MACRO: Fiscal Policy (Ch. 13)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
fiscal policy
government decisions about the level of taxation and public spending
Automatic Stabilizers
Built-in features of the government budget that automatically cushion economic fluctuations without new legislation.
Examples of Automatic Stabilizers
progressive income taxes, unemployment insurance, and programs like SNAP and Medicaid
Aggregate Demand Formula
C + I + G + NX
What happens to aggregate demand when government increases spending?
Aggregate demand curve shifts to the right
How do tax rates impact consumer spending?
Lower tax rates = More Consumer Spending
Higher tax rates = Less Consumer Spending
expansionary fiscal policy
Decisions about government spending and taxation are intended to increase aggregate demand.
contractionary fiscal policy
Decisions about government spending and taxation are intended to decrease aggregate demand. The government tends to raise taxes and cut spending to slow down an overheated economy.
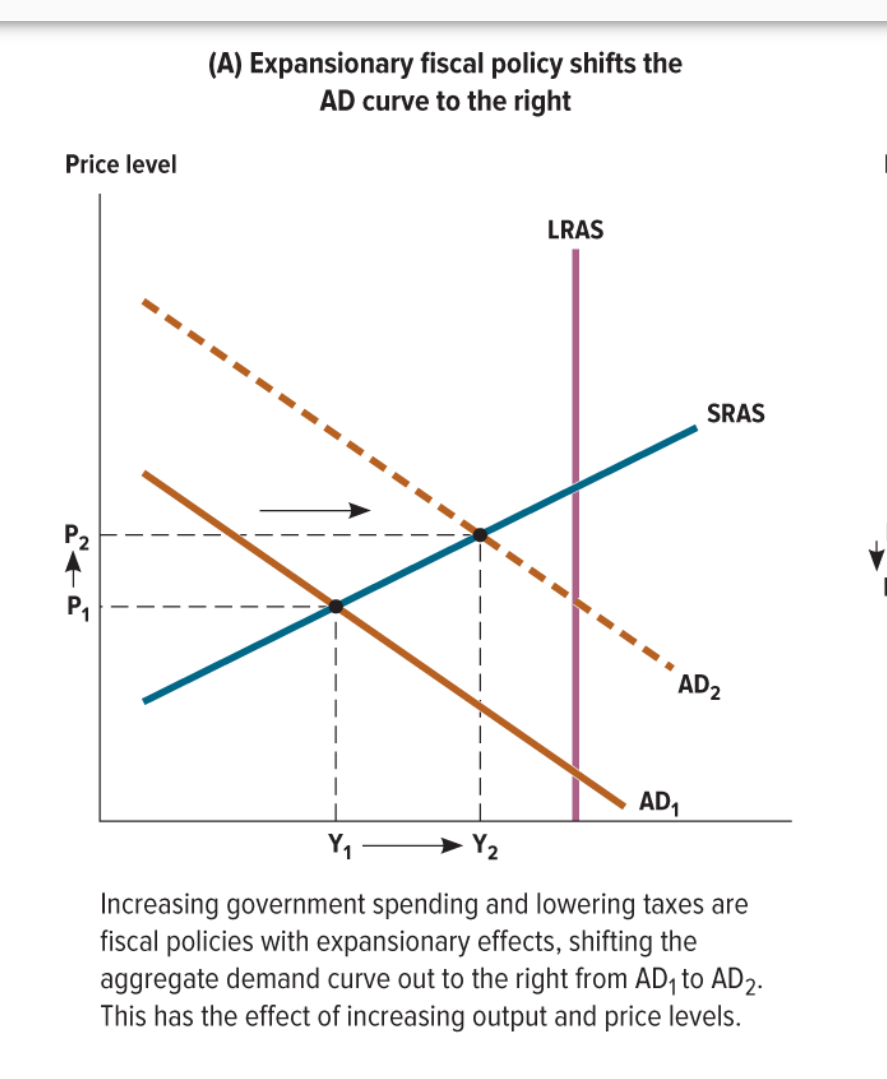
How do expansionary fiscal policies impact the output and price levels of the AD (Aggregate Demand)? This means an increase in government spending and lower tax rates.
Output and price level both increase
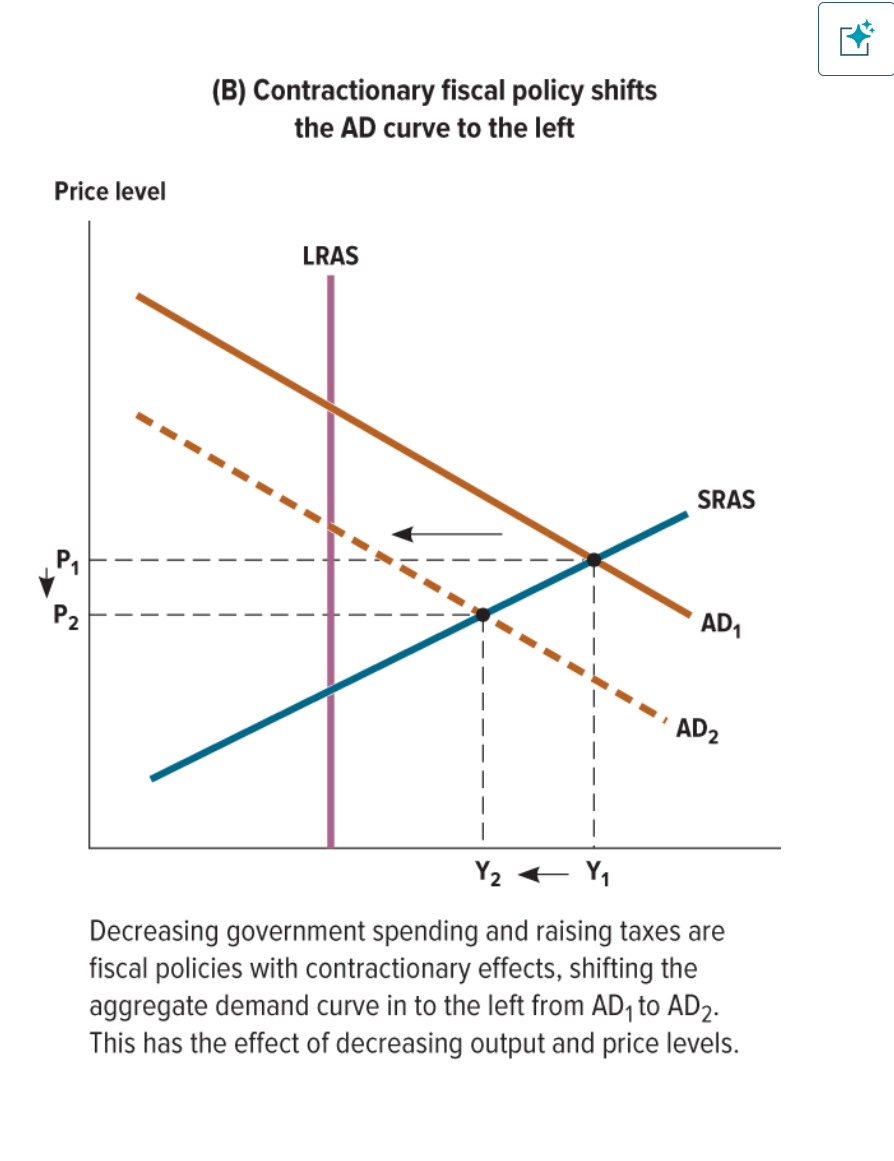
How do contractionary fiscal policies impact the output and price levels of the aggregate demand when government spending decreases and taxes are raised?
Output and price levels both decrease
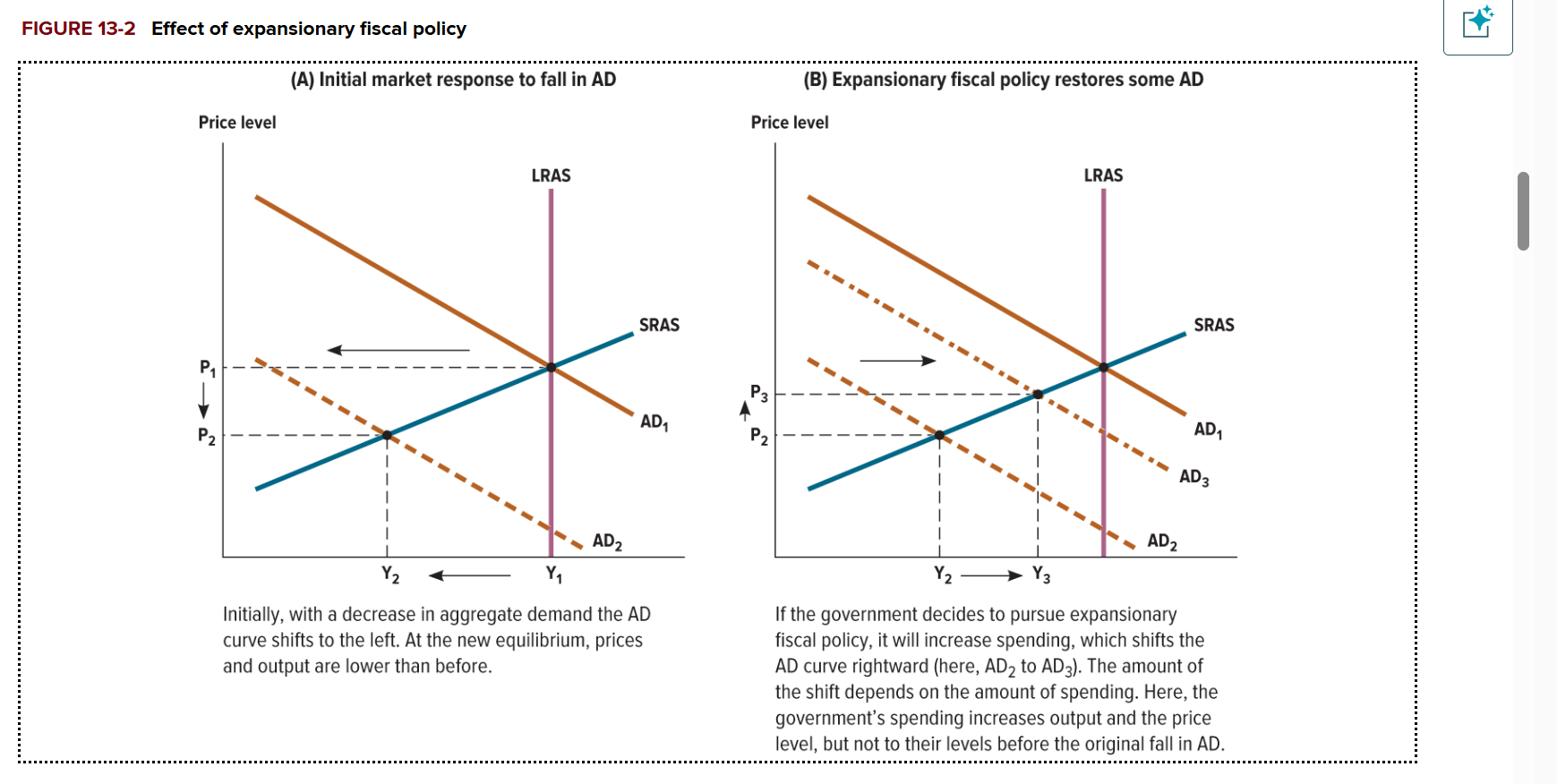
Let’s say the initial aggregate demand (AD) shifts to the left and the new prices and output are lower than before. What effect does the government pursues an expansionary fiscal policy?
Increase in spending, which will cause AD to shift to the right
Government spending will increase output and price level, but not to their original levels
What if the government stimulus were completely successful? How would this impact AD?
AD curve would shift back to its original position
What if the government stimulus was partially successful? How would this impact AD?
The AD would shift rightwards, but not to its original position
What is a contractionary fiscal policy good for?
It is good for slowing down rapidly growing economy that is growing too fast. This big boom may cause inflation and asset bubbles to quickly rise before a large crash occurs.
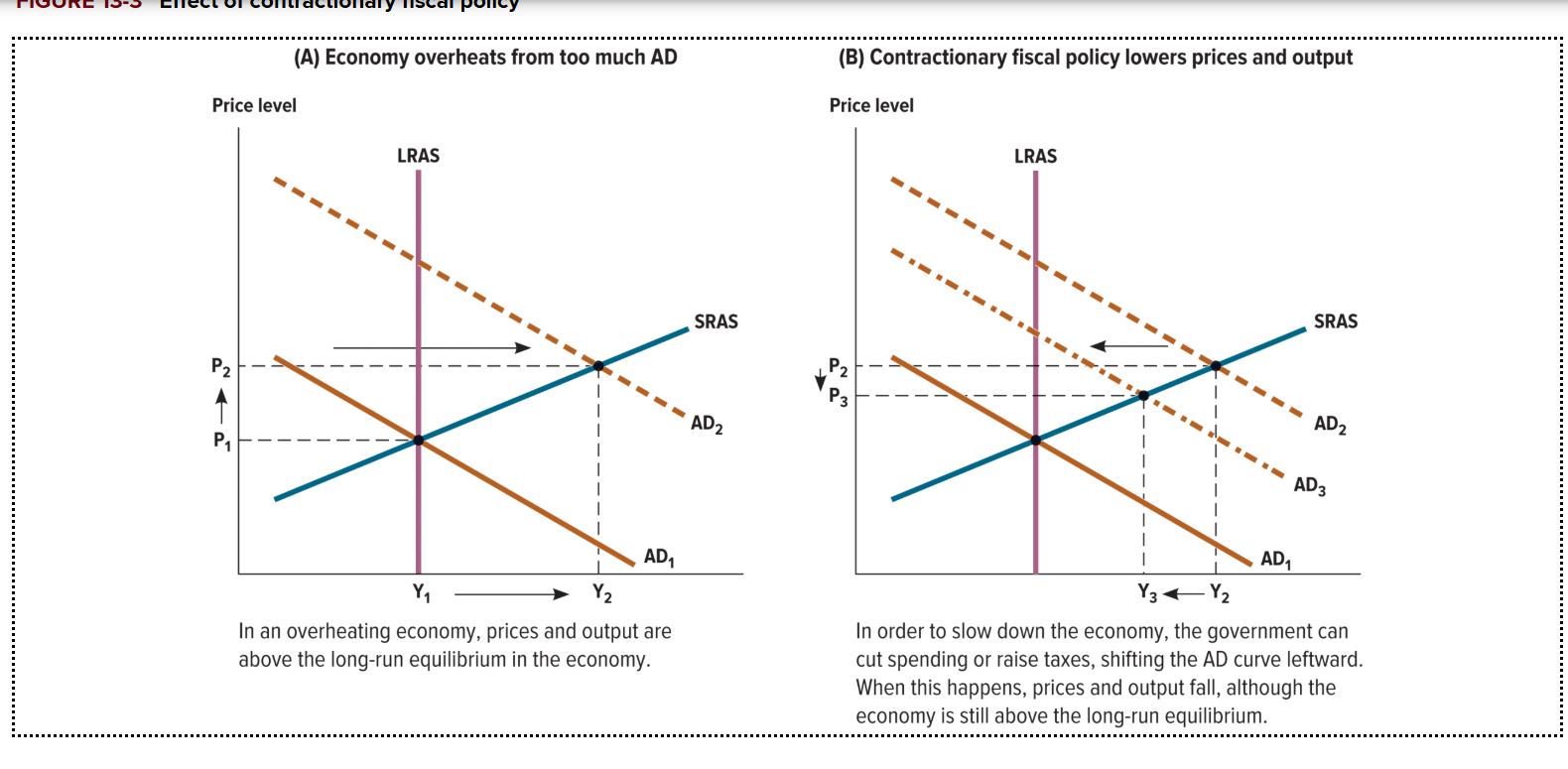
What effect does a contractionary fiscal policy in an overheated economy? What will happen if the government raises taxes and cuts government spending?
AD will shift to the left
Price and output levels will fall
However, the economy is still above the long run equilibrium
crowding out
the reduction in private borrowing caused by an increase in government borrowing
Information lag
Understanding what the current economic situation is.
What is the problem with Information lag
It can take a long time to collect data that tell policy makers about key economic metrics (Inflation, employment rate, etc.)
Formulation lag
Deciding and passing legislation through democratic means can stall the government from implementing key economic policies
Implementation lag
It may take time for a policy to come into full effect even if it is passed.
automatic stabilizers
taxes and government spending that affect fiscal policy without specific action from policy-makers
How do taxes act as an automatic stabilizer?
When the economy booms, people’s income tend to increase, meaning they will have to pay more in taxes, and the inverse effect occurs when there’s an economic downturn.
How do automatic stabilizers impact government spending, and how does this impact the economy?
When the economy booms, fiscal policy is automatically contractionary (Taxes go up and low government spending), which causes the AD to shift to the left.
When there are economic downturns, fiscal policy automatically becomes expansionary (Taxes go down and hight government spending), which causes AD to shift to the right.
budget deficit
an amount of money a government spends beyond the revenue it brings in
budget surplus
an amount of revenue a government brings in beyond what it spends
Transfer payments
Payments from government accounts to individuals for programs. Does not counts towards GDP. (Ex: Social Security)
public debt
the total amount of money that a government owes at a point in time; the cumulative sum of all deficits and surpluses
Deficit
How much money/revenue the government lacks within a given year
Debt
The TOTAL amount of money the government owes from borrowed money
Treasury securities/Treasury bills
Debt-financing arrangements made by the U.S. government.
Short term Treasury Bills (T-Bills)
Loans to the government that mature less than a year.
Long Term Treasury Notes
Usually lasts for 2-10 year. Every 6 months, you receive an interest payment at a set rate. Pays more interest than T-Bills. Most widelt traded bond in the world
Who buys treasury securities?
Individual investors, banks, and foreign governments
Why do people, banks, and governments flock to US Treasuries/US Debt?
B/c U.S. Treasuries are the safest investment compared other investments such stocks, real estate, etc. Investors are confident that the US government will not declare bankruptcy.