neurones
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
what are the 3 types of neurones
sensory relay motor
describe the sensory neurone
transmits signal back from the skin/ muscle back to the CNS
describe the relay
This connects the sensory and motor neurones. They are found in the CNS. They have short dendrites and axons.
describe the motor
These are connected to the relay neurone and at the other end the effector.
what is an effector
muscle and glands
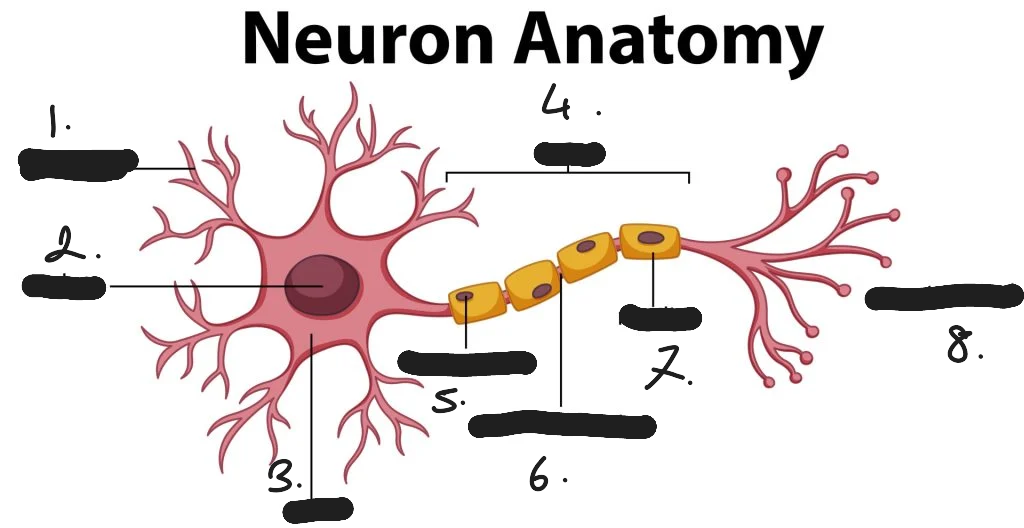
dendrites
nucleus
soma/ cell body
axon
scwann cells
node of Ranvier
myelin sheath
axon terminals
how can you identity which neurone is which
Neuron Type | Direction of Info | Key Structural Features | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
Sensory | Receptors → CNS | Long dendrites, short axon, cell body in middle | PNS → CNS |
Relay | Within CNS | Short axons & dendrites also don’t often have myelin sheath | CNS only |
Motor | CNS → Muscles/Glands | Short dendrites, long axon, cell body at one end | CNS → PNS |
reflex arch
stimulus, sensory neurone, relay(CNS), motor neurone, effector responds. At each synapse the electrical signal is converted into a chemical signal.
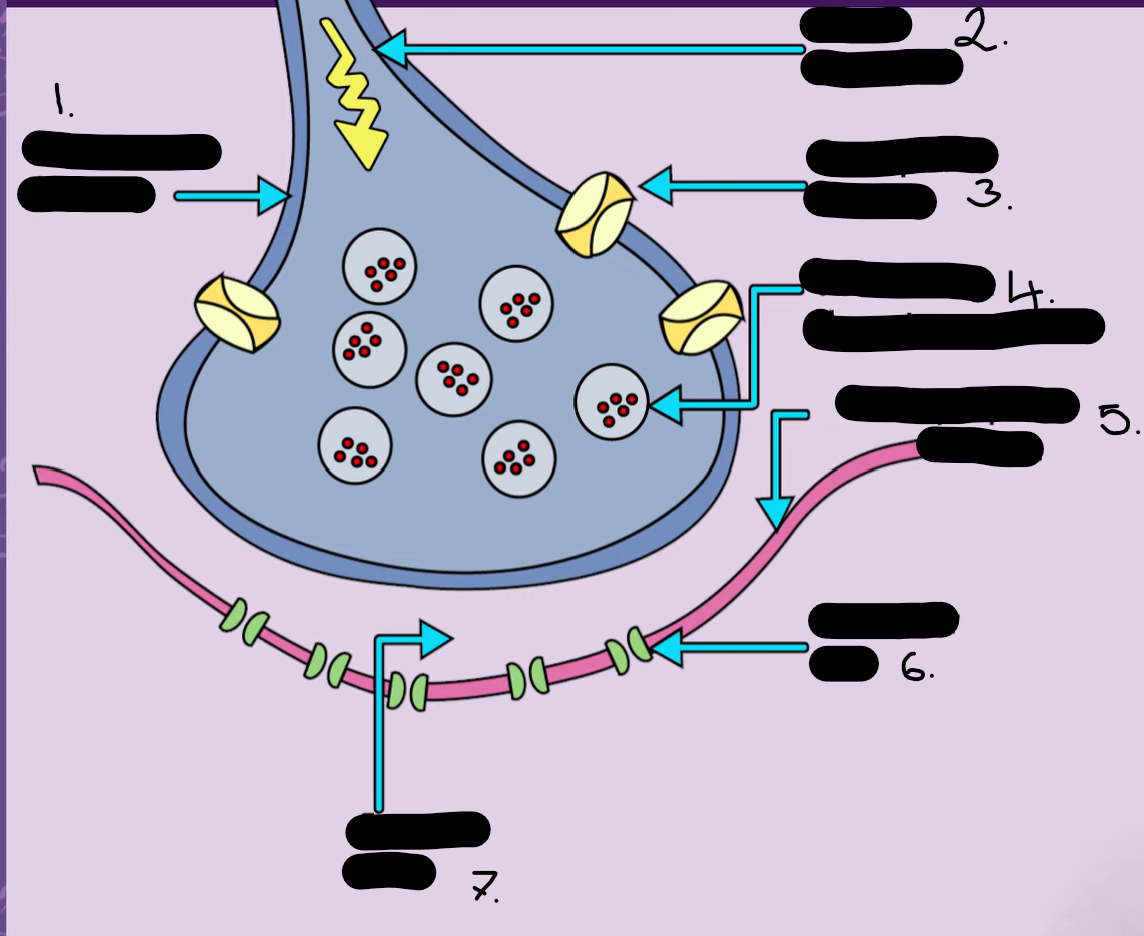
presynaptic neurone
action potential
transport protein (no key just on the diagram)
vesicles with neurone transmitters
postsynaptic neuron
receptor / receptor sites
synaptic cleft/ gap
describe how messages get across a synapse
An electrical impulse travels down the axon into the presynaptic neurone this is know as an action potential
The electrical impulse stimulates the vesicles to merge with the membrane of the presynaptic neurone and release the neurone transmitters into the synaptic cleft.
The neurone transmitters diffuse across the gap reaching the postsynaptic neurone and binding to receptors on its surface.
To make an action potential fire the electrical charge has to reach a threshold.
when the neurone transmitters bind to the receptors they can either give and excitory or inhibitory response depending on the neurotransmitter.
excitory effect the electrical charge is more positive this is called depolarization. This happens when the receptors allow positively charged sodium ions enter the cell. This increases the likelihood that a new action potential will be fired.
An inhibitory effect is when the cell become hyperpolarised (more negative) this happens when positive potassium ions released out of the cell making it negative. This decreases the likelihood that a new action potential will be fire
The sum of all the exitory and inhibitory neurone transmitters and added up. If the sum meets threshold the action potential will fire this is called summation
after this a process called reuptake occurs. This is when the neurotransmitters are reabsorbed into the presynaptic cell after transmitting a neural impulse. This happens at transport proteins and prepared the cell to fire again .