Cofactors/Coenzymes
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
structure of ATP
why is ATP a high energy molecule?
ATP is considered a high energy molecule due to the presence of its three phosphate groups, which are negatively charged and repel each other. The hydrolysis of these phosphate bonds releases significant energy, making ATP a key energy carrier in cellular processes.
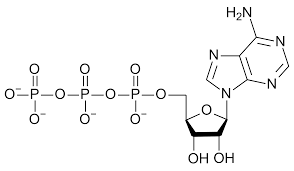
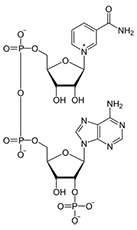
structure of NAD+
structure of NADH
two electron carriers
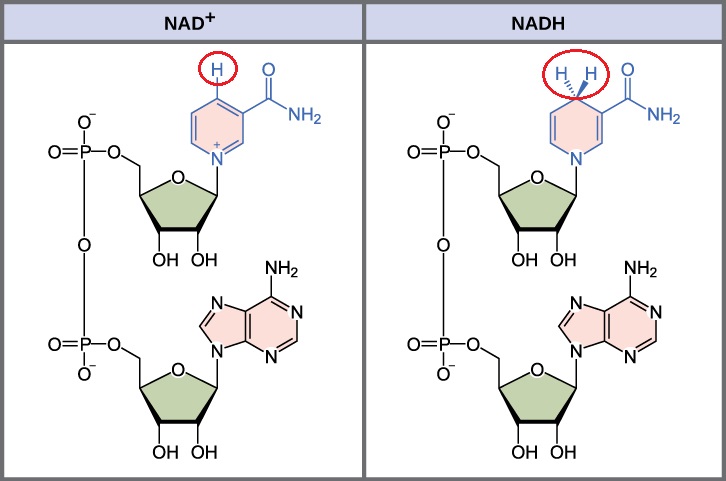
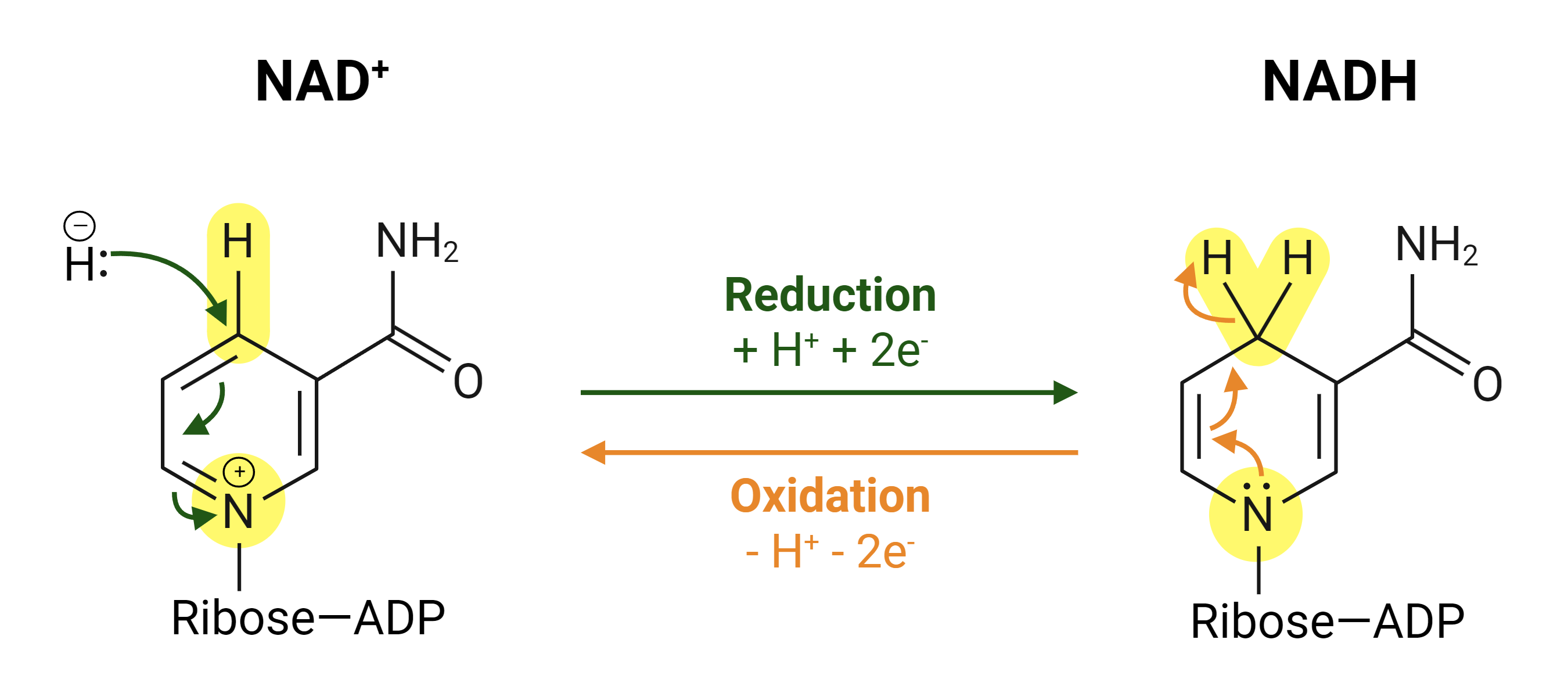
how does NAD+ act as a cofactor for oxidation-reduction reactions?
NAD+ functions as an electron carrier, accepting electrons during the oxidation of substrates and being reduced to NADH, which can then donate electrons in subsequent reactions.
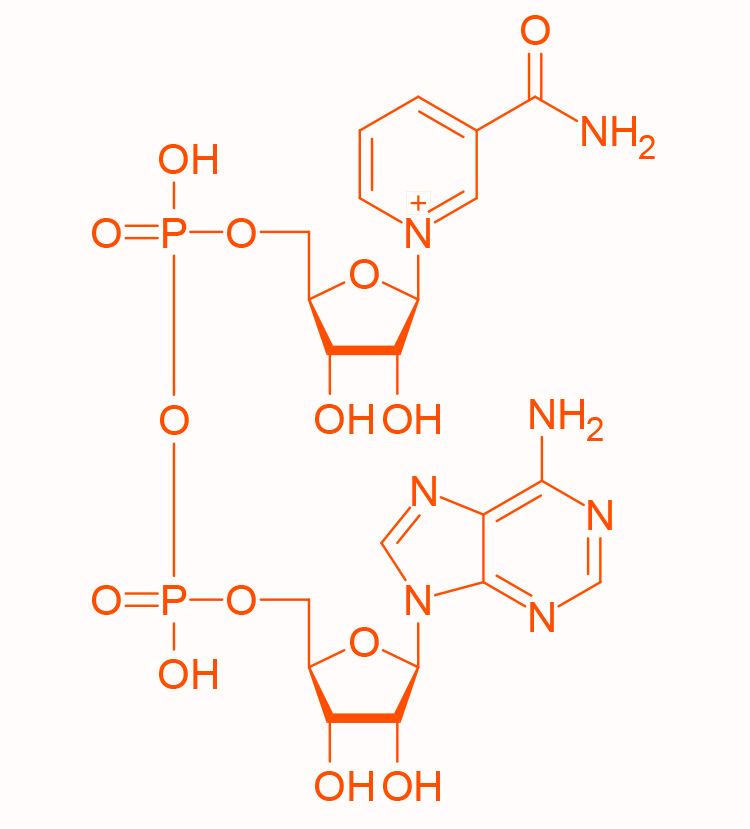
structure of NADP+
similar to NAD+/NADH, provides the reducing power for anabolic processes
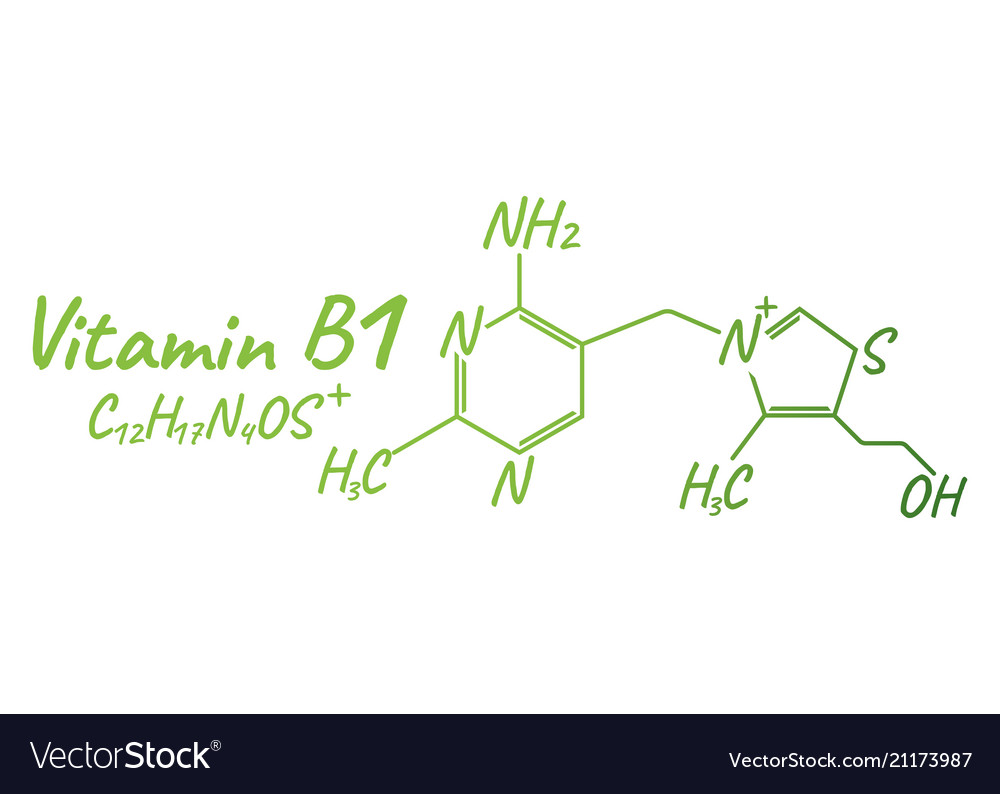
vitamin B1 (thiamine) structure
inactive form
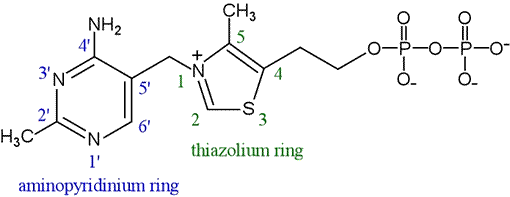
structure of TPP (thiamine pyrophosphate)
active form
what is the role of TPP?
Acts as a coenzyme in the decarboxylation of alpha-keto acids and the formation/cleavage of alpha-hydroxyketones. It plays a crucial role in carbohydrate metabolism.
role of the thiazolium nitrogen in TPP
provides electrostatic stabilization for the carbanion intermediate during the decarboxylation process, facilitating the transfer of acetyl groups
vitamin B2 structure
active forms are FMN and FAD (one or two e- transfer agents)
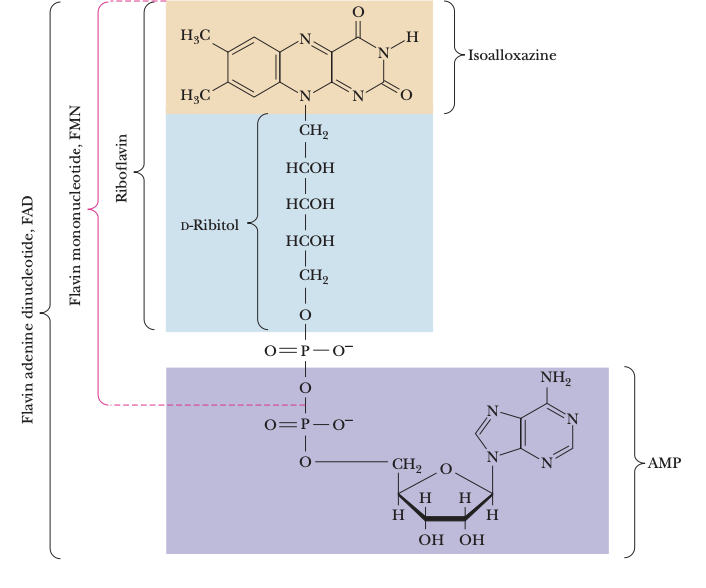
role of the isoalloxazine ring in vit B2
conjugation allows it to absorb electrons and free radicals; can stabilize different structures and one or two electrons for protonation
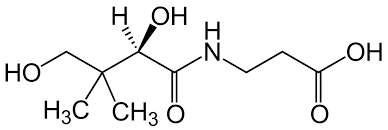
what is pantothenic acid?
A water-soluble vitamin that is a precursor to coenzyme A, essential for fats, protein, and carbohydrate metabolism
structure of coenzyme A
acyl groups form thioester linkages with the -SH group of the beta-mercaptoethylamine moiety (active site)
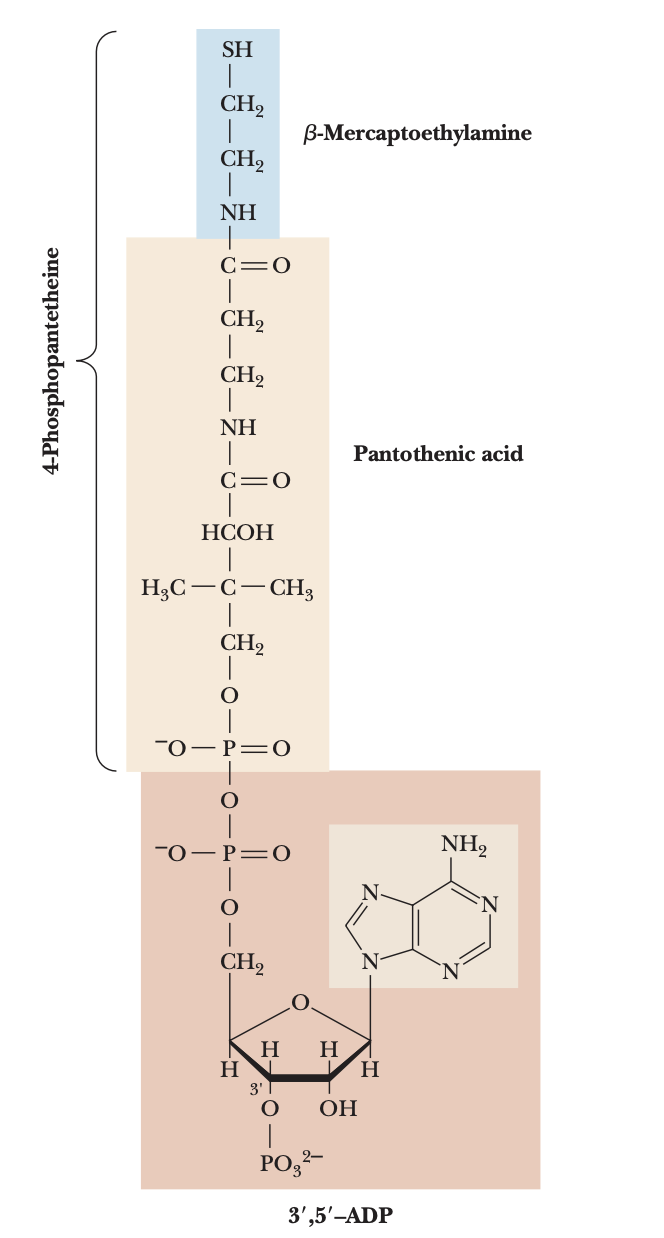
functions of CoA
activation of acyl groups by thioester formation, and activation of the alpha-hydrogens of the acyl group for proton abstraction
hydrolysis of esters and thioesters
ester hydrolysis is faster, since O is more electronegative than S
RS- is more stable than RO- as sulfur is bigger with lower charge density
vitamin B6: pyridoxine and pyridoxal phosphate structure
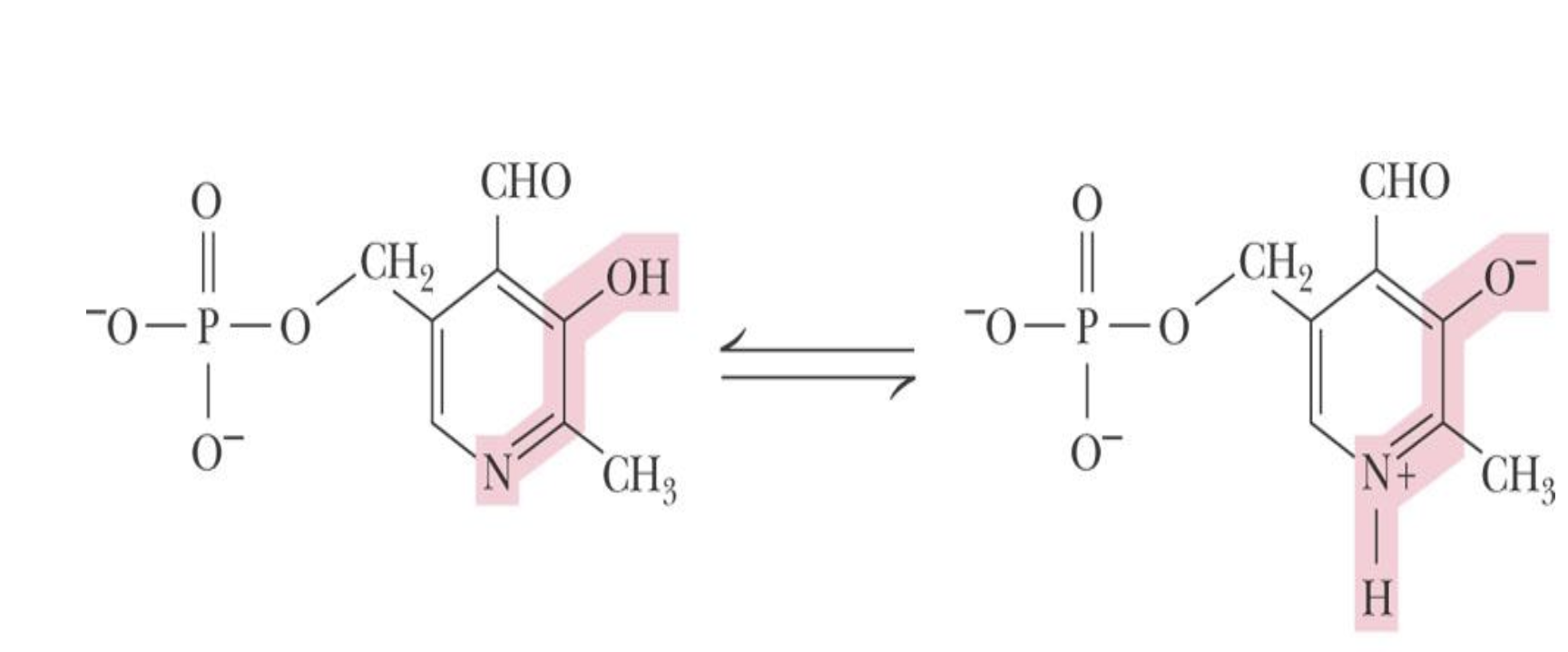
function of pyridoxal phosphate
acts as a coenzyme in amino acid metabolism, facilitating transamination and decarboxylation reactions.
how does pyridoxal phosphate catalyze amino acid racemizations?
It acts as a coenzyme, forming a temporary Schiff base with the amino acid, allowing for the conversion between different enantiomers. acts as an electron sink
vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin)
converted into two coenzymes: 5’-deoxyadenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin
vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
functions as an e- carrier and has an enediol active site that captures free radicals
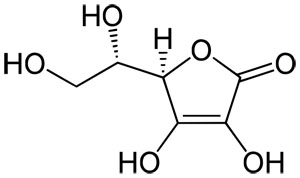
biotin
functions as a mobile -COOH carrier
in any carboxylation reaction, we need ATP and biotin
folic acid
active form is tetrahydrofolate (THF), formed by 2 successive reductions of folate
lipoic acid
couples acyl-group transfer and e- transfer during oxidation/decarboxylation of alpha-keto acids
found in pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase