(MAR3023-0003.su15) Basic Marketing Concepts Exam 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What is Marketing?
The answer to the question of why you buy a product
What is the aim of Marketing?
To make selling, promotion, and advertising unnecessary
-Peter Drucker
What are the 4 P's?
→ 4 levers
→ Marketing Mix
• Product
• Price
• Place (Distribution)
• Promotion
What is the most important of the the 4 P's?
Product
What are the 4 P's?
→ Product
• Most Important
→ Sells itself
What are the 4 P's?
→ Price
• The RIGHT Price is NOT always the LOW price
→ Starbucks
• Exclusivity
• Quality Perceptions
What are the 4 P's?
→ Place
• Getting the product where people can buy it
→ How you Distribute
What are the 4 P's?
→ Promotion
• Don't need it if you have a good product
• Time/Reality
→ Leads to Imitators
What is the FIRST goal of marketing?
• To identify unmet consumer needs and then develop products that fill those needs.
→ Model T
Great marketers do 3 things to make GAME CHANGER Products:
1. Develop PRODUCTS that people want or need
2. PRICE them at a level that maximizes profits
3. DISTRIBUTE them to where consumers are
You'll pay more for a product because of:
• Brand
→ Coke & Pepsi & Publix
• People don't buy product they're not use to
→ Ex. McDonalds on side of the Road
Marketing is
→ The process by which companies determine what products and services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. - kotler
→ The foundation of every business.
What is the Misconception of Marketing?
Promotion
Marketing is actually:
• COMPLEX
• Strategic
→ Segmentation
→ Positioning
→ Reposition
• Quantitative
• Multifaceted
So what about the visible side of marketing?
Why is it needed and so prominent?
What forces competitors firms to promote products?
• Time/Reality
→ Make Imitator Products
→ → Often Food Restaraunts
Time/Realty
• Over time, the market reacts with competitor products that have similar benefits
• Now the dominant firm has to convince customers its product is superior
__ Are VERY powerful ???
Advertising and Branding
→ Old Milwauke's Light
What are the 4 things to take away from day 1?
• The primary goal of marketing is to develop good PRODUCTS that consumers want and need
→ They also have to be priced appropriately and delivered to where consumers are...
• If firms do marketing correctly, they don't need to advertise much... for a while anyway...
• Over time, competitors force firms to promote their products in order to differentiate them from close competitors
• In reality, firms need to perform all 4 Ps well in order to drive profits ... and everything else
Consumer Reports
Rates all of the imitation products you saw as objectively the SAME as - or better than - the branded products
History of Marketing
• Simple Trade Era (Pre-1860s)
• Production Era (Pre-1920s)
• Sales Era (1920s)
• The Marketing Era (1940s-1990s)
• Relationship Marketing Era (1990s-2010)
• Societal Marketing Era (1960s- present)
Simple Trade Era
(Pre-1860s)
• Products were made by hand, grown, or traded in small quantities INEFFICIENT
→ Lasted up until the Industrial Revolution
Production Era
(Pre-1920s)
• "You can buy any color Model T...."
→ Inward Focus
→ Technical Development
• Condition: Seller's Market; Demand Exceeded Supply
→ Consumers didn't have alternatives / Little Competition
Sales Era
(1920s)
• Sell what we make
• "Changing their minds"
• Focus on:
→ Sell what we make
→ Aggressive promotion - vacuum cleaners
→ Short-term profit maximization
The Marketing Era
(1940s-1990s)
• The "great awakening" where customers became the central focus of the organization
• Began with the development of marketing departments (1940-1960) and then transferred to the rest of the firm (1960-1990)
• Focus on:
→ Customer is the key — "delight"
→ Make what we sell
What are the Key terms that came out of the Marketing Era?
• Customer Centric Marketing: CCM
• Relationship Marketing: RM
• Customer Relationship Management: CRM
• Green Marketing: GM
The Marketing Era (1940s-1990s) Key Terms:
Customer Centric Marketing:
• Collaborative relationships based on customers' individual needs and concerns
→ Understanding Customer
→ → WHY you're making product
The Marketing Era (1940s-1990s) Key Terms:
Relationship Marketing:
• Long term MUTUALLY satisfying, buyer seller relationships.
→ Foster relationship with customer
→ Keeping customers is easier than getting customers
The Marketing Era (1940s-1990s) Key Terms:
Customer Relationship Management:
• Using information about customers to develop and sustain desirable customer relationships.
→ Gets information about you to give you the product you want
The Marketing Era (1940s-1990s) Key Terms:
Green Marketing:
• Meaningful long-term relationships while
→ Maintaining
→ Supporting
→ Enhancing the Natural Environment
→ Piece of CSR to make a company socially responsible
Relationship Marketing Era
(1990s-2010)
• The focus is on LONG-TERM relationships and customer retention.
→ → → (Fostering long term relationships)
→ A 5% increase in customer retention yields up to a 95% improvement in NPV delivered by customers
Societal Marketing Era
(1960s- present)
• "Green Marketing"
• Focus on:
→ Adds society's best interest to the mix
→ Corporate social responsibility
→ Firm now serves three entities
→ Taking care of customers, employees and society at large while still making money for share holders
Marketing Mix / 4 P's
• Product
• Higher Quality/ Lower Quality
→ Goods
→ Services
→ Ideas
Marketing Mix / 4 P's
• Place (Distribution)
• Into RIGHT place/ take out of WRONG place
• Minimize costs:
→ Inventory
→ Transportation
→ Storage
→ Walmart/Detergent
Marketing Mix / 4 P's
• Promotion
• WHEN/WHERE people are most accepting
→ Advertising
→ Public Relations
→ Personal Selling
→ In-Store Promotions
→ Street Teams/Guerilla Marketing (3M)
→ Viral marketing
Marketing Mix / 4 P's
• Price
• Decisions and actions associated with establishing pricing objectives and policies
• Determining product prices and bottom line
• Determines the value of the exchange.
→ Estimate how much to make
→ Price at level that maximizes
→ Determines profit - drives financial indicators
Popular Macro-Marketing Strategies
• Creating
→ Value
→ Relationships
• Segmenting Markets
→ Departments
→ Course Delivery
• Identifying Opportunities
What is Value?
What You Get (Benefits)
------------------------------
What you Give Up (Costs)
How have some firms Created Value in the past?
• Small Banks
→ Some serve Starbucks coffee
• Sheraton Hotel
→ Offers 24 Hour Check-in
Relationship Marketing
Establishing long term mutually satisfying, buyer seller relationships.
→ Ex. Charmin
→ Ex. Chick Fil A
→ Build a relationship when you think its HARD
Segmenting Customers
• Provide different options for the consumers needs.
•• COKE → Diet Coke, Coke Zero, Cherry Coke, Coke Zero, Coca Cola light, Diet coke, etc.
→ Best Buy - Separate "Devils from Angels"
Customer Oriented Firm
A FIRM Level concept NOT a Product Level concept
People To Know:
Warren Buffet
• One of the Wealthiest Men in the World
• Based in Omaha
"It takes 20 years to build a reputation and 5 minutes to ruin it"
Firms To Know:
Berkshire Hathaway
• A conglomerate holding company with a DIVERSE portfolio of businesses
→ Started out as a textile company in Massachusetts that Buffett took over
Firms To Know:
Pepsi
• Created by Caleb Bradham to be sold in his drug store in New Bern, NC.
• Originally called "Brad's Drink"
• Named after the digestive enzyme "PEPSIN"
→ Coca-Cola was offered the opportunity to buy Pepsi three different times (the latest in 1933).
→ Coca-Cola declined each time.
Internal Environment
• What your Employees see
→ NOT what the Customers see
Market Opportunity
• Where circumstance and timing meet to create strategic windows
→ Ex. ebay first mover in C-to-C marketing
→ Ex. Recession and Wal-Mart
→ Ex. Starbucks was an opportunity for McDonald's
Core Competencies
• Things a firm does well
→ Product Development?
→ Distribution
→ Low Price Leaders
Competitive Advantage =
Opportunity + Competency
Strategic Business Unit (SBU)
A division or unity within a larger parent company
→ Ex. iPhone & iPad
Market Share
Percentage of the total market your product is selling to
What is the Key to Internal Marketing?
Empowerment
Empowerment
Allowing your employees to make the right decisions and giving them the power to act on those decisions
→ Ex. Ritz allows employees to spend $2000 to fix a problem
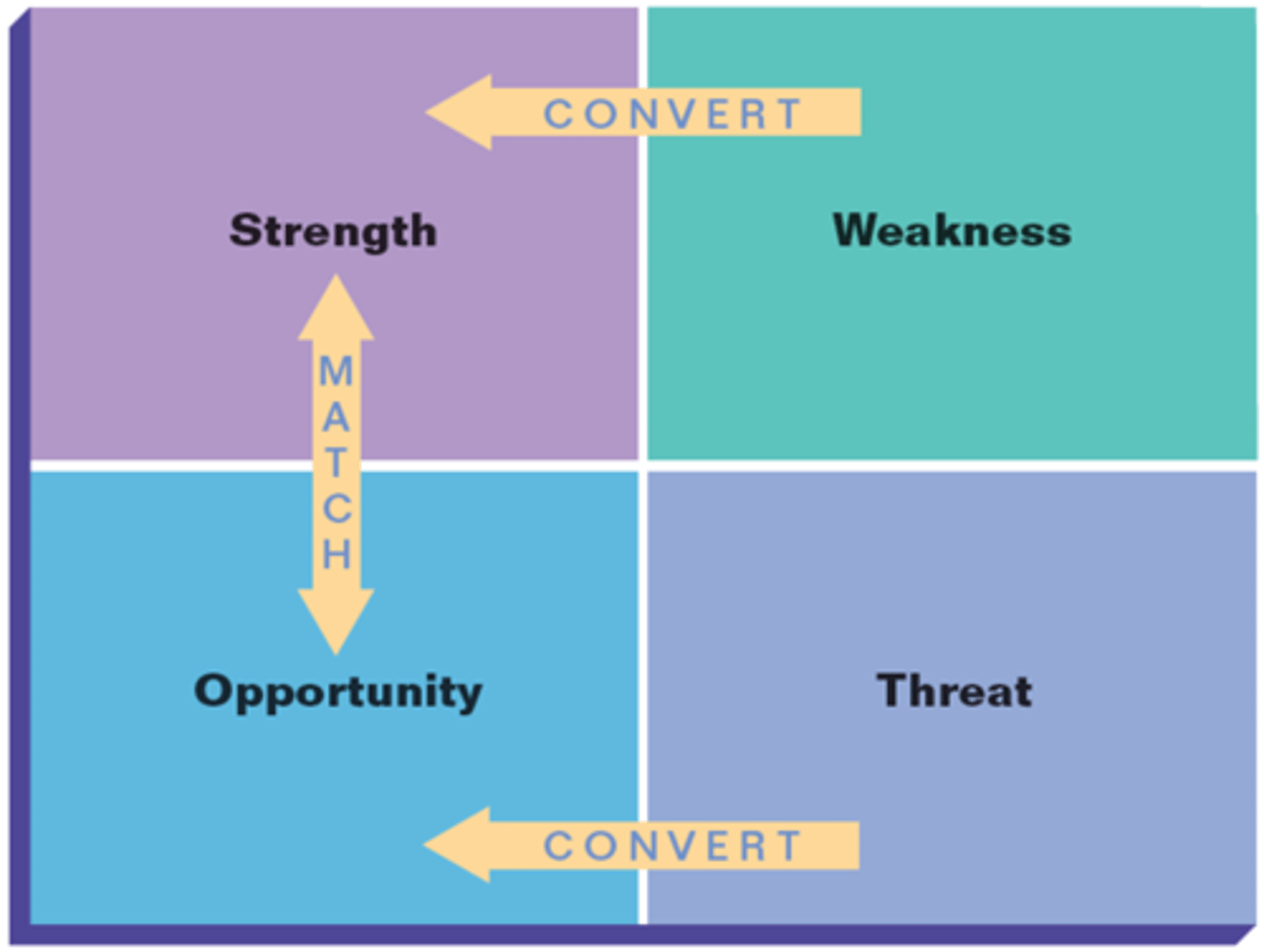
SWOT Analysis
Assesses an organization's
*→ Strengths
→ Weaknesses
→ Opportunities
→ Threats*
Using information gathered from the preceding component—the environmental analysis
Market Strategy
Mission Statement
↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
Corporate Strategy
↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
Business-Unit Strategy
↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
Marketing Strategy
↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
Marketing Mix-Elements
→ Product, Distribution, Promotion, & Pricing
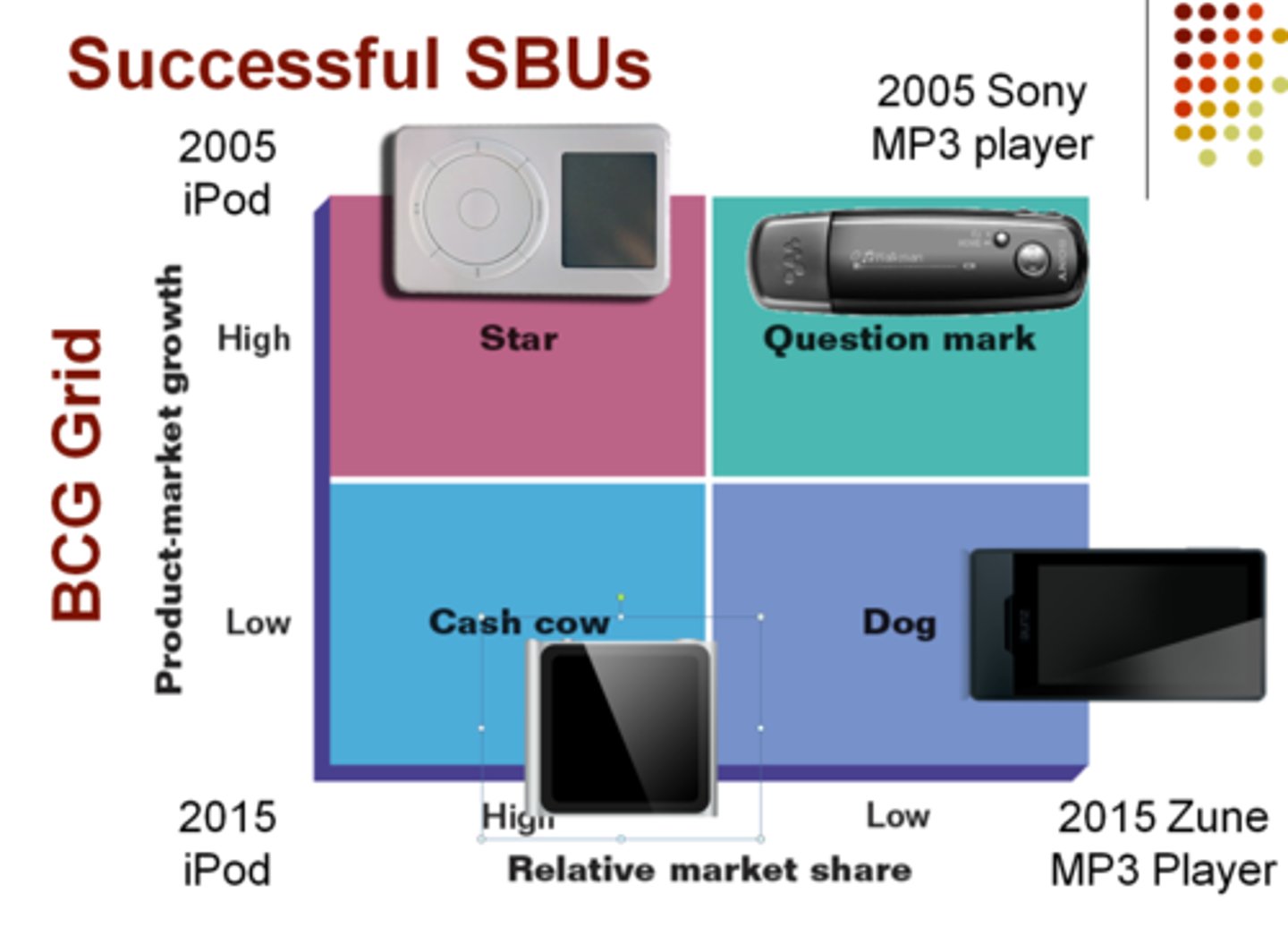
BCG Grid
• Boston Consulting Group
• Top 10 best companies for companies to work for
→ Vertical Axis: Product-Market Growth
→ Horizontal Axis: Relative Market Share
GOOD Internal Marketing Strategies lead to
Good External Service Quality
External Marketing Environment
External pressures that help you decide what to do with the marketing mix
6 Environmental Forces
→ Competitive
→ Political
→ Technological
→ Sociocultural
→ Legal and Regulatory
→ Economic
Environmental Forces
COMPETITIVE Forces
The numbers of similar competitive product brands' marketers in your industry, their size and market capitalizations.
4 COMPETITIVE Structures
• Monopoly
• Oligopoly
• Monopolistic
• Pure Competition
COMPETITIVE Forces
TYPES of Competitors
• Brand Competitors
→ Coke v Pepsi
• Product Competitors
→ Walgreens Water
• Generic Competitors
→ Stars & Stripes
• Total Budget Competitors
→ Do you spend money on drink or food?
COMPETITIVE Structures
Monopoly
• When an organization has no competitors so that it is the sole source of supply.
→ Ex. Comcast
COMPETITIVE Structures
Oligopoly
• When a few sellers control supply.
→ Usually due to hard entry barriers
→ Ex. Airlines
COMPETITIVE Structures
Monopolistic
When firms in competitive industries attempt to differentiate a product.
→ A "normal" market
→ Ex. Shoes
COMPETITIVE Structures
Pure Competition
• Exists when there are a large number of sellers with similar products and low barriers to entry.
→ Farmer's Market? Ebay?
Environmental Forces
POLITICAL Forces
Irans Oil getting on the market
→ Offshore drilling
• Top Corporate donors
→ UPS
→ AT&T
→ Pfizer
• Pro Consumer Laws are bad for pharmaceutical companies
Environmental Forces
TECHNOLOGICAL Forces
If a researcher finds a new technology, the companies that are able to develop products more quickly, then they will have a better positioning in the markets
Environmental Forces
3 SOCIOCULTURAL Forces
→ Demographic and Diversity Characteristics
→ Consumerism
→ Cultural Values
SOCIOCULTURAL Forces
Demographic and Diversity Characteristics
Descriptive Characteristics of a Population
→ Ex. Whites, Hispanics, African American, Asians
SOCIOCULTURAL Forces
Cultural Values
• Based on social norms, what we think is normal in every day life.
→ American Ex. Directness, Individuality, Informality, Equality, Work Orientation
SOCIOCULTURAL Forces
Consumerism
• Protecting Consumers Rights
→ Subliminal Perception
• Ex. Jet Blue's Customer Bill of Rights
→ Trapped on plane without bathroom
SOCIOCULTURAL Forces
→ Consumerism
Subliminal Perception
• Really doesn't work, but controversial
• Works in controlled environments
• James Vicary
→ Buying popcorn at movies
→ Ex. Sex on Pepsi can
Environmental Forces
Legal and Regulatory Forces
Whether or not you're allowed to make a similar product
Ex. Samsung battle
→ Rules on Advertising
→ Where you're allowed to sell
→ Not able to price gauge
Environmental Forces
Economic Forces
The Business Cycle
Prosperity (2006)
↓↓↓
Recession (2007)
↓↓↓
Depression (2010)
↓↓↓
Recovery (2015)
Major Federal Regulatory Agencies
Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
• Most heavily influences marketing activities
• Large portion of its resources spent on CURBING:
→ False Advertising
→ → Duncan Hines versus Betty Crocker
→ Misleading Pricing
Major Federal Regulatory Agencies
Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Enforces laws and regulations to prevent distribution of adulterated or misbranded foods, drugs, medical devices, cosmetics, veterinary products, and potentially hazardous consumer products
Major Federal Regulatory Agencies
Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC)
Ensures compliance with the Consumer Product Safety Act; protects the public from unreasonable risk of injury from any consumer product not covered by other regulatory agencies
Major Federal Regulatory Agencies
Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
Regulates communication by:
→ Wire
→ Radio
→ Television in interstate
→ Foreign Commerce
Major Federal Regulatory Agencies
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Develops and enforces environmental protection standards and conducts research into the adverse effects of pollution
Major Federal Regulatory Agencies
Federal Power Commission (FPC)
Regulates rates and sales of natural gas producers, thereby affecting the supply and price of gas available to consumers; also regulates wholesale rates for electricity and gas, pipeline construction, and U.S. imports and exports of natural gas and electricity
Major Federal Regulatory Agencies
Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB)
Regulates the offering and provision of consumer financial products and serves to protect consumers from deceptive financial practices
People You Should Know:
Who is the Father of Consumerism?
• Ralph Nader
→ Ran for president 1996 and 2000
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
A code of conduct and a collection of actions BEYOND what is required by laws, regulations, and trade rules
→ Ethically treating your employees & customers
→ Being good to the environment
→ "When companies do good"
→ Has a direct impact on the bottom line, intangible, has a direct impact on market capitalization
→ 80% of market cap based on intangibles
Most consumers say they want to purchase from Corporate Social Responsibility, but say they need __?
• Ability & Motivation to process the fact that the corporations are socially responsible
What are the barriers to Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
• Consumers have to be aware of CSR initiatives
• Must be motivated to process these messages
Most consumers say they want to purchase from Corporate Social Responsibility, but __?
People don't process messages of corporate responsibility correctly
→ Central Route
→ Peripheral Route
Central Route
• 100% concentrated on an idea
Peripheral Route
• NOT paying attention to an idea
→ Low Motivation
→ Low Ability
4 Peripheral Judgements
• Category Bias
• Brand Bias
• Senior Leadership
• CSR Form
Peripheral Judgements
Category Bias
• If you see a Gas Company you think they're NOT responsible
• If you see a Tech Company you think they ARE responsible
Peripheral Judgements
Brand Bias
• Everyone think Disney is a good company (they make people happy)
• Walmart is a big bad company
Peripheral Judgements
Senior Leadership
• Founders of Google seem like they would recycle
• Goldman Sachs are perceived mean and BAD
Peripheral Judgements
CSR Form
People think that Toyota is the most fuel efficient car company because they make the Prius
In the past, most of the Corporate Social Responsibilities have been centered on the ____ View?
• Other-Oriented
• Extrinsic
→ ETHICS
What is Customer Value Typology?
• Where is the benefit?
→ Intrinsic v. Extrinsic View
• Who benefits?
→ Self-Oriented v Other-Oriented
What are the bad companies doing to improve their Category Bias?
Walmart, Wells Fargo & Bank of America are all thought of badly (category bias) so they are donating money to look socially responsible
What 5 things do you do to be a Socially Responsible Corporation?
• Cumulative Value Creation
• Focus on Self-Oriented Value
• Embed Messages across Touchpoints (peripheral processing)
• Mitigate Spillover Effects
• Match Value to Category and Brand
What to do to be a Socially Responsible Corporation
Cumulative Value Creation
• Not only should it be good for other people, but it should also be good for the people buying the product
When a brand/company composes ALL 4 quadrants of customer value typology (e.g. Chik-fil-a)
What to do to be a Socially Responsible Corporation
Focus on Self-Oriented Value
• Customer
• Business
→ Ex. Organic Bleach
→→ Business will only buy organic bleach if it saves them money
• Stressing how it will help the consumer
→ Ex. Organic Bleach
→ → Company needs to stress how its powerful and good for environment
What to do to be a Socially Responsible Corporation
Embed messages across Touchpoints (peripheral processing)
• Because we don't decipher the message through the central route we have to them imprinted on our minds a lot
→ Packaging works with product-related decoding biases through many different ways