H.A 18 Mouth, Throat, Nose, and Sinuses
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Mouth contains
tongue, teeth, gums, the salivary glands (parotid gland, submandibular, and sublingual).
The tongue
a mass of muscle, attached to the hyoid bone and styloid process of the temporal bone.
It is connected to the floor of the mouth by a fold of tissue called the frenulum.
The gums (gingiva)
are covered by mucous membrane and normally hold 32 permanent teeth in the adult
Teeth
The top, visible, white enameled part of each tooth is the crown.
The portion of the tooth that is embedded in the gums is the root.
The crown and root are connected by the region of the tooth referred to as the neck.
Papillae
Small bumps cover the dorsal surface of the tongue.
Three pairs of salivary glands
Saliva (watery, serous fluid containing salts, mucus, and salivary amylase) into the mouth
Amylase digests carbohydrates
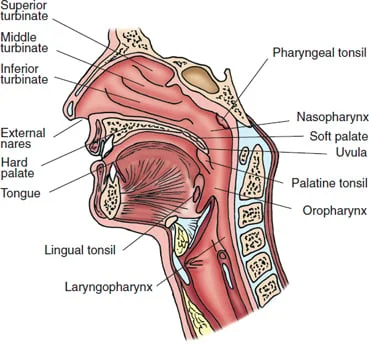
Throat (pharynx)
Pharyngeal tonsils, or adenoids, are found high in the nasopharynx. Because tonsils are masses of lymphoid tissue, they help protect against infection
Located behind the mouth and nose
• Serves as a muscular passage for food and air
• Nasopharynx
• Oropharynx
• Laryngopharynx
• Masses of lymphoid tissue
• Palatine tonsils
• Lingual tonsils
• Pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids)
Kiesselbach area.
The front of the nasal septum contains a rich supply of blood vessels
Known for nose bleeds
Sinuses
Four pairs of paranasal sinuses: frontal, maxillary, ethmoidal, and sphenoidal
These air-filled cavities decrease the weight of the skull and act as resonance chambers during speech.
lined with a ciliated mucous membrane that traps debris and propels it outside, easily blocked.
Nose
Consists of an external portion covered with skin and an
internal nasal cavity
• External nose: Bridge, Tip, Two oval openings called nares
• Internal nose: Nasal cavity, Nasal septum, Kiesselbach area, Superior, middle, and inferior turbinates
Receptors for cranial nerve I (olfactory)
epistaxis
nosebleeds
local causes: trauma, mucosal irritation, septal abnormality, inflammatory diseases, tumors
systemic causes: blood dyscrasias, arteriosclerosis, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia), and idiopathic causes
rhinorrhea
Thin, watery, clear nasal drainage
Gingivitis
Red, swollen gums that bleed easily occur in early gum disease
Periodontitis
Recession of the gums accompanied by tooth loss occurs in more advanced gum disease
Periodontal disease
correlated with cardiovascular disease.
Dysphagia
difficulty swallowing
odynophagia
painful swallowing
bruxism
Grinding the teeth
precipitate temporomandibular joint (TMJ) problems and pain.
Leukoplakia
(Chalky thick white patches of cells), precancerous condition.
halitosis
bad breath
Sinusitis may also be caused by
infection, a fungus, a deviated nasal septum, nasal polyps, or, in rare cases, an immune system deficiency.
palatine tonsils
located on either side of the oropharynx
pharyngeal tonsils
or adenoids are located high in the nasopharynx.
lingual tonsils
lie at the base of the tongue.
Most lip cancers are
squamous cell carcinomas
caries
Tooth decay
may appear as brown dots or cover more extensive areas of chewing surfaces.
hyperplasia
Enlarged, reddened gums
seen in pregnancy, puberty, leukemia,
Burton line
seen in lead poisoning
A bluish-black or gray-white line along the gum line
Candida albicans
Also called thrush
Whitish, curd-like patches that scrape off over reddened mucosa and bleed easily
Koplik spots
Tiny whitish spots that lie over reddened mucosa are an early sign of measles.
Black hairy tounge
Papillae overgrowth
poor hygiene/antibiotics
Tonsilitis
tonsil infection
Fruity or acetone breath is associated with
diabetic ketoacidosis.
Older adult considerations
Cervical curvature may increase due to kyphosis.
• Accumulation of fat around cervical vertebra “dowager’s hump”
Thyroid may feel more nodular or irregular due to fibrotic
changes. May be lower in neck.
• If have arthritis or osteoporosis, may experience neck pain and
decreased range of motion (flexion, extension, lateral bending,
rotation)
Masses of lymphoid tissue
Palatin tonsils
Lingual tonsils
Pharyngeal tonsils Adenoids
1+
Visible, an obstruction of up to 25% of midline.
2+
Midway between tonsillar pillars and uvula
tonsils obstruct 25-50% of midline
3+
Touch uvula, an obstruction of 50-75% of midline
4+
Touch each other, obstruct 75-100% of midline
Vagus (CN X)
cranial nerve is associated with the movement of the uvula
herpes simplex virus
recurrent vesicular eruptions of the lips and surrounding skin.
Angular cheilitis
presence of fissures at the edges of the mouth.
Actinic cheilitis
Affects the lower lip and is characterized by scales, thickening, and eversion of the lip tissue.
Angioedema
diffuse swelling of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue.
most common site of oral cancer is
underneath the tongue.
carbon monoxide poisoning
The finding of reddish lips
Pallor around the lips is a finding in clients with
anemia
aphthous stomatitis
Painful, recurrent ulcers in the mouth (canker sores).