cc5 - nucleic acids
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
A nucleotide (NOT A NUCLEIC ACID) consisting of a molecule of ribose joined to the nitrogenous base adenine and three phosphate groups. Its known as the ‘universal energy currency’ because it's a source of energy for all cells in all reactions
ATPase
Emzme that hydrolyses the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate
This releases 30.6kJ of energy
Why is ATP a supplier of energy rather than glucose?
ATP releases energy in a simgle reastion, glucose takes many
ATP uses only one enzyme, glucose requires many
ATP releases energy as and when needed, glucose releases it all at once
What is ATP used for?
Metabolic processes, active transport, movement, nerve transmission and secretion
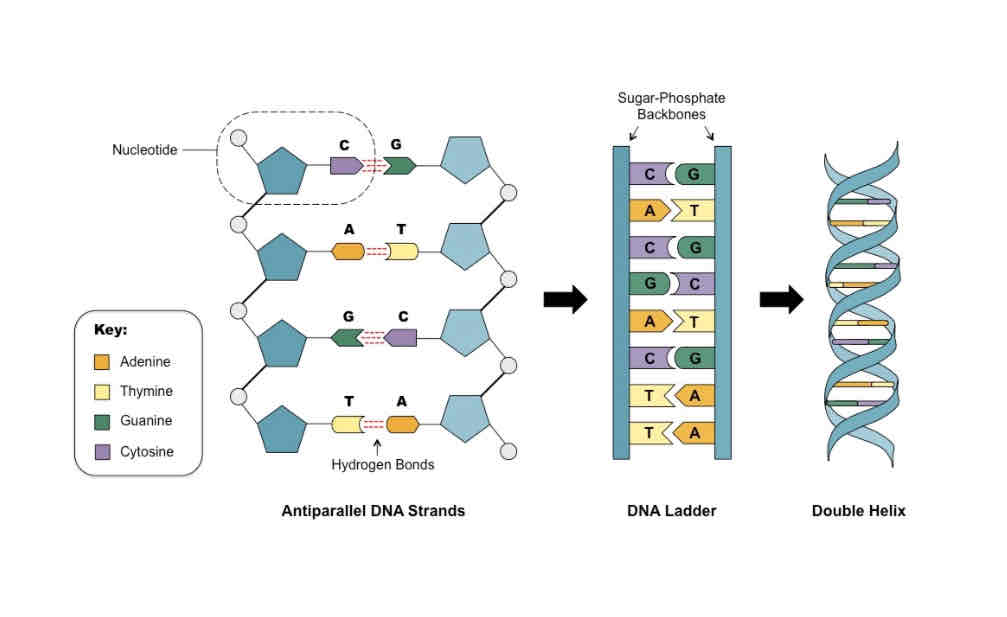
Antiparallel
Describes the complementary strands of a DNA double helix which run parallel but in opposite directions (5’ to 3’ and 3’ to 5’).
Complementary base pairing
Describes how hydrogen bonds form between complementary purine and pyrimidine bases, with two bonds between A and T (or U) and three bonds between G and C.
Degenerate
A feature of the genetic code where more than one triplet can code for a particular amino acid.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
A double stranded polynucleotide containing the genetic material of an organism made up of deoxyribonucleotide monomers joined together by phosphodiester bonds.
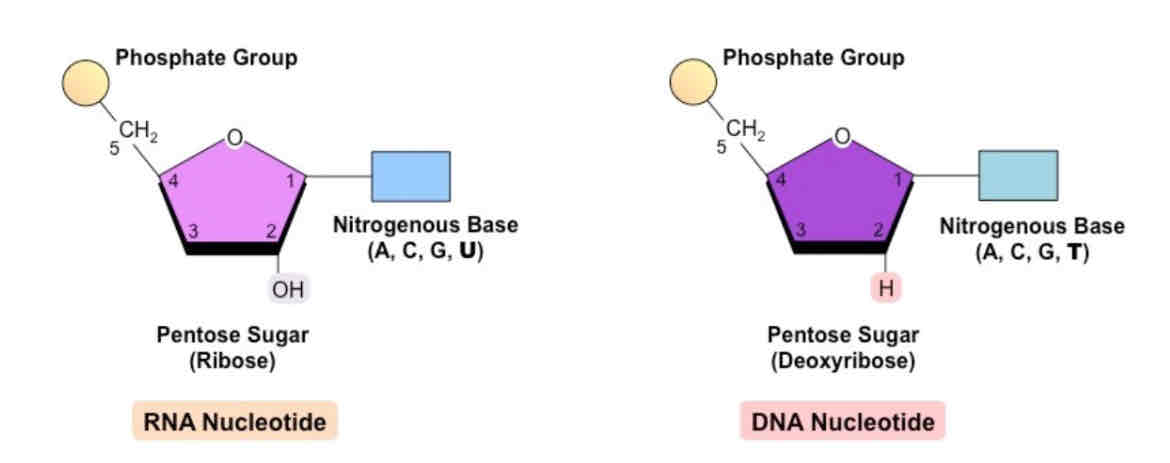
DNA nucleotide
The monomer that makes up DNA, consisting of deoxyribose, a nitrogenous base (A, T, C or G) and a phosphate group.
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that catalyses the formation of phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides during the synthesis of a new DNA strand.
Endergonic reaction
A non-spontaneous reaction that requires an input of energy, for example, ATP formation.
Exergonic reaction
A spontaneous reaction that overall releases energy, such as ATP hydrolysis.
Exons
Regions of DNA that code for amino acid sequences.
Introns
Non coding regions of pre-messenger RNA which need to be removed
Genetic code
The rules by which triplets in a DNA base sequence code for the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Helicase
An enzyme that catalyses the unzipping of double-stranded DNA into single strands during semi-conservative replication.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
A type of RNA that carries genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes for protein synthesis.
Ribosomal rRNA
Found in the cytoplasm, large complex molecules, site of translation of the genetic code
Explain how the genetic code is non-overlapping
Each base in a sequence is read once and is only part of one triplet
Nucleotide
The monomer from which nucleic acids are made, consisting of a pentose sugar, nitrogenous base, and phosphate group.
‘One gene-one polypeptide’ theory
The theory that each gene encodes a single protein.
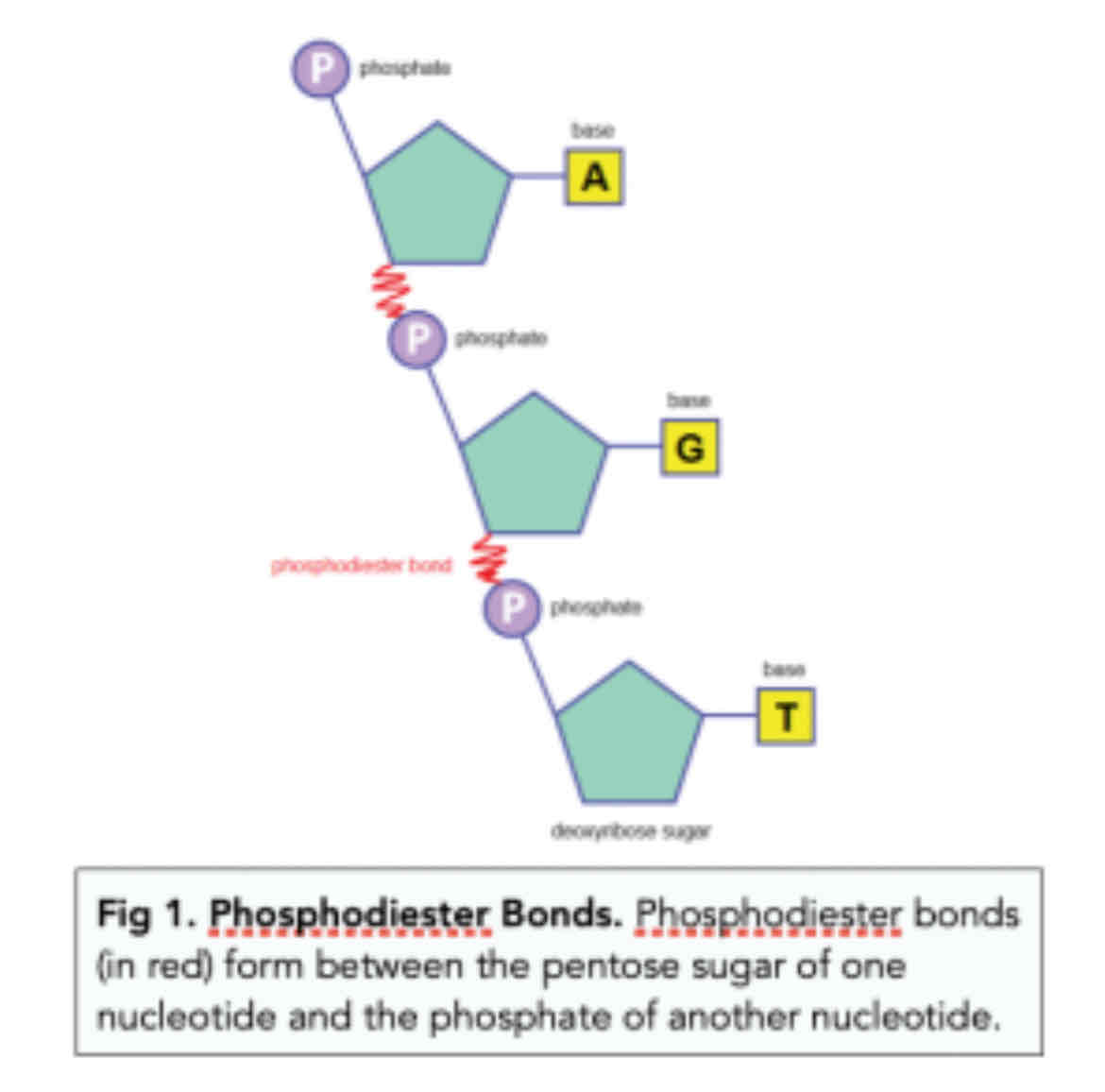
Phosphodiester bond
A type of bond that joins nucleotides together to create polynucleotides.
What is a polypeptide
A molecule formed by the condensation of many amino acids.
Protein synthesis
The formation of proteins from amino acids, occurring in two stages: transcription and translation.
Purines
A class of nitrogenous bases made up of two rings; adenine and guanine are members.
Pyrimidines
A class of nitrogenous bases made up of a single ring; cytosine, thymine, and uracil are members.
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
A short single stranded molecule made up of ribonucleotide monomers joined together by phosphodiester bonds.
Ribosomes
Organelles involved in the synthesis of proteins, found either free in the cytoplasm or membrane-bound.
RNA nucleotide
The monomer that makes up RNA, consisting of ribose, a nitrogenous base (A, U, C or G), and a phosphate group.
Semi-conservative replication
The replication of DNA to produce two new DNA molecules, each containing one new strand and one old strand.
Transcription
The formation of pre-mRNA in eukaryotes and mRNA in prokaryotes from a section of the template strand of DNA.
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
A form of RNA that carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes, taking a clover-leaf shape.
Translation steps
tRNA brings an amino acid to ribosome
Each tRNA has a specific amino acid
Anticodon matches to mRNA codon
A second amino acid is brought to the ribosome
Condensation reaction
Ribosome moves along a mRNA by one codon
Triplet code
A specific sequence of three nucleotides on a molecule of DNA or RNA that codes for a particular amino acid. 64 possible combinations
Universal
A feature of the genetic code; the same codons code for the same amino acids in almost all organisms.
Structure of DNA
Difference between RNA and DNA nucleotide structures
Structure of polynucleotides
Joined by condensation reaction formation between sugar of one and phosphate of the next, the bonds between are sugar-phosphate bonds
Cytosine always bonds to guanine by __ hydrogen bonds
3
Thymine always bonds to adenine by __ hyrdrogen bonds
2
How are polynucleotides?(nucleus acids) formed?
The joining of monomers (nucleotides) together
RNA primase
An enzyme that adds RNA nucleotides to DNA strands after separated
DNA ligase
An enzymes that joins the DNA fragments together in DNA replication
The Mesleson and Stahl experiment
Used the bacteria E.Coli grown in ¹⁵N medium which is transferred to ¹⁴N medium to show replication of DNA, proves semi-conservative replication with ultracentrifugation showing DNA bands getting lighter with each replication cycle
How the M-S experiment disproved conservative replication
There would always be a DNA molecule made from only heavy nitrogen
There would never be intermediate mass DNA
The mass of light DNA would increase
Heavy DNA would never split
How the M-S experiment disproved dispersive replication
Except for Gen O, all DNA would be intermediate mass
The heavy DNA would be split between all molecules
How many amino acids are there?
20
What are codons used for?
They determine the base pairs to attach to create the amino acids
How is mRNA made for transcription?
DNA helicase breaks hydrogen bonds between complimentary base pairs of a gene of DNA to separate the helix, RNA polymerase attaches free RNA nucleotides to the complimentary bases on one strand of the gene template to synthesise mRNA, a stop signal at the end of the gene tells the RNA polymerase to stop adding the nucleotides