Chapter 2: Darwin's Big Idea + How It Changed Biology
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Open questions in Darwin’s Time
(biology before Darwin and Wallace)
where do species come from?
how can we explain complex adaptations?
traits with clear and elaborate function for the survival and reproduction of organisms?
William Pale’s Argument from Design
(biology before Darwin and Wallace)
highly complex and functional things are designed for a purpose by a Creator (e.g. tree and watch)
Jean- Baptiste de Lamarck (1744-1829)
(biology before Darwin and Wallace)
first to use the term evolution
first to provide a hypothesis for the casual mechanism: inheritance of acquired characters (adaptation)
Why was Lamarck wrong? : August Weiman’s Germplasm Theory (1889)
inheritance only by germ cells (gametes); somatic cells (soma/body) do not function as agents of heredity
thus, genetic info cannot pass from soma to gametes to next gen
modern interpretation molecular terms: genetic info flows in one direction only. from DNA to protein, but never the reverse!
Darwin + Wallace
Darwin developed first comprehensive theory of evolution
Darwin and Wallace independently discovered the chief mechanism of evolution: natural selection
Darwin’s and Wallace’s Theory of Evolution
all organisms have descended with modification from a common ancester
the process leading to evolution is natural selection operating on variation among individuals
Development of Darwin’s ideas on evolution
exploration
voyage on HMS Beagle around the world (1831-1836) as ship’s naturalist
made numerous observations and collections of plants, animals, fossils
returned and spent rest of life in seclusion at Down House developing his ideas, conducting experiments and writing 25 books
Development of Darwin’s ideas on evolution
gradualism
Darwin read Lyell’s book “Principles of Geology’ (1830)
Lyell argued for uniformitarianism
the forces and processes that shape the earth’s surface are uniform through time
i.e. the forces we see today are the same as previous eons
he argued that present day geological processes can explain the history of the earth (gradualism of erosions, earthquakes, volcanoes)
2 implications for Darwin
notion of dynamic rather than a static world
changes build up gradually, by the same mechanisms today as in the past
Development of Darwin’s ideas on evolution
species vary
variation patterns of Galapagos mockingbirds
there are four similar species endemic to the islands descended from South American mainland ancestor
darwin doubt fixity of species (mar. 1837)
Development of Darwin’s ideas on evolution
struggle for existence
Darwin reads Thomas Malthus’ ‘An essay on the principle of population’ (1798) in Sept. 1838
Thomas talks about struggle for existence
favorable variations tend to be preserved and unfavourable ones would be destroyed
since resource grow geometrically and human population grow exponentially, resource would run out → competition
events leading up to the publication of the Origin of Species
1831-1836: voyage of Beagle
+20 years : evidence acumulation
1844: wrote essay on natural selection - not publish
1856: start natural selection book
June 1858: receive Wallace’s article “On the tendency of varieties to depart indefinitely from the original type”
July 1858: Linnean Society presentation of Darwin-Wallace paper
Nov. 1859: publication 490-page book “On the origin of species by means of natural selection or the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life” by Darwin
Darwin’s mechanism of Natural selection
variation: individual variation in a population
heredity: progeny resemble their parents more than unrelated individuals
differential fitness: some forms are more successful at surviving and reproducing than others in a given environment
*evolution = natural selection is heritable variation in fitness
important elements of Darwin’s Theory
evolution occurs primarily at the level of populations (individuals don’t exist)
variation is not directed by environment (individuals don’t induce adaptive variation when needed)
most fit type depends on the environment
‘survival of the fittest’: evolution works with available variation, and will not necessarily achieve perfection
implications of Darwin’s Theory of evolution
concept of a changing universe
replaced view of a static world
a phenomenon with no purpose
natural selection revealed how complex adaptations with important ‘functions’ can arise through an unplanned process
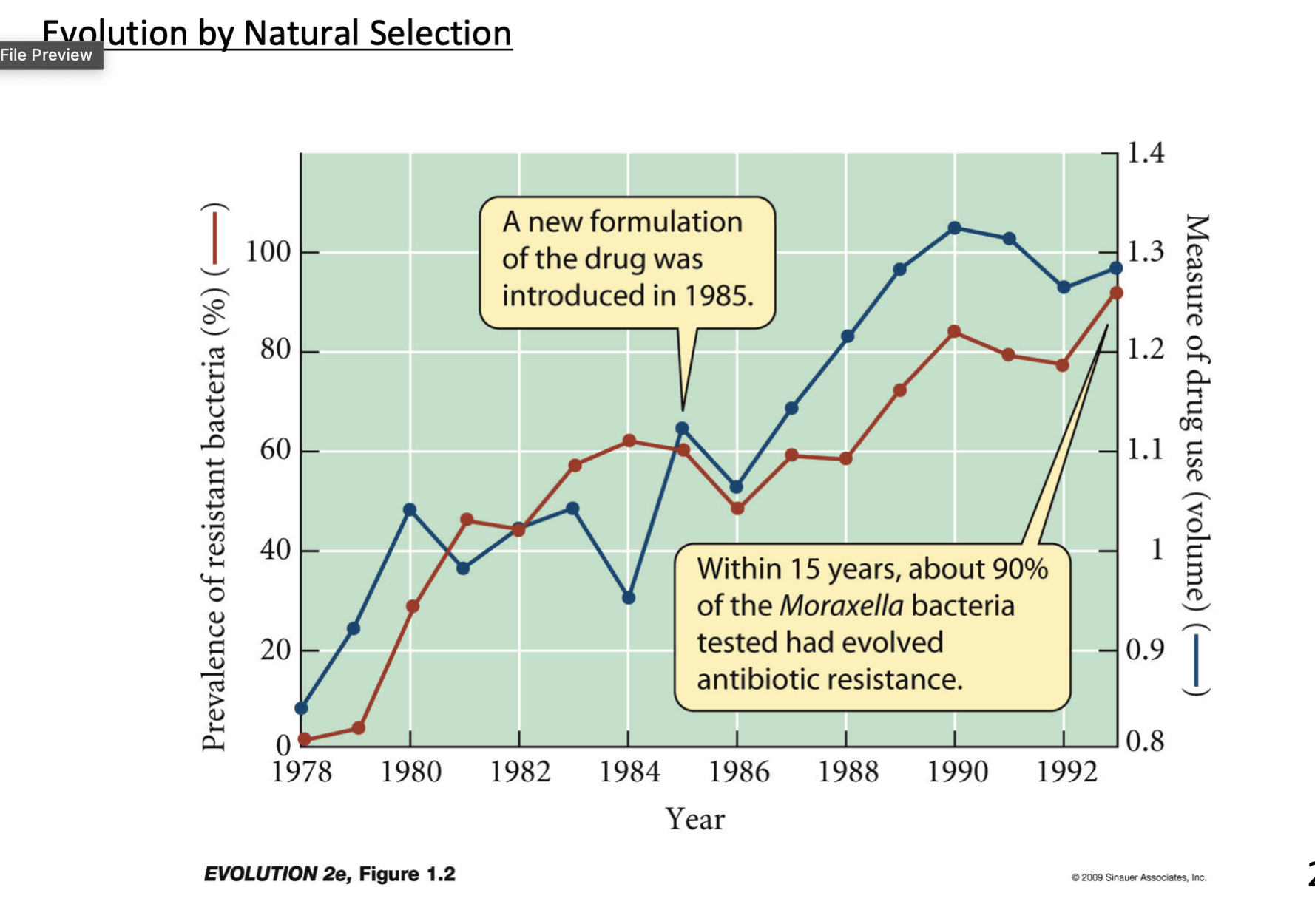
examples of natural selection
needs to use more drug over time because bacteria evolves to being more resistant to antibiotics
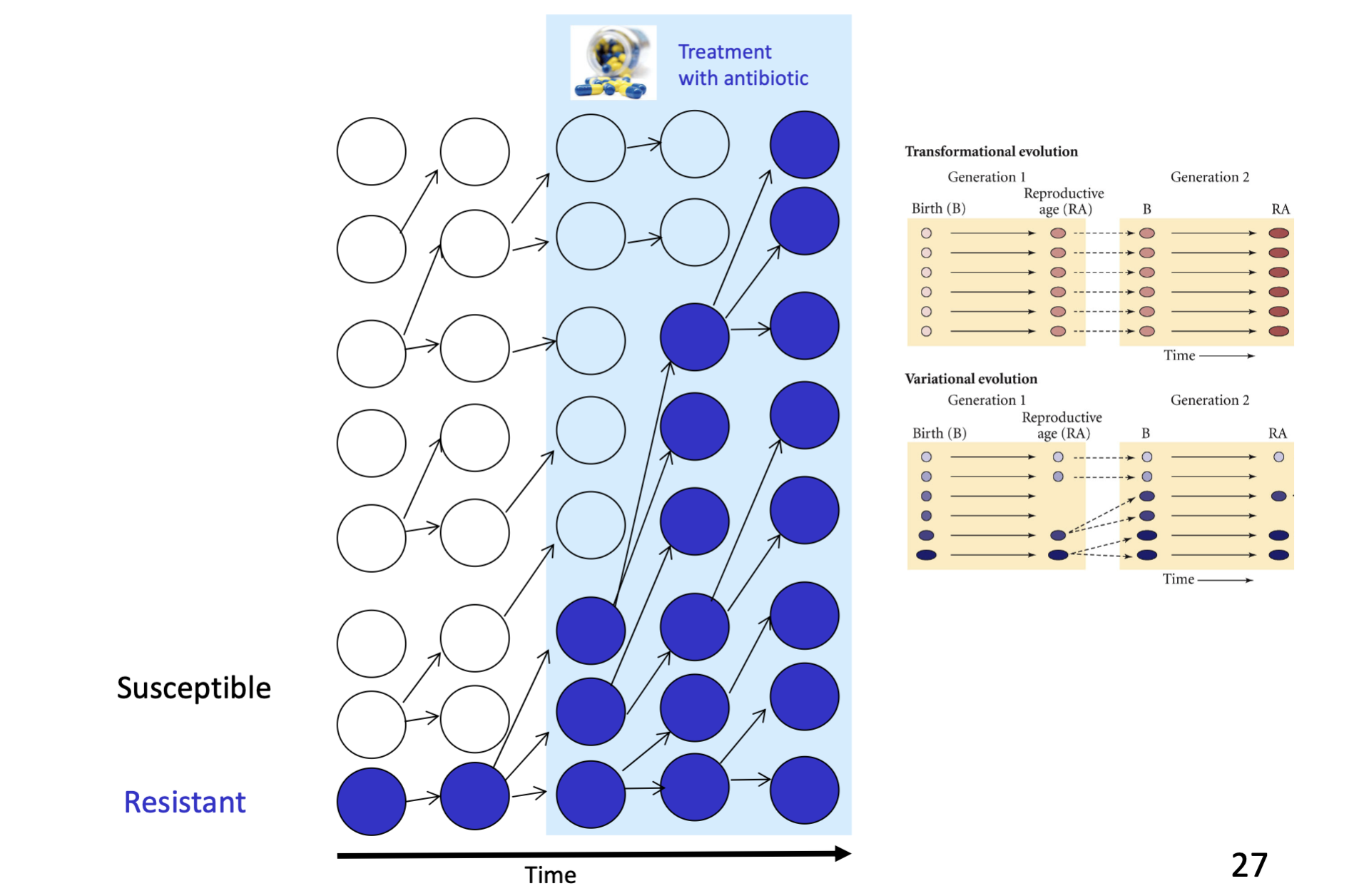
examples of natural selection (cont.)
blue ones (antibiotic resistant) reproduce more than white ones (susceptible)