Physics Refraction and Lenses
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
The critical angle and formula
When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, the angle of incidence with a corresponding angle of refraction of 90 degrees. When this is surpassed it creates total internal reflection.
Formula: sin I/sin 90 → Sin C/1 → Sin C
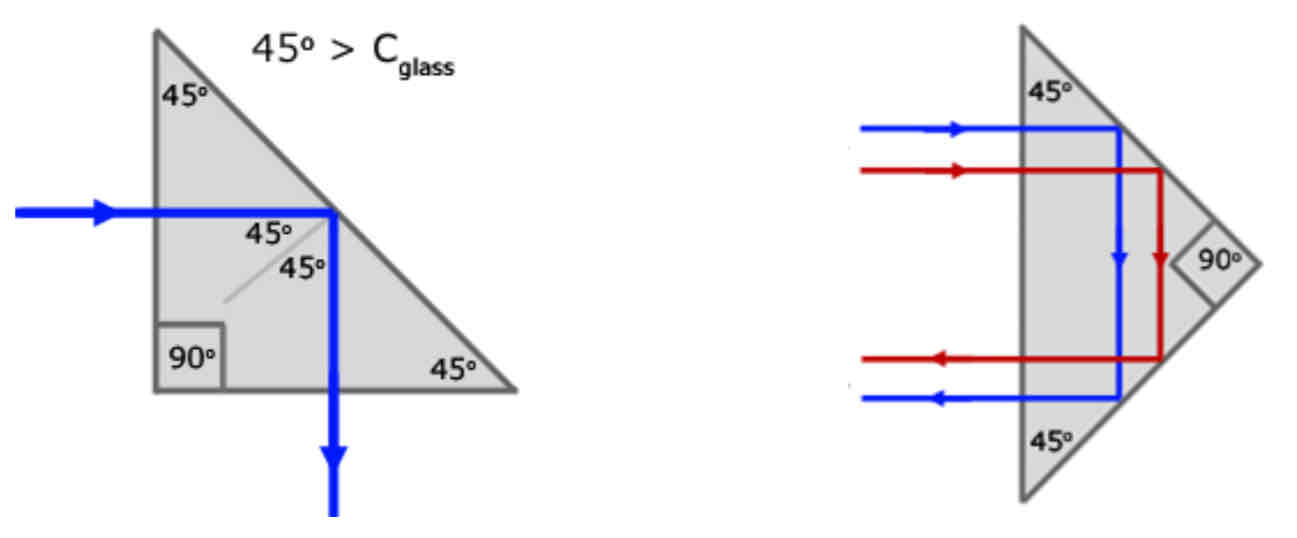
Shining light into prisms
the critical angle between glass and air is less than 45° so internal reflection occurs
Refraction from rarer to denser medium
The light is refracted towards the normal.
Refraction from denser to rarer medium.
The light is refracted away from the normal.
Laws of Refraction
The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the refracted ray all lie in the same plane.
The ratio of sine of the angle of incidence to sine of the angle of refraction is a constant.
Snell's Law
sin(i(angle of incidence)) /sin(r(angle of refraction)) = a constant, N(refractive index)
Real and Apparent depth formula:
N=Real depth/apparent depth
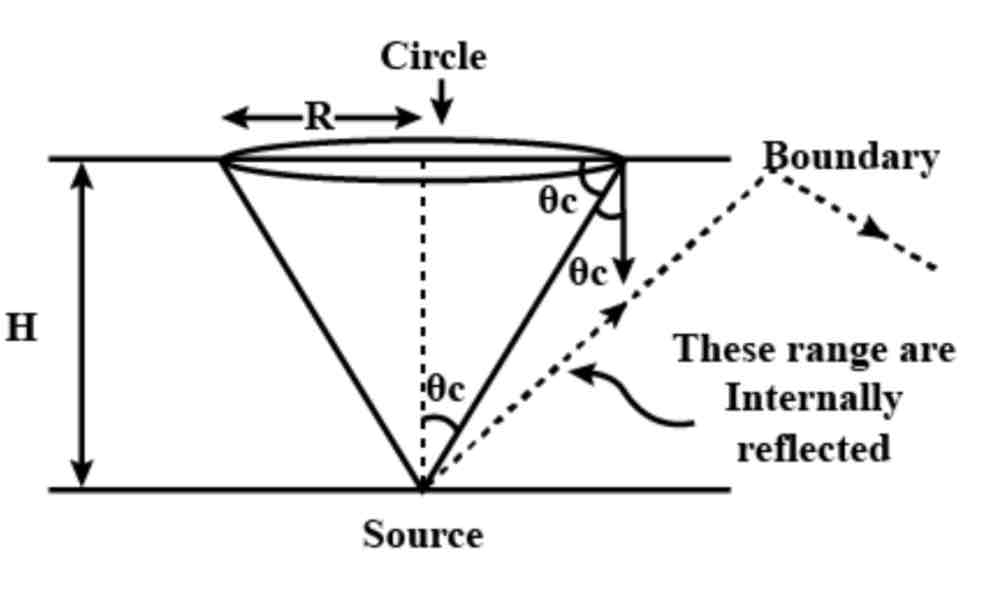
Snells window
A phenomenon by which an underwater viewer sees everything above the surface through a cone of light
total internal reflection
the complete reflection that takes place within a substance when the angle of incidence of light striking the surface boundary is less than the critical angle and light is reflected in the medium.
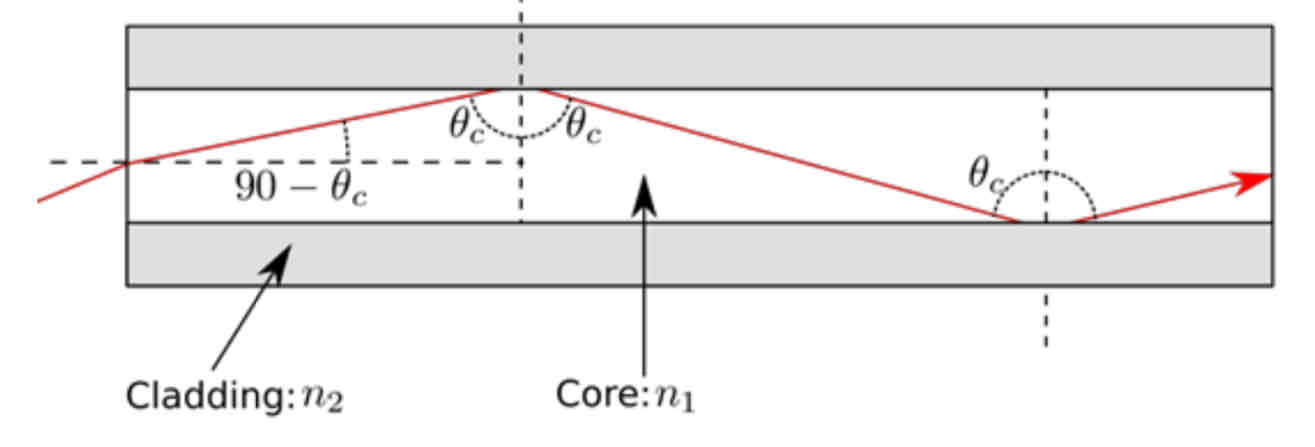
Optical fibres
Optical fibres enable information to be carried using light.
They work by Total internal reflection
An optical fibre consists of a glass pipe coated with a second material of lower refractive index.
Light enters one end and strikes the boundary at an angle greater than the critical angle. Reflected light strikes the interface on the opposite wall and gets totally reflected again.
process continues until the light emerges at the end.
Using relative speeds of light to find the refractive index of a medium
N = C(speed of light in air(3x10^8m/s)/V(speed of light in a medium)
Power of a Lens
The power of a lens is how much a lens diverges or converges light. The power of a convex lens is positive(+) The power of a concave lens is negative(-)
Formula for power of a lens
P = 1/f
Formula for the power of a combination of lenses.
P = P1 + P2
The Retina's role in the eye
The Retina is a light sensitive screen at the back of the eye that allows a real image to be seen clearly when brought to focus.
The Blind Spot
the point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye
Focusing Light on the Retina
Ciliary muscles give the eye the ability to focus a real image of objects on the retina by being able to change the shape of the lens.
If an object is viewed from a large distance how would the ciliary muscles act to bring it to focus?
The ciliary muscles would be relaxed
If the object is viewed from a close distance how would the ciliary muscles be when the image is brought to focus?
The Ciliary muscles would be contracting.
Optic centre
The centre of a lens
Principal axis
A line running through the pole of a mirror or the optic centre of a lens
Focus/focal point of a lens
The point at which light converges or where the diverging rays meet virtually
Images formed on a concave lens
The closer the object is to the lens, the bigger the image is.
The image is always on the same side of the lens as the object.
Image is always diminished
Real images in a convex lens
If an object is placed behind the focal point the image will be real and inverted (The closer the object is to the focal point the larger the image will be)
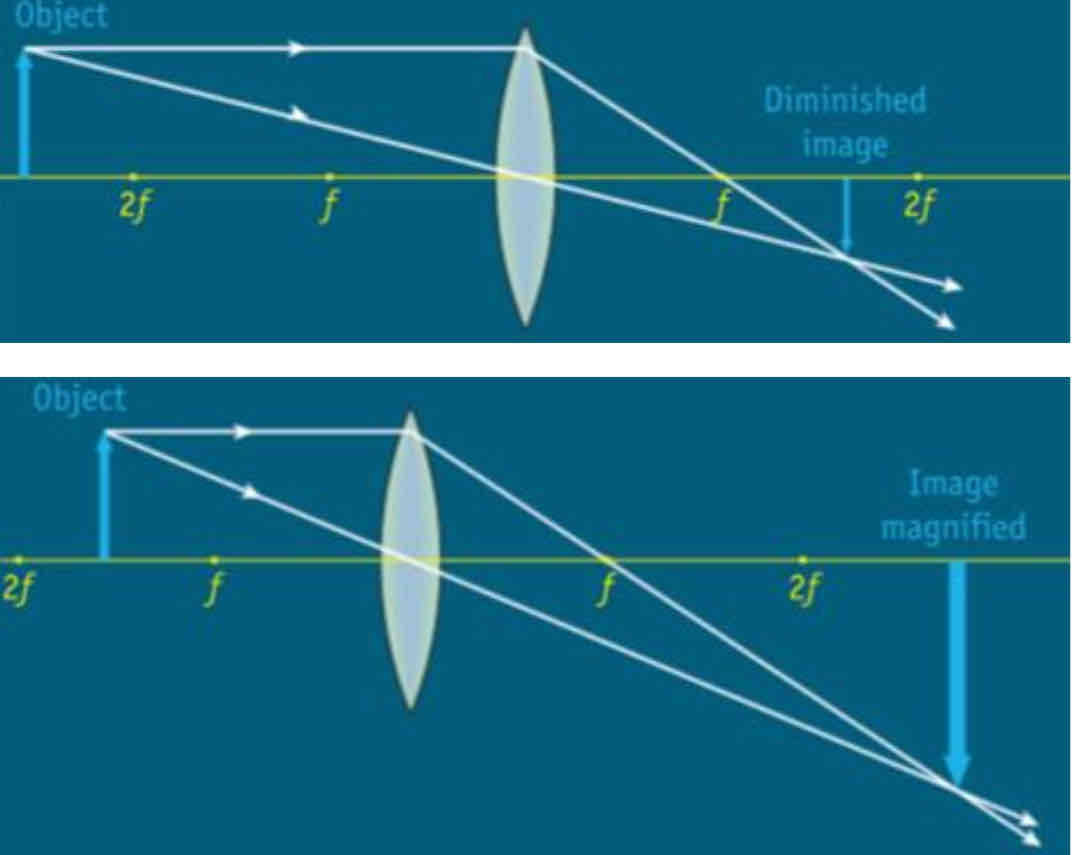
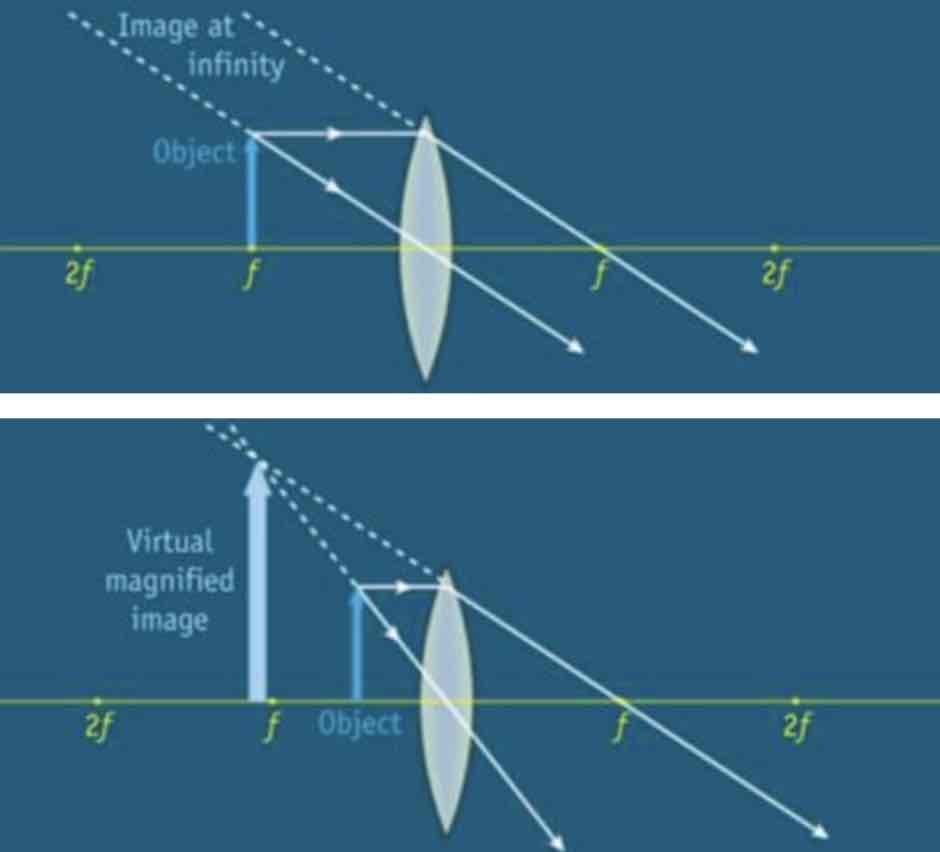
Virtual images formed on a convex lens.
If an object is placed in front of the focus, the image produced will be virtual and upright. (The closer the object is to the focus, the larger the image will be)
Refraction
The bending of Light as it travels from one medium to another.
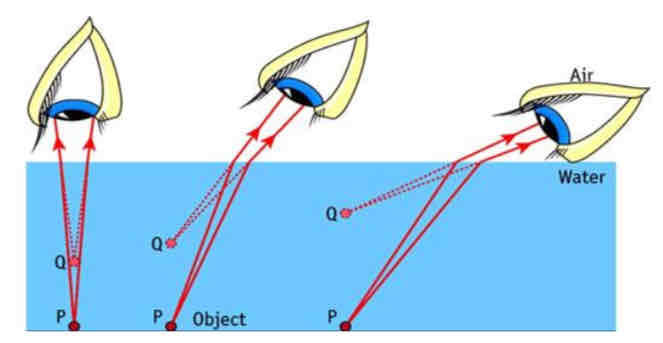
Draw a diagram to explain why someone underwater would not appear to be at their real depth from an observer.
Which lens corrects myopia?
Concave
Which lens corrects hyperopia
Convex