Overview of Spinal Cord Anatomy and Functions
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Spinal cord
Information highway between brain and torso/limbs; extends through vertebral column to L1.
Functions of spinal cord
Conduction, locomotion, reflexes.
Conduction
Move information up/down cord, connects different levels of trunk to each other and to brain.
Locomotion
Repetitive movements coordinated in spinal cord; brain initiates motor neurons, determines speed, distance, and direction.
Reflexes
Involuntary stereotyped responses to stimuli; involve brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
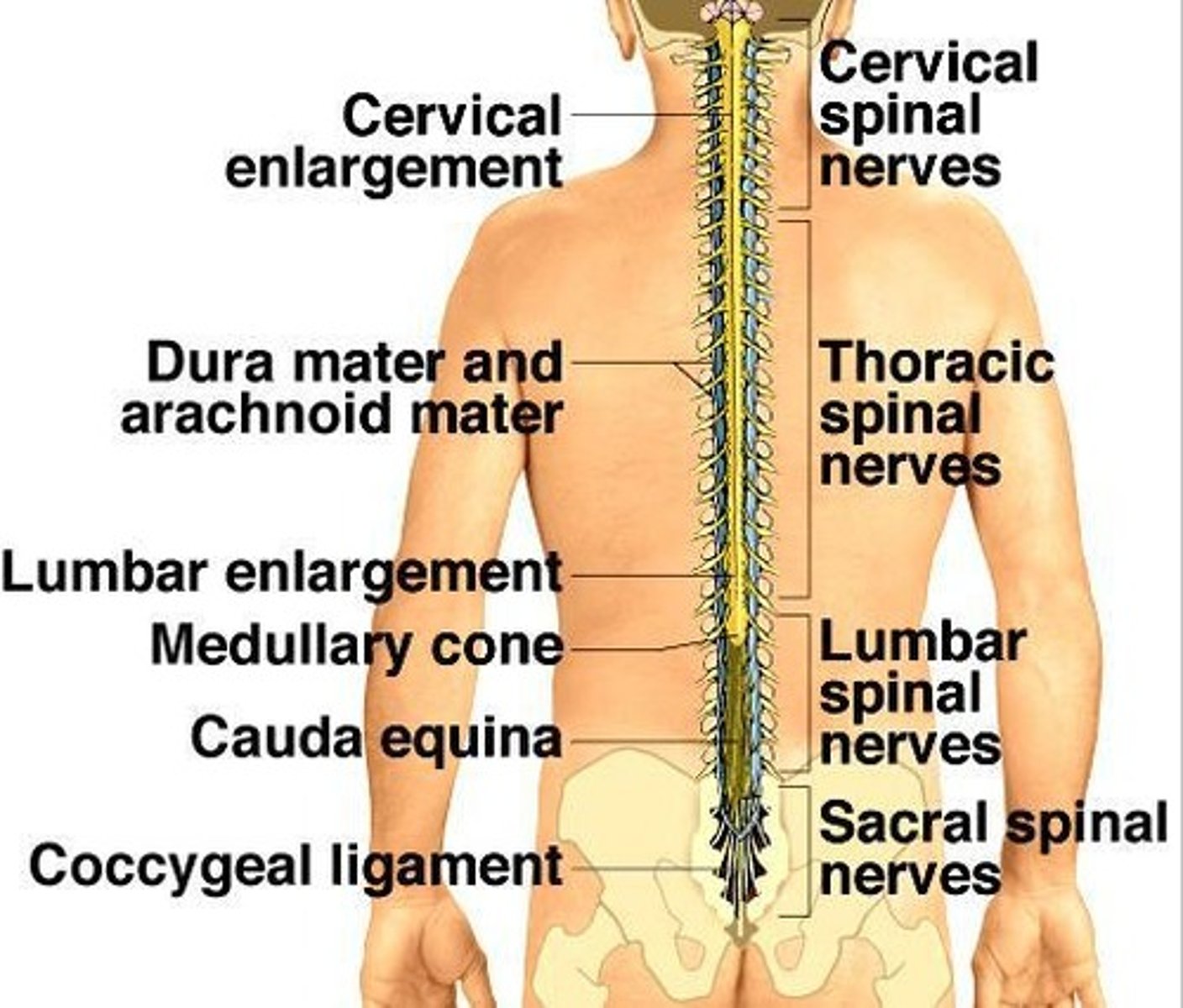
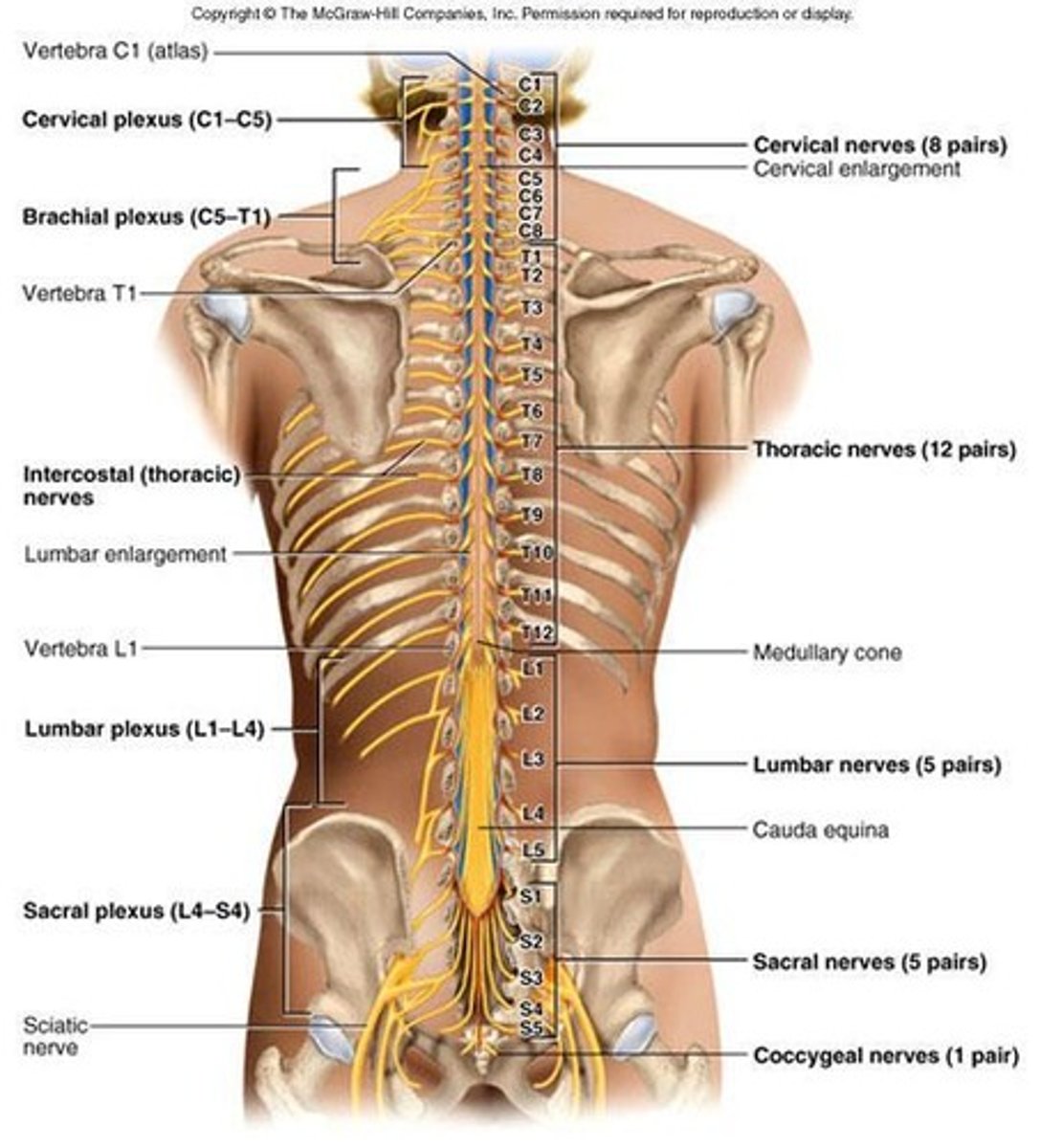
Regions of the Spinal Cord
Spinal cord has 4 regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions; does not extend past L1.
Cervical enlargement
Nerves of upper limbs.
Lumbar enlargement
Nerves of pelvic region and lower limbs.
Medullary cone
Cord tapers to form point; lumbar and medullary cone give rise to nerves of the cauda equina (travel through L2-S5).
Meninges
3 fibrous membranes; dura, arachnoid, and pia mater.
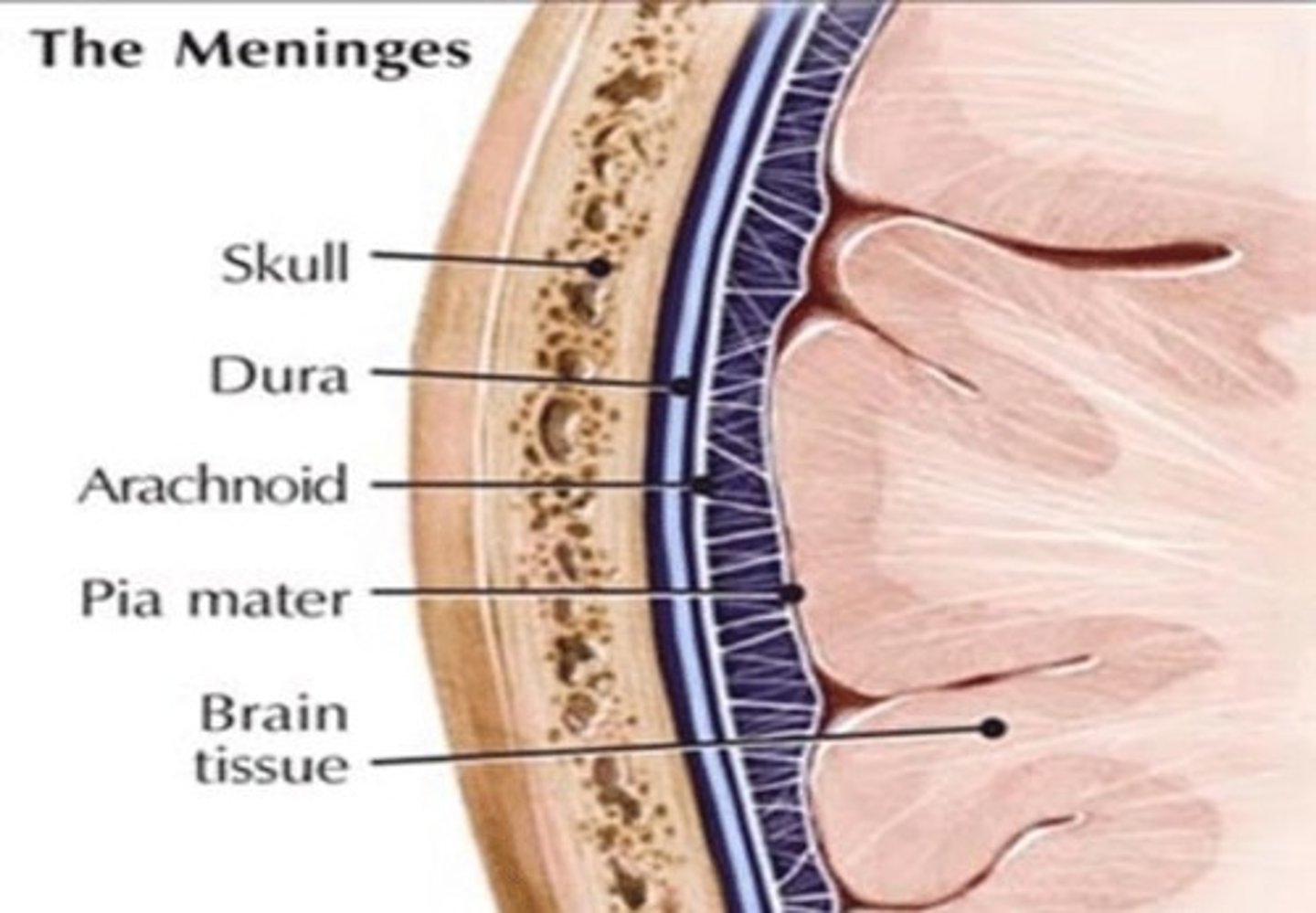
Dura mater
Forms loose dural sheath around spinal cord; tough, rubbery collagen.
Epidural space
Space between dura mater and bone; contains blood vessels, adipose, and loose connective tissue.
Arachnoid mater
Arachnoid membrane adheres to dura and has a layer of loose mesh of collagen and elastic fibers spanning space until pia mater.
Subarachnoid space
Gap filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Pia mater
Deepest layer, delicate membrane closely following contours of spinal cord; continues beyond medullary cone as the terminal filum.
Denticulate ligaments
Extensions that anchor cord to dura to prevent side-to-side movements.
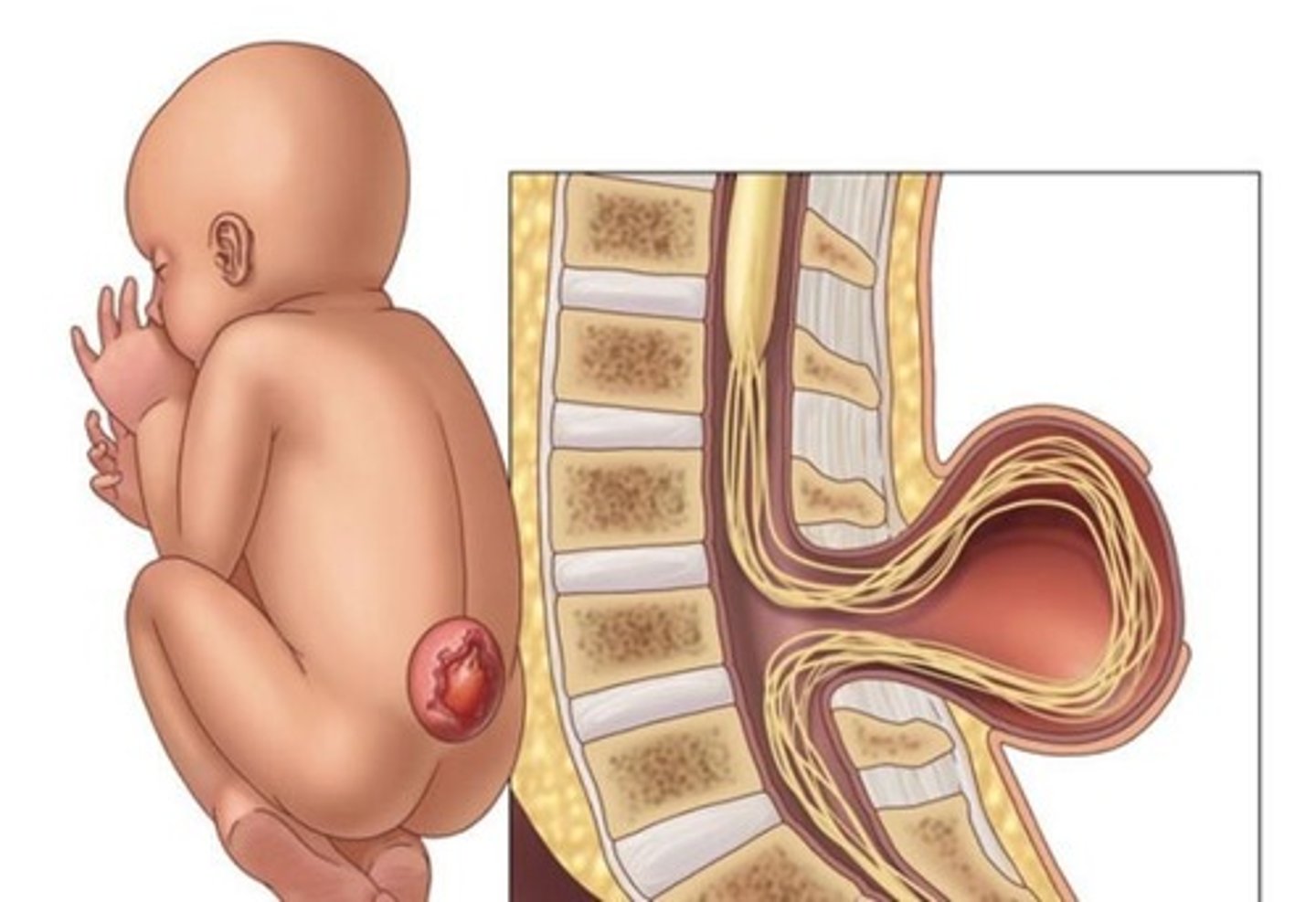
Spina Bifida
Condition where 1 in 1000 born with 1+ vertebrae fail to form complete arch, thus enclosing spinal cord; severity depends on number of vertebrae affected.
Gray matter
Dull in color due to little myelin; contains somas, dendrites, proximal parts of axons; involved in synaptic transmission and integration of information within CNS.
White matter
Abundance of myelinated axons; carries signals within CNS.
Gray commissure
Connects left-right halves of gray matter.
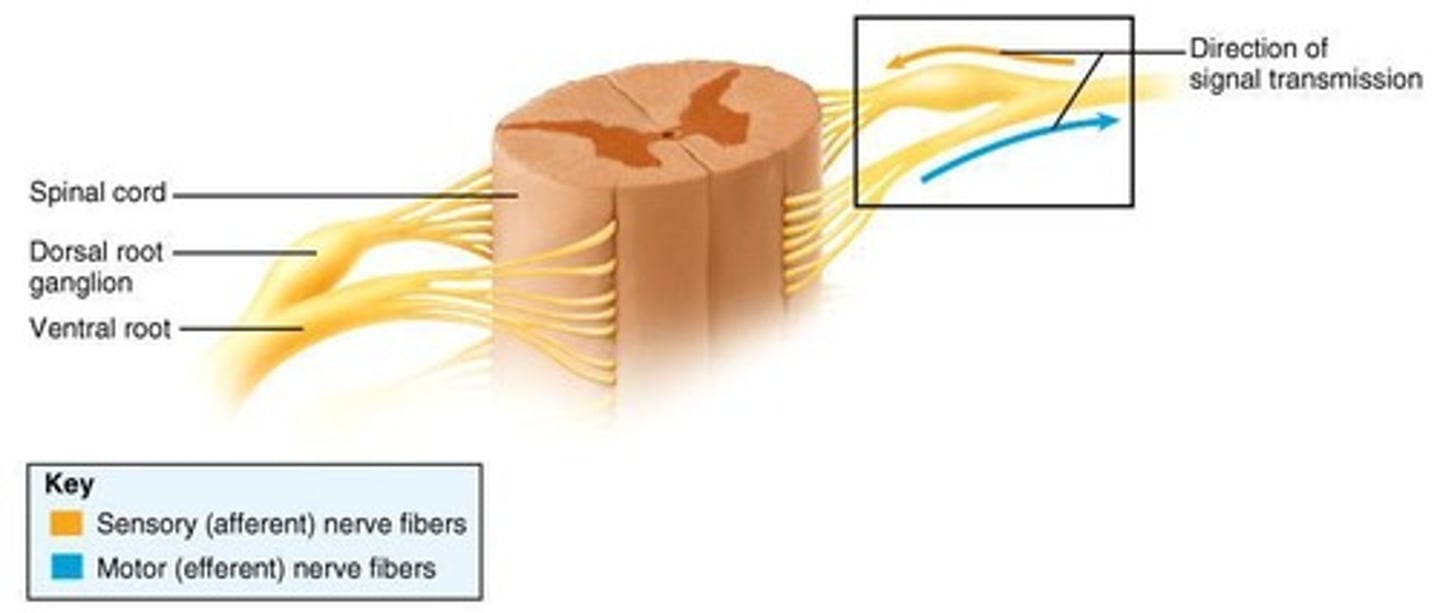
Dorsal root
Carries sensory fibers into dorsal horn; fibers either continue up spinal cord or may synapse with an interneuron.
Ventral root
Axons of motor fibers leaving spinal cord; somas in ventral horns.
Spinal tracts
Ascending and descending tracts; all fibers in a tract have similar origin, destination, and function.
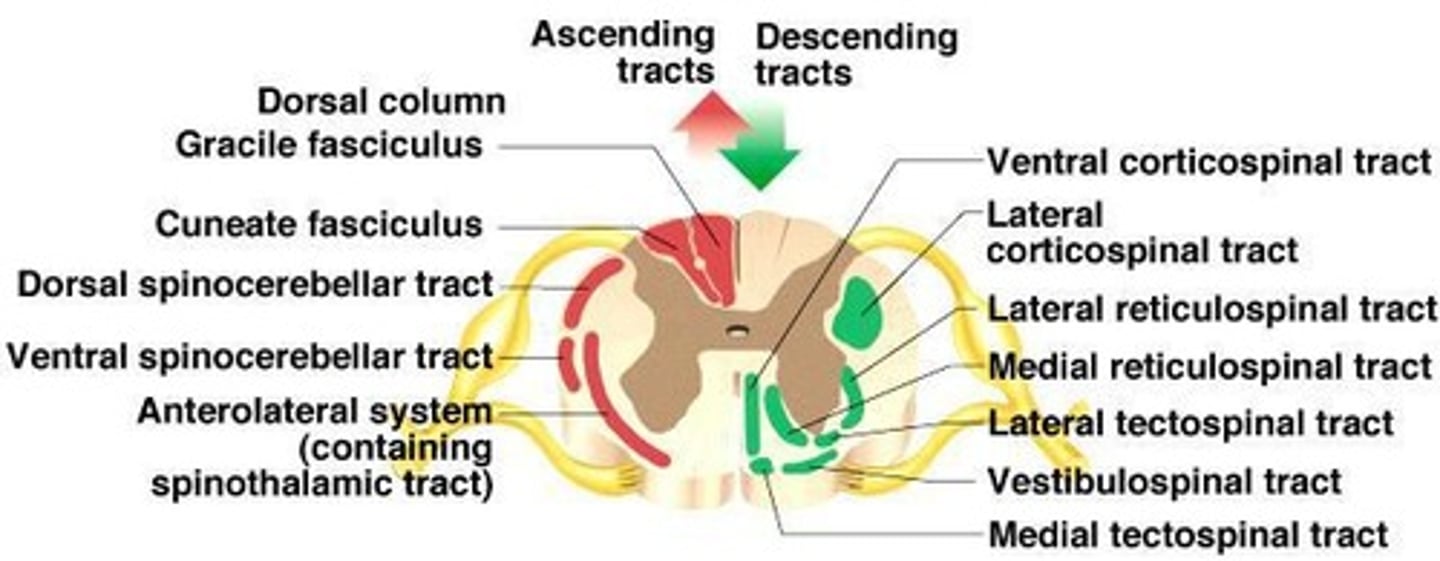
Ascending tracts
Sensory signals travel via 3 neurons to sensory areas of brain.
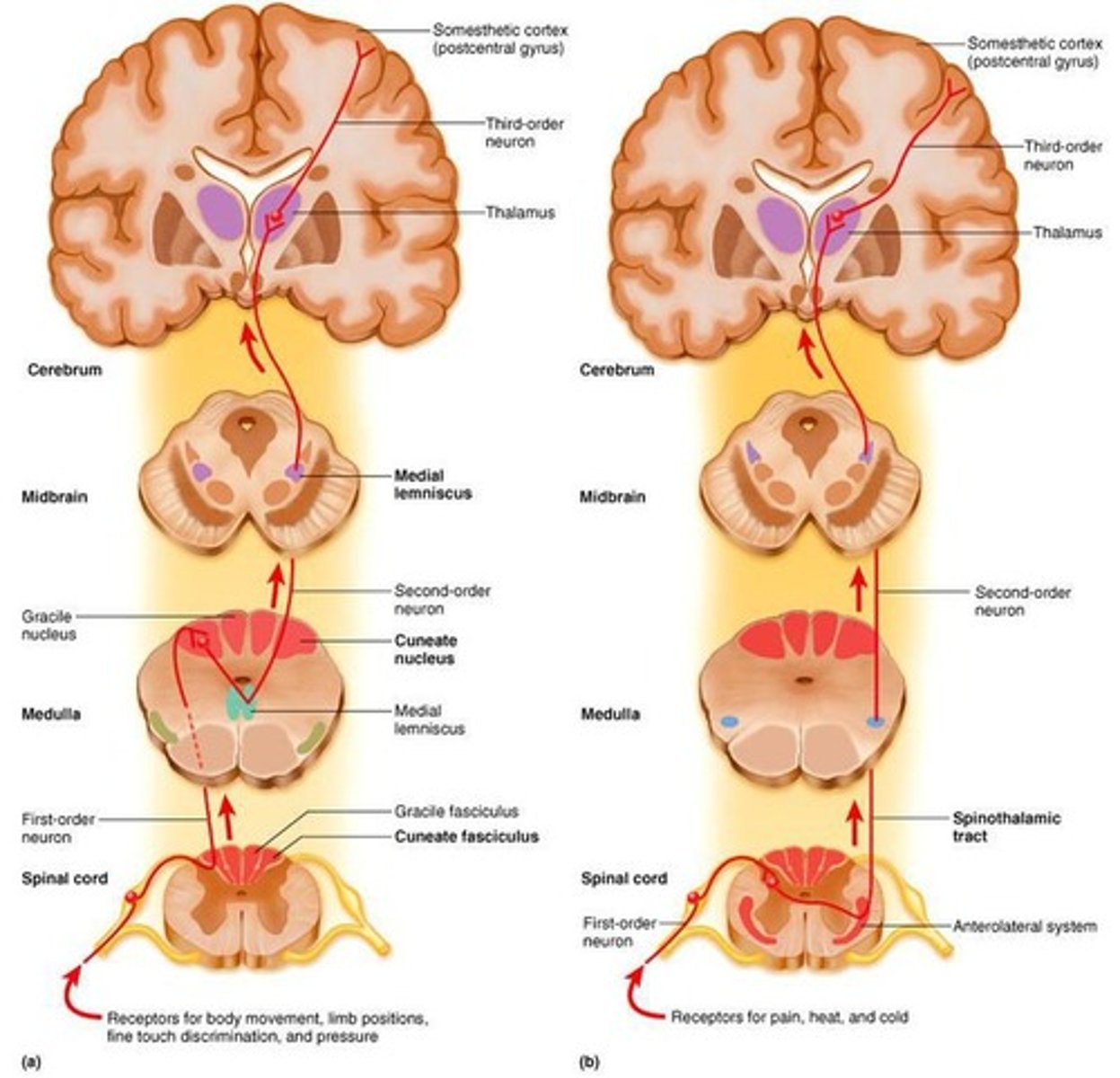
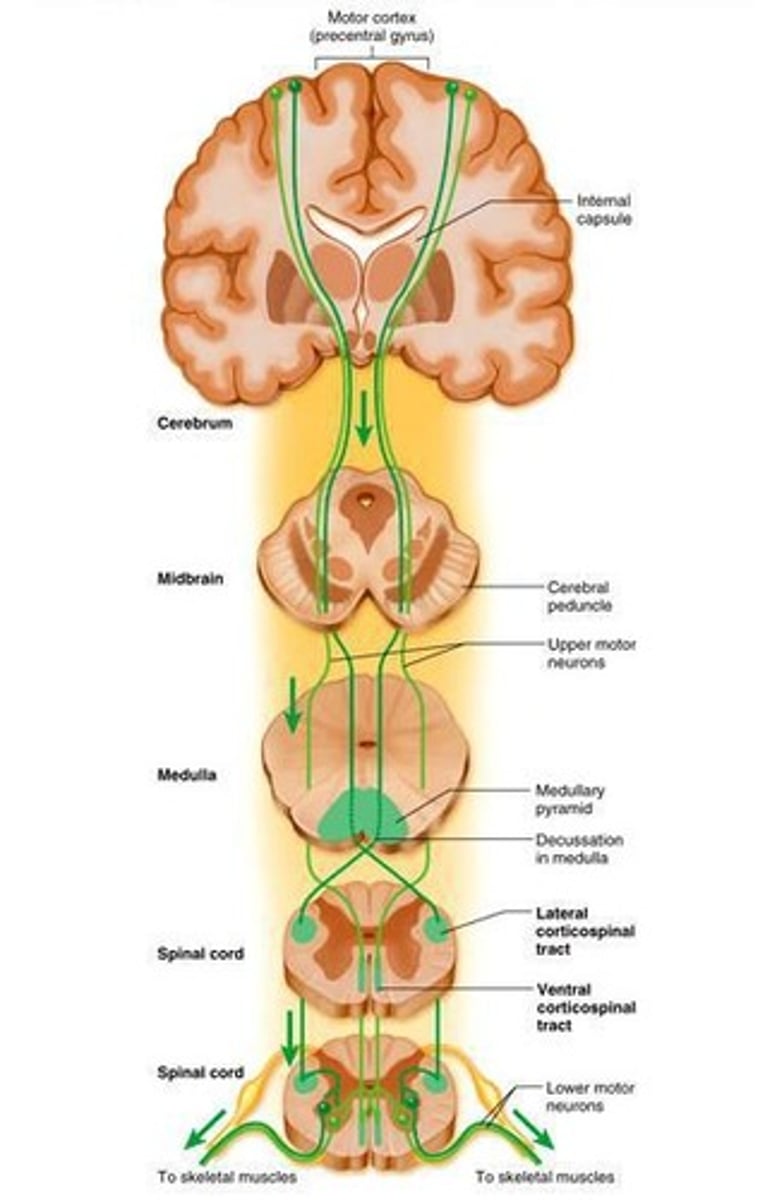
Descending tracts
Typically have 2 neurons; upper motor neuron has a soma in cerebral cortex or brain stem and axon that ends at a lower motor neuron.
Nerve
cordlike organ of few-1 mil axons bound together by connective tissue
PNS nerves
ensheathed in Schwann cells
Neurilemma
the outermost layer of PNS nerves
Perineurium
wraps fibers bundled into fascicles
Epineurium
wraps fascicles bundled together to form a nerve
Dorsal root ganglion
somas of afferent neurons that form prior to rootlets branching to spinal cord
Spinal nerves
31 pairs of spinal nerves: 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 coccygeal
Dorsal rami
innervates muscles/joints in region and skin of back
Ventral rami
innervates ventral and lateral muscles/skin of trunk and forms nerves of limbs
Meningeal branch
reenters vertebral canal to innervate meninges, vertebrae, and spinal ligaments
Nerve plexuses
ventral rami branch and merge to form 5 weblike nerve plexuses from neck to coccyx
Shingles
a painful condition caused by the chickenpox virus that remains in dorsal root ganglia for life
Radial nerve injury
vulnerable to injury due to location, such as being pinched against humerus
Sciatic nerve injury
vulnerable to injury due to location, such as herniated disc or pressure due to pregnancy
Dermatosome
specific skin region from which each spinal nerve (except C1) receives sensory information
Dermatosome map
a diagram of skin regions innervated by each spinal nerve
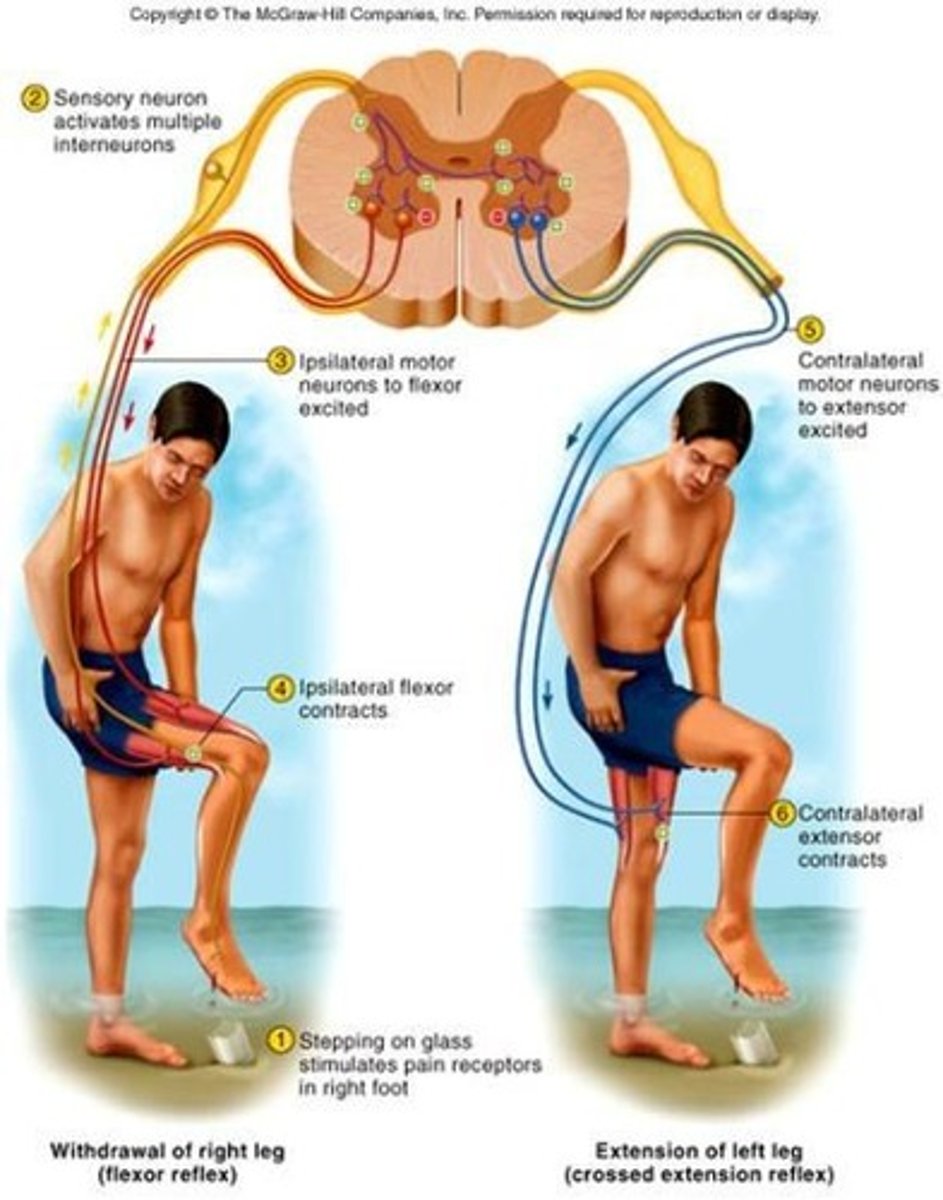
Properties of a reflex
require stimulation, quick with few-no interneurons, involuntary, and stereotyped
Somatic reflexes
involuntary contraction of muscle or glandular secretion occurring via a reflex arc
Muscle spindle
stretch receptors within skeletal muscle that serve as proprioceptors