Chapter 11
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Personality
One’s characteristic pattern of behaving, thinking, feeling, attitudes, temperament, ideology, beliefs.
Personality Disorder
A type of mental disorder where individuals experience a rigid, dysfunctional, and unhealthy pattern of thinking, functioning, and behaving.
Freud’s Psychoanalytic Theory of Personality
Freud proposed three levels of consciousness - Conscious, Preconscious, and Unconscious.
Id
Contains life and death instincts, operates on the pleasure principle, and is the source of libido.
Ego
The rational part of personality that mediates between the id and superego, operates on the reality principle.
Superego
Moral system of personality formed around ages 5-6, judges behavior based on past experiences.
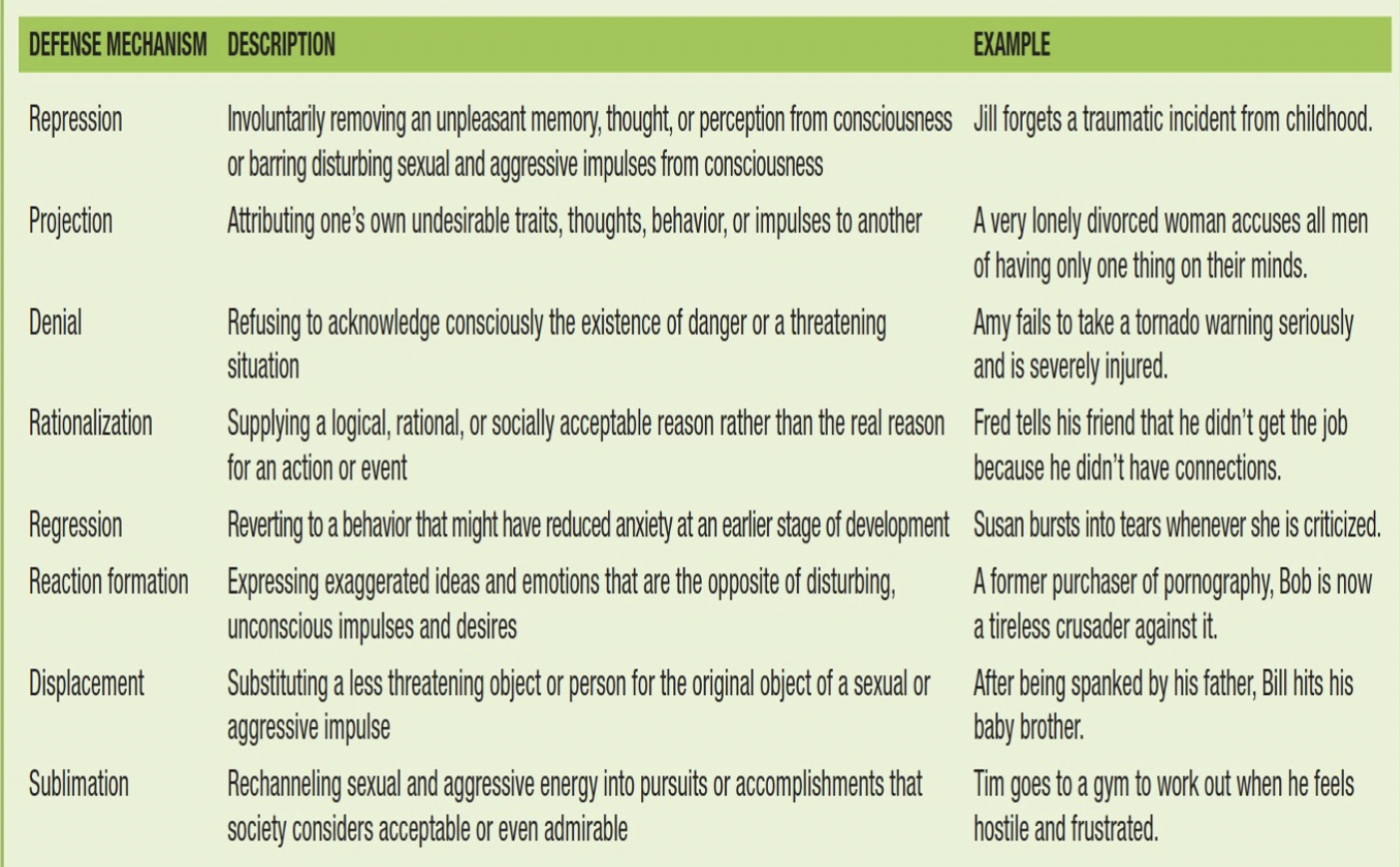
Defense Mechanisms
Used by the ego to maintain self-esteem and defend against anxiety.
Psychosexual Stages of Development
Developmental stages involving erogenous zones and conflicts, can lead to fixations if not resolved.

Neo-Freudians
Adler:Alfred Adler focused on the drive to overcome feelings of inferiority and unity of personality.
Horney:Karen Horney emphasized the need to overcome irrational beliefs about perfection and focused on feminine psychology.
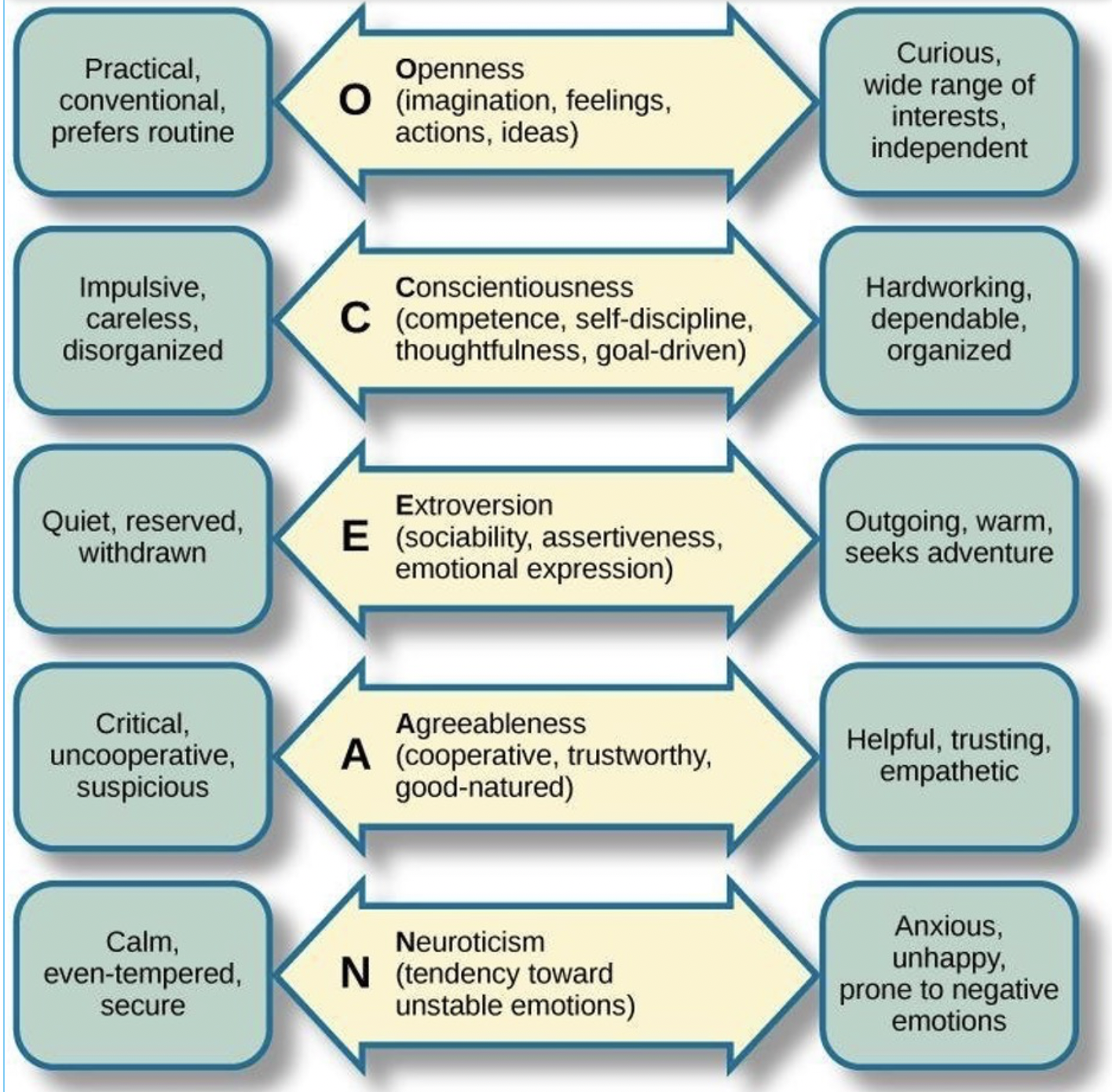
OCEAN
Humanistic Theories
Maslow:Abraham Maslow proposed a hierarchy of needs with self-actualization as the highest need.
Humanistic Theories
Carl Rogers:Carl Rogers introduced conditions of worth and person-centered therapy.
Trait Theories
Allport:Gordon Allport proposed cardinal and central traits to explain personality differences.
Trait Theories
Cattell:Raymond Cattell identified surface and source traits to understand personality.
Five-Factor Model
Robert McCrae and Paul Costa's model includes openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism.
Genetics in the Development of Traits
Behavioral genetic theory asserts that heredity plays a significant role in individual differences.
Personality and Culture
Cultural factors influence personality development, with individualist and collectivist cultures emphasizing different values.
Social-Cognitive Theory
Personality is influenced by learned behaviors acquired through interactions with others.
Bandura’s Reciprocal Determinism Model
Internal, environmental, and behavioral variables interact to influence personality.
Personality Assessment
Methods include observation, interviews, rating scales, and personality inventories like MMPI, CPI, and Myers-Briggs.
Projective Tests
Rorschach Inkblot Methods
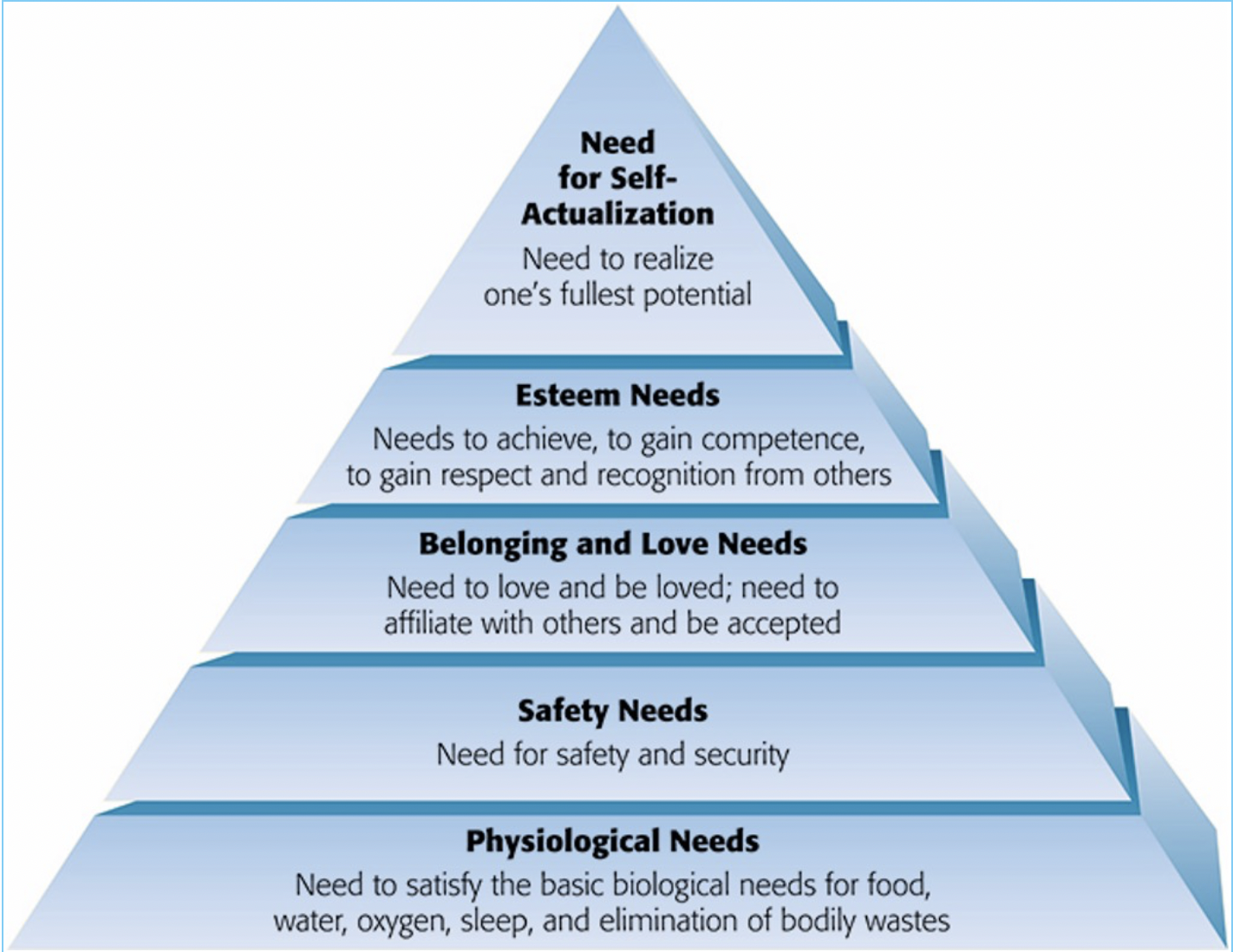
Hierarchy of needs (Abraham Maslow)
physiological needs> Safety needs> Belonging and Love Needs> Esteem Needs> Need for self actualization
Exner's Comprehensive System
(1993) developed the comprehensive system for scoring
provides normative data for comparison of responses
Components of Language
phonemes, morphemes, syntax, semantics, pragmatics
Projective Tests
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
consist of inkblots, drawings of ambiguous human situation, or incomplete sentences
no correct or incorrect responses
the subject projects their inner thoughts, feelings, fears, or conflicts onto the test materials
include Rorschach Inkblot Test and Thematic Apperception Test
undefined
Critics of Projective Tests
The test relies too heavily on the interpretation of the examiner
Responses may reflect temporary states and may not indicate more permanents aspects of personality
Freud’s Defense Mechanisms