Biology Exam 1
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
which organ helps regulate blood sugar but also aids in digestion?
pancreas
what protects the digestive system lining from damage due to acid?
mucus
the longest part of the digestive system is the
small intestine
how many deciduous teeth does the average person have?
20
which of the following is not absorbed into the blood supply of the digestive system after digestion?
oils
what is the role of the colon
absorb water and form stool
what part of the digestive system does the appendix attach to?
colon
a ___ muscle is one that is circular and opens and closes the diameter of a tube
sphincter
what is the name of the muscular movement that pushes food through the digestive tract?
peristalsis
what organ produces hydrochloric acid?
stomach
plasma membrane
controls what enters and exits the cell
golgi apparatus
modification and packaging of proteins and lipids
flagella
provides cell motility
peroxisome
detoxify compounds and breakdown fatty acids
mitochondria
ATP synthesis
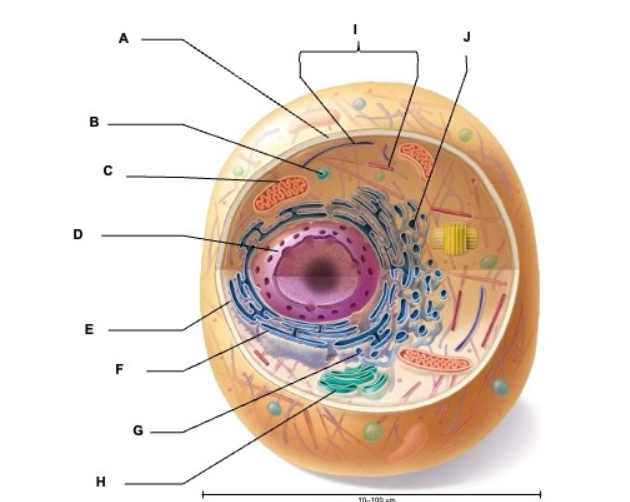
what is A
plasma membrane
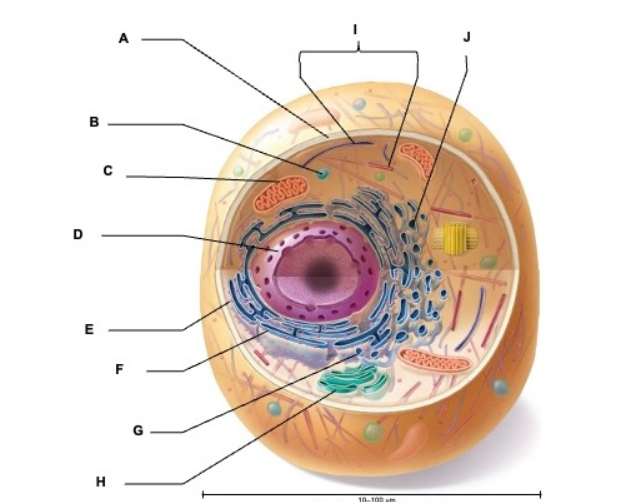
what is B
vesicle
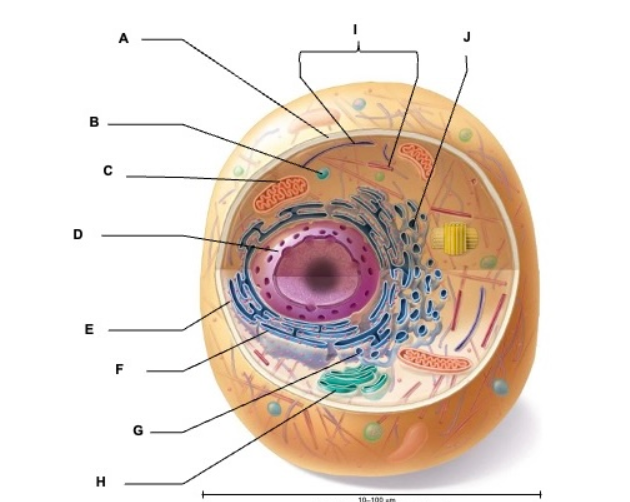
what is C
mitochondrion
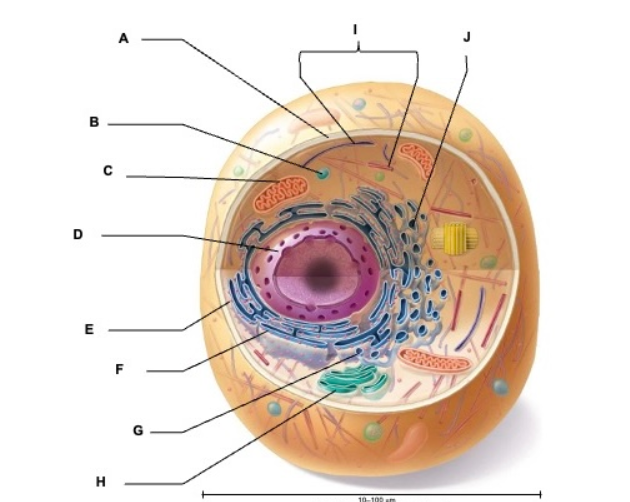
what is D
nucleus
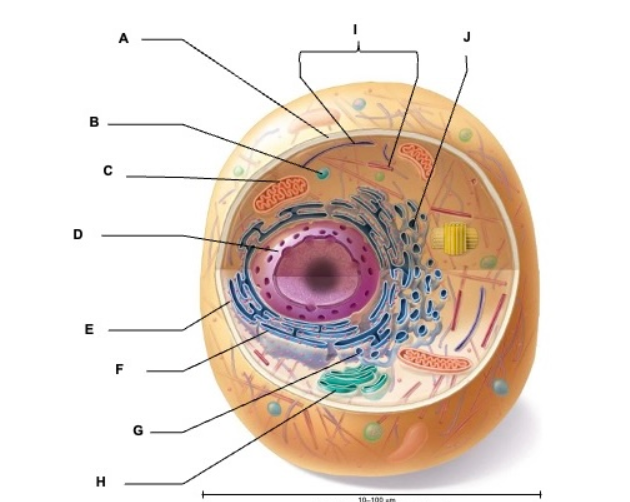
what is E
ribosome
what is the order of how we receive energy?
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum, jujenum, ileum), colon/large intestine (ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid), rectum
what is there in the small intestine?
digestion, absorption
what is villi and why is it important?
lines small intestine, creates larger surface area which means more nutrients
what is the main job of the small intestine?
absorption
true or false: the oral cavity IS a digestive organ
true
are teeth mechanical or chemical
mechanical
where does the esophagus start and end?
starts at the pharynx, ends at the diaphragm
what are the layers of the teeth
enamel, dentin, pulp cavity
chemical digestion
enzymes used to chemically change intake
mechanical digestion
chewing, breaking physically, no chemical changes to the food
whats an example of an accessory organ
liver
vitamin D
found in milk, we make vitamin D
vitamin K
produced by bacteria in colon and green leafy vegetables
B9 (folic acid)
important for cell production. adequate intake = decrease in spinal cord issues
B12
available in animal products or other outside source
vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
citrus are good source. deficiency causes scurvy
what are essential minerals
NA, Cl, F, I, fe
what’s the major element in protein
CHON
how many amino acids are there? how many are essential?
20, but 8 are essential
which vitamins are fat soluble
ADEK, can be stored
which vitamins are water-soluble
BPCN, not stored
saturated fat
max number of hydrgens possible
unsaturated fats
liquid at room temperature
lysosome
breaks down cellular waste
cilia
propels cells
ribosome
synthesis protein
prokaryotic cells
simple, smaller, lack membrane-bound organelles
eukaryotic cells
complex, larger, membrane bound organelles
smallest to largest
atom, molecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ systems, individual
scientific method
systematic logical approach to gathering information and reaching conclusions