MSK 2: Clinical Correlations + Imaging of UE
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
How to elicit deep tendon reflexes
Tap on end of tendon to elicit reflex to test if nerve intact
-ie. + reflex s/p tapping on biceps tendon → can assume C5 and C6 are still intact/ functional
-ie. + reflex s/p tapping on triceps tendon → can assume C7 and C8 are still intact/ functional
What is Erb-Duchenne Palsy?
Upper Trunk Lesion
Typically C5 and C6 involved
Clinical Presentation:
-affected arm is adducted, medially rotated, forearm is extended
-diminished sensation over lateral arm and forearm
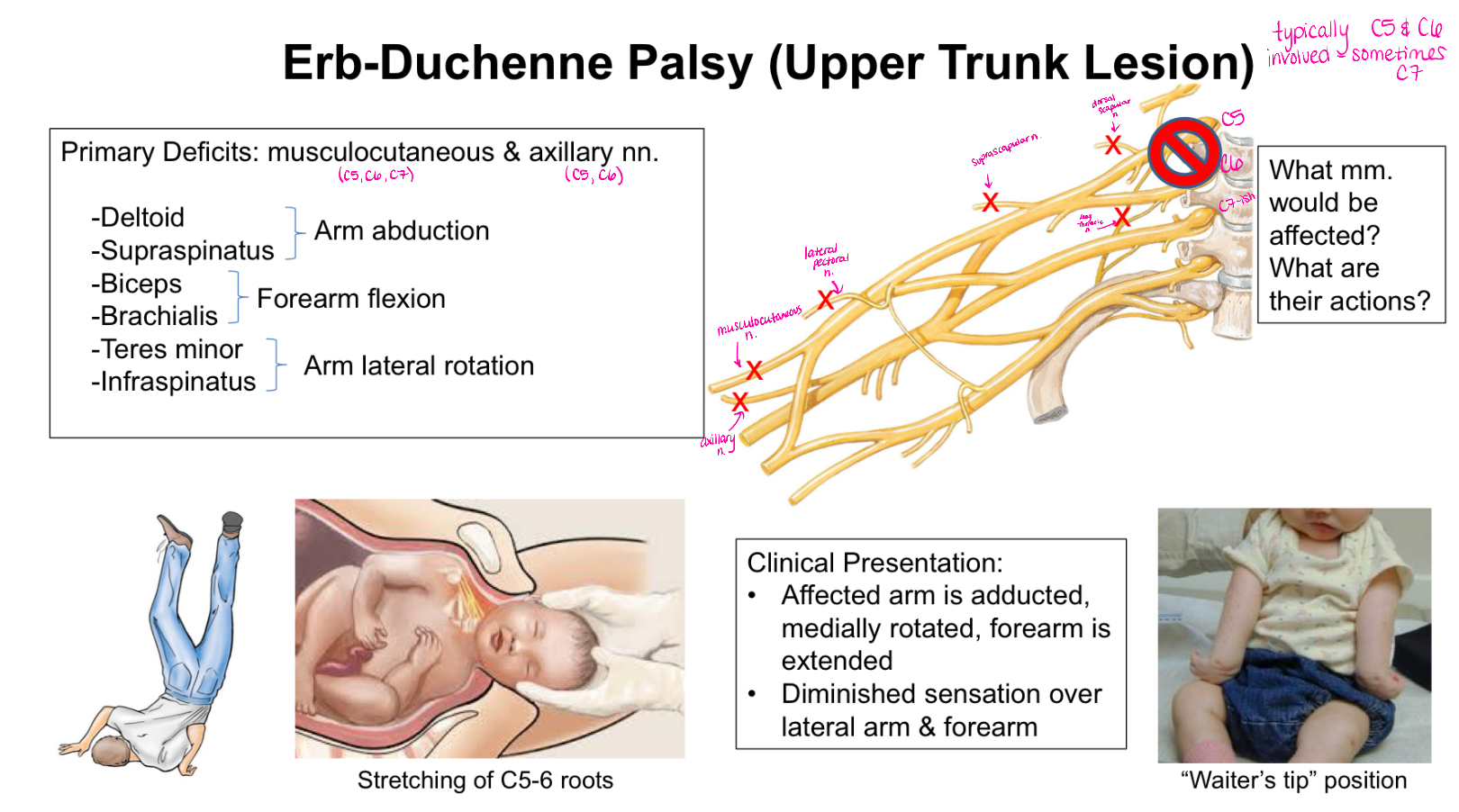
What muscles/ muscle actions are affected with Erb-Duchenne Palsy?
Deltoid and Supraspinatus - arm abduction
Biceps and Brachialis - forearm flexion
Teres Minor and Infraspinatus - arm lateral rotation
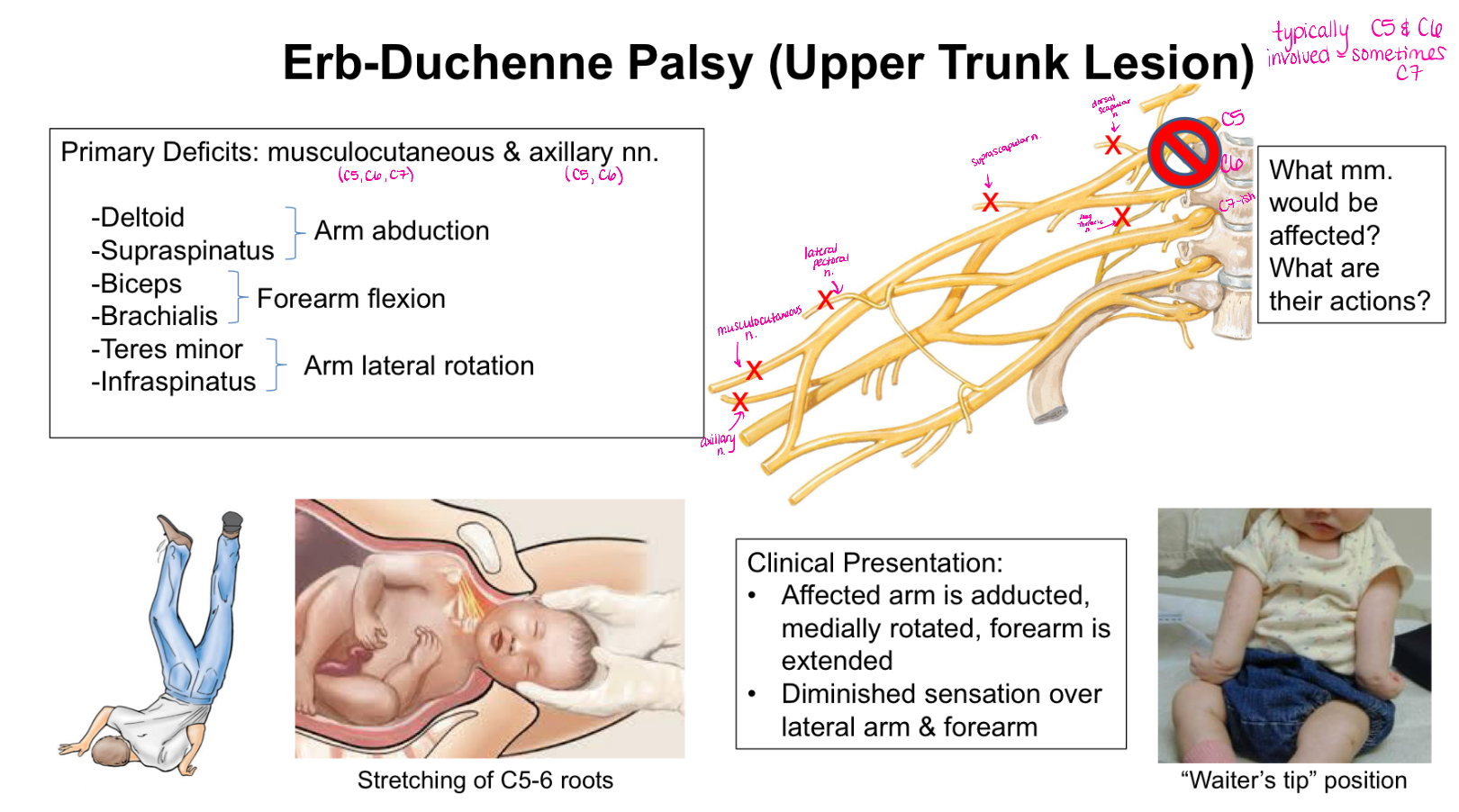
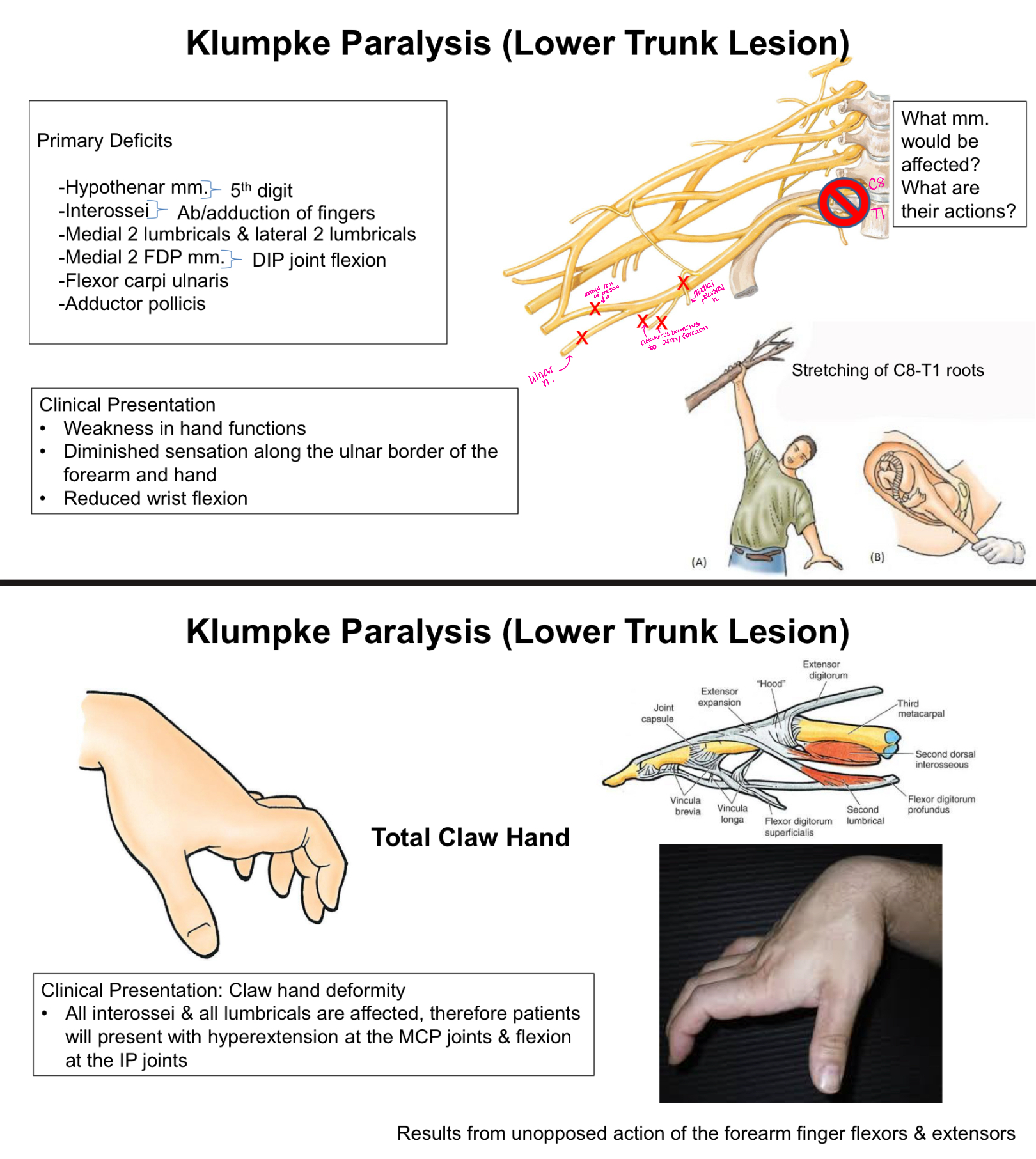
What is Klumpke Paralysis?
Lower Trunk Lesion
Clinical Presentation:
-Weakness in hand functions
-Diminished sensation along the ulnar border of the forearm and hand
-Reduced wrist flexion
TOTAL Claw Hand - hyperextension at the MCP joints and flexion at the IP joints
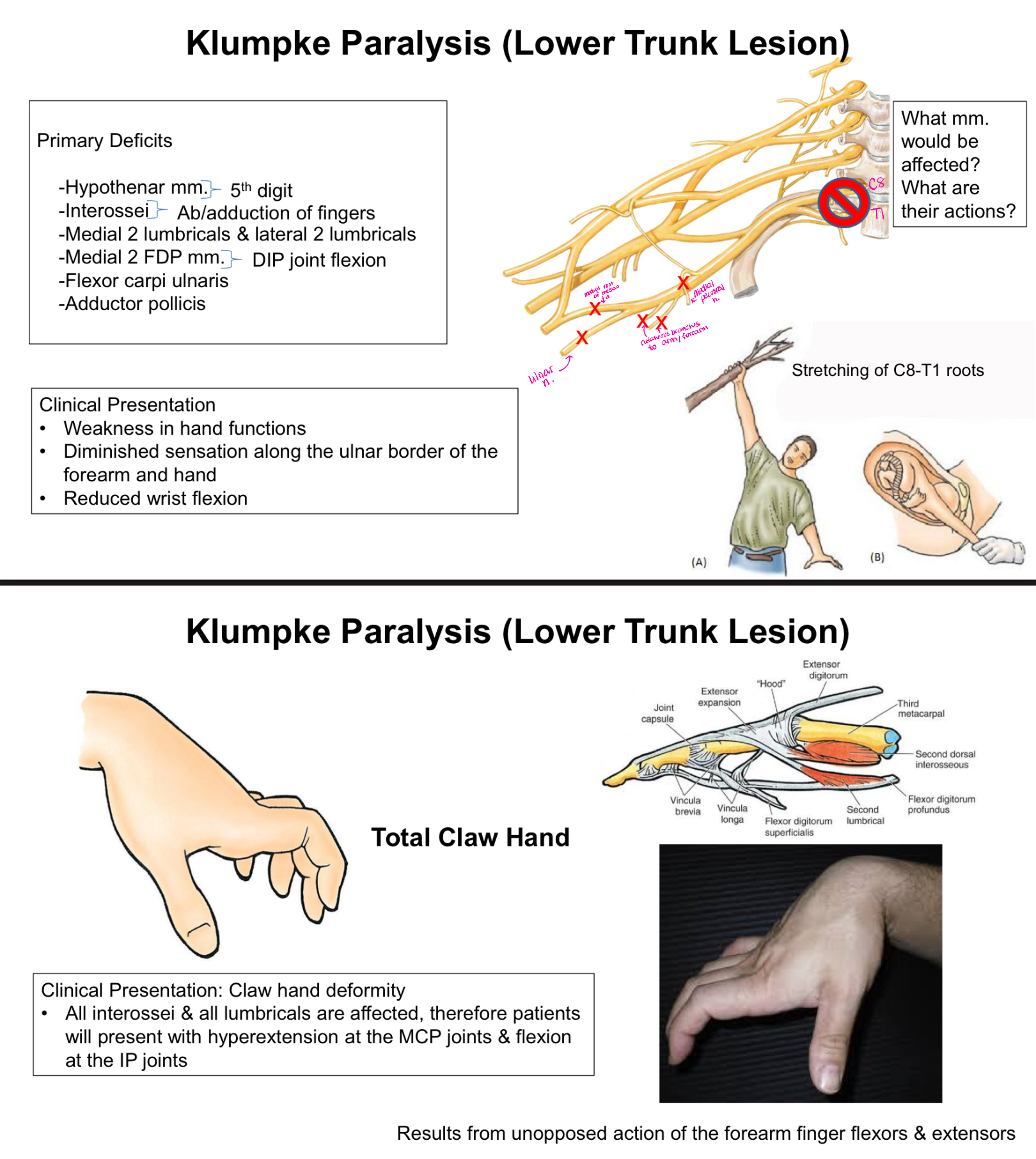
What muscles/ muscle actions are affected with Klumpke Paralysis?
Hypothenar mm. - 5th digit
Interossei - ab/adduction of fingers
Medial 2 lumbricals and lateral 2 lumbricals
Medial 2 FDP mm. - DIP joint flexion
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Adductor pollicis
Long thoracic nerve damage
Very superficial → fairly common injury
Clinical Presentation: medial border of the scapula moves laterally and posteriorly away from the thoracic wall resulting in a winged scapula bc serratus anterior no longer functioning
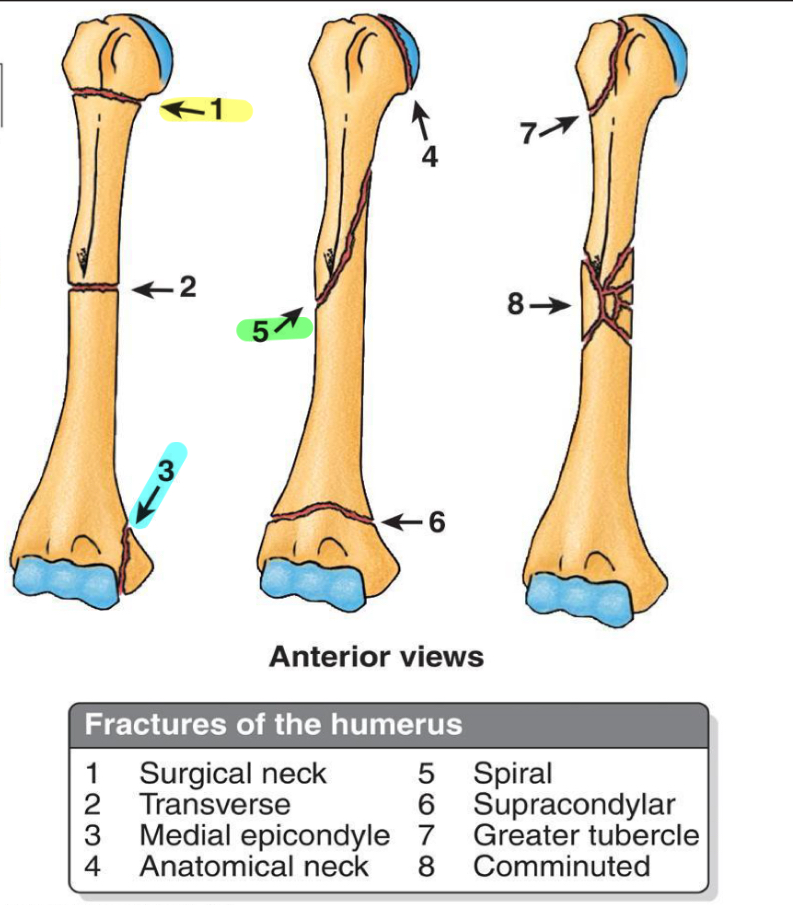
What nerves/vessels are we concerned about if there is a 1, 3 or 5 fracture?
1- axillary nerve and anterior/posterior circumflex humeral arteries
3- ulnar nerve
5- radial nerve and deep brachial artery
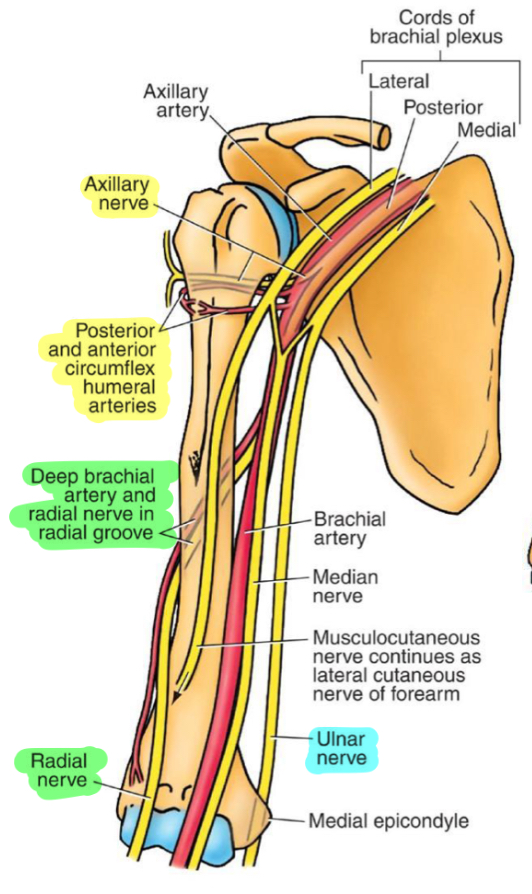
What happens with an axillary nerve injury?
Primary deficits: deltoid and teres minor
Clinical presentation: weakness in shoulder abduction and external rotation, atrophy of the deltoid, decreased sensation over the posterior/lateral shoulder
What happens with a radial nerve injury?
Clinical presentation: wrist drop, sensory deficits along posterior arm, dorsal hand, and thumb, inability to extend fingers (MCP Joints), inability to extend of abduct thumb, weakened grip strength
What happens with a musculocutaneous nerve injury?
Clinical presentation: impaired elbow flexion and forearm supination bc biceps brachii, brachialis, and coracobrachialis all affected
What happens with a median nerve injury above the elbow?
Hand of Benediction/ Pope’s Blessing
-when asked to form a fist, only digits 4 and 5 will flex (thumb and digits 2 and 3 will stay extended); weakened pronation; impaired flexion of wrist and sensory deficits to digits 1-3
Primary deficits:
-Thenar mm. (except adductor pollicis)
-All FDS
-Lateral 2 FDP mm.
-Flexor pollicis longus
-Flexor carpi radialis
-Pronator teres and pronator quadratus
What happens with a median nerve injury in the carpal tunnel?
Clinical presentation:
-thenar muscle wasting; tingling and pain in lateral 3.5 digits; difficulty with grasp reflex; possible median claw (injury to lateral lumbricals)
Primary deficits:
-Thenar mm. (except adductor pollicis); flexor pollicis brevis (superficial head), abductor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis brevis; weakness upon flexion, abduction, and opposition of the thumb
What happens with a proximal ulnar nerve injury?
Clinical Presentation:
-weakened hand opening and grip strength; weakened grasp and pinch responses; “OK gesture” - weakened flexion of digit 4 and 5 when making a fist
Primary Deficits:
-weakened wrist flexion and adduction; weakened flexor digitorum profundus (medial part); paralysis of hypothenar mm., interossei, medial 2 lumbricals; sensory loss along ulnar distribution
What happens with a distal ulnar nerve injury?
Clinical Presentation: Ulnar claw hand deformity - hyperextension of the MCP joint bc of the unopposed extensors and flexed IP joints due to unopposed flexors in digits 4 and 5
Primary Deficits: paralysis of hypothenar mm., interossei, medial 2 lumbricals, flexor pollicis brevis (deep head), adductor pollicis; sensory loss along ulnar distribution
Ulnar Claw
Ulnar nerve lesion at wrist
Can see at rest
Digits 4 and 5 affected
Lumbricals to digits 4 and 5 are paralyzed
Hand of Benediction/ Pope’s Blessing
Median nerve lesion at elbow
See when attempting to make a fist but cannot flex digits 2 and 3
Digits 2 and 3 affected
Lumbricals and flexor digitorum profundus tendons to digits 2 and 3 paralyzed
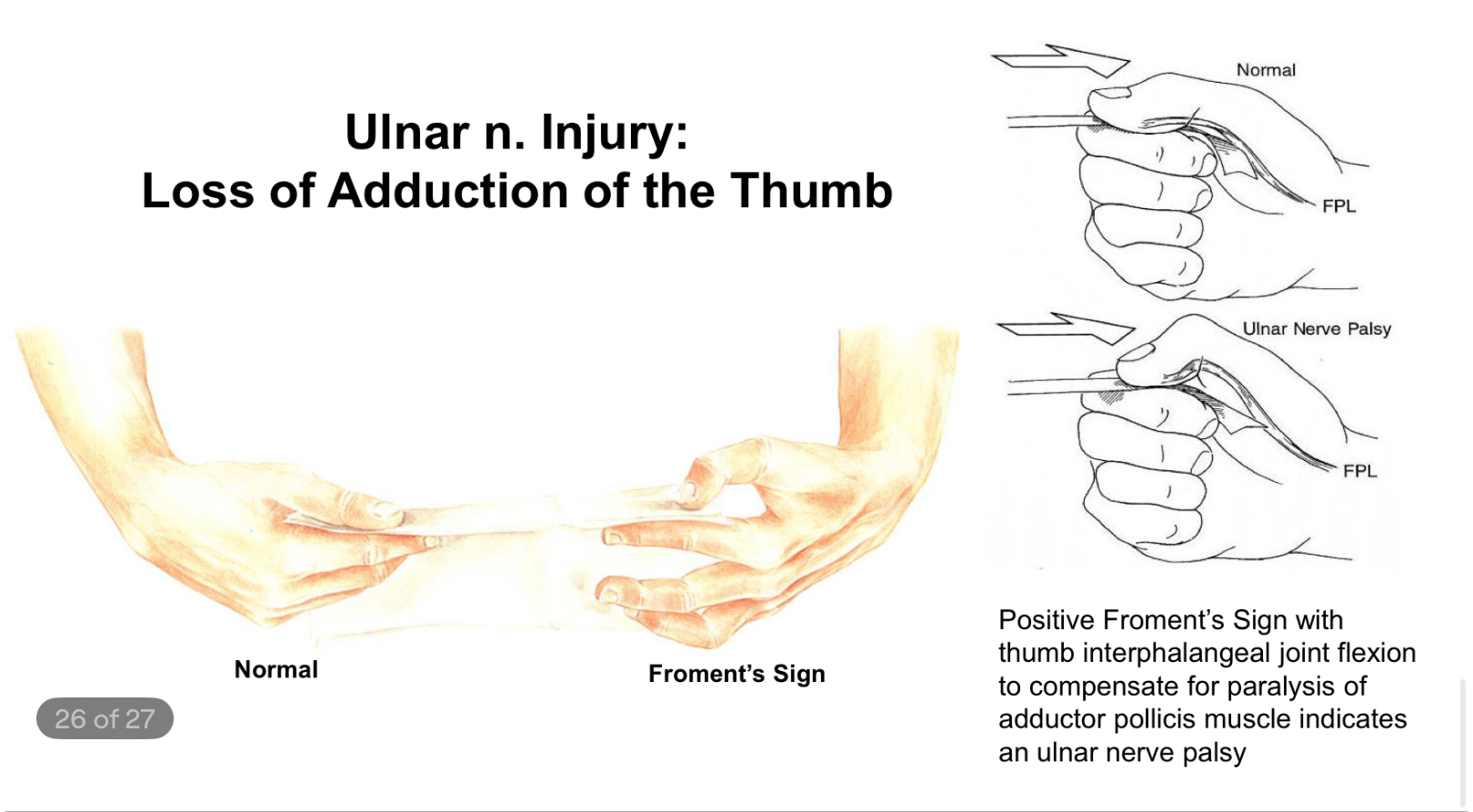
What indicates an ulnar nerve palsy?
Positive Froment’s Sign with thumb interphalangeal joint flexion to compensate for paralysis of adductor pollicis muscle
What are you looking for with an XR?
Fx
Dislocation
Joint spaces/ edema/ arthritis
Lytic lesions
Foreign bodies
Basic hardware positioning
What are you looking for with a CT?
Occult fx, osteomyelitis, boney tumors, soft tissue lesions/ infections
Assessment of fx union/ osseous bridging (postop/ assess healing)
Evaluation of hardware integrity and loosening
Improved detail of boney lesions
CTA for arterial occlusion
CT with IV contrast for better detail of soft tissue masses, abscess, infection
What are you looking for with an MRI?
Soft tissue
Occult fx, bone contusions
Rotator cuff pathology, labral/ capsular injury
Muscle/ tendon tears, cartilage injury
Osseous and soft tissue neoplasm
Discerning infections
Ideal for joints
What are you looking for with nuclear medicine?
Both planar and cross sectional imaging
Increased bone turnover
Osteomyelitis
Malignancy
Avascular necrosis
PET (+CT and MRI) essential in diagnosing and staging malignancies
What are you looking for with ultrasound?
Tendon injuries
Fluid collections
Joint effusion
Procedural guidance
Nerve impingement assessment
Types of incomplete fxs
Torus/ Buckle fx
Greenstick - does not go through boney cortex
Distracted vs Overriding vs Comminuted
Distracted fx - transverse with space between
Overriding - transverse with shortening and overlapping
Comminuted - busted/burst; many pieces