Lecture 20: Social Systems
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What factors influence a species' social system?
Typical group size: how many individuals generally occur together
Social organization: what is the nature of social interactions and who interacts
Philopatry (staying in natal group): remaining in a natal group or in a natal territory
Dispersal patterns: movement to a new group or territory to reproduce
What is the difference between honey bee and fly maggot social organization?
Honey bees are highly organized, have different job and a hierarchy
Fly maggots have no organization
Note: this indicates that a lot of members does not mean same social systems
What are some axes of social structure variation?
Presence/absence of in-group v. out-group behavior
Nature of interactions (cooperative, competitive, etc)
Types of individuals in the group (males, females, young)
Dominance hierarchy within the group
Reproductive division of labor and/or task specialization
What does philopatry influence?
Whether or not you will be around relatives. Family groups depend on philopatry
How do ocean species demonstrate dispersal?
Many species in the ocean have long distance dispersal of larvae driven by currents, so individuals are not near relatives
Ex: After hatching, clownfish larvae swim into the water column and are dispersed by currents
How do small species demonstrate dispersal?
On land, many small animals disperse via the wind.
Ex: ballooning in spiders. No direct dispersal
Does one sex disperse further than the other?
Yes, this reduces inbreeding
In birds, females tend to disperse
In mammals, males tend to disperse
Note: there are plenty of exceptions in both birds and mammals to the general pattern
What are two consequences of staying at home in social groups?
Formation of family groups and cooperation.
Risk of inbreeding
What is an example of a family where non-breeding individuals help raise the young?
Meerkats have adult helpers that:
Babysit the pups
Feed the pups
Stand guard while group forages
Does evolution favor individuals that have behaviors that promote their own success?
Yes
What are meerkat adult helpers an example of?
Altruism: when an individual’s behavior provides a benefit to another individual at a cost to it self. Costs can be both negative consequences of a behavior or the missed opportunities caused by helping.
What is hamilton’s rule?
A way to explain why animals sometimes help others, even if it costs them something
What is Hamilton’s rule equation?


In Hamilton’s rule equation, what does the r, b and c refer to?
Relatedness: The proportion of ancestry shared between two individuals through common descent
For sexually reproducing species, this means that each pedigree link needed to connect individuals reduces relatedness by 50%
Benefits: The additional offspring that the recipient will have as a result of the altruist’s behavior
Costs: The loss in offspring that an altruist will have a result of the helping behavior
What are some key things to understanding relatedness?
Each parent passes on 50% of its DNA to offspring
All offspring get 50% from each parent, which is a random assortment of the DNA that came from each grandparent
Each sibling gets a different subset of the parent’s DNA
Which sections are passed on in each egg/sperm is random
To calculate relatedness we multiply within a path of relatedness. The we need to sum different paths of relatedness
For meerkat adult helpers, what is the pay off?
They (typically) raise their full siblings
Pup production is easiest in large groups
Leaving to start your own group means you will be in a small group and you will produce few pups
What does mating with close relatives increase?
The chances that a negative genetic trait for which you are a carrier will be expressed
Are many negative mutations present in populations recessive?
Yes, meaning they have little or no impact on the phenotype when there is only one copy
What gets reduced when one sex regularly leaves social groups?
Inbreeding gets reduced
How does lion social structure actually work?
Males: compete for access to mates
Solitary males or coalitions compete for access to prides of females
When males are deposed, the new males will kill any nursing cubs present in the pride
Females: compete for resources
The core unit of the pride is group of related females. They cooperate to defend territory and hunt. They will also provide care for others’ cubs.
How can shared DNA similarity be measured?
In many ways (in this classic work using DNA ‘fingerprints). The important point is to assess similarity of variable DNA elements among individuals
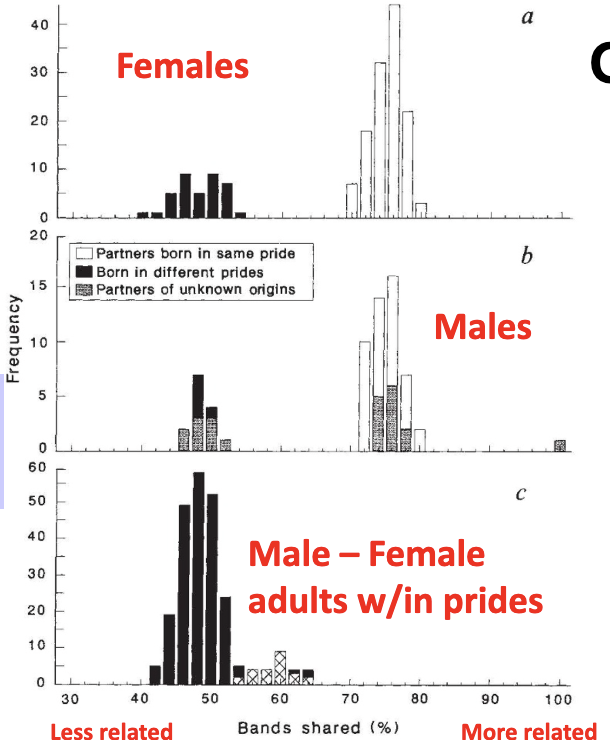
What does DNA show about lions?
For lions, DNA shows that females within a pride are relatives
Male partners tend to be relatives
Breeding males and females are not related to each other.
Do lion coalitions vary in size?
Yes
What is the difference between large and small lion coalitions
Large coalitions a made of close relatives that dispersed single pride
Small coalitions may have unrelated males.
Is there a single king in lions?
Multiple males sire cubs when there are coalitions. There is no single ‘king’ of the pride that gets all the matings.
What can larger coalitions control?
Prides for longer (avoid infanticide). They can hold larger prides and they sire more young