Identification of Semen
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
semen is important in
sexual assault cases and is a alrge percentage of forensic casework
semen is comprised of
spermatozoa and seminal fluid
what is the confirmation of the presence of semen
spernatazoa
what is the secretions from seminal glands
seminal fluid
spermatozoa is about
10-25% of semen composition
spermatozoa is formed in the
testes
spermatozoa is transported and stored in the
epididymis where they undergo functional maturation
spermatozoa are transferred through the
vans deferens to the ejaculatory duct into the urethra
once spermatozoa reaches the urethra, they are joined with
secretions from the prostate
the head of a sperm cell contains
nucleus with densely packed chromosomes
the mid-piece of the sperm is a
short neck containing mitochondria that provides energy for moving tail
the sperm tail offers
sperm motility
accessory gland secretions (75-90%) are from the
prostate (30%) and seminal vesicles (60%)
the prostate produces
high concentrations of acid phosphatase and prostate specific antigen (PSA) used in forensic testing
the seminal vesicles secrete proteins that
play a role in the coagulation of the ejaculate, also contains flavins
what causes semen to fluorescence?
flavin proteins
typical ejaculation amount is
1-6 mL (average 3 mL)
what does the volume of ejaculate depend on?
time from previous ejaculate
metabolic activity of glands
partial ductal obstruction and retrograde ejaculation
normospermia makes up about
50-150 million/mL (average is 100 million/mL)
aspermia means
no sperm
oligospermia is also called
aspermia
oligospermia/aspermia can be caused by
illness
nutritional deficiency
therapeutic drug use
chronic cases due to
congenital deformities
chemotherapeutic drugs
exposure to industrial chemicals
vasectomy
how many vasectomies fail
1-2%
what is a polyamine in the presumptive test
spermine - barberio crystal test
choline - florence crystal test
what enzymes are used in presumptive screening tests
seminal acid phosphatase (SAP)
where is spermine synthesized
in the prostate
what is the barberio test
spermine phosphate crystals formed by reaction of spermine with anions (phosphate or picrate)
spermine enhances
sperm motility
where is phosphorycholine (PC) synthesized
in the seminal vesciles
how is choline formed
by hydrolysis of PC by SAP
what is the most common screening test
seminal acid phosphatase presumptive test
SAP enzyme cleaves a variety of organic phosphates such as
phenyl-
p-nitrophenyl
a-naphhyl
thymolpthalien-
elevated levels of SAP in the blood is indicative of
prostate cancer
seminal acid phosphatase is how much greater than any other body fluid
100-1000 fold
phenyl phosphate
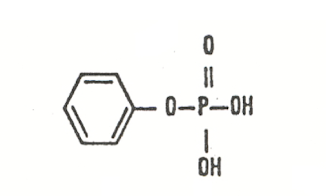
p-nitrophenyl phosphate
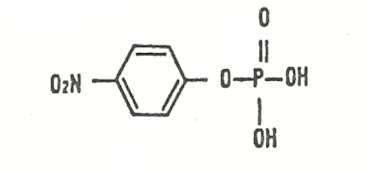
a-naphthyl phosphate
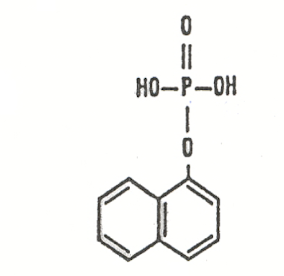
thymolphthalien monophosphate
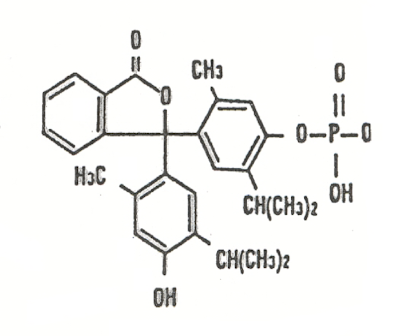
seminal acid phosphatase comes from glands that are not
affected by vasectomies
seminal acid phosphatase is active at what pH
acidic
prostate specific antigen is not a
confirmatory test
prostate specific antigen is a major protein in
seminal fluid
prostate specific antigen nis responsible for hydrolyzing
semenogelin
prostate specific antigen creates a
gel matrix around ejaculated sperm
prostate specific antigen is an important clinical indicator of
malignancy
prostate specific antigen is present in
urine and peripheral blood
P30 identification methods consist of
crossover electrophoresis
ouchterlony double diffusion
immunochromatography
ELISA
p30 ELISA uses what type of ‘sandwich’
antibody-antigen-antibody (ab-ag-ab)
normal semen contains up to
96% abnormal forms of sperm, 1-2% immature forms
immature germinal cells, leucocytes, epithelial cells can all be used in
DNA recovery
abnormal sperm have
multiple heads
single head, multiple tails
cytoplasmic droplets
sperm can be visualized using what stains
nuclear fast (NF), red/picroindigocarmine solution (PICS)
hematoxylin/eosin (H&E)
what animals have sperm that is hard to distinguish from humans
rabbit
boar
ram
bull
other primates
mouse and rat sperm has a
hook shaped head
SAP is available for
12-48 hours
p30 is available for
1-3 days
sperm is available for
3-5 days
ability to test sperm on post-coital individuals is
dependent on the environmental conditions
semen can be lost from the vaginal environment due to
drainage
dilution with vaginal fluid
phagocytosis of spermatozoa by neutrophilic lymphocytes and mononuclear cells
vaginal swabs can be collected up to
120 hours (5 days)
anal swabs can be collected up to
72 hours (3 days)
oral swabs can be collecetd up to
24 hours (1 day)
bite marks and saliva on skin can be collected up to
96 hours (4 days)