Metabolism 2 - Oxidative phosphorylation
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is a substrate level phosphorylation reaction (SLP)
It couples a really exothermic reaction with the phosphorylation of ADP → ATP
Examples of SLP
in Glycolysis - convert 3 - bisphophate glycerotae into 3-phosphaglycerate (1 Pi lost used to amke ATP)
Cotric acid cycle breaking bond between succinil and CoA enzyme realease engy to make GTP (or ATP)
where does most of out ATP form cells come from
oxidative phosphorylation
What happens in oxidative phosphorylation
reduced Co-enzymes like NADH and FADH2 become oxidized by passing on their hydrogen and this is coupled with synthesis of ATP
Structure of mitrochondria
Outer membrane → highly permeable, large protein channels , high [H+] so low pH in inter membrane space and in cystol
Inner membrane → highly impermeable, highly folded, selective what it lets through, less [H+] in matrix so high pH
Source of reduced Coenzymes?
get it through oxidation of fatty acid, amino acids as well as in citric acid cycle get reduced Coenzymes
Glycolysis formed NADH but happens in cystol
use Maltate - Aspartate shuttle to get it through to be used in matrix
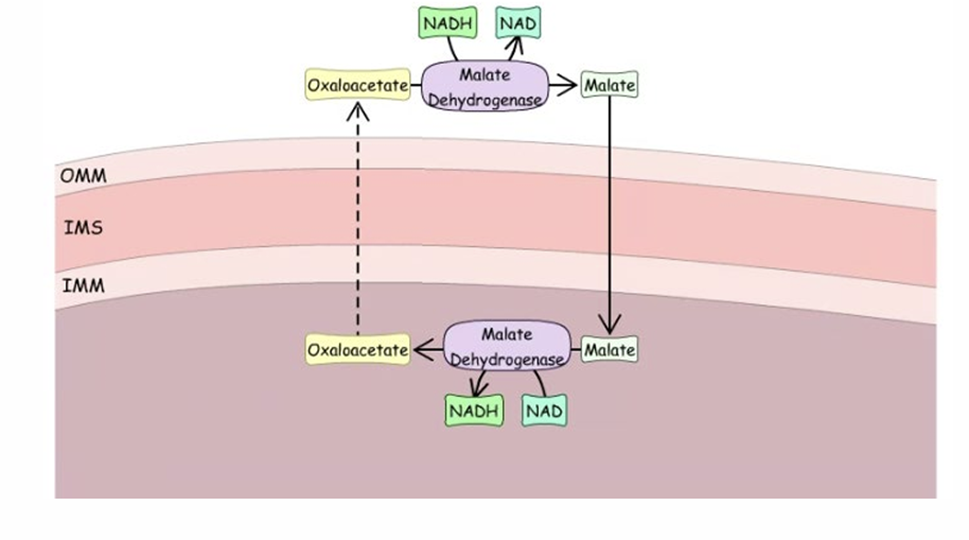
How does teh Maltate -Aspartate shuttle work
what happens in in the cytosol oxalacetate is reduced to make Maltate
Maltate can move into mitrchondria as has a channel for it
once in matrix maltate is oxidized to make oxolactate again and forming reduced NADH in the matrix
Oxolactete moves out and whole things starts again
so we use NADH outside of cell to make NADH inside
both reactiosn done by Maltate dehydrogenase
What are the parts of OP
2 parts:
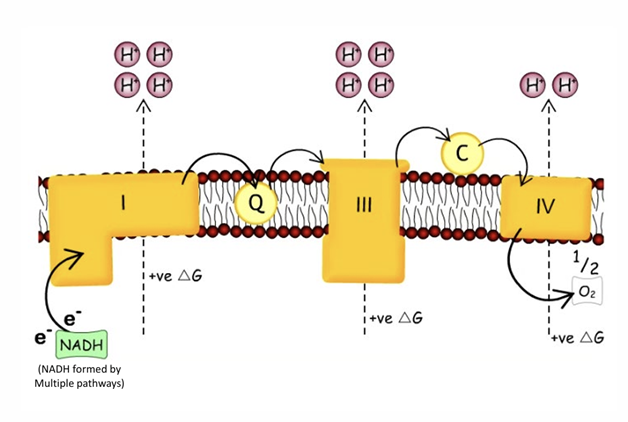
Oxidation → done by ETC (using complexes 1-4)
Phosphorylation
What happens at Complex 1
Complex 1 is an enzyme that catalyses the process of :
NADH oxidation
Transfers 2 electrons to Co-enzyme Q so this Co enzyme is reduced (small dissolved molecule found in inner mitochondrial membrane)
What happens at complex 3
Catalyses the transfer of electrons form Co-Enzyme Q to cytochrome C
Cytochrome C is a small molecule that is loosely attached to outside of inner membrane
What happens at complex 4
Enzyme that catalyses the transfer of electrons form cytochome C to oxygen
makes ½ oxygen - need 4 electrons to make full Oxygen
Oxygen gets transferred to water
What is the energy used taht is realeased by ETC raections
ETCR are very exothermic
this energy released is used to pump H + out of matrix (which has a positive Gibbs free energy)
complexes constantly pumping H+ out leading to high pH in matrix
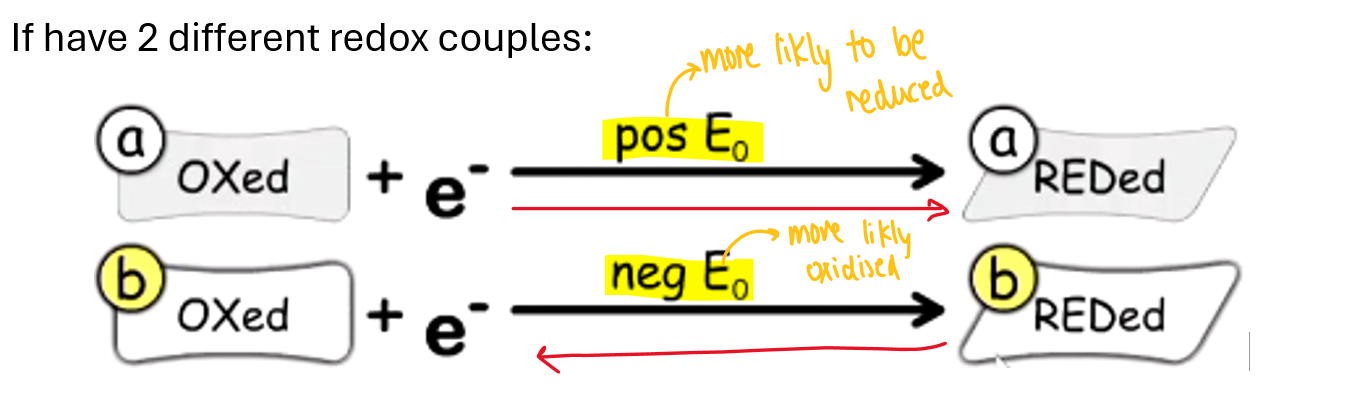
If a compound rather be reduced it has…
a positive reductive potential
a negative Gibbs free energy
If a compound rather be oxidized it has….
relatively negative reduction potential
has a positive Gibbs free energy
Whihc reaction goes in forward and backward direction
positive reduction potential → forward direction
Negative reduction potential → backward direction

how to work out change in reduction potential
more positive reduction potential - more negative reduction potential (answer in V)
The higher the difference in reduction potential..
the more energy is released by transfer
How do we work out how much energy is realeased
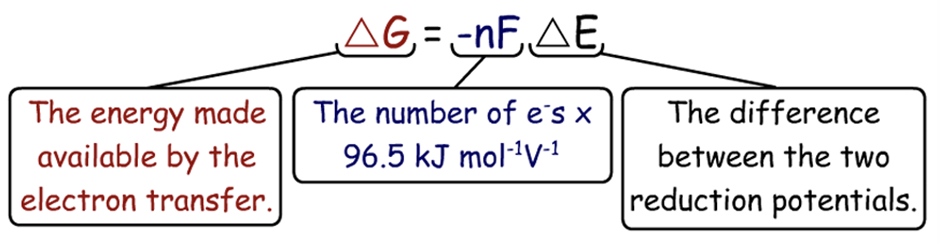
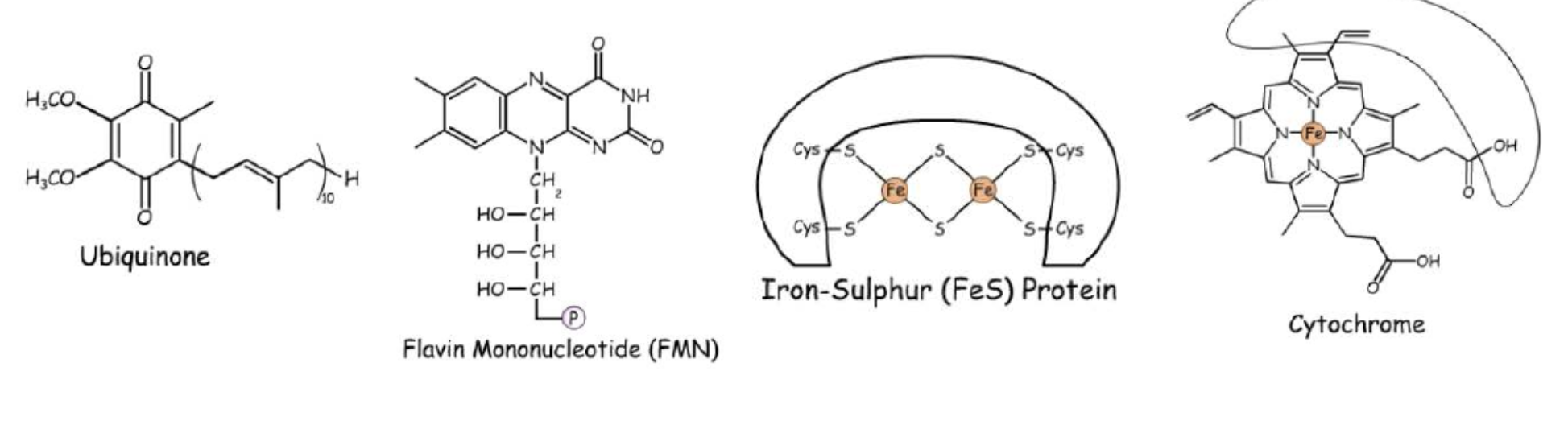
Electron carrieres
found in complexes and help them carry out redox reactions
Examples of these protein carriers
Iron sulfur protein → has iron, sulfur and cysteine residues, take part in 1 electron transfer
Cytochorme → has heam group contently boned together, iron ion in center, takes part in directly 1 electron transfer
Flavin mononuclotide → looks like FAD can tarnsfer or hold 2 hydrogen’s
Ubiquonone→ can transfer electrons through hydrogen
how many protons get pummped out from 1 NADH
10 protons
What are these protons used for
ATP synthase uses this proton gradient (high concentration of protons outside then inside ) and the charge element (more positive charge on outside then inside) a 2 reasons why its favorable for protons to enter
ATP synthase uses this gradient to make ATP
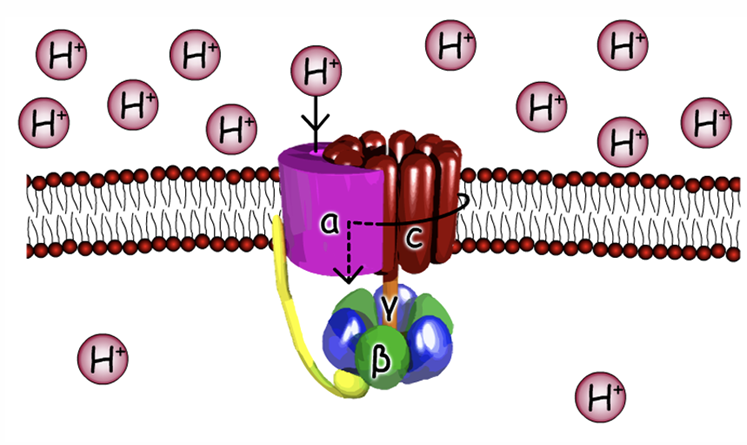
What does Beta subunit do
hold together ADP and Pi to be converted into ATP
there are 3 of them and blue ones hold them together
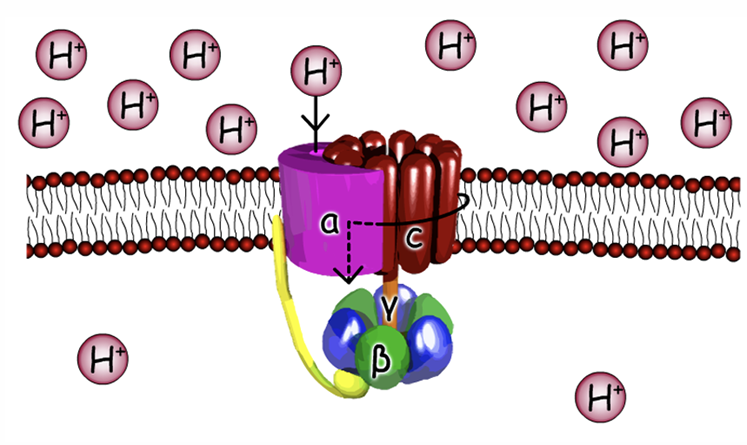
Gamma and C subunits
Gamma sub-unit interact with B sub-unit
Gamma stalk can turn to help change shape of beta sub-unit to bind to ADP and Pi
Gamma is able to turn because of C sub-unit turning
Why are C sub-units turning ?
In C sub unit have an aspartate residue where protons can bind
When have proton bound 0 no change , no protein -1 charge
when charge is 0 easy of it to turn
A sub-unit has 2 half channels for protein one to go into matrix and one for protons to wait before

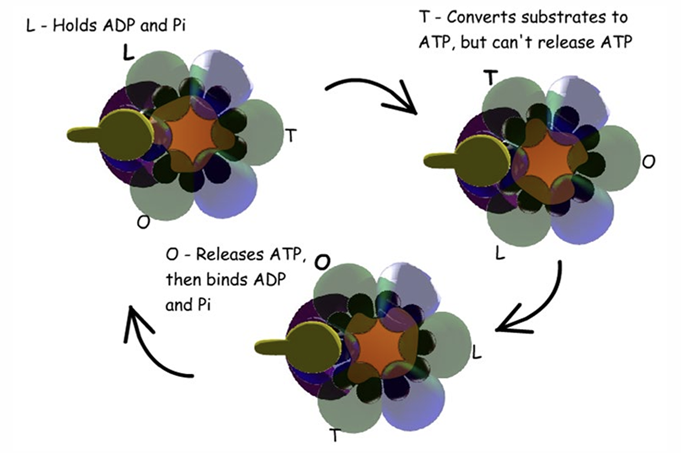
Beta subunit conformtaion
Open → can bind ADP and Pi and can loose them
Loose → binds ADP and Pi but cannot loose them
Tight → can only bind ATP
every time gamma stalk turns causes change in beta sub-unit conformation
calculate P:O ratio for NADH with ATP synthase with 8 sub-units

If ETC is not working the..
ATP synthase is also not working
have coupling of the 2 processes