nucleic acids and DNA replication
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
give five structural differences between a DNA molecule and an mRNA molecule.
1. DNA has deoxyribose, mRNA has ribose
2. DNA has thymine, mRNA has uracil
3. DNA long, mRNA short
4. DNA is double stranded, mRNA is single stranded
5. DNA has complementary base pairing, mRNA does not
function of DNA
in all living cells, DNA holds genetic info
function of RNA
in all living cells, RNA transfers genetic info from DNA to ribosomes
DNA molecule
an antiparallel, double helix with two polynucleotide chains help together by hydrogen bonds between specific complementary base pairs
RNA molecule
a relatively short polynucleotide chain
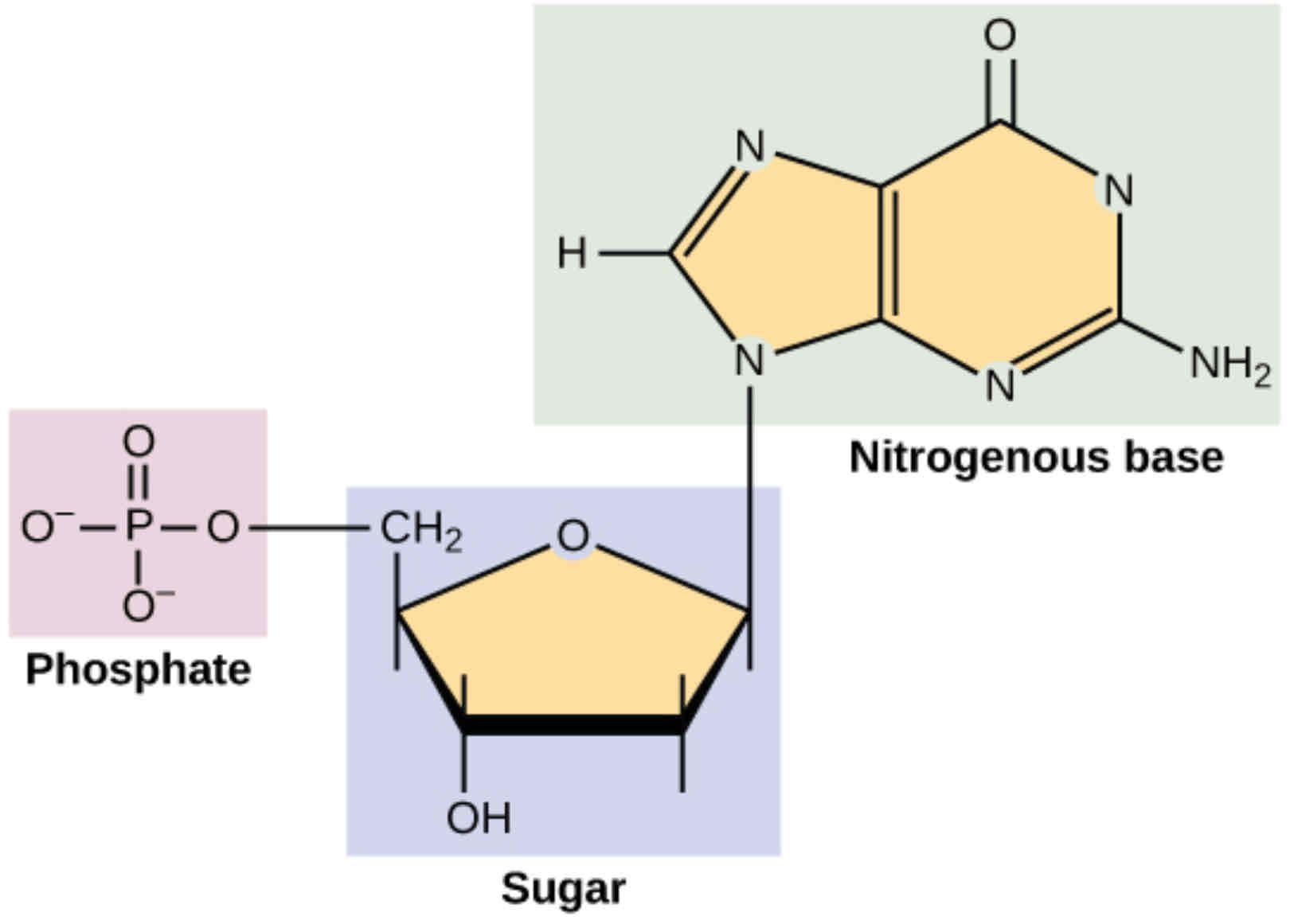
nucleic acids
in all living cells
binding DNA nucleotides
pentose sugar bonds to the phosphate group via condensation reaction → phosphodiester bond
continued condensation reactions form a polynucleotide chain
RNA structure
components of an RNA nucleotide: ribose, a phosphate group and one of the organic bases adenine, cytosine, guanine or uracil
single stranded, shorter than DNA, less stable than DNA
3 forms: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
purines
adenine and guanine are double-ring structures (making them purines)
pyrimadines
cytosine and thymine are single-ring structures (making them pyrimadines)
DNA structure
1. polymer of nucleotides
2. each nucleotide formed from deoxyribose, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base
3. phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides
4. double helix held together by hydrogen bonds
5. complementary base pairing between adenine, thymine and cytosine, guanine
give the two types of molecule from which a ribosome is made
formed from rRNA and proteins
name the two scientists who proposed models of the chemical structure of DNA and of DNA replication
Watson and Crick
explain how the organic bases help to stabilise the structure of DNA
1. hydrogen bonds between the base pairs holds two strands together
2. many hydrogen bonds provides strength
describe how a phosphodiester bond is formed between two nucleotides within a DNA molecule
1. condensation reaction
2. between phosphate and deoxyribose
3. catalysed by DNA polymerase
how is the structure of DNA related to its function?
1. double stranded helix with a sugar phosphate backbone, so provides strength and stability
2. long, large molecule, so can store lots of information
3. coiled into a helix, so compact
4. sequence of bases, so allows information to be stored and codes for protein
5. double stranded, so both strands can act as templates
6. many hydrogen bonds, so stable and strong
outline the similarities, and the differences between, the structures of DNA and RNA molecules.
similarities:
1. polymers of nucleotides
2. nucleotide has pentose, nitrogen-containing organic base and a phosphate group
3. cytosine, guanine and adenine as bases
differences:
1. deoxyribose vs ribose
2. thymine vs uracil
3. long vs short
describe how DNA is replicated / semi-conservative replication
1. DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the two DNA strands
2. both strands act as templates
3. free DNA nucleotides line up in complementary pairs
4. complementary base pairing between adenine and thymine and between guanine and cytosine
5. DNA polymerase joins nucleotides of new strand
6. each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one new strand
describe and explain how the structure of DNA results in accurate replication
1. two strands therefore semi-conservative replication possible
2. hydrogen bonds hold strands together
3. hydrogen bonds weak, so easily broken, allows strands to separate
4. base sequences exposed so act as template
5. adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine
use your knowledge of semi-conservative replication of DNA to suggest the role of the single-stranded DNA fragments
1. template
2. determines order of nucleotides
use your knowledge of semi-conservative replication of DNA to suggest the role of DNA nucleotides
forms complementary base pairs, adenine with thymine and guanine with cytosine
explain the role of two named enzymes in the process of semi-conservative replication of DNA
1. DNA helicase causes breaking of hydrogen bonds between DNA strands
2. DNA polymerase joins the DNA nucleotides
3. forming phosphodiester bonds
explain why the arrows point in opposite directions
1. DNA has antiparallel strands
2. nucleotides align differently
3. enzymes have active sites with specific shape
4. only substrates with complementary shape can bind with active site of DNA polymerase
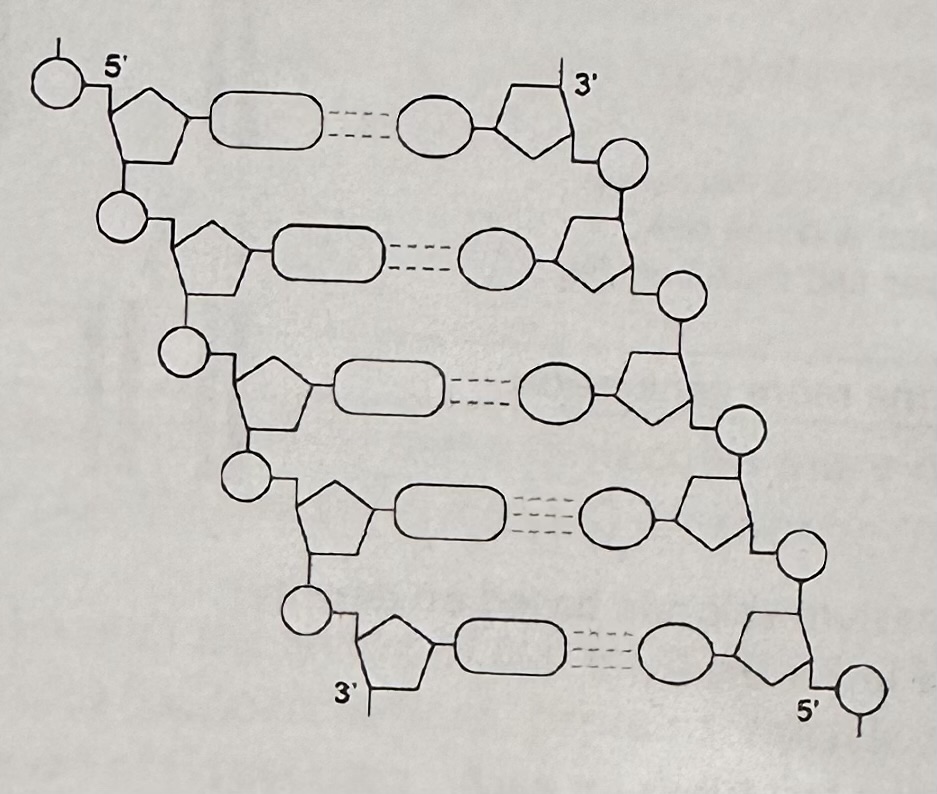
use the image and your knowledge of enzyme action and DNA replication to explain why new nucleotides can only be added in a 5’ to 3’ direction
1. DNA polymerase
2. which is specific
3. only complementary with 5’ end of strand
4. shapes of 5’ end and 3’ end are different
what does semi-conservative replication mean?
- each strand acts as a template
- daughter DNA has one new strand and one original parent strand