Binary fission, mitosis, and meiosis
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Binary fission
passing on genetic information for bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts
Mitosis
passing on genetic information for eukaryotes, somatic cells, and some single-cell organisms
Meiosis
passing on genetic information for eukaryotes, sexual reproduction; single-cell or multicellular
During replication, chromosomes assort to ________ ______ of cell
opposite sides
Chromosomes associate with _______ that anchor them to poles
proteins
Steps of binary fission (prokaryotes)
as chromosome replicates, each origin of replication segregates to opposite sides
proteins anchor chromosomes to poles
cell divides in middle, partitioning chromosomes
plasmids are distributed equally
Somatic eukaryotic cells reproduce by
mitosis and cytokinesis
daughter cells are essentially ______ in asexual reproduction
clones
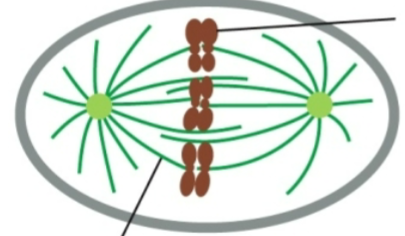
mitosis
nuclear division
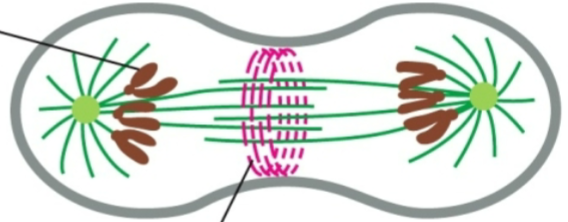
cytokinesis
cytoplasmic division
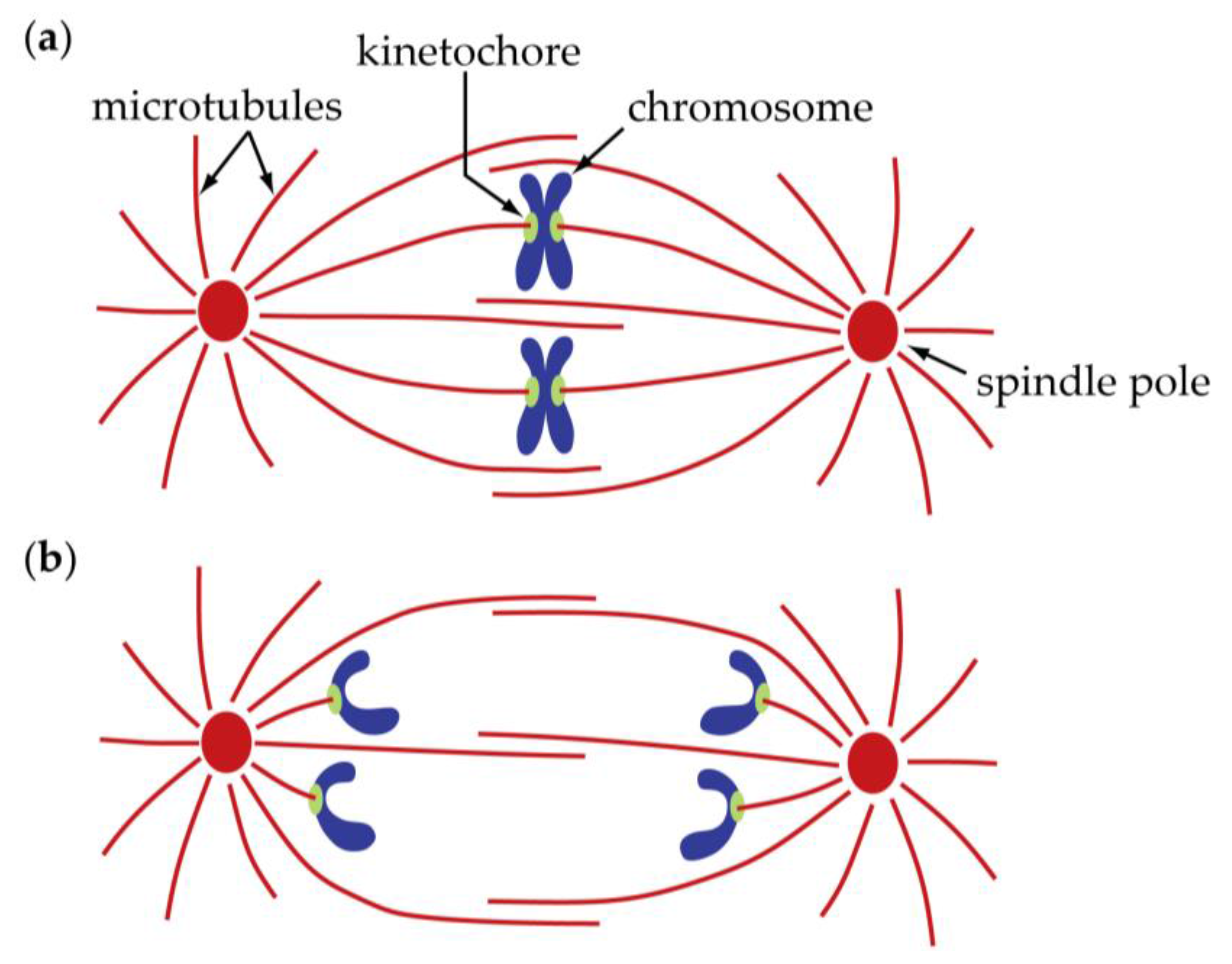
temporary cytoskeletal machine for mitosis
mitotic spindles with microtubules
temporary cytoskeletal machine for cytokinesis
contractile ring with myosin filaments
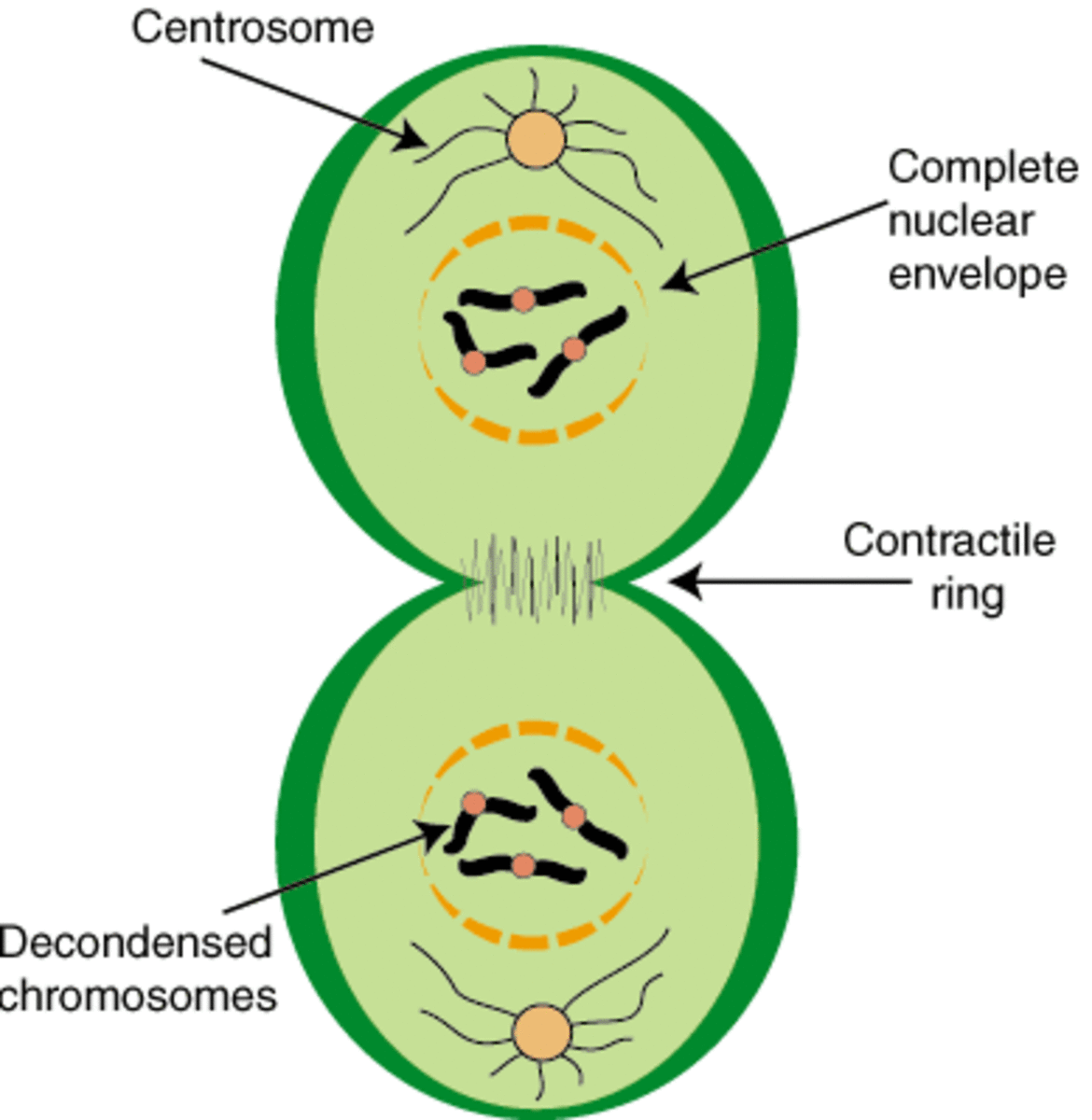
when does mitosis happen?
prophase → telophase
interphase
nuclear membrane is present and chromosomes are relaxed
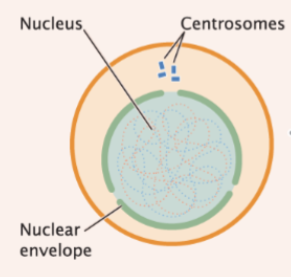
prophase
chromosomes condense (each possess 2 chromatids) and mitotic spindle forms
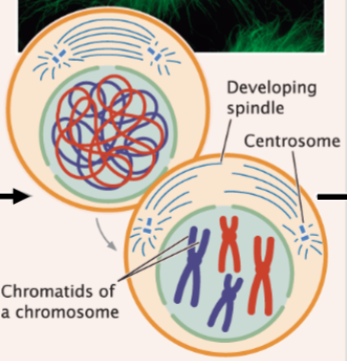
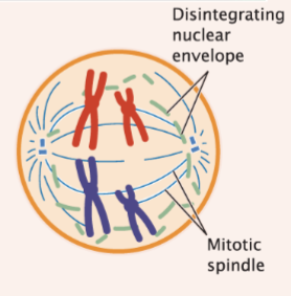
prometaphase
nuclear membrane disintegrates and spindle microtubules attach to chromatids
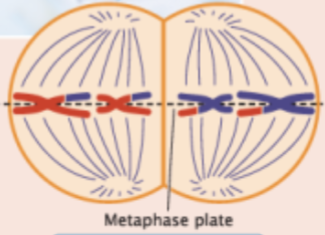
metaphase
chromosomes line up on metaphase plate
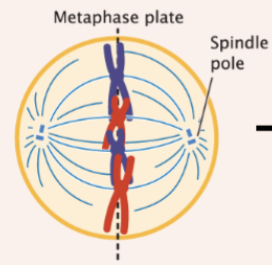
anaphase
sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite poles
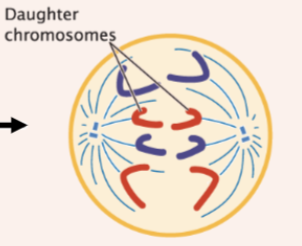
telophase
chromosomes get to spindle poles, nuclear membrane re-forms, and chromosomes relax
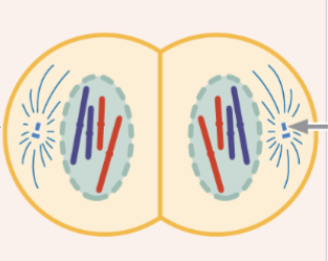
phases of mitosis (in order)
interphase
prophase
prometaphase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
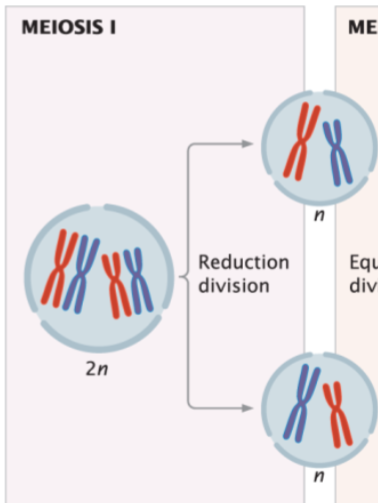
meiosis consists of __ divisions
2
2 divisions of meiosis
reduction division
equational division
reduction division
reduce chromosome number by half (2n → n) and separate homologous chromosomes
equational division
separate sister chromatids
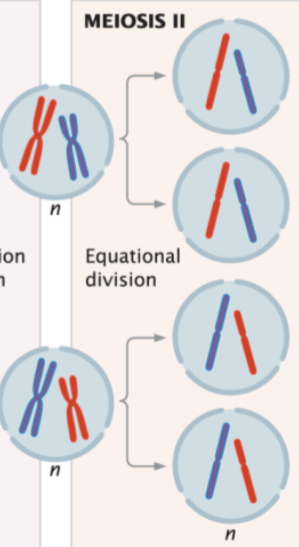
meiosis produces
4 haploid gametes
first step of sexual reproduction
meiosis
second step of sexual reproduction
fertilization
meiosis increases
genetic variation
how does meiosis increase genetic variation
crossing over and/or random separation of chromosomes
__________ occurs prior to Meiosis I
replication
middle prophase I
chromosomes begin to condense and the spindle forms
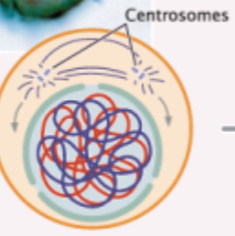
late prophase I
homologous chromosomes pair, crossing over occurs, and nuclear membrane breaks down
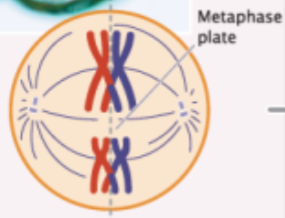
metaphase I
homologous pairs of chromosomes line up along metaphase plate
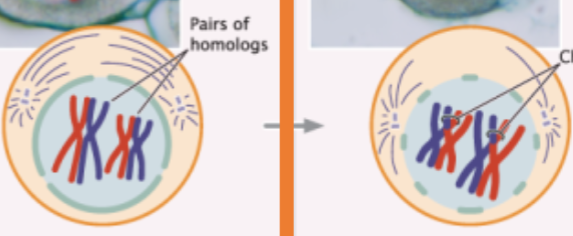
when are sister chromatids no longer identical during meiosis?
prophase I (allele shuffling)
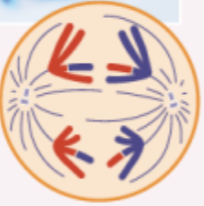
anaphase I
homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles
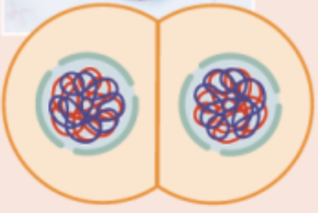
telophase I
chromosomes arrive at spindle poles and cytoplasm divides
steps of meiosis I in order
middle prophase I
late prophase I
metaphase I
anaphase I
telophase I
prophase II
chromosomes recondense
metaphase II
individual chromosomes line up on the equatorial plate
anaphase II
sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
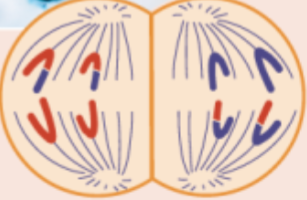
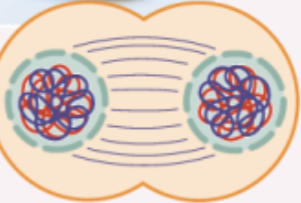
telophase II
chromosomes arrive at the spindle poles and the cytoplasm divides
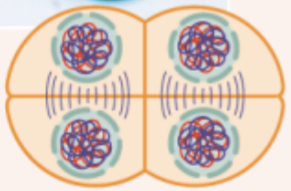
steps of meiosis II in order
prophase II
metaphase II
anaphase II
telophase II
products of meiosis II
four haploid gametes carrying a unique combination of alleles