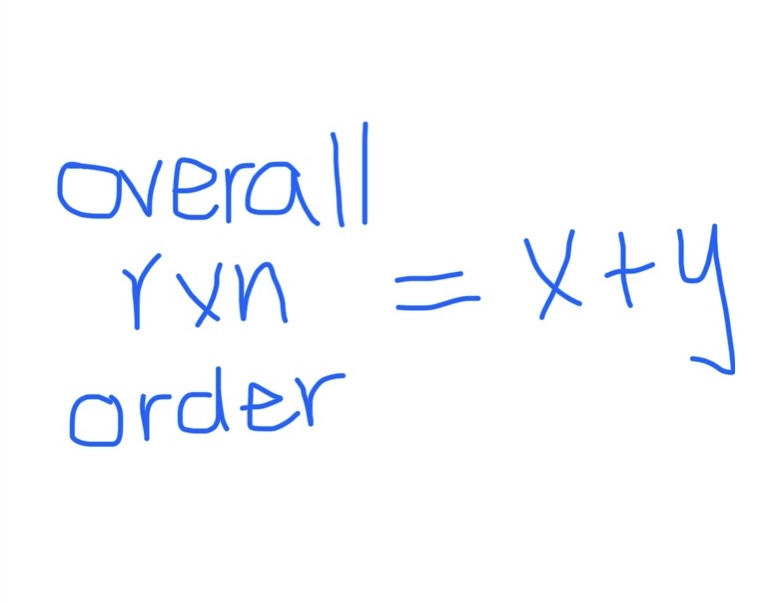
Formula for Overall Rxn Order
Elementary Rxn Definition
1 step/collision rxn
Composite Rxn Definition
Rxn with multiple elementary steps
opposite of elementary rxn
Method of Initial Rates Definition
Using different trials to determine individual rxn orders
Steps to Determine Individual Rxn Order
Determine what trials to use to determine order for [A]
use trials where the non-finding concentration’s values are the same
Identify if [A] exactly doubled between both trials
Yes: Compare value of rates of both trials
Rate doesn’t change → 0 order
Rate 2X → 1st order
Rate 4X → 2nd order
No: Use eqn and solve for order
Do same process to find order for [B]
![<ol><li><p>Determine what trials to use to determine order for [A]</p></li></ol><ul><li><p>use trials where the non-finding concentration’s values are the same</p></li></ul><ol start="2"><li><p>Identify if [A] exactly doubled between both trials</p></li></ol><ul><li><p>Yes: Compare value of rates of both trials</p><ul><li><p>Rate doesn’t change → 0 order</p></li><li><p>Rate 2X → 1st order</p></li><li><p>Rate 4X → 2nd order</p></li></ul></li><li><p>No: Use eqn and solve for order</p></li></ul><ol start="3"><li><p>Do same process to find order for [B]</p></li></ol>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c73891d3-4d1b-4eac-bbfe-80bbcff9278b.jpg)
Integrated Rate Laws Definition
Laws that relate concentration to time
Zero Order Integrated Rate Law Formula
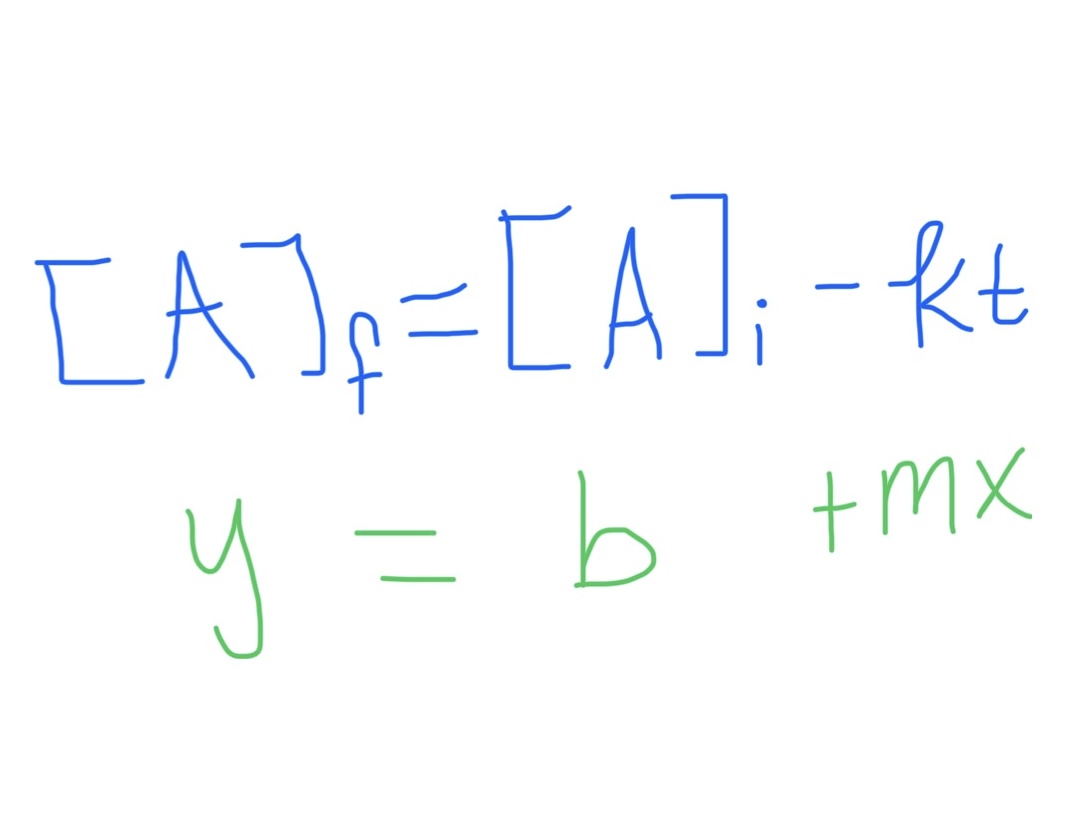
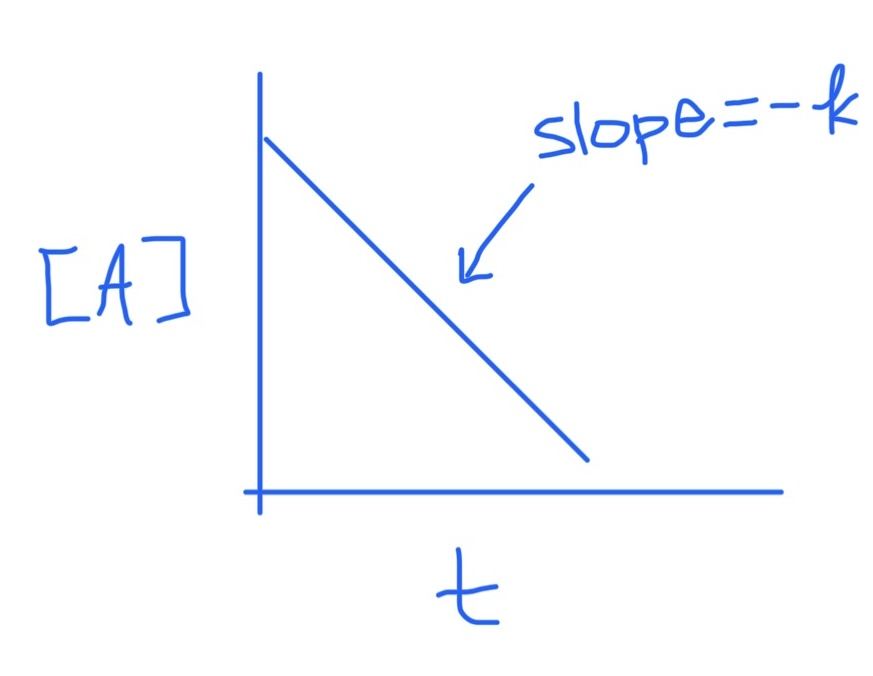
Zero Order Integrated Rate Law Graph
Slope = -k
First Order Integrated Rate Law Formula
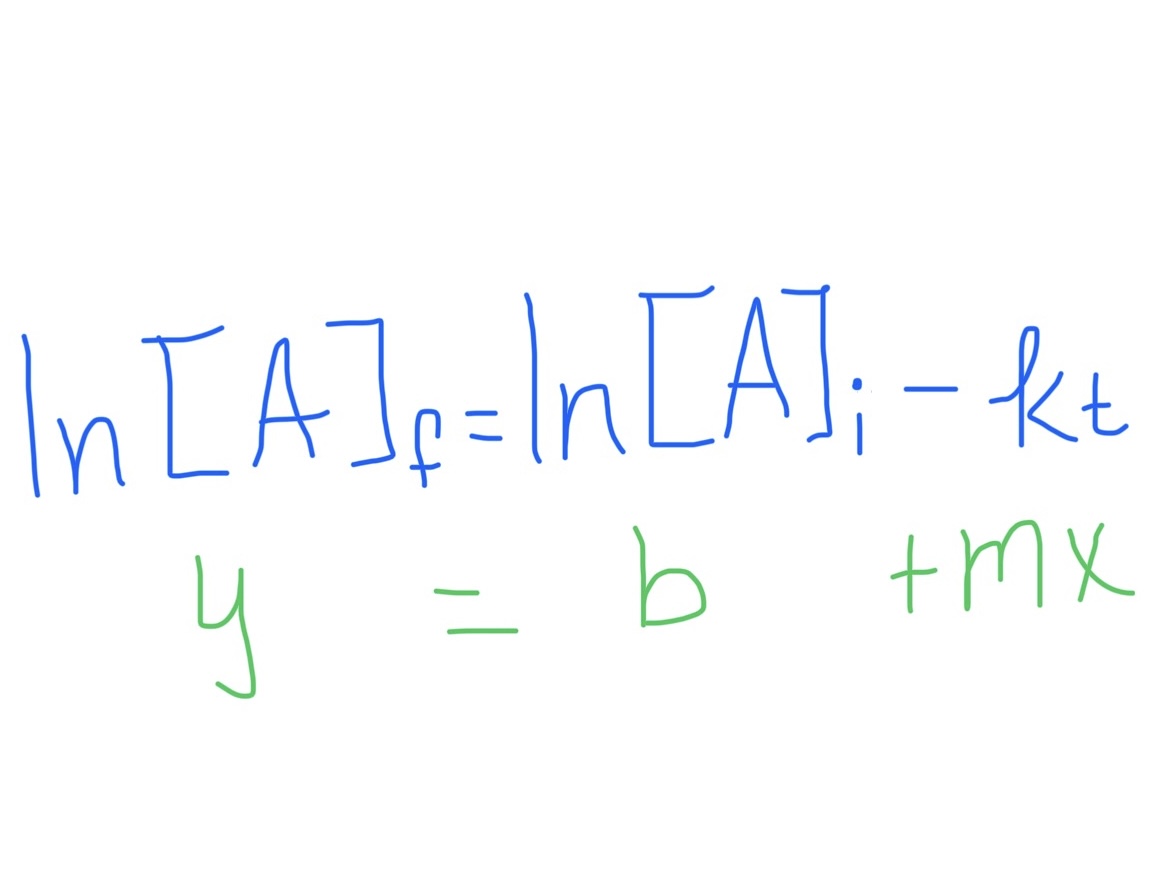
First Order Integrated Rate Law Graph
Slope = -k
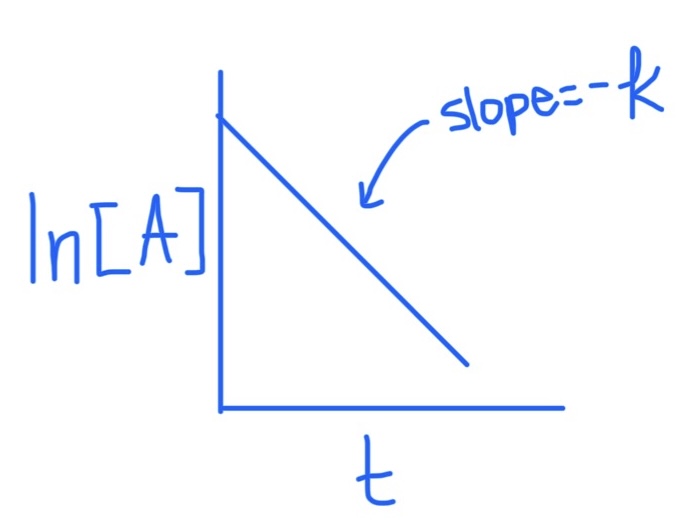
Second Order Integrated Rate Law Formula
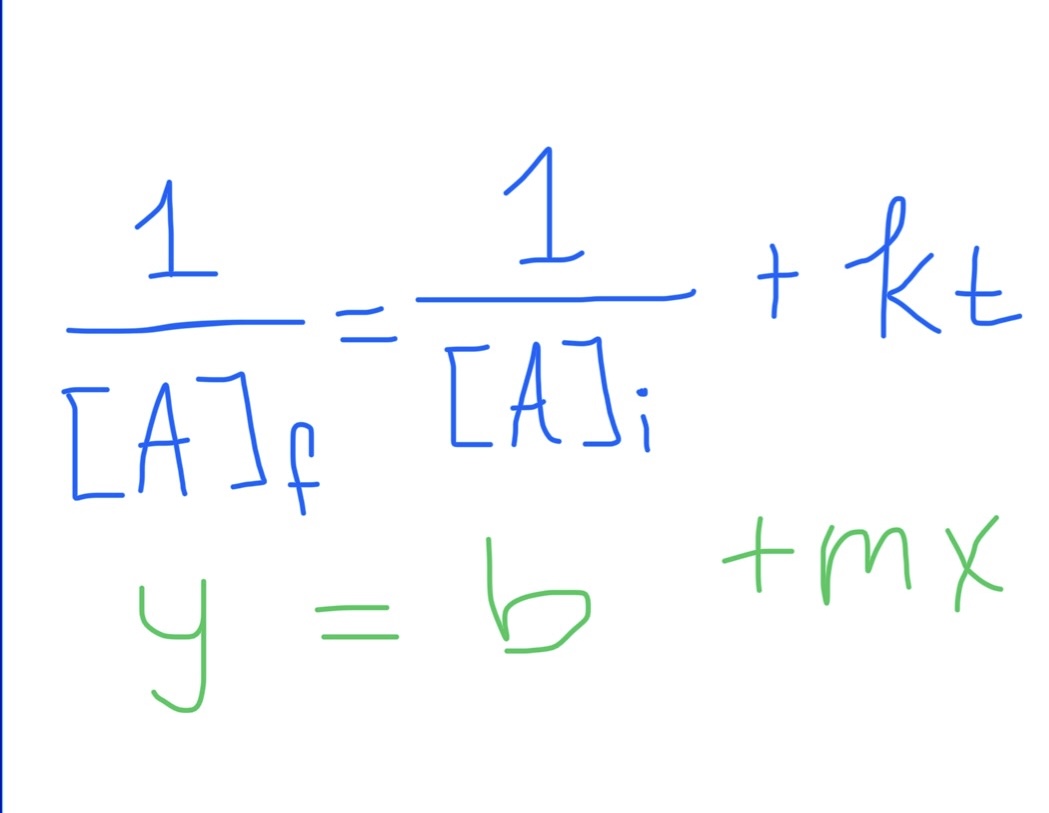
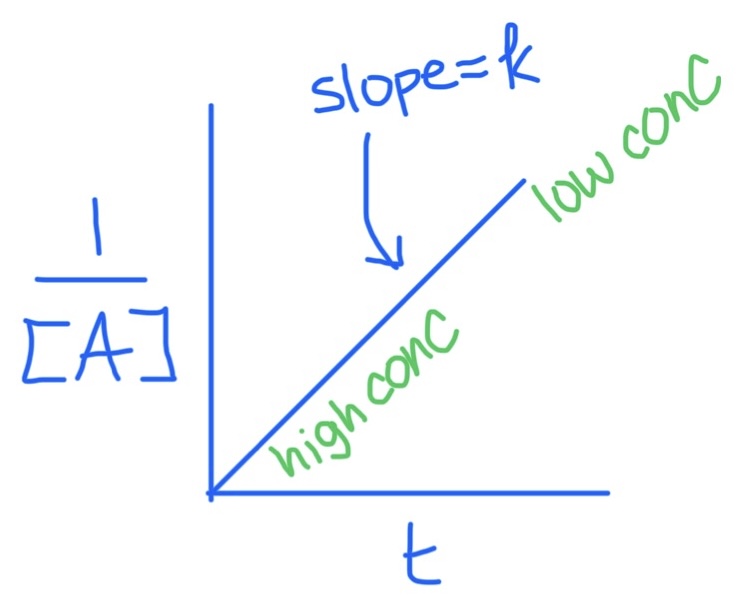
Second Order Integrated Rate Law Graph
Slope = k
High mi means …
Larger boiling point elevation
higher boiling point
Larger freezing point depression
lower freezing point
Low mi means …
Lower boiling point elevation
Lower freezing point elevation
When Calculating Molality, If Mass of Solvent Isn’t Given …
You can assume the denominator (kg solvent) is just 1 kg
if you’re given a mass, just convert it to kg
For Carbohydrate Compounds, i is usually
1
Equation for Average Rate of Formation
Product Specific
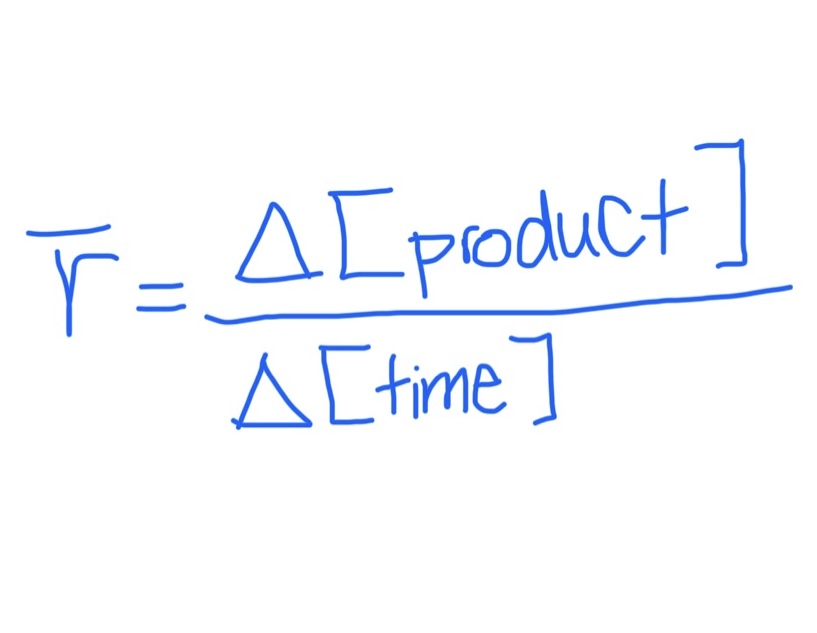
Equation for Average Rate of Consumption / Disappearance
Reactant specific
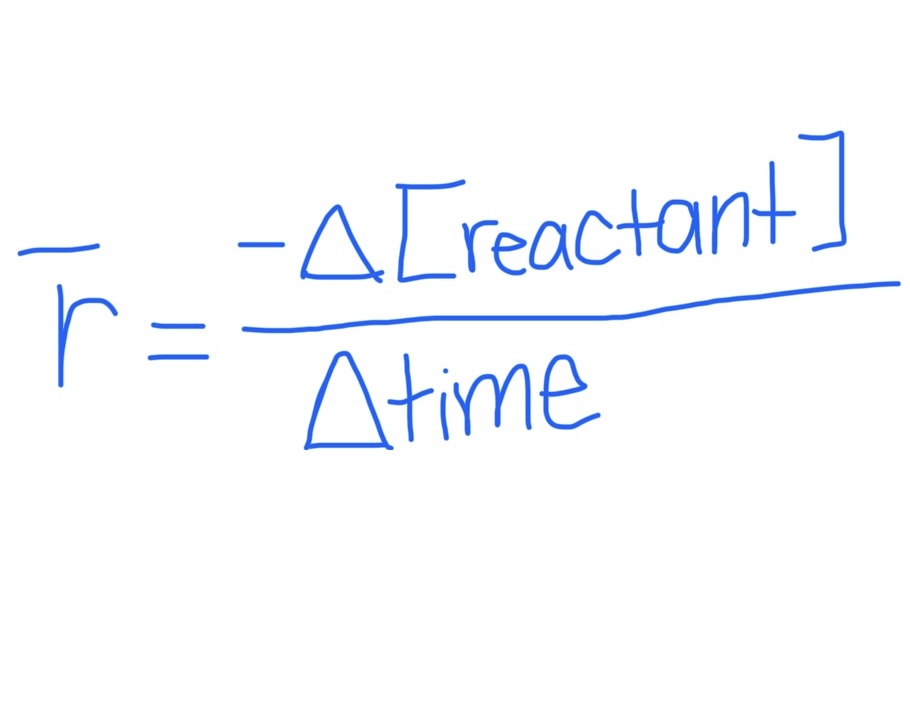
If Solute-Solvent Interactions are Weaker than Solvent-Solvent, Then Actual Vapor Pressure …
Will be higher than that predicted by Raoult’s law
If Solute-Solvent Interactions are Stronger than Solvent-Solvent, Then Actual Vapor Pressure …
Will be lower than that predicted by Raoult’s law
In Integrated Rate Laws, Time is In Units of …
Seconds
may have to convert to minutes if needed
Rate Law If x = 0
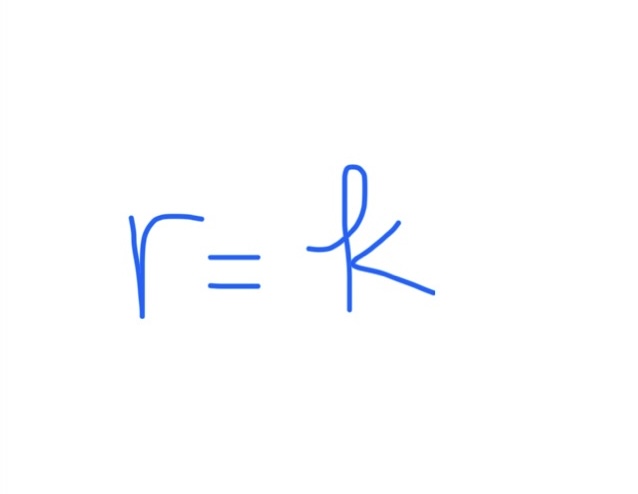
Rate Law If x = 1
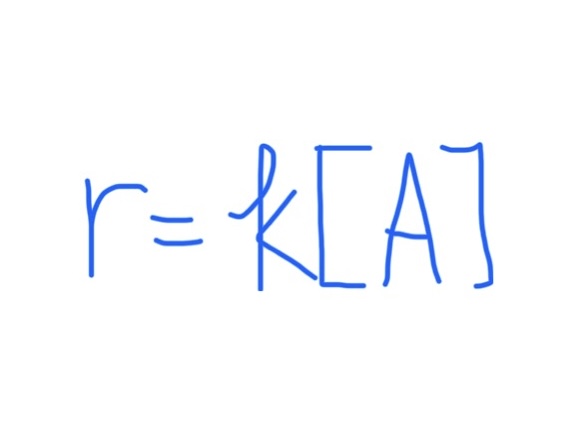
Rate Law If x = 2
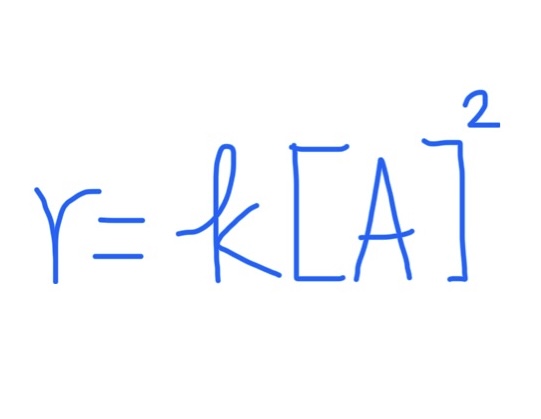
In Clausius-Clapeyron Eqn, ∆Hvap must be in …
J/mol
so multiply kJ by 1000 to get J
i (Van’t Hoff factor) depends on …
Solute
Density Formula

A liquid-liquid solution is ideal if …
It obeys Raoult’s Law
Solute-solute, solvent-solvent, and solute-solvent interactions are very similar
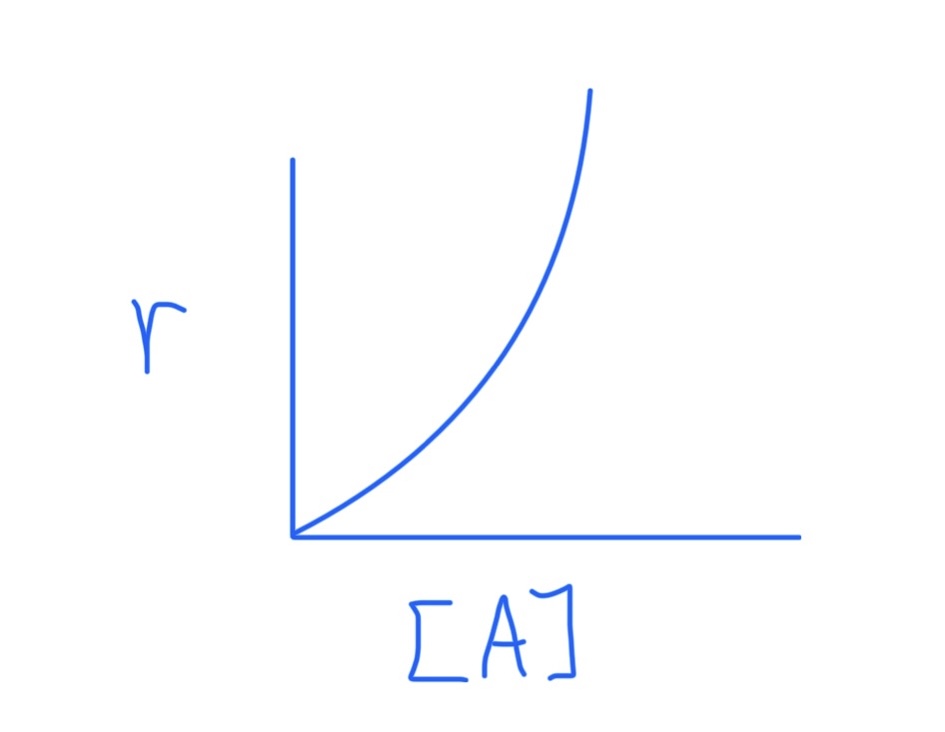
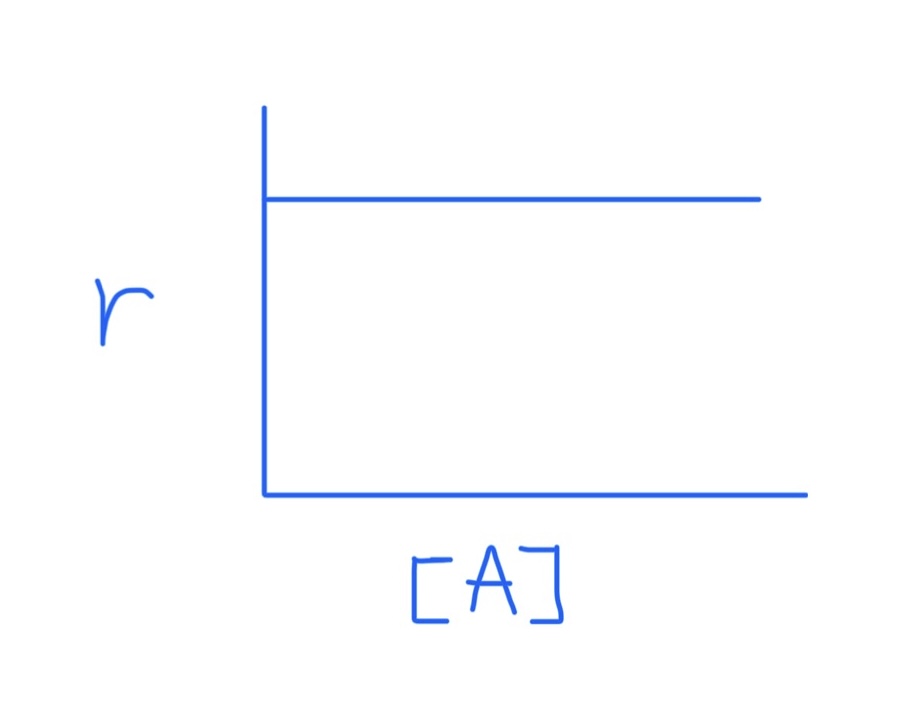
Graph for r = k
Graph for r = k[A]
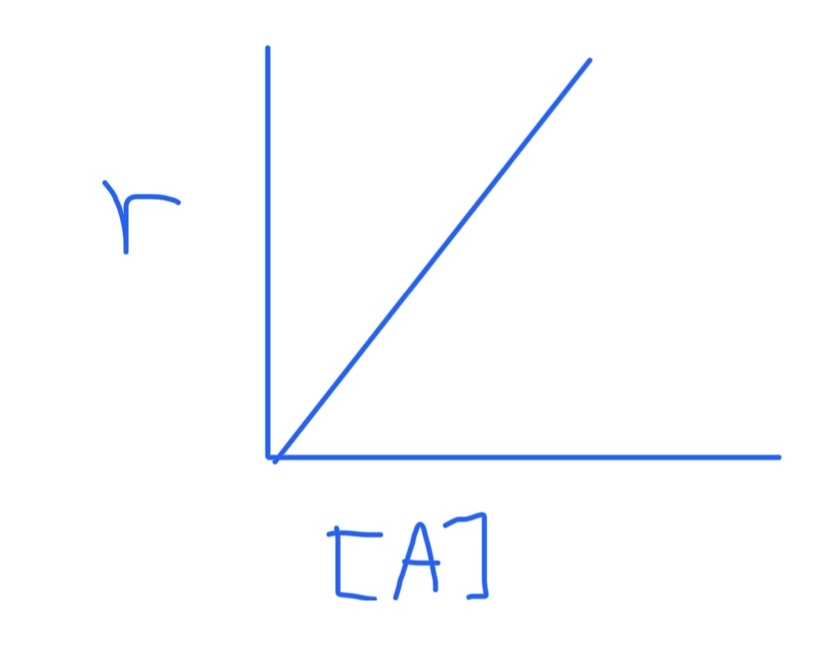
Graph for r = k[A]²