Chapter 18: Externalities (Micro)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Externality
If a transaction has an effect on others. It could be positive or negative.
private benefits
benefits that accrue directly to the decision maker
External cost
a negative externality
External Benefit
a positive externality
network externality
the effect that an additional user of a good or participant in an activity has on the value of that good or activity for others
production externality
an externality that occurs when a good or service is being produced
consumption externality
an externality that occurs when a good or service is being consumed
negative production externality
Any external costs that occurs when a good is being produced.
Example of negative production externality
environmental pollution from the factory
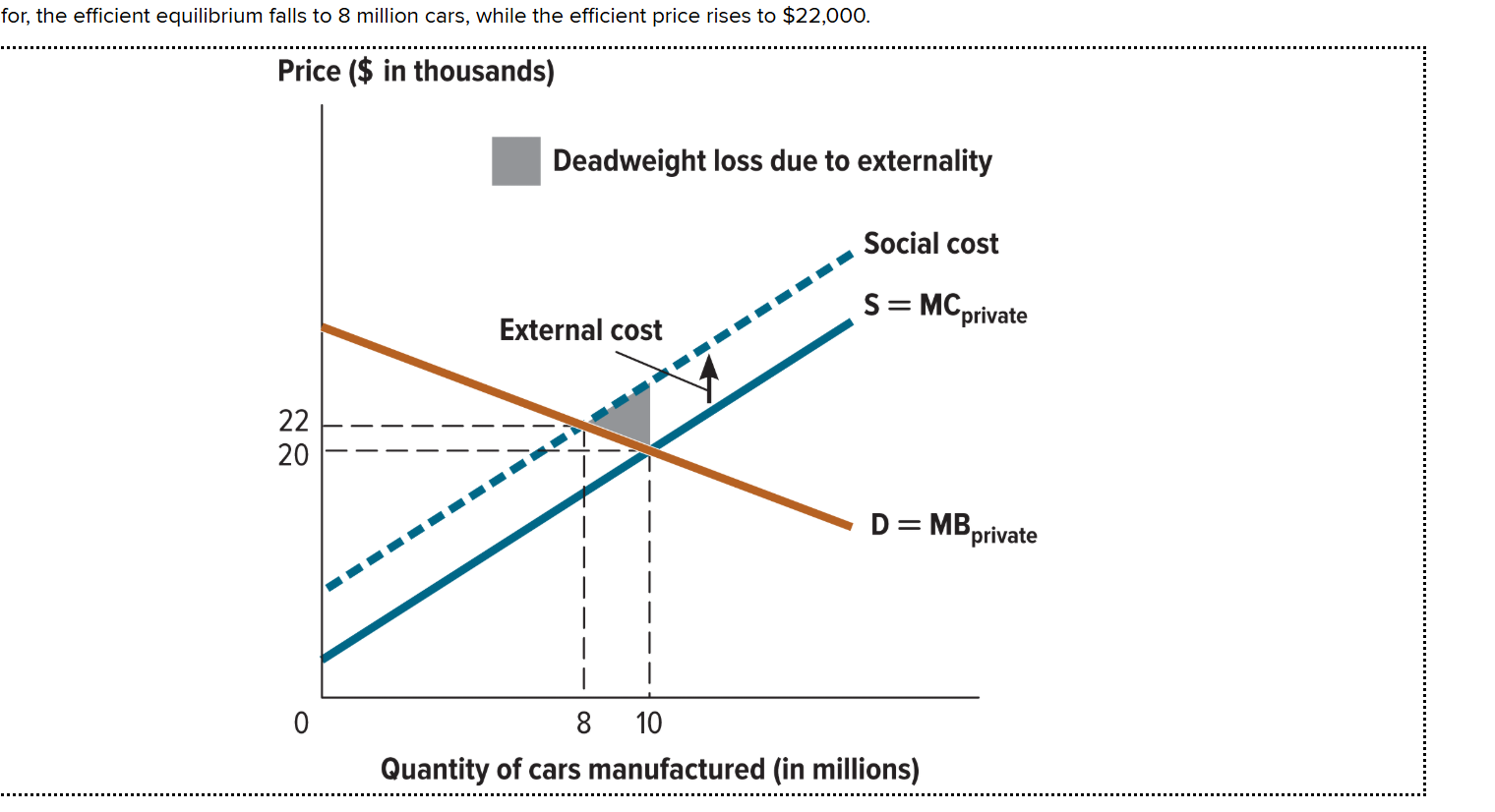
Where is the external cost located in the graph?
It is between the private supply curve (S=MC private) and the social cost curve
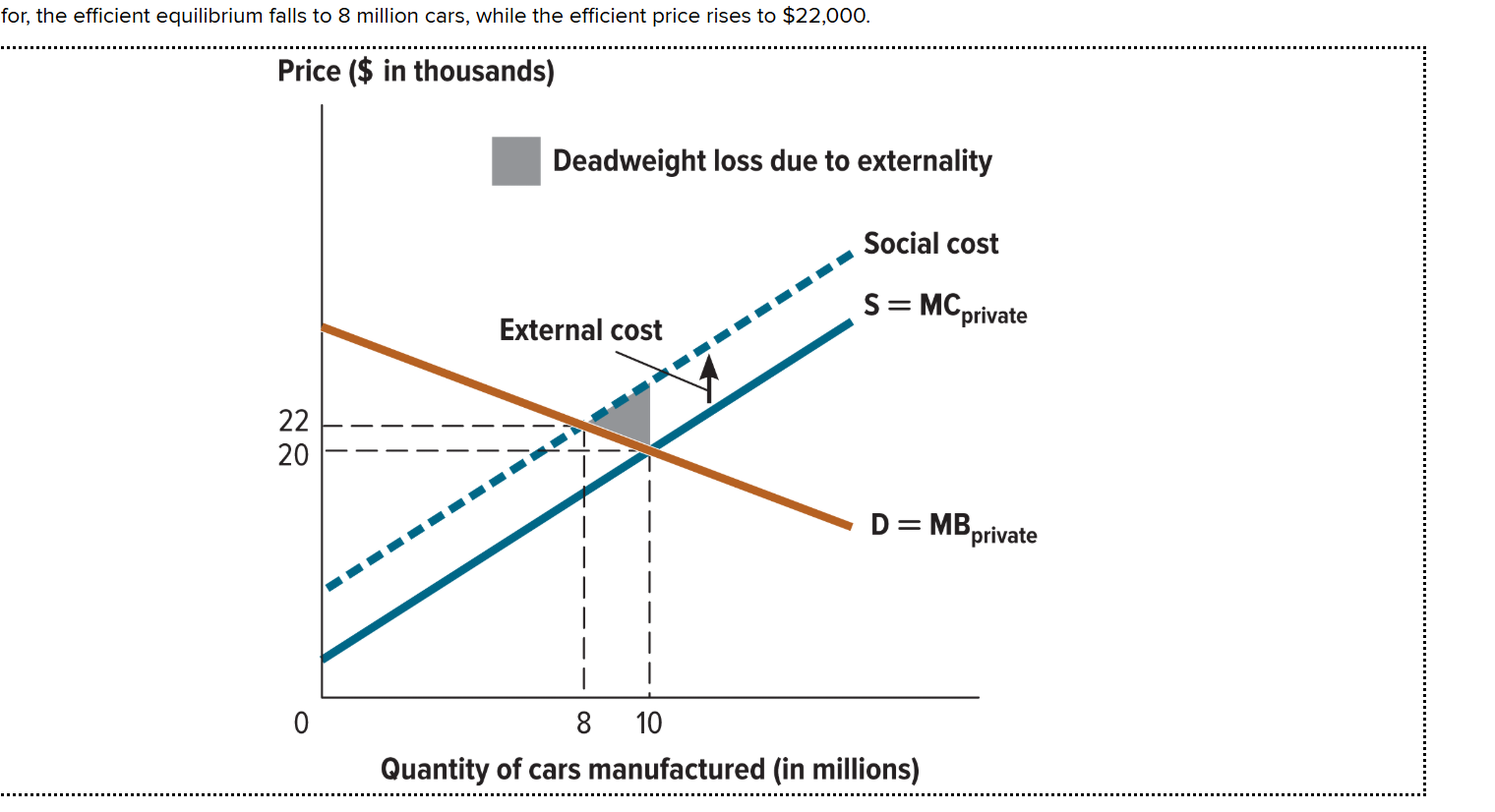
What is the equilibrium price and quantity of cars traded in an unregulated market?
Occurs when S=MC private and the market demand (D=MB) curve intersect. (10 million cars, $20,000)
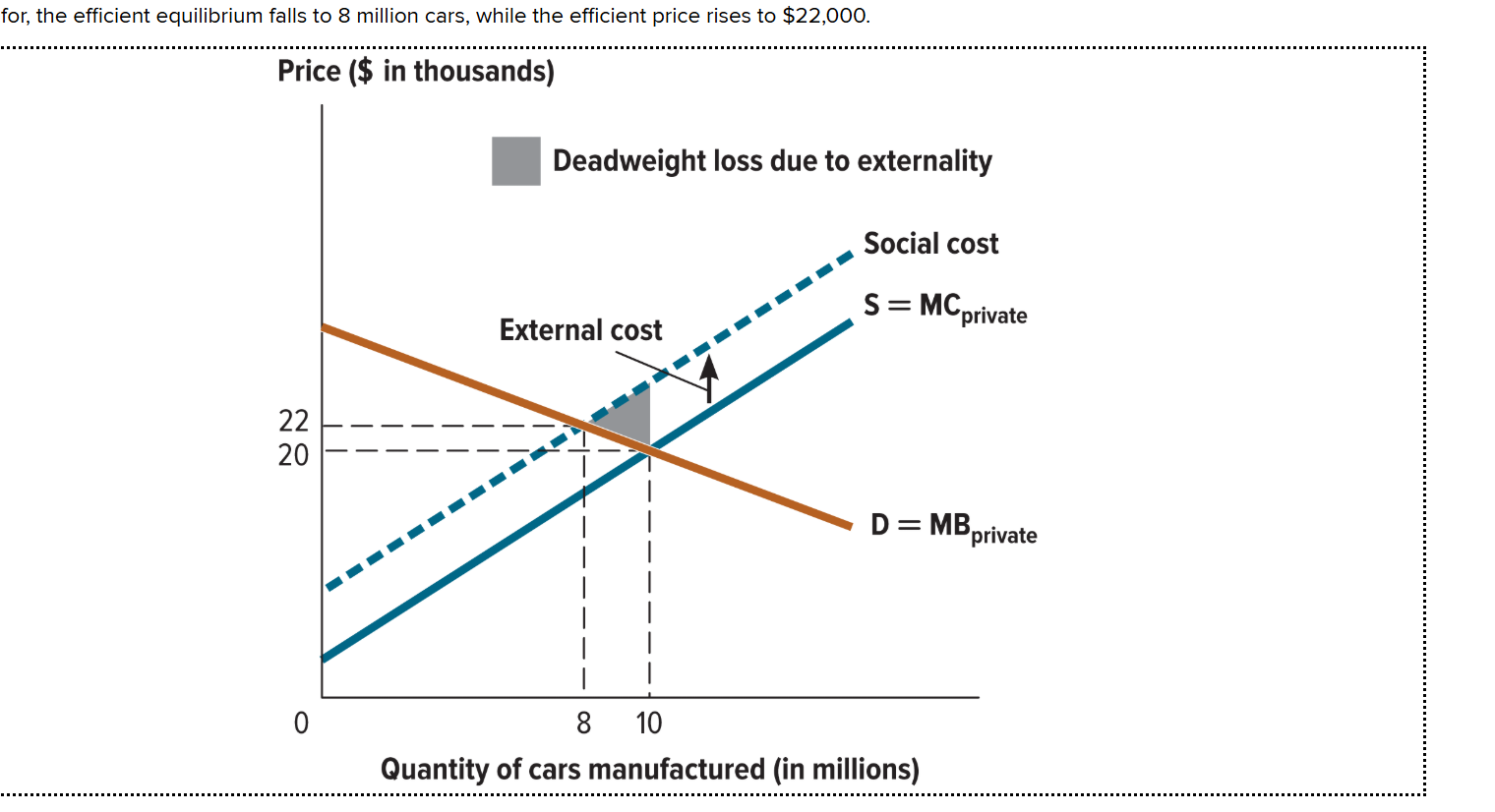
Where is the negative external cost?
When the social cost and market demand curve intersects. It occurs at (8 million cars, $22,000).
Negative consumption externality
a cost imposed on others when a good or service is consumed.
positive consumption externality
a third party benefit that occurs when a good or service is being produced.
Example of positive consumption externality
A homeowner will paint their house if the private benefits outweighs the private costs. Although they have to spend money and time to paint the house, they are able to increase their property value in return.
Coase theorem
The idea that even in the presence of an externality, individuals can reach an efficient equilibrium through private trades, assuming zero transaction costs
Markets fail to maximize total surplus when:
A) individual choices impose costs or benefits on others.
B) society's choices impose costs or benefits on other societies.
C) all costs and benefits are received by participants in transactions.
D) producer surplus is not exactly equal to consumer surplus.
A) individual choices impose costs or benefits on others.
When is the Pigovian Tax applied?
Pigovian Tax is applied when goods and services cause negative externalities. Prices are raised to reduce the quantity consumed.
If people took external costs, such as pollution, into consideration when deciding how many externality-causing goods to consume, then they would:
A) consume a socially non-optimal amount.
B) not change their consumption behavior.
C) consume more.
D) consume less.
D) consume less.
DWL on externalities
occurs when market transactions lead to inefficiencies due to unaccounted-for costs or benefits affecting third parties. This can happen in cases of negative externalities (e.g., pollution) or positive externalities (e.g., education).
![<p><span style="color: #dbdada">Which of the following statements is correct?</span><span style="color: #dbdada"><br></span></p><p><span style="color: #e9e2e2">[a] It shows a positive consumption externality.<br>[b] It shows a negative consumption externality.<br>[c] Deadweight loss is represented by A + B.<br>[d] Deadweight loss is represented by D + F</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/212ae8c8-a8ce-4328-b060-2440f4a42c38.png)
Which of the following statements is correct?
[a] It shows a positive consumption externality.
[b] It shows a negative consumption externality.
[c] Deadweight loss is represented by A + B.
[d] Deadweight loss is represented by D + F
[a] It shows a positive consumption externality. Graph shows a social benefit curve.