(pt 3) exam #3 - immunohematology (cls 544)
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
uncommon blood groups
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
genomic testing
allows for discovery of new blood group antigens that are either of high or low prevalence
The corresponding antibodies are rarely encountered
Knowledge of these least common antigens and/or antibodies better prepares laboratory personnel for when they encounter an uncommon antibody
blood group system
one or more antigens governed by a single gene or complex of two or more closely linked homologous genes; the genetic basis confirmed
Antigens where the genetic basis is unknown are placed into collections
what must happen for an antigen to form a new blood group?
antigen must be:
Defined by a human alloantibody
Inherited character
Encoding gene must be known
Gene location on chromosome must be known
Gene must be unique from other blood group system genes
ISBT 200 series (general)
collections are antigens that have a biochemical, serologic, or genetic relationship but do NOT meet the criteria for a system
Antigens classified as a collection are assigned a 200 number
ISBT 700 vs 900 series
All remaining RBC antigens NOT associated with a system or collection are catalogued into the ISBT 700 series (low prevalence antigens)OR the ISBT 901 series (high prevalance antigens)
700 series: low prevalence antigens in occur in less than 1% of the population
901 series: high-prevalence antigens occur in greater than 90% of the population
paroxysmal COLD hemoglobinuria (PCH)
acquired hemolytic anemia–seen in children w viral infections or idiopathically in adults
IgG cold autoantibody (Autoanti-P) reacts in cold areas of the body
Hemolysis occurs when antibody is incubated w/ cells
antibody often demonstrates specificity towards the high-prevalence P antigen
Antibody screen usually negative
Positive DAT (with complement only)
Complement-mediated hemolysis
Hemoglobinuria
Intravascular and extravascular hemolysis
Donath-Landsteiner test is diagnostic for PCH
Biphasic hemolysin has anti-P specificity
paroxysmal NOCTURNAL hemoglobinuria (PNH)
acquired stem cell disorder caused by a variant in the PIGA gene
Presents with pancytopenia
Cells deficient in glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins (GPI-APs)
DRBCs in PNH patients lack DAF (CD55) & MIRL (CD59)
Both regulate complement → more sensitive to complement mediated hemolysis
Leads to an immune response which triggers hemolysis of these cells
Hemosiderin present in the urine
Intravascular hemolysis
Determined with flow cytometry of BM analysis
rare blood types by ethnic group
African-American: U-, Fy(a-b-)
Native American and Alaskan Native: RzRz
Pacific Islander and Asian: Jk(a-b-)
Hispanic: Dib- (Diego B-negative)
East European and Russian Jewish: Dra- (Drori A-negative, Cromer blood system)
Caucasian: Kpb- and Vel-
(general) diego blood group system (DI; 010)
Named after the first antibody maker in a Venezuelan family during an investigation of HDFN (caused by anti-Dia)
Antigens carried on Band 3, chromosome 17
Anion exchanger (AE1 transporter)
diego blood group system antigens
23 antigens designated to this blood group system (expressed on newborn RBCs)
Antigens of interest (antithetical pairs): Dia/Dib and Wra/Wrb
High prevalence antigens: Dib and Wrb
Low prevalence antigens: Dia and Wra
Wrb expression dependent on interaction of Band 3 and normal GPA (MNS)
Note: GPA-deficient RBCs are also Wr(a-b-)
(diego blood group) enzyme treament + antibodies
Resistant to ficin, papain, DTT, and glycine-acid EDTA
Antibodies are usually IgG, sometimes IgM
Anti-Dia, anti-Dib, and anti-Wra implicated in HTRs and/or HDFN (anti-ELO)
Autoanti-Wra common in serum of patients diagnosed with WAIHA
(general) YT blood group system (YT; 011)
Six antigens (Yta / Ytb antithetical)
Yta is high prevalence antigen
Ytb is a low prevalence antigen
Three phenotypes: common Yt(a+b-), Yt(a+b+), and rare Yt(a-b+)
Represent amino acid substitution on the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked RBC glycoprotein acetylcholinesterase or (AchE), chromosome 7
Antigens are absent from RBCs of people with PNH III
(YT blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/chemical treatment
Results of ficin and papain treatment varies
DTT destroys antigens
Resistant to glycine-acid EDTA
Antibodies NOT implicated in HDFN
Monocyte phagocytosis assays (MPA) helpful in determining clinical significance of anti-Yta
(general) Xg blood group system (XG; 012)
Two antigens: Xga & CD99
The gene coding for Xga antigen is located on the X chromosome
More commonly seen in females (89%) than males (66%)
Phenotypic relationship
Xga positive ppl = high expression of CD99 on RBCs
Xga negative females = low expression of CD99 on RBCs
(XG blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/chemical treatment
Sensitive to ficin and papain
Resistant to DTT treatment
Antigens weakly expressed on cord RBCs and some adult females
Anti-Xga usually IgG with some examples naturally occurring
Not implicated in HDFN or HTRs
Few examples of anti-CD99 reported
(general) scianna blood group system (SC; 013)
Currently consists of eleven antigens: Sc1, Sc2, Sc3 etc
Found on RBC adhesion protein, erythroid membrane-associated protein (ERMAP) located on chromosome 1
Antigens expressed on cord RBCs
(SC blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Resistant to enzymes
DTT treatment varies on blood group antigens
Antibodies
Alloantibodies rarely encountered
Usually IgG (react at AHG phase)
May cause HTR, mild HDFN has been reported
Autoantibodies to Sc1 and Sc3 have been reported
(general) dombrock blood group system (DO; 014)
3 phenotypes: Do(a+b−), Do(a+b+), and Do(a−b+)
ART4 gene encodes for Dombrock GPI-linked glycoprotein, chromosome 12
Ten antigens
Doa and Dob are antithetical antigens
High-prevalence antigens, Gya and Hy, have phenotypic relationship
Gy(a-) phenotype is null phenotype
Antigens are found on cord RBCs but absent on PNH III RBCs (absent GPI anchor)
(DO blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Resistant to ficin, papain, and glycine-acid EDTA
DTT treatment weakens antigenic expression (sensitive)
Antibodies
Usually IgG and react optimally with enzyme-treated RBCs
Anti-Doa and anti-Dob implicated in delayed HTRs but not HDFN
Difficult to identify = weakly reactive and disappear
(general) colton blood group system (CO; 015)
The high-and low- prevalence antithetical antigens are Coa and Cob, respectively
Co3 present on all RBCs except for rare Co(a-b-) phenotype
Co4 seen on two individuals with rare null phenotype
Located on integral membrane protein, aquaporin-1 (AQP1), chromosome 7
Accounts for 80% of water reabsorption in the kidneys
Antigens expressed on RBCs of newborns
(CO blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Resistant to ficin, papain, chloroquine, and DTT
Antibodies
Usually IgG antibodies
Enhanced with enzyme-treated RBCs
Anti-Coa, anti-Cob, and anti-Co3 implicated in HTRs and HDF
(general) landsteiner-wiener blood group system (LW; 016)
4 LW antigens, chromosome 19
LWa and LWab are the common, high-prevalence antigens
LWb = low-prevalence
Resistant to enzymes and glycine-acid EDTA
Antigens depressed during pregnancy, lymphoma, and leukemia
Autoanti-LW common in serum from patients with WAIHA
Anti-LW not implicated in serious HDFN or HTRs
(LW blood group) similarities bewteen Rh & LW systems
Rh(D) positive RBCs will react strongly in the presence of anti-LW
Rh(D) negative RBCs may be nonreactive or react only weakly with anti-LW
Anti-LW reacts equally well with cord cells regardless of their D type
Anti-LW never reacts with Rhnull cells
(LW blood group) how to distinguish between anti-LW & anti-D?
test with DTT-treated D+ RBCs
D antigen not denatured by DTT, LW antigen destroyed by DTT
Positive reaction (anti-D), negative reaction (anti-LW)
(general) chido-rodgers blood group system (CH/RG; 017)
Located on the fourth component of complement C4
Nine antigens, chromosome 6
Not intrinsic to RBC membrane; antigens are adsorbed onto RBCs after birth
Crossmatch-compatible units may not be located due to high prevalence
(CH/RG blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Enzymes destroy these antigens
Resistant to DTT and glycine-acid EDTA
Antibodies
Usually IgG and react weakly (clinically insignificant for transfusion)
Both anti-Ch and anti-Rg can be neutralized with pooled plasma
(general) gerbich blood group system (GE; 020)
six high-prevalence Gerbich antigens
Ge2, Ge3, Ge4, GEPL, GEAT, and GETI
Seven low-prevalence antigens
Antigens expressed at birth (located on sialoglycophorin C and D)
RBCs of Gerbich or Leach phenotypes have weak expression of Kell blood group antigens
(GE blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Ficin destroys Ge2 and Ge4 antigens
Ge3 is ficin resistant
Resistant to DTT treatment and glycine-acid EDTA
Antibodies
Some are IgM but mostly IgG
Clinical significance varies
Can be eluted from DAT+ cord RBCs
Most common: Anti-Ge2, anti-Ge3 causes HDFN
(general) cromer blood group system (021)
21 high-prevalence antigens and low-prevalence antigens, chromosome 1
Carried on decay accelerating factor (DAF/CD55), a complement regulatory protein
PNH III RBCs deficient in DAF will lack Cromer antigens (absent GPI linkage)
(cromer blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme Treatment
Resistant to ficin, papain, and glycine-acid EDTA
DTT weakens antigenic expression
Destroyed by chymotrypsin
Antibodies
Usually IgG
Not implicated in HDFN
DAF strongly expressed on placenta and absorbs antibodies
(general) knops blood group system (022)
14 blood group antigens, chromosome 1
Kna, McCa, SI1, Yka high-prevalence antigens
Weak at birth; later expressed on complement receptor 1 (CR1)
(knops blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Weakened by ficin and papain
Destroyed by DTT
Resistant to glycine-acid EDTA
Antibodies
Primarily IgG antibodies (react at AHG)
Difficult to absorb and elute
Reactivity enhanced with longer incubation at 37°C
Clinically insignificant for both HTRs and HDFN
(general) indian blood group system (IN; 023)
6 antigens in the system
Mainly discuss Ina (IN1, low-prevalence) and Inb (IN2, high-prevalence)
Located on CD44 glycoprotein, chromosome 11
Weakly expressed on cord RBCs
(IN blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Sensitive to enzymes and DTT
Resistant to glycine-acid EDTA
Antibodies
Usually IgG (react at AHG phase)
Does not bind complement
Seen in positive DATs but not implicated in HDFN
Rare cases of HTRs reported
OK blood group system (OK; 24)
3 high-prevalence antigens
Carried on CD147, or basigin, a receptor essential for Plasmodium falciparum invasion, noted as gene BSG, chromosome 19
Oka well developed on RBCs from newborns
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Resistant to enzymes, DTT, and glycine-acid EDTA
No reports of anti-Oka (IgG) implicated HDFN reported
(general) raph blood group system (025)
only antigen is MER2; originally defined by two monoclonal antibodies, chromosome 11
Encoded by the CD151 gene
Essential for the assembly of basement membranes in the skin and the kidneys
has been recognized by human polyclonal antibodies
MER2 is abundant on platelets; decreases over time with maturation of erythroid cells
Alloanti-MER2 has been found in patients with end-stage renal disease
(raph blood group) enzyme treament + transfusion considerations
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Resistant to ficin and papain
Sensitive to trypsin, a-chymotrypsin, pronase, and AET
Transfusion Considerations
Little is known about the clinical significance of anti-MER2, may cause HTR
8% of the population has MER2- RBCs; transfuse with crossmatch-compatible units
(general) john milton hagen blood group system (JMH; 026)
Established after it was shown that the JMH protein is the GPI-linked glycoprotein CD108 and the gene (SEMA7A) was cloned, chromosome 15
Consists of 8 antigens
JMH is a high-prevalence antigen & present on glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) linked glycoprotein
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinemia (PNH) - Lack all GPI linked glycoproteins
(JMH blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Destroyed w ficin, papain, and DTT
Resistant to glycine-acid EDTA
Anti-JMH often found in elderly patients (usually IgG)
Antibodies are generally clinically insignificant
(general) GIL blood group system (GIL; 029)
only one high-prevalence antigen, GIL
Genetically discrete from all other blood group systems
Located on the glycerol transporter aquaporin 3 (AQP3); AQP3 gene, chromosome 9
(GIL blood group) enzyme treatment + testing considerations
Results of enzyme treatment
Enhanced with ficin and papain
Resistant to DTT and glycine-acid
Testing considerations
DAT positive noted
No clinical HDFN occurrences
One occurrence of HTR associated with anti-GIL
rh-associated glycoprotein blood group system (RHAG; 030)
RhAG does not have Rh blood group antigens
Presence is essential for Rh antigen expression
Absence of RhAG due to inactivating mutations in the RhAG gene results in the Rh null phenotype
Partial suppression of RH gene expression caused by mutations in the RHAG gene occurs in the Rh mod phenotype
Consists of 6 antigens: Duclos, Ola, and DSLK…, chromosome 6
Clinical significance unknown for anti-Duclos and anti-Ola
(general) FORS blood group system (FORS; 031)
only one antigen, FORS1, low prevalence ; originally though to be a subgroup of A
GBGT1 gene produces glycosyltransferase causing the formation of Forssman glycosphingolipid by the addition of N-acetylgalactosamine to the P antigen, chromosome 9
Group O RBCs expressing FORS1 antigen do not react with Dolichos biflorus or monoclonal anti-A
Forssman glycolipid serves as pathogenic receptor for E. coli & increased susceptibility for E. coli infection in human cells
(FORS blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Enhanced with ficin and papain; resistant to DTT and glycine-acid EDTA
Mostly IgM antibodies with optimal reactivity at RT or 4°C
Clinical significance = unknown
(general) JR blood group system (JR; 032)
only one antigen, Jra
High-prevalence in most populations
Located on ABCG2 gene on chromosome 4
Fully developed at birth
Presents as a problem in chemotherapy due to its involvement in multidrug resistance in tumor cells
Jr(a-) phenotype more common in Japanese population
Anti-Jra is usually IgG (rare antibody)
(JR blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Resistant to ficin, papain, DTT, and glycine-acid EDTA
Documented in severe cases of HDFN
Some anti-Jra patients have been transfused with Jr(a+) RBC units [incompatible] without issue; others have led to HTRs
(general) LAN blood group system (LAN; 033)
only one antigen, Lan (high-prevalence > 99% population)
Lan- phenotype occurs in about 1 in 20,000 people
Lan gene, ABCB6, encodes for ATP-binding cassette transporters, chromosome 2
Lan null phenotype: other porphyrin transporters compensate for the ATP- dependent uptake of heme
Cord RBCs have a stronger reaction with monoclonal anti-Lan versus adult RBCs
(LAN blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies + transfusion considerations
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment: resistant to ficin, papain, DTT, and glycine-acid EDTA
Anti-Lan formed due to exposure via pregnancy or transfusion
IgG antibody; reacts optimally at AHG phase; some able to bind complement
Transfusion Considerations
Due to clinical significance, Lan- RBCs should be used
Not known to cause HDFNS but has been observed in positive DAT of newborns
(general) vel blood group system (VEL; 034)
only one antigen (high-prevalence), Vel
Gene SMIM1 located on chromosome 1 → absence of gene results in null phenotype
Weak antigen expression on cord RBCs; varies on adult RBCs
(VEL blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Antigen resistant to glycine-acid EDTA and DTT
Anti-Vel enhanced with enzyme-treated RBCs
Some examples of anti-Vel did not react with DTT treated RBCs
Antibodies
Mostly IgG but can be IgM as well
Ability to cause severe immediate HTR and HDFN
In testing, anti-Vel may cause in vitro and in vivo hemolysis
Characterized by its ability to activate complement
(general) CD55 blood group system (035)
Only one antigen, CD59.1; chromosome 11
CD59 plays major role in protecting against complement-regulated hemolysis by binding to C8 and C9 → interference with MAC formation
PNH (acquired hemolytic anemia) caused by mutation in the GPI-linker gene
PNH patients are deficient in all GPI-linked proteins including CD59
Symptoms include hemolysis, strokes, and neuropathy
(CD55 blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Demonstrate increased reactivity with enzyme-treated RBCs, not affected by DTT-treated RBCs
Antibodies: one example of anti-CD59.1 (IgG)
(general) augustine blood group system (AUG; 036)
4 antigens, AUG1, AUG2 (Ata), AUG3 (ATML) and AUG4 (ATAM)
AUG1, AUG2 (Ata) and AUG 4 are high-prevalence
At(a-) only identified in the AA population
AUG gene, SLC29A1 located on chromosome 6
Antigens are fully developed at birth
(AUG blood group) enzyme treatment + antibodies
Enzyme/Chemical Treatment
Resistant to ficin, papain, DTT, and glycine-acid EDTA
Antibodies
Anti-Ata usually IgG and reacts at AHG phase, cause HTR
Anti-AUG3 cause HDFN
Associated with severe HTRs; one case of HDFN
Low prevalence antigen AHG 3 has corresponding antibody that caused severe HDFN
SID blood group system (SID; 038)
1 high-prevalence carbohydrate antigen, soluble form is Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein found in urine (96%)
B4GALNT2 gene, located on chromosome 17
Variable in RBC expression, weakens during pregnancy, not detected at birth
Antigen resistant to ficin, papain, DTT and glycine acid-EDTA
Antibody usually IgM, can naturally occur, can react at AHG phase
(SID blood group) testing considerations
Known to have characteristically shiny, refractile agglutinates under microscope
Inhibited/neutralized with urine from Sd(a+) individuals, clinically insignificant
Enhanced with enzyme treated RBCs
Er blood group system (ER; 044)
High prevalence antigens Era and Er3
Low-prevalence: Erb, ERSA, and ERAMA
5 antigens, PIEZO1 gene, chromosome 16
IgG antibody, anti-Er3 indicates HTR
EMM blood group system (EMM; 042)
1 antigen, high prevalence, PIGG gene, chromosome 4
Located on GPI-anchored protein, deficiencies in GPI synthesis can lead to the Emm-negative phenotype, e.g. PNH III
Resistant to enzyme treatment
Anti-IgG or IgM, naturally occurring, clinically insignificant
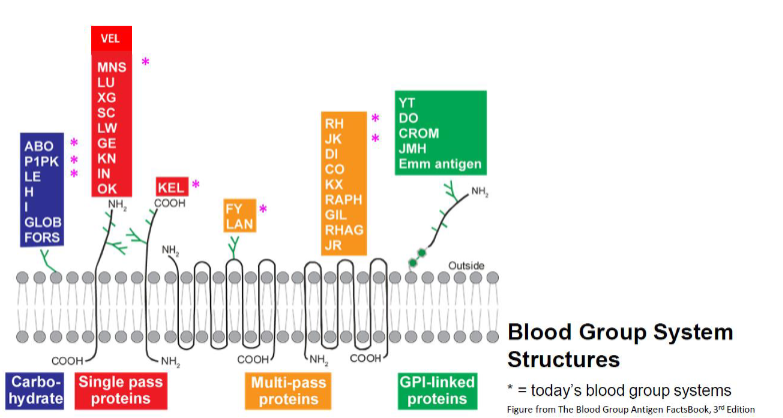
which blood group structures are carbohydrates? (7)
ABO
P1PK
LE ; H ; I
GLOB ; FORS
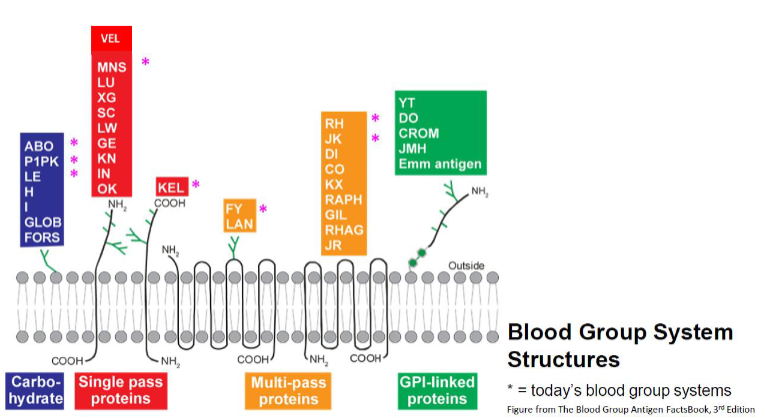
which blood group structures are single pass proteins? (11)
MNS ; LU ; XG ; KEL
SC ; LW ; GE
KN ; IN ; OK
Vel
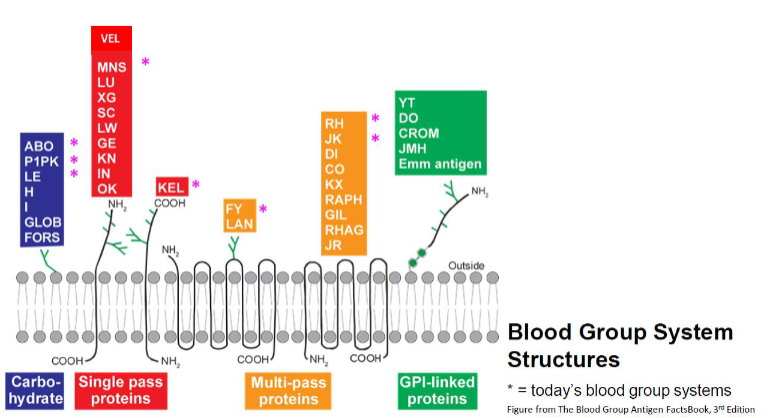
which blood group structures are multi-pass proteins? (11)
FY ; RH ; JK
LAN ; DI ; CO
KX ; RAPH ; GIL
RHAG ; JR
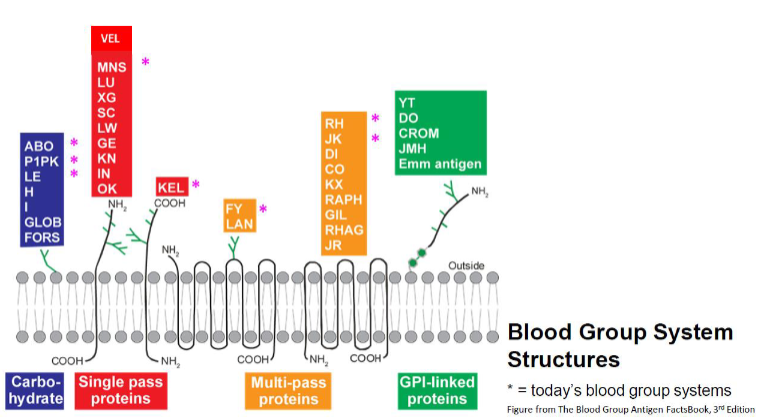
which blood group structures are GPI-linked proteins? (5)
YT
DO
CROM
JMH
EMM
ISBT Ii collection 207
One antigen: i
i antigens are found on most human and on soluble glycoproteins in body fluids
Strongly expressed on cord cells
ISBT collection 210 + MN CHO collection 213
Collection 210
Two antigens Lec and Led, precursors to Lewis antigens
MN CHO Collection 213
Six polymorphic antigens
Hu, M1, Tm, Can, Sext, and Sj
Associated with the M or N antigen in the MNS system
ISBT 700 series
Low-prevalence of less than 1% of most random populations
Gene for these antigens is unknown
When identified is placed into a blood group system
Antigens currently make up the 700 series of the ISBT classification:
By, Chra, Bi, Bxa, Toa, Pta, Rea, Jea, Lia, Milne, RASM, JFV, JONES, HJK, HOFM, and REIT
May cause HDFN
ISBT 901 series
High-prevalence antigens that represent more than 90% of most random populations
Gene for these antigens is unknown
When identified is placed into a blood group system
Antigens currently make up the 901 series of the ISBT classification:
ABTI: weak Vel expression I ABTI- RBCS
LKE
HLA antigens on RBCs (general)
HLA class I antigens (HLA-A, -B, and -C) are present on all nucleated cells
Mature RBCs are not nucleated and generally do not have detectable level of HLA antigens
HLA antigens are not considered a blood group antigen
Three antigens: Bga, Bgb, and Bgc, detectable on mature RBCs
(HLA antigens) BG antigens
Bga (HLA-B7), Bgb (HLA-B17), Bgc (HLA-A28)
HLA antigens on RBCs not destroyed by enzyme, removed by chloroquine
Bg antibodies can be adsorbed by using platelet concentrate
IgG class antibodies, react weakly in serologic tests
Clinically insignificant, rare delayed HTR, no HDFN, significant in TRALI
uncommon blood groups applications to routine blood banking
Identification of uncommon blood group antibodies
Prevalence (low or high), known ethnicity, effect of enzymes, and chemical treatments is critical
Antibodies to low-prevalence antigens: HDFN, incompatible crossmatch
Antibodies to high-prevalence and other uncommon antigens