Orgo Lab Exam 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
1
New cards
matter
Any substance that is made up of small tiny particles “atoms”, occupies space, and has a mass is called matter
2
New cards
Physical Properties of matter
Characteristics of matter that can be observed \n without changing its nature or reacting with \n other substances. \n
Ex: volume, mass, boiling point, melting point, \n density...
Ex: volume, mass, boiling point, melting point, \n density...
3
New cards
Chemical Properties of matter
Characteristics of matter that can be observed and determined only during chemical changes.
Ex: reactivity, flammability, toxicity, stability.
Ex: reactivity, flammability, toxicity, stability.
4
New cards
extensive vs intensive properties
Physical Properties of Matter
5
New cards
extensive properties
These properties depend on the amount of the substance such as the mass, volume
6
New cards
Intensive Properties
These properties don’t depend on the amount of the substance such as boiling point, melting point, density, conductivity
7
New cards
Intramolecular Forces
These forces exist between the elements within the same compound and help them to stay intact. These forces mainly determine the **chemical properties** of a substance
8
New cards
Intermolecular Forces
These forces exist between separate molecules of a certain substance. These forces mainly determine the **intensive physical properties** of a substance
9
New cards
Intermolecular forces are ____ than intramolecular ones
weaker
10
New cards
Intermolecular Forces are measured using
melting and boiling points
11
New cards
Dipole-Dipole Interactions (Keesom Forces)
strongest
12
New cards
Induced Dipole-Dipole Interactions (Debye Forces)
They exist between non-polar molecules (Induced dipole) and polar ones (Dipole)
13
New cards
Strength of induced-dipole-dipole interactions depends on the
• Polarity of the polar molecule.
• Polarizability of the non-polar one
• Polarizability of the non-polar one
14
New cards
Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole Interactions (London-Dispersion Forces)
• They exist in all molecules polar and nonpolar
• They are important only in nonpolar molecules.
\
• They are important only in nonpolar molecules.
\
15
New cards
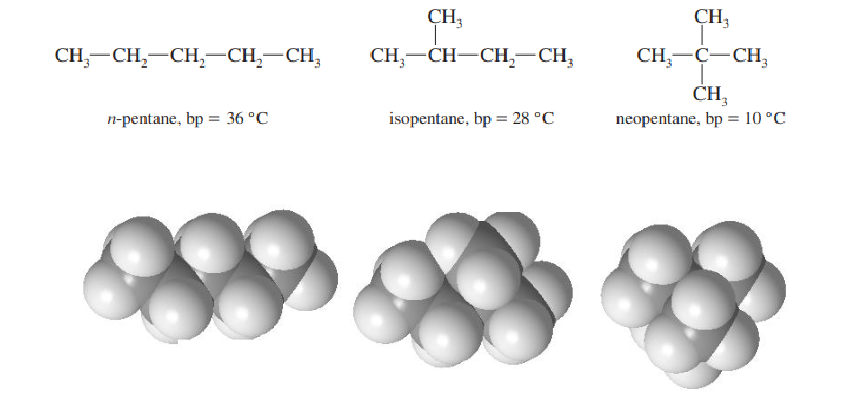
Strength of induced-dipole-induced dipole interactions
As surface area of the compound increases, their strength increases
16
New cards
Solubility
Is the maximum amount of solute that can be completely dissolved in a certain amount of solvent at a certain temperature
17
New cards
Factors Affecting Solubility
• Properties of Solute & Solvent
• Temperature
• Temperature
18
New cards
Recrystallization
Is a purification technique that is mainly used to purify solids
19
New cards
Recrystallization principle
• Different solutes have different solubilities in the same solvent.
• Solubility decreases as temperature decreases.
• Molecules of the same compound have higher tendency to stick together (crystallize together)
• Solubility decreases as temperature decreases.
• Molecules of the same compound have higher tendency to stick together (crystallize together)
20
New cards
choosing solvent for recrystallization
Solvent should be a poor solvent at room temperature and good at high temperature
21
New cards
Extraction
a purification /separation technique that can be used to separate compounds based on their partition between two media (one compound has more affinity toward one media than the other
22
New cards
Extraction principle
Compounds have different solubilities in different solvents
23
New cards
Usually aqueous layer is the bottom one except for halogenated organic solvents like DCM. Why??
DCM has a higher density than water
24
New cards
Multiple extractions with smaller volumes are more efficient.
3 extractions with 20 mL is better than 1 extraction with 60 mL
25
New cards
K equation
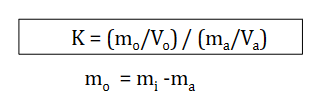
26
New cards
To move organic acids like carbolic acid to the aqueous layer,
add a base like NaOH
27
New cards
To move organic bases like RNH2 to the aqueous layer,
add an acid
28
New cards
Chromatography
Chromatography is the separation of a mixture of two or more compounds into its constituents
29
New cards
Stationary phase
Interacts with the mixture and causes separation
30
New cards
Mobile phase
Push the mixture to move over the stationary phase
31
New cards
Chromatography Principle
• Different compounds interact in different ways with the stationary phase.
• Strongly interacting ones will be delayed.
• Weakly interacting ones will move quickly
• Strongly interacting ones will be delayed.
• Weakly interacting ones will move quickly
32
New cards
Why do why have a mix of polar and nonpolar solvents in chromatography ?
addition of only a minor amount of a polar solvent can result in a large increase in the eluting power of the mixture
33
New cards
Thin Layer Chromatography Uses
• To purify small amounts of compounds (rare)
• Qualitative test for purity of mixtures.
• Identify number of compounds in a mixture
• To identify unknowns.
• To monitor separation in column chromatography (CC)
• To find the best solvent for CC
• Qualitative test for purity of mixtures.
• Identify number of compounds in a mixture
• To identify unknowns.
• To monitor separation in column chromatography (CC)
• To find the best solvent for CC
34
New cards
Explain the correlation between Retardation Factor and polarity
Rf = Dspot / D solvent
The more polar a compound is, the smaller the Rf value
The more polar a compound is, the smaller the Rf value
35
New cards
melting point
Temperature at which the solid and liquid phases of a pure substance coexist at 1 atm
36
New cards
Increase in atmospheric pressure, (Blank) the m.p.
increases
37
New cards
Compounds with Crystal lattice structure have a (blank) m.p
higher
38
New cards
What does impurities do to the melting point
Impurities reduce the m.p. and increase the range of melting
39
New cards
Boiling Point
Temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the atmospheric pressure
40
New cards
As the strength of intermolecular forces increases, vapor pressure (blank)
decreases
41
New cards
As vapor pressure increases, b.p. (blank)
decreases
42
New cards
As atmospheric pressure decreases, boiling point (blank)
decreases
\
Vapor pressure will equalize the atmospheric temperature at a lower temperature
\
Vapor pressure will equalize the atmospheric temperature at a lower temperature
43
New cards
Distillation
Is a separation/purification technique that can be used to purify volatile liquids based on the difference between their boiling points
44
New cards
Fractional Distillation
• Separate liquids with very close boiling points.
• Use a fractionating column Mixture: Consists of a mixture of (A, b.p. = 100 °C) & (B, b.p. =75 °C )
• Upon heating, vapor goes up, consists of A & B
• “A” has higher b.p. so it starts to condense
• As we move up the column, the vapor fractions will consist more of “B”
\
• Use a fractionating column Mixture: Consists of a mixture of (A, b.p. = 100 °C) & (B, b.p. =75 °C )
• Upon heating, vapor goes up, consists of A & B
• “A” has higher b.p. so it starts to condense
• As we move up the column, the vapor fractions will consist more of “B”
\
45
New cards
Vacuum Distillation
• Distillation under vacuum (reduced pressure)
• The reduced pressure lowers the boiling point.
• This makes the distillation faster.
• The reduced pressure lowers the boiling point.
• This makes the distillation faster.
46
New cards
Steam Distillation
• Mixing of organic solvent and water (immiscible).
• The organic solvent will distill at a low temperature.
• Each solvent exerts its own pressure
• The total pressure will get closer to the atmospheric pressure faster.
• The organic solvent will distill at a low temperature.
• Each solvent exerts its own pressure
• The total pressure will get closer to the atmospheric pressure faster.
47
New cards
Qualitative Tests
It uses chemical tests “visual” to confirm the presence or absence of a certain functional group
48
New cards
Jones Oxidation
• The oxidizing agent is **CrO3, H2SO4**
• 1’ alcohol to carboxylic acid
• 2’ alcohol to ketone
• aldehydes to carboxylic acid
• Color changes from orange “Cr(III) to green to blue color Cr(IV)
• 1’ alcohol to carboxylic acid
• 2’ alcohol to ketone
• aldehydes to carboxylic acid
• Color changes from orange “Cr(III) to green to blue color Cr(IV)
49
New cards
Lucas Test
• It is used to differentiate between primary, secondary & tertiary alcohols
• The reagents used are **HCl with ZnCl2**
• Converts alcohols into alkyl halides
• Primary alcohols doesn’t react unless it is heated
• Secondary alcohol turns turbid and forms an oily layer in three to five minutes
• tertiary alcohols react rapidly and give turbid solution with oily layer
• The reagents used are **HCl with ZnCl2**
• Converts alcohols into alkyl halides
• Primary alcohols doesn’t react unless it is heated
• Secondary alcohol turns turbid and forms an oily layer in three to five minutes
• tertiary alcohols react rapidly and give turbid solution with oily layer

50
New cards
Ferric Chloride Test
• **FeCl3** is used to test for phenols.
• Phenol forms red-blue-violet complex with Fe(III)
• Phenol forms red-blue-violet complex with Fe(III)
51
New cards
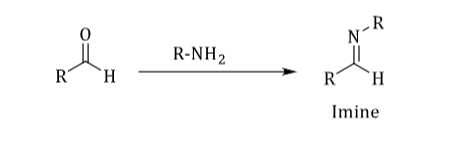
Derivative Test
• Convert aldehydes and ketones into other derivatives.
• 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine & semicarbazone
• They convert liquid aldehydes and ketones into solids
• 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine & semicarbazone
• They convert liquid aldehydes and ketones into solids
52
New cards
Tollen’s Test
• It is used to test for aldehydes
• The reagents used are **AgNO3 and HO-**
• The aldehyde is oxidized to carboxylic acid.
• Ag(I) is reduced to Ag (silver mirror)
\
• The reagents used are **AgNO3 and HO-**
• The aldehyde is oxidized to carboxylic acid.
• Ag(I) is reduced to Ag (silver mirror)
\
53
New cards
Iodoform Test
• Test for presence of methyl ketones
• Reagents used are iodine **I2 and -OH**
• It gives a carboxylate and Iodoform (HCl3) (yellow precipitate)
• Reagents used are iodine **I2 and -OH**
• It gives a carboxylate and Iodoform (HCl3) (yellow precipitate)
54
New cards
Bromine Test
• Test for presence of double or triple bonds
• Reagent used is bromine **Br2** (red color)
• Bromine adds to the double bond or triple bonds and since it is consumed the red color disappears
• Reagent used is bromine **Br2** (red color)
• Bromine adds to the double bond or triple bonds and since it is consumed the red color disappears
55
New cards
Permanganate Test
• Test for presence of double or triple bonds
• Reagents used are **KMnO4 & HO-** (purple color)
• It adds two hydroxyl groups to the double bond
• Since the permanganate is consumed the color disappears
• Reagents used are **KMnO4 & HO-** (purple color)
• It adds two hydroxyl groups to the double bond
• Since the permanganate is consumed the color disappears

56
New cards
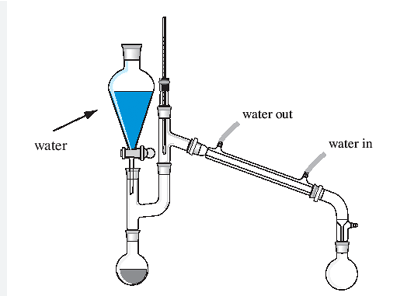
In distillation, the cold water should enter from the top side of the condenser (T/F)
False
57
New cards
Which will have a lower Rf value, chlorobenzene or phenol?
phenol
58
New cards
rotary evaporator
The reduced pressure in the apparatus causes the solvent to boil at a lower temperature than normal (see vacuum distillation), and rotating the flask increases the liquid's surface area and thus the rate of evaporation
59
New cards
the most polar compound will be
the one with the oxygen
60
New cards
steam distillation use is to
purify volatile liquid(s)
61
New cards
Which solvent mixture is better to separate B & C? Explain briefly (2 points)
I: Hexane: Ethyl acetate (5:3)
II: Hexane: Ethyl acetate (5:1)
I: Hexane: Ethyl acetate (5:3)
II: Hexane: Ethyl acetate (5:1)
II: Hexane: Ethyl acetate (5:1)
We need a less polar solvent
We need a less polar solvent