Cardiovascular Toxicology
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the formula for cardiac output?
heart rate x stroke volume
(CO = HR x SV)
What is the formula for blood pressure?
Blood pressure = cardiac output x systemic vascular resistance
(BP = CO x SVR)
Describe the flow of different ions during cardiac myocyte action potential
Phase 0 (depolarization)
Ca and Na rush in
Phase 1
Na channels close
Phase 2
Ca comes in
K goes out
Phase 3 (rapid repolarization)
K goes out
Ca channels close
Phase 4 (resting potential)
Leaky K channels
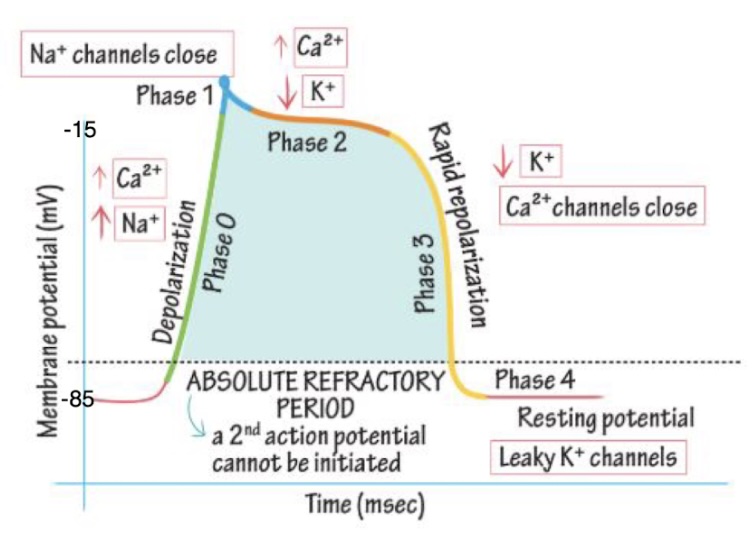
When is the cardiac myocyte absolute refractory period?
Phase 0 - phase 3: a second action potential cannot be initiated
What are the roles of NKA and NCX pumps in reestablishing the resting state prior to the next AP?
NKA pumps: reset intracellular K+ and extracellular Na+ levels
NCX: use Na+ (moves in) gradient to extrude Ca2+ (moves out)
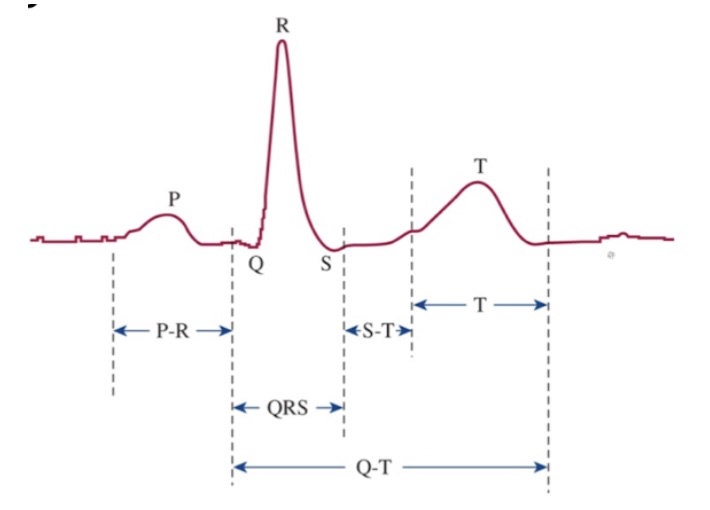
What is the P wave?
Atrial depolarization
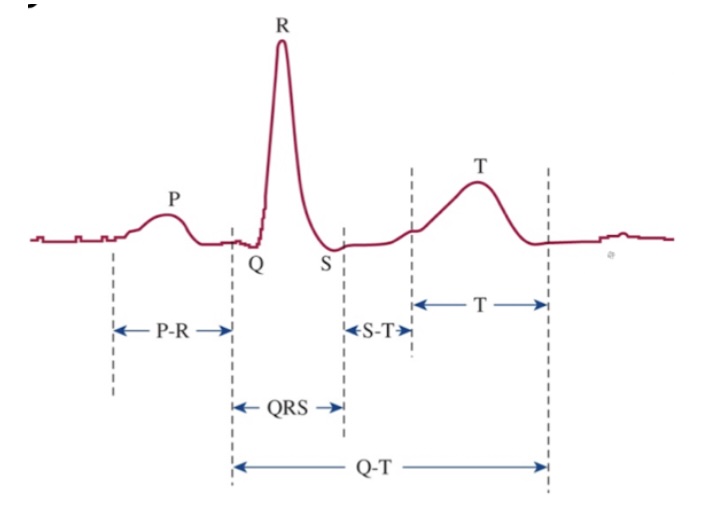
What is the P-R interval?
Speed of conduction through AV node
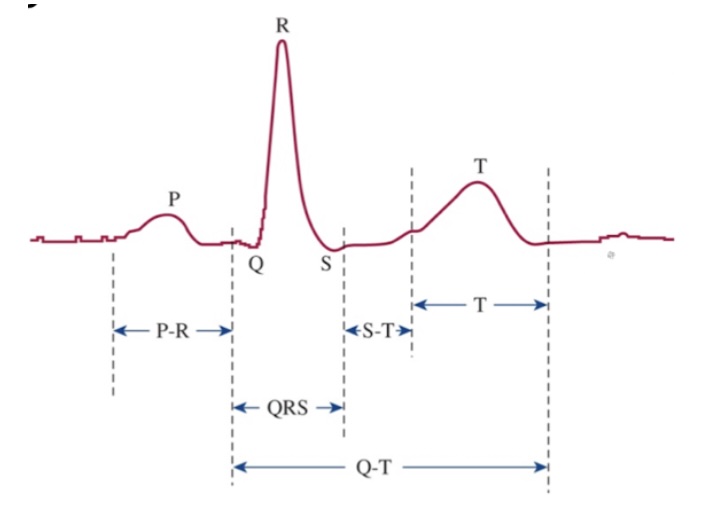
What is the QRS complex?
Ventricular depolarization
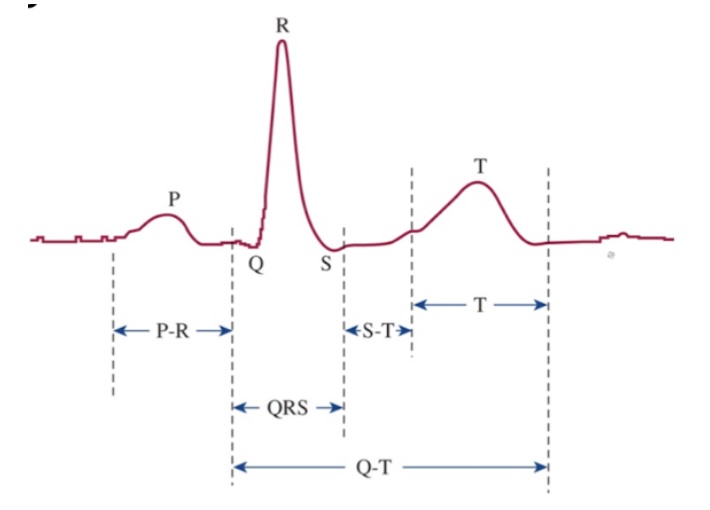
What is the S-T segment?
Time which entire ventricular myocardium is depolarized
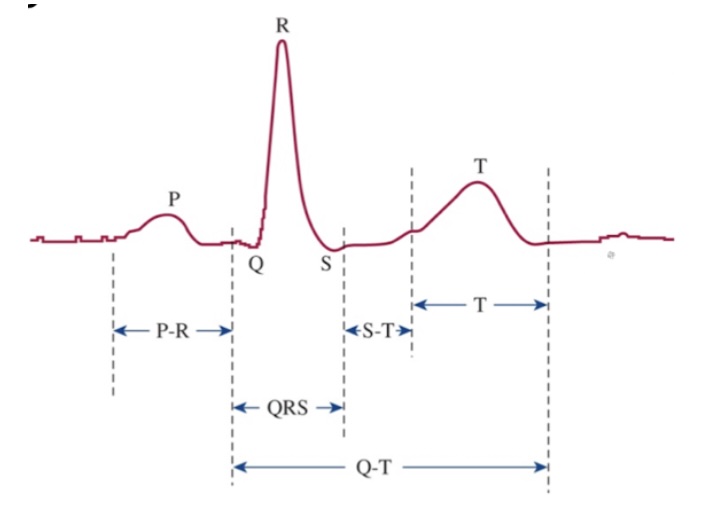
What is the T wave?
Ventricular repolarization
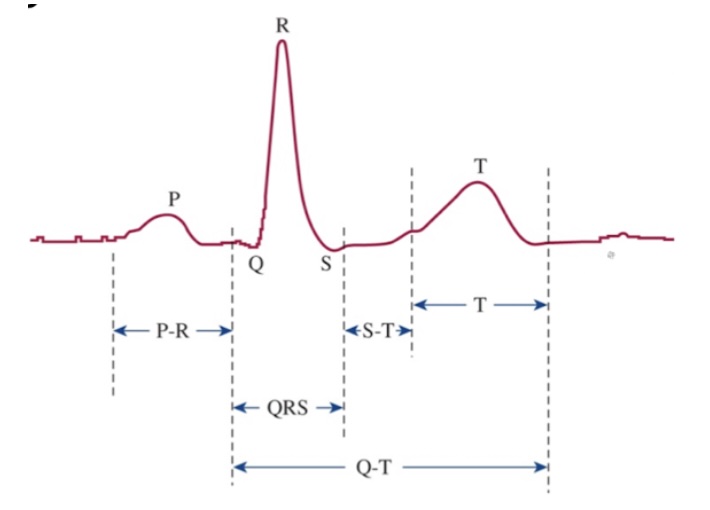
What is the Q-T interval?
Time for ventricular depolarization and repolarization
What are the effects of digoxin?
↑ contractility (inotropy) → ↑ stroke volume → ↑ cardiac output (CO = HR * SV)
↓ HR (chronotropy) to allow ventricles more time to fill → increase CO via increasing SV
Increases CO and BP
What is the MOA of digoxin?
Inhibits NKA pumps → increase intracellular Na and Ca, which causes more muscle contraction
Increases vagal tone → decrease chronotropy
What are treatments for digoxin toxicosis?
Activated charcoal
Fluid therapy
Antiarrhythmics
Digoxin-specific antibody fragments (Fab)
What are beta blockers’ MOAs?
B1 and B2 antagonism
a1 antagonism for carvedilol
What are common effects of B blockers in an overdose?
Bradycardia
Hypotension
Lethargy
Weak, shaky
How do B blockers affect CO and BP?
Lower CO and BP
What are treatments for B blocker overdose?
Emesis, activated charcoal, hemoperfusion
IV fluids (for hypotension)
Atropine (for bradycardia)
Glucagon therapy
What is the MOA of CCBs (calcium channel blockers)?
Affect L-type calcium channels in cardiac myocytes and vascular smooth muscle
Decrease chronotropy
Decrease inotropy
Decrease vascular resistance
What are common effects of CCB toxicosis?
Hypotension
Sinus bradycardia
Sinus tachycardia
Lethargy, depression
Vomiting
What are treatments for CCB overdose?
Emesis, AC, intralipids
Fluids, calcium, vasopressors
High-dose insulin/dextrose therapy (preferred therapy)
Glucagon treatment (if others not effective)
What is the impact of NKA antagonism on intracellular and plasma K+?
Intracellular: decrease
Plasma: increase
Causes hyperkalemia
What is the impact of NKA agonism on intracellular and plasma K+?
Intracellular: increase
Plasma: decrease
Causes hypokalemia
How do CCBs affect blood glucose levels and intracellular glucose levels?
CCBs effects on glucose regulation:
1) ↓ insulin release from pancreatic beta cells
L-type calcium channels involved in insulin release
2) Inhibit protein kinase B in cardiac myocytes -> glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) does not insert in plasma membranes
Result: ↓ glucose in cardiac cells -> ↓ ATP production.
Increase glucose in blood
How do beta blockers affect blood glucose levels and intracellular glucose levels?
Blood glucose levels: decrease
Intracellular glucose levels: increase
Decrease glucagon and increase insulin
How do beta agonists affect blood glucose levels and intracellular glucose levels?
Blood glucose levels: increase
Intracellular glucose levels: decrease
Increase glucagon and decrease insulin
How does glucagon therapy function to treat beta blocker toxicoses?
B1 adrenergic receptors and glucagon receptors mediate activation of cAMP → increase Ca2+ entry → improve inotropy
Improves chronotropy by How does high-dose insulin/dextrose therapy function to treat CCB toxicoses?
How does high-dose insulin/dextrose therapy function to treat CCB toxicoses?
Insulin improves cardiac myocyte functioning:
1) ↑ inotropy (mechanism not entirely clear)
2) Provides more fuel for ATP production in myocytes.