BIOS 325 / Human Embryology / Units 3-5 / Exam 2
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Human Cleavage refers to the early rapid cell division that occurs immediately after ______.
fertilization
In early rapid cell division, cell division occurs _____ _____ than a normal cell cycle takes.
more quickly
Once cleavage starts in human cleavage, the cells are known as ______.
blastomeres
T or F:
Human cleavage begins 24 hours after fertilization, and each division takes 12-24 hours.
True
What does "cleavage is rotational" mean?
> Cells are taking turns in what orientation they are dividing
> The first and second division occurs at a perpendicular angle.
** Meaning the cells will divide up and down then left to right. This cycle will repeat.
Not all blastomeres divide at the same time, so the embryo often has an odd number of cells. This means cleavage is __________.
Asynchronous
T or F
Cleavage is asynchronous.
True.
Reason:
We go from having one large cell to each cell being smaller. The overall size of the embryo is not growing. The embryo is the exactly the same size. It is just made up of an increasing number of cells.
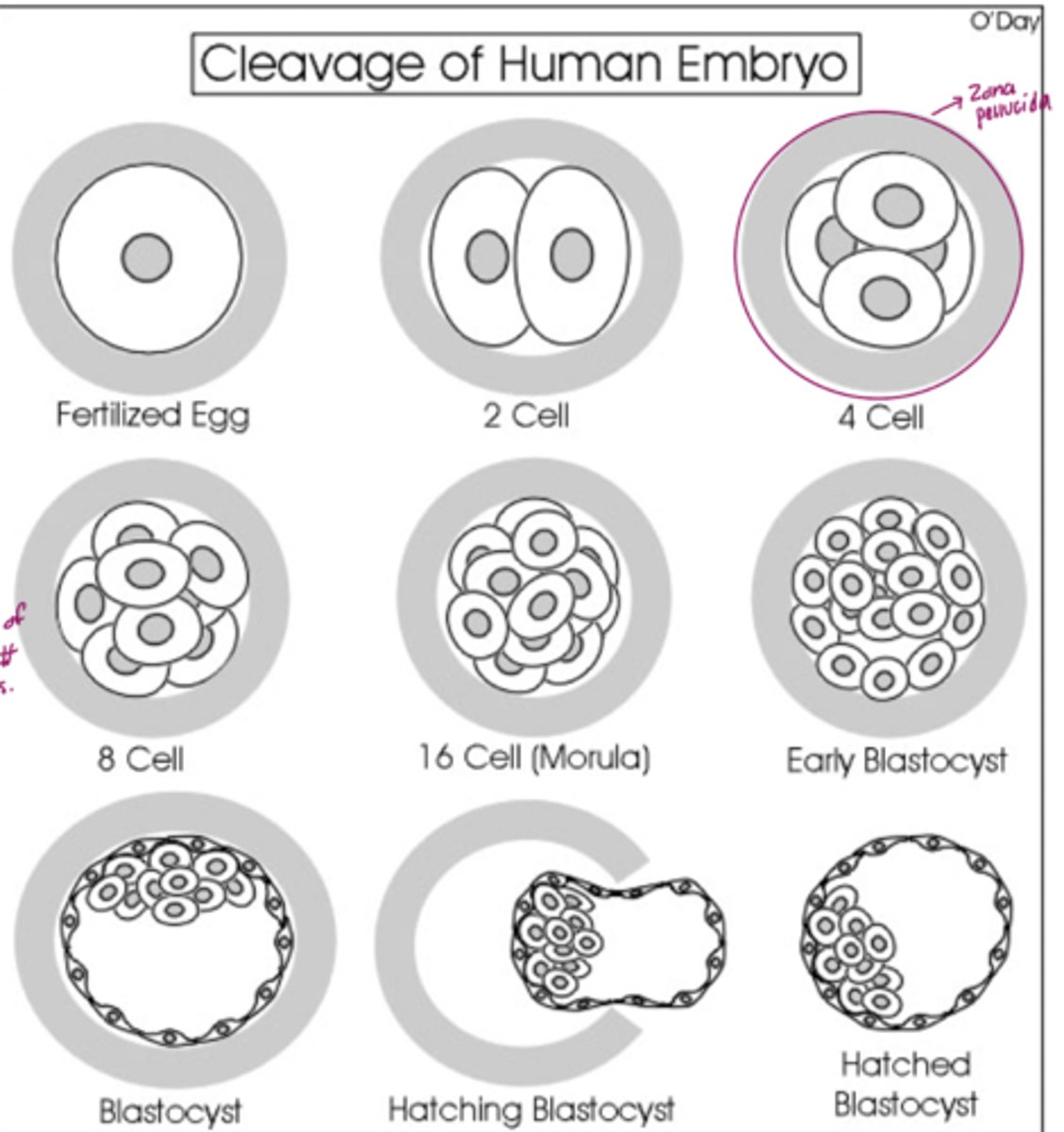
Explain why the embryo is not getting larger during cleavage.
During cleavage, the cells divide without an increase in mass; that is, one large single-celled zygote divides into multiple smaller cells. Each cell within the blastula is called a blastomere.
Compaction is __________.
a process where the blastomeres start to stick together.
What is a blastomere?
individual totipotent cells at the early cleavage stage (cells that makeup the embryo).
During compaction _______.
the cells smash up against each other. The embryo is physically compacting and the boundaries between cells are not distant anymore.
Totipotent means
cells that have a the ability to do and become anything.
T or F:
Some of the blastomeres get moved to be outside of the embryo. Some of the them get moved to be inside of the embryo (inside the "mulberry").
True
T or F:
At 8-16 cell stage the embryo undergoes compaction, when the blastomeres flatten and adhere to one another tightly.
True.
Reason:
This is the first differentiation event in the embryo: after compaction, cells on
the inside and outside of the embryo have different fates.
Why is compaction important?
After several cellular divisions in the initial stages of embryonic development, the intercellular boundaries become obscured in a process called compaction, which maximizes intercellular contact and results in the formation of the morula
T or F:
Totipotent cells have the ability to do and become anything they want even after compaction.
False
Reason:
After compaction their potential fates have been limited meaning no more totipotent makes a decision to become either embryo cells of trophoblast cells.
This is the first differentiation event in the embryo: after compaction, cells on
the _________ _______ __________ of the embryo have different fates.
inside and outside
How many cells is the embryo composed of at four days?
16-32 cells and is called a morula
At the fourth day of development, the embryo consists of inner cell mass and epithelial cells, what is the difference between the two types of cells?
> Inner Cell Mass: a cluster of cells at one side of the blastocoel (also called embryo-blast). These cells are located on the inside! These cells are PLURIPOTENT (they have the ability to become most of the structures within the embryo. They form the embryo's body itself, since they are NO LONGER TOTIPOTENT, they NO LONGER have the capacity to form placental tissues).
> Epithelial Cells (trophoblast): these cells are fated to become part of the extra-embryonic tissues (the placenta).
T or F:
Cells outside of the embryo are trophoblast cells.
True
T or F:
Cells that are outside of the ICM are pluripotent.
False.
The cells inside of the ICM are pluripotent
At the fifth day of development the blastocyst hatches from the zona pellucida, they can now attach to the _____ ______.
Uterine Endometrium
We want implantation to happen in the _____.
uterus
Ectopic Pregnancy
implantation of the fertilized egg in any site other than the normal uterine location.
What may cause ectopic pregnancy?
all of the above
What are the two names of the layers that are formed at the 2nd week of human development?
Epiblast, hypoblast
Epiblast (or primary ectoderm) is
a layer of external cells that located closest to the side that implants.
Hypoblast (primary endoderm) is
a layer of internal cells
What do hypoblasts form?
yolk sac
What is the two-layered embryo-blast called
bilaminar germ disc
> Hypoblast and Epiblast both form a bilaminar germ disc. Why? because they are both shaped like a disc. (Bilaminar = 2 layer)
What does the rule of twos refer to?
Bilaminar germ disc
How is the amniotic cavity formed?
The separation of the inner cell mass from the Thophoblast gradually increases and begins to form a fluid filled chamber
What is the name of the cells that are amnioblasts and become the amniotic membrane?
Epiblast cells
T or F:
The amniotic cavity is the 2nd cavity that is formed inside of the embryo.
True
T or F:
Hypoblast cells migrate out to cover the inner surface of the cytotrophoblast
True
The blastocoel cavity is now called the primary_______.
primary yolk sac
What forms the extraembryonic endoderm that lines the blastocoel cavity?
Hypoblast cells (migrate out to cover the inner surface of the cytotrophoblast) form the extra-embryonic endoderm that lines the blastocoel cavity
After embryonic folding, the connecting stalk is located _______ to the yolk sac
You are an obstetrician working with a couple in the 20th week of their pregnancy. At their 20-week ultrasound, you can see a well-formed fetus and make measurements of the head, body length, limbs, and heart rate. Unfortunately, you also notice a large protrusion at the base of the fetus' umbilical cord, along the ventral midline. It appears the walls of the abdomen did not fuse together properly, and some of the baby's digestive system is stuck outside of the body wall. The parents ask you how this happened, and you explain this is probably a problem with
tail folding
When the lateral plate mesoderm splits into two layers,
the somatic mesoderm is closest to the ectoderm.
Primary neurulation is triggered by
a signal secreted from the notochord.
What type of mesoderm will line the walls of future body cavities?
lateral plate mesoderm
What structures does the intraembryonic coelom give rise to?
The pericardial, pleural, and peritoneal cavities
What structures do the oropharyngeal and cloacal membranes cap and What do they rupture to form?
The oropharyngeal membrane cranially caps the foregut, while the cloacal membrane caps the hindgut. The oropharyngeal membrane ruptures to form the mouth, and the cloacal membrane ruptures to form the anus.
T or F:
Neurulation begins at the caudal end of the embryo while gastrulation is still occurring
False
Neurulation begins at the cranial end of the embryo while gastrulation is still occurring at the caudal end.
Which of the following is true regarding umbilical blood vessels?
a. Umbilical arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the embryo to the placenta
b. Umbilical vein carries oxygenated blood from placenta to embryo
c. There are two umbilical veins and one umbilical artery
d. A and C
e. A and B
f. A, B and C
e. A and B
>>>> a. Umbilical arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the embryo to the placenta
b. Umbilical vein carries oxygenated blood from placenta to embryo <<<<
What is the first stage of development where a fluid-filled cavity is formed?
Bastula
What is a hydatidiform mole? Describe how they develop
Hydatidiform moles are growths of abnormally fertilized eggs in place of a normal embryo. They can form if 2 sperms fertilize an egg with no nucleus, resulting in the mole being diploid and only containing paternal DNA.
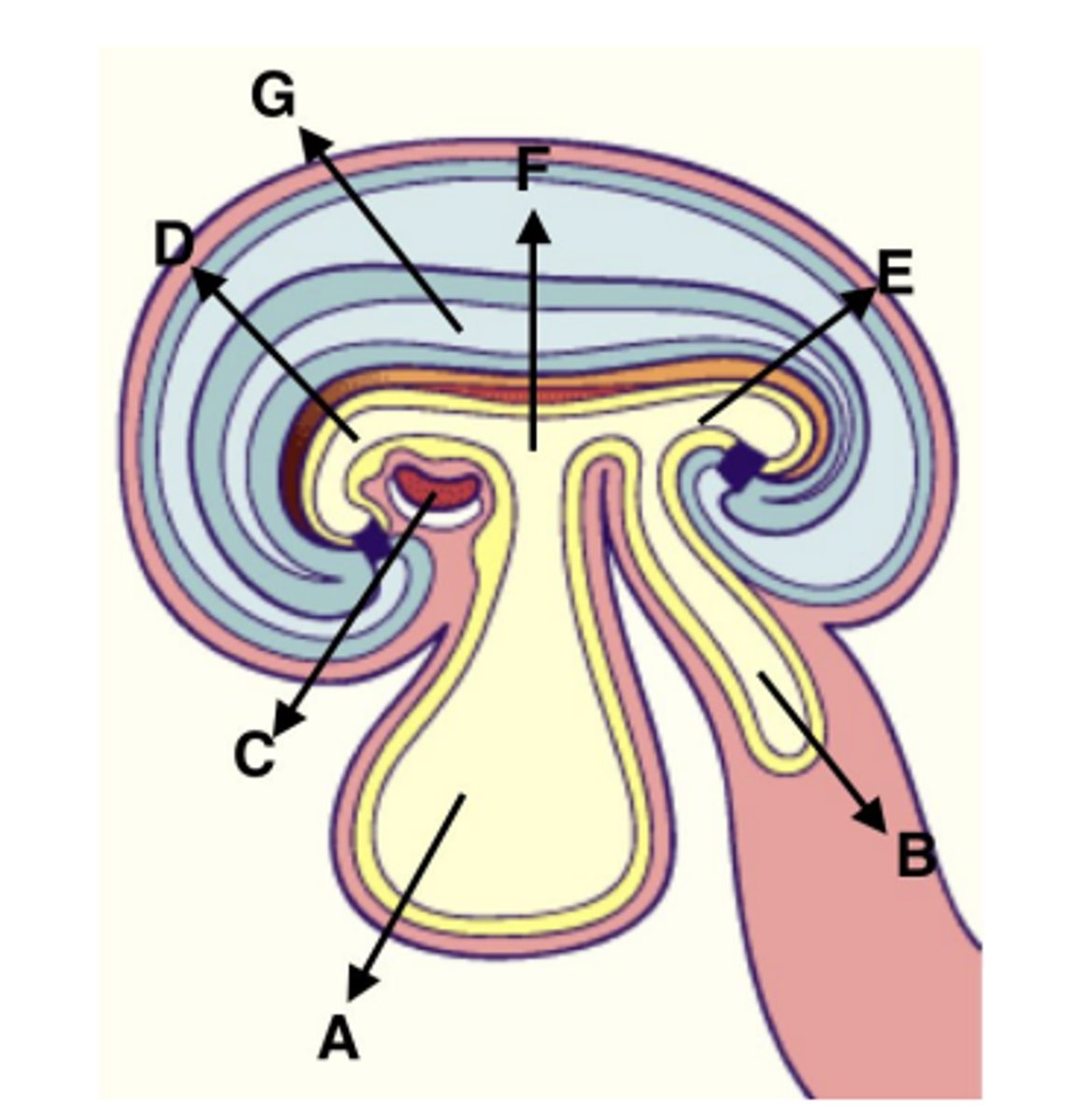
Which of the labeled structures was formed from the blastocoel cavity?
A
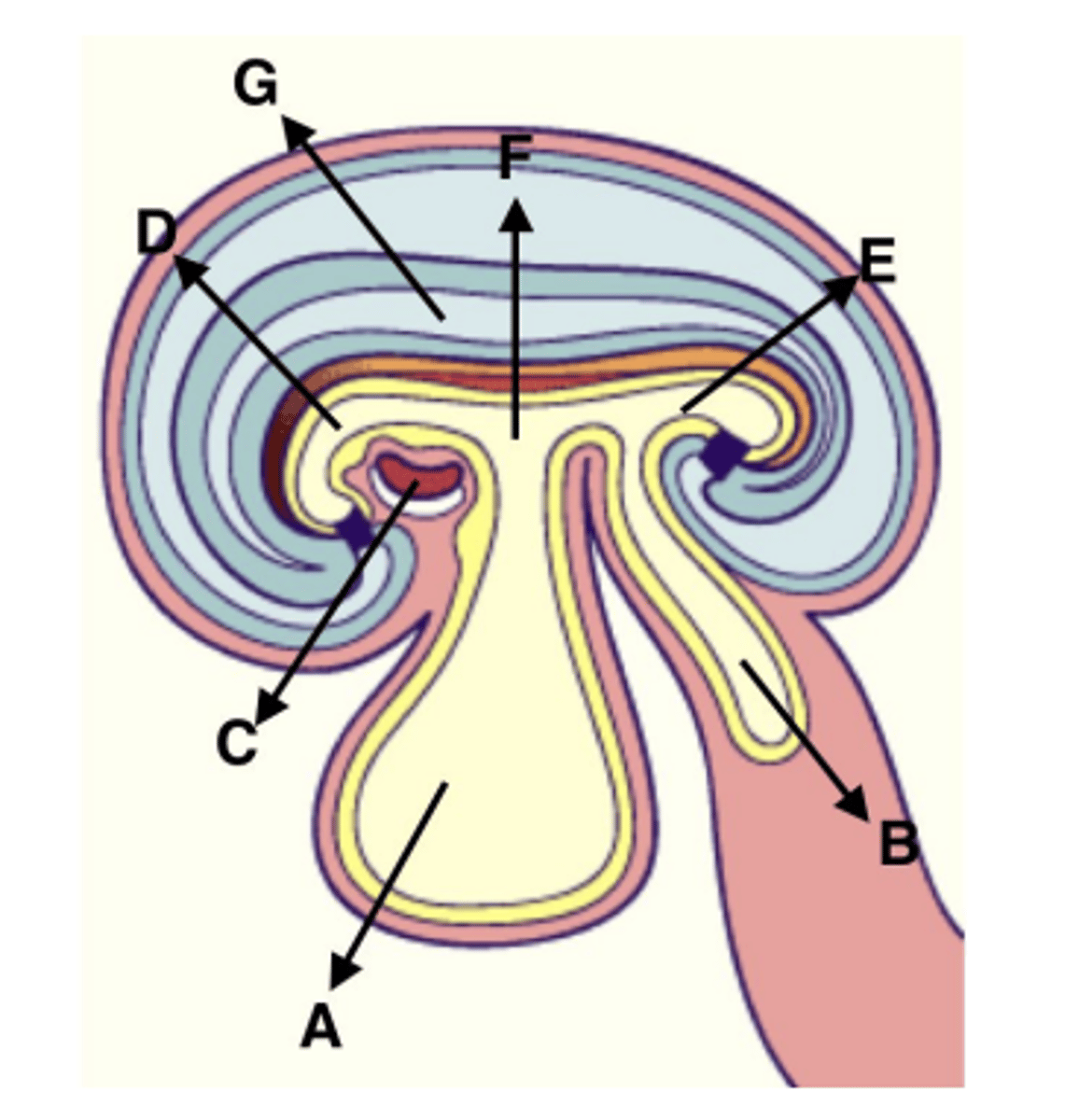
Which of the labeled structures is created from the cardiogenic plate?
C
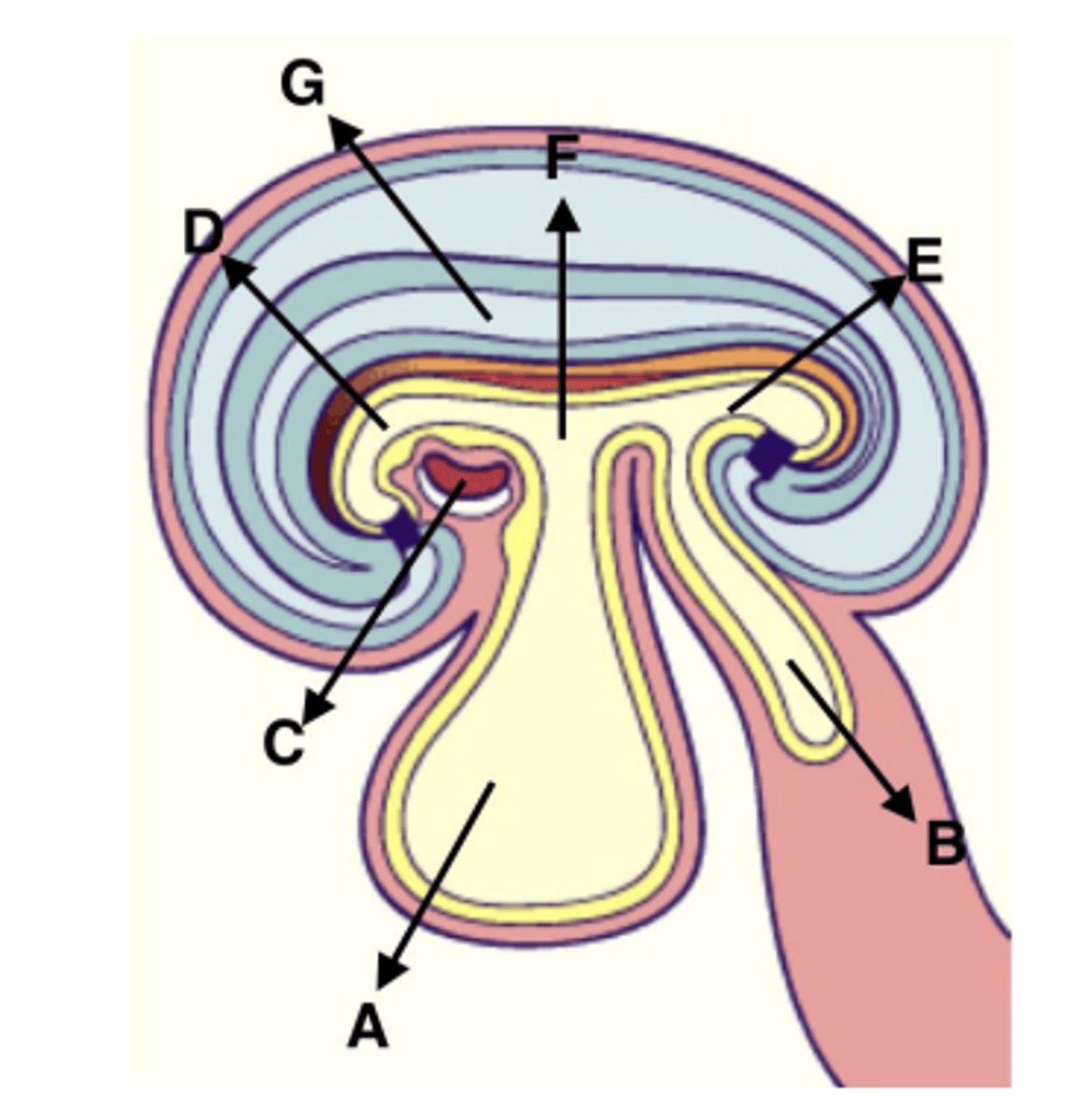
Which of the labeled structures are included in the gut tube? (more than one may apply)
D, E, & F
Is the following sentence a fucntion of the caudal flexure?
>>> Folding the amniotic cavity so it surrounds the dorsal and ventral regions of the posterior of the embryo <<<
Yes
Splanchnic mesoderm _____.
Formed from splitting of lateral plate mesoderm; will cover future organs
Hypoblast ____.
Layer of inner cell mass facing yolk sac
DNA methylation ____.
Adding methyl groups to the 5-carbon of cytosine; usually occurs at CG dinucleotides
Chorion _____.
Embryonic portion of placenta; derived from trophoblast
Placental Abruption _____.
Premature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall
Hydatidiform mole _____.
Abnormality where the conceptus consists only of extraembryonic tissue (embryo is absent)
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) _____.
Hormone that maintains the corpus luteum to ensure production of progesterone
Ectopic pregnancy _____.
Results when embryo implants somewhere other than the uterus
Somatic mesoderm _____.
Formed from splitting of lateral plate mesoderm; will line walls of future body cavities
Caudal eminence _____.
Where secondary neurulation happens (can also be called the tail bud)
X-inactivation _____.
Process by which one copy of the X chromosome is silenced
Epigenetics _____.
Heritable processes that alter the activity or expression of a gene through modifications that do not change the sequence of DNA
Decidua _____.
Maternal portion of placenta; derived from endometrium
Somitogenesis
Process of segmentation of the paraxial mesoderm
Compaction _____.
First differentiation event in the embryo; blastomeres develop an inside-outside polarity
Imprinted Genes _____.
Genes whose ability to be expressed depends upon the sex of the parent that contributed them
Epiblast _____.
Layer of inner cell mass facing amniotic sac
T or F:
Cleavage increases the size of the embryo?
False
What is X inactivation? Describe the process by which it occurs.
X inactivation is the process by which one copy of the X chromosome is inactivated in females (or individuals with more than one X chromosome). This dosage compensation process has three steps: first, a cell will count the number of X chromosomes it contains; next, one of the chromosomes is randomly chosen to remain active, while the rest are chosen to be inactivated ("rest" is only if there are multiple X chromosomes instead of just 1); finally, the chromosome(s) to be inactivated is inactivated starting in the X Inactivation Center by turning on the XIST gene. This gene makes ncRNA that coats the chromosome and compacts it.
What are the three body axes that are defined by the formation of the primitive streak? How is each axis defined?
The formation of the primitive streak defines the caudal-cranial axis, the medial-lateral axis, and the ventral-dorsal axis. The caudal-cranial axis is defined by the position of the primitive pit; the side of the embryo it points towards is its cranial end. Since the primitive streak forms down the midline of the bilaminar germ disc, a clear left and right, or medial-lateral axis, is defined. Finally, the primitive streak forms on the epiblast, which the future dorsal surface of the embryo, while the hypoblast, or the future ventral surface, is underneath (the dorsal surface is the back of the organism while the ventral surface is the front)
In the trilaminar germ disc human embryo, the cavity located closest to the epiblast layer is the:
amniotic cavity