Endocrine and Reproductive Systems
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
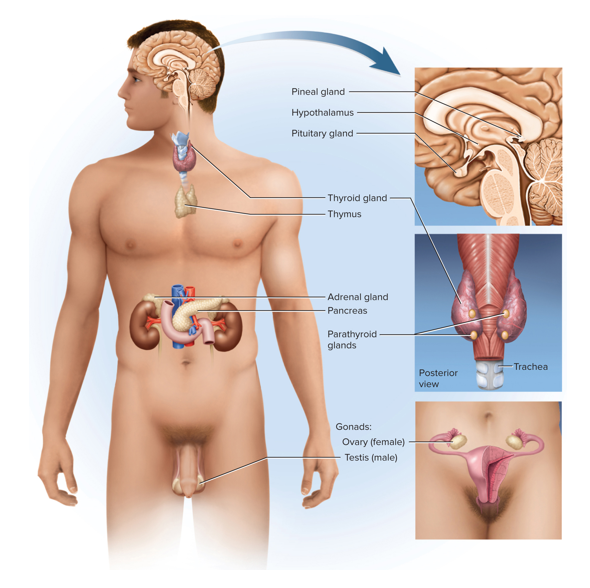
This system is a network of glands, tissues and cells that produce and release hormones
The endocrine system
What are hormones?
Chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream to specific organs and tissues, where they regulate various physiological processes and functions
What is the difference between exocrine glands and endocrine glands?
Exocrine glands secrete substances through ducts to epithelial surfaces or into body cavities; Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream
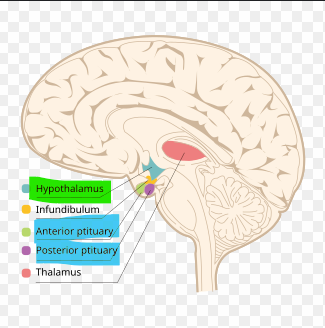
The pituitary gland is composed of two main structural and functional components; what are they?
Anterior pituitary - secretes hormones that regulate endocrine glands; Posterior pituitary - nuero portion
This bone houses the hypothalamus
Sphenoid bone
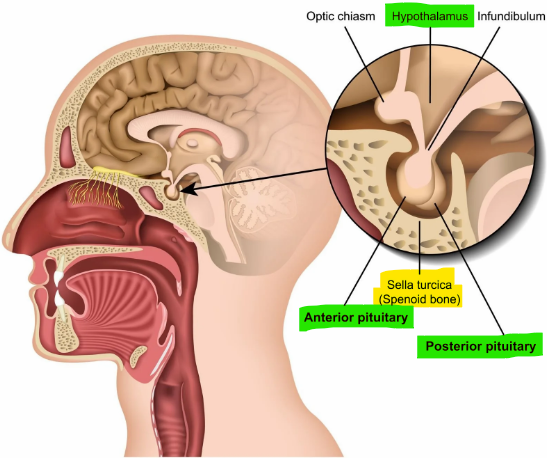
What regulates the pituitary gland?
Hypothalamus
Eight hormones are produced in the hypothalamus; how many regulate the anterior pituitary and how many are released into the posterior pituitary?
6 regulate the anterior pituitary; 2 are released into the posterior pituitary
These six hormones are synthesized and secreted by the anterior pituitary
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), prolactin and growth hormone
This hormone stimulates secretion of ovarian sex hormones, development of ovarian follicles and sperm production
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
This hormone stimulates ovulation, secretion of progesterone and stimulates testes to secrete testosterone
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
This hormone stimulates secretion of the thyroid hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
This hormone stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
After birth, this hormone stimulates mammary glands to synthesize milk
Prolactin
This hormone stimulates mitosis and cellular differentiation
Growth hormone
These two hormones are produced in the hypothalamus and are transported to the posterior pituitary
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin
This hormone increases water retention which reduces urine volume and prevents dehydration
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Oxytocin has various functions; name one
Stimulates labor contractions during childbirth, stimulates the flow of milk during lactation and promotes feelings of sexual satisfaction and emotion bonding between partners
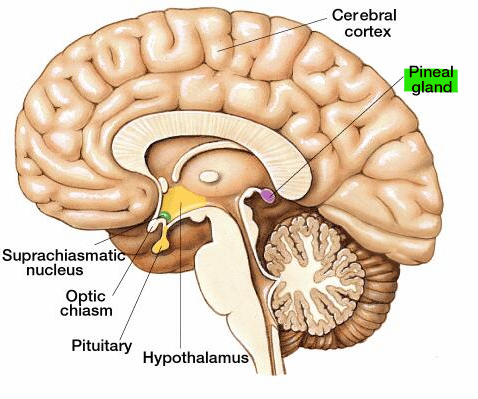
This gland synthesizes melatonin at night
Pineal gland
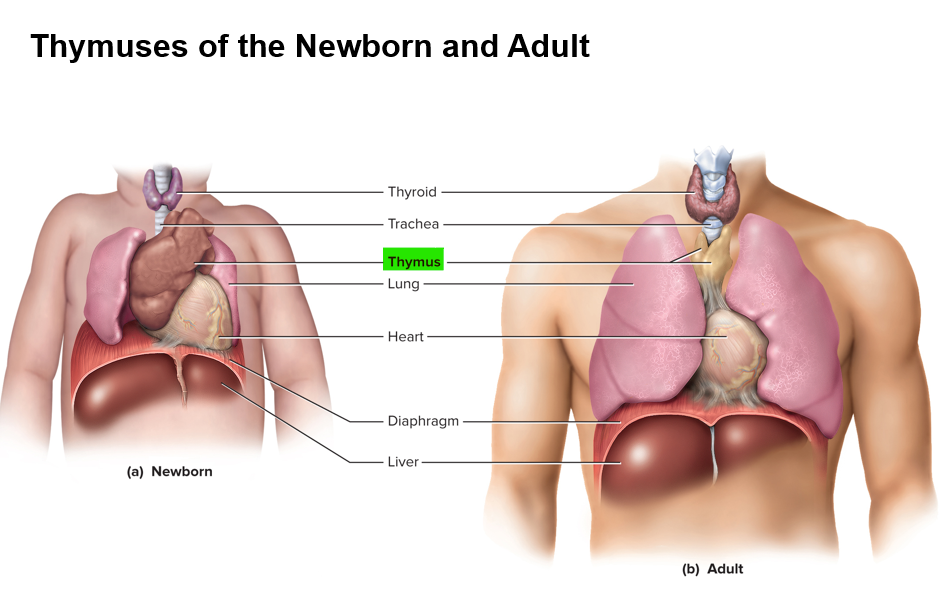
What 3 systems does the thymus play a role in?
Endocrine, lymphatic and immune systems
These are adaptive cells, that are always learning and are a part of our adaptive immune system
Lymphocytes (WBCs): T-cells - mature in thymus, B-cells - mature in bone marrow and produce antibodies and natural killer (NK) cells
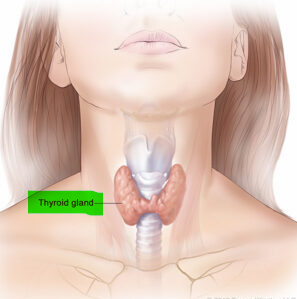
This is the largest gland and is purely endocrine
The thyroid gland
What does the thyroid gland secrete in response to TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) and what does it increase?
Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) - this increases metabolic rate, O2 consumption, heat production and appetite
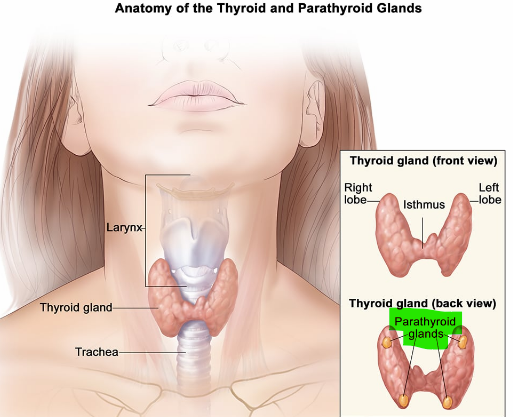
This hormone is secreted by the parathyroid glands and increases calcium levels in the blood
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
This part of the adrenal gland has a dual nature of acting as an endocrine gland and a ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system
Adrenal medulla
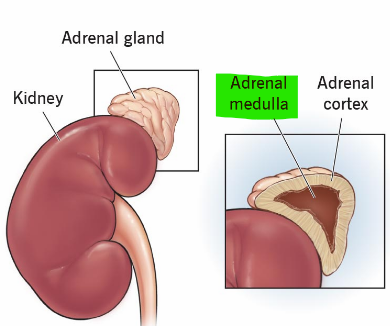
What releases catecholamines and what are the effects?
Adrenal medulla releases catecholamines when stimulated - increases blood pressure, heart rate, blood flow to muscles, pulmonary airflow and metabolic rate
This part of the adrenal gland secretes several corticosteroids from it’s 3 layers of glandular tissue
Adrenal cortex
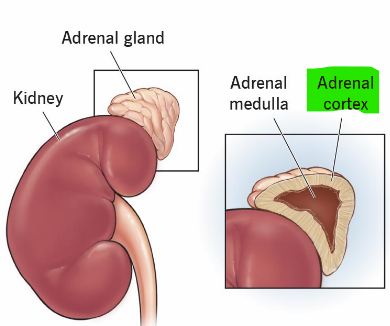
This hormone stimulates the adrenal cortex
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
This layer of the adrenal cortex is responsible for producing mineralocorticoids like aldosterone the stimulate NA retention
Zona glomerulosa
These layers of the adrenal cortex are responsible for producing sex hormones and sex steroids
Zona fasciculata and zona reticularis
These are secreted by the zona fasciculata and zona reticulata of the adrenal cortex and regulate metabolism of glucose and other fuels
Glucocorticoids
This hormone is produced by the pancreas and is released between meals when blood glucose concentration is falling
Glucagon - to raise glucose levels
This hormone is produced by the pancreas and is secreted during and after a meal when glucose and amino acid blood levels are rising
Insulin - to lower glucose levels
Are ovaries and testes an endocrine or exocrine organ? What are the exocrine and endocrine products?
Ovaries and testes are both an endocrine and exocrine organ; exocrine product: eggs and sperm; endocrine product: gonadal hormones - estrogen and progesterone in females; testosterone in males
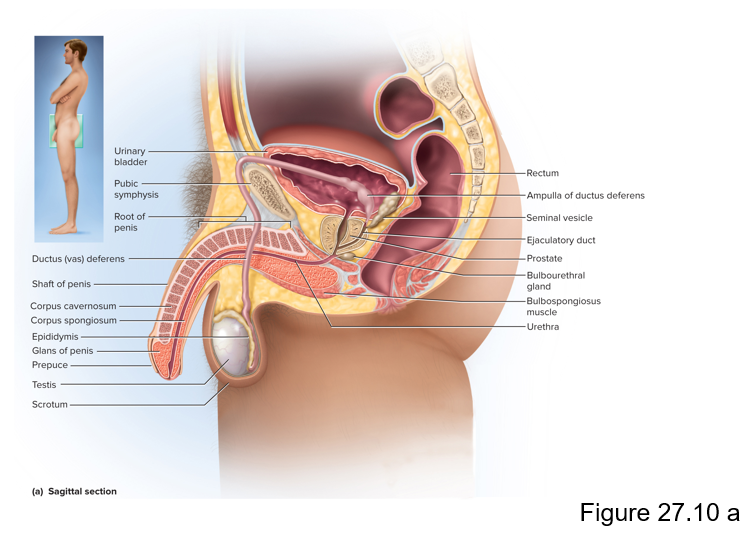
What is the purpose of the male reproductive system?
To produce sperm and introduce them into the female body
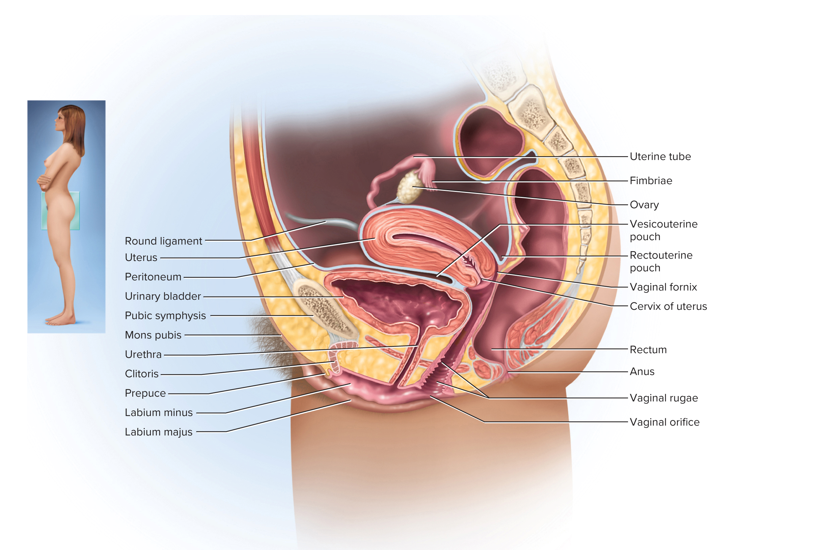
What is the purpose of the female reproductive system?
To produce eggs, receive sperm, provides for gametes’ union, harbor the fetus and nourish offspring
Describe the testes of the male reproductive system
Testes are a combined endocrine and exocrine gland that produce sex hormones like testosterone (endocrine) and sperm (exocrine)
These ducts are where sperm is produced
Seminiferous tubules
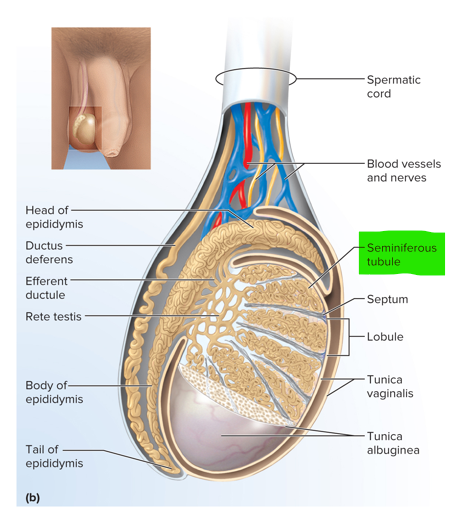
Within the seminiferous tubules of the testes, these interstitial endocrine cells between tubules produce what hormone?
Testosterone
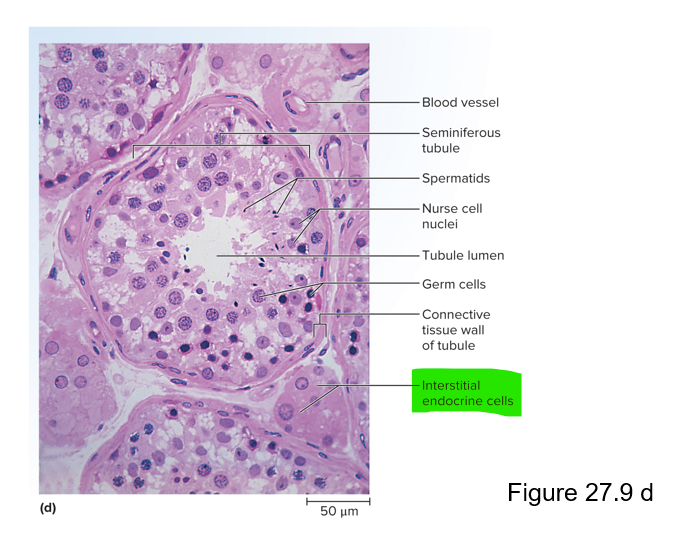
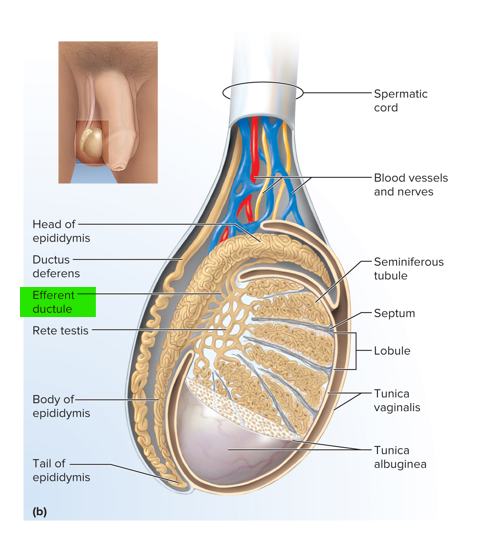
This is where sperm is collected from the rete testes and transported to the epididymis
Efferent ductule
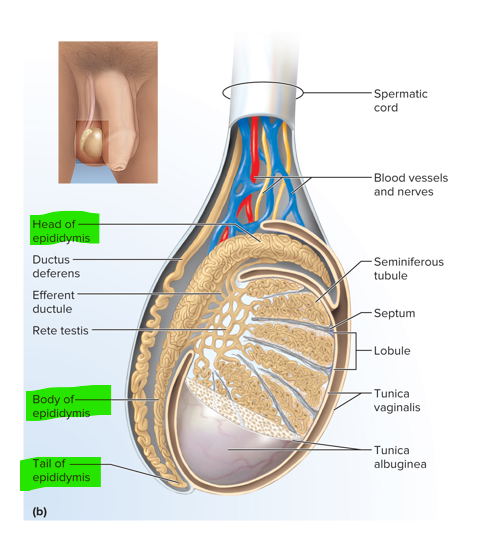
This is the site of sperm maturation and storage
Duct of the epididymis (head, body and tail)
This muscular tube transports sperm from the epididymis to the urethra, where it can be expelled during ejaculation
Ductus (vas) deferens
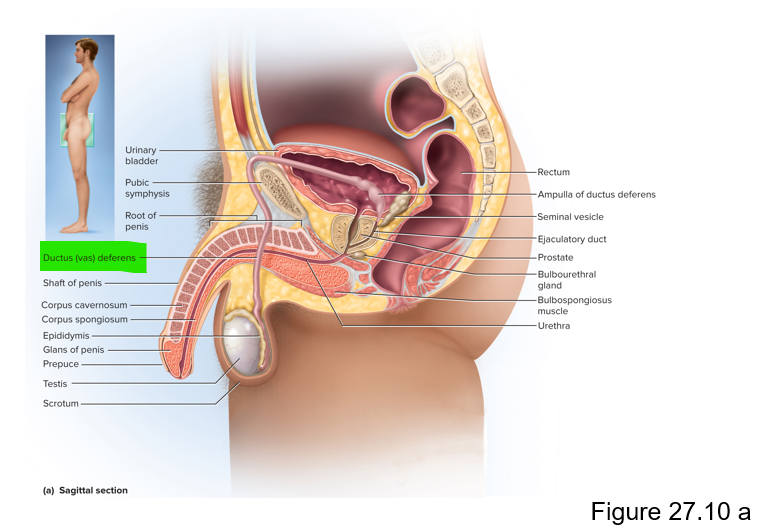
The vas deferens joins with the seminal vesicle to form this duct
Ejaculatory duct
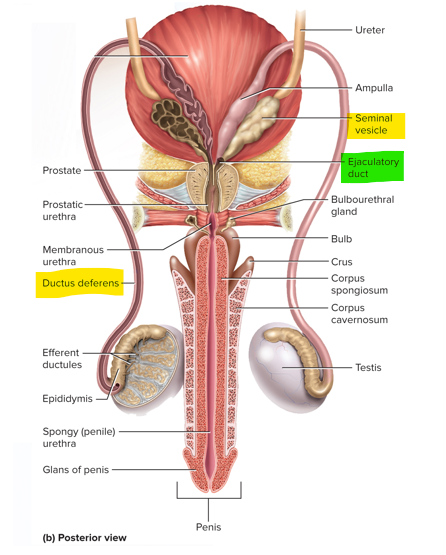
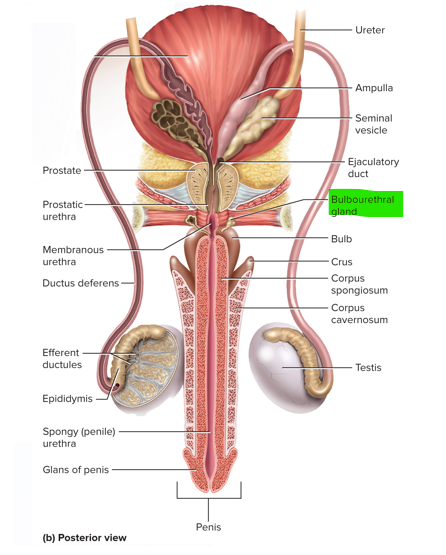
These are the 3 sets of accessory glands in the male reproductive system
Seminal vesicles, prostate and bulbourethral glands
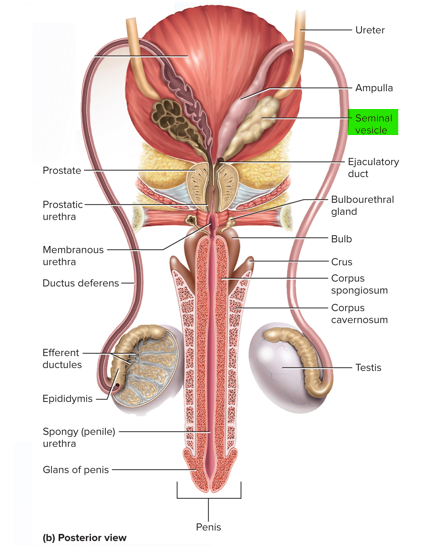
This pair of glands in the male reproductive system contributes about 60% of the semen volume
Seminal vesicles
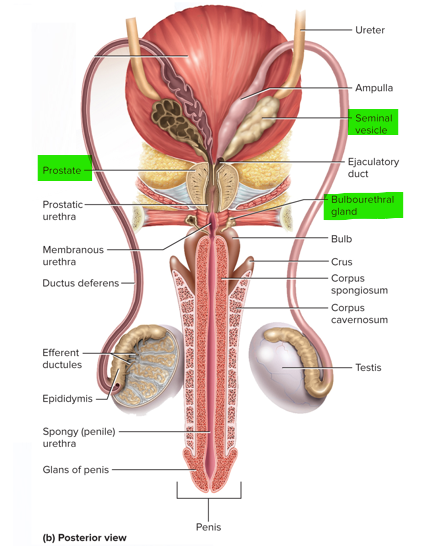
This gland of the male reproductive system surrounds the urethra and ejaculatory duct and contributes about 30% of the semen volume
Prostate
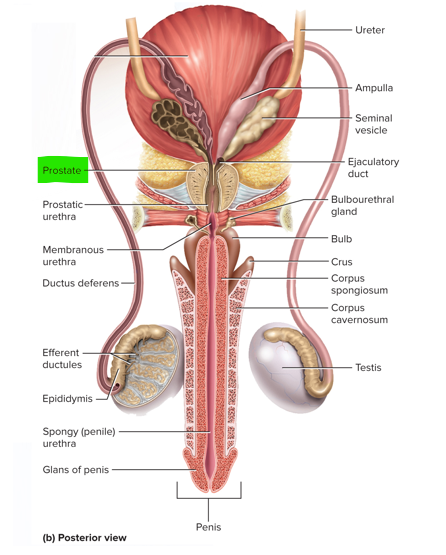
The bulbourethral glands of the male reproductive system produces pre-ejaculate; what is the function of this fluid?
It lubricates the head of the penis and protects the sperm by neutralizing the acidity of residual urine in the urethra
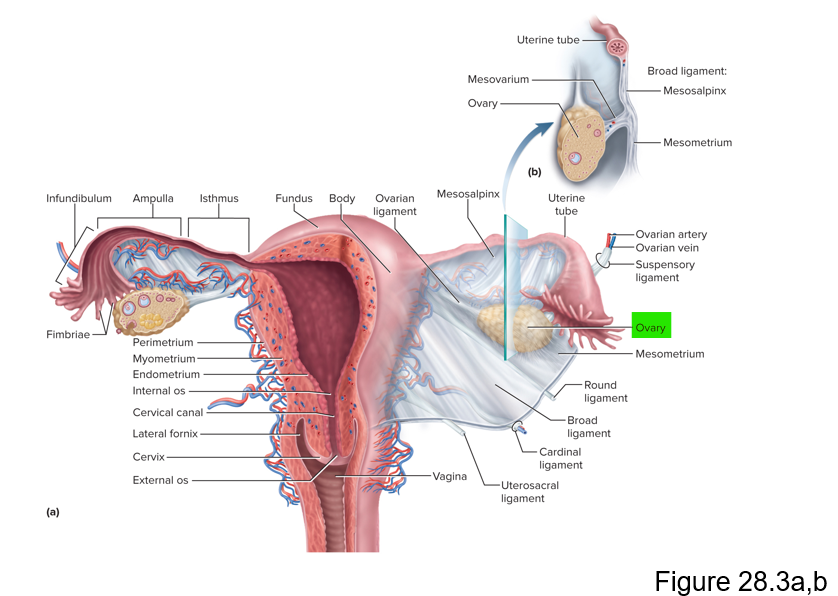
Describe ovaries
Female gonads that produce egg cells and sex hormones
In the female reproductive system, each egg develops in its own fluid-filled follicle. What hormone stimulates this follicle and what happens during ovulation?
Stimulated by FSH (follicle stimulating hormone); the follicle bursts and releases the egg into the fallopian tube
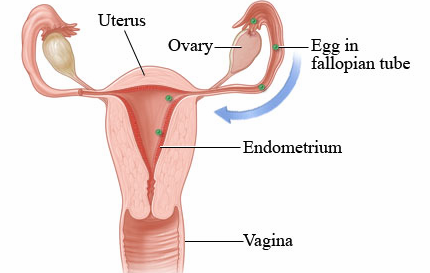
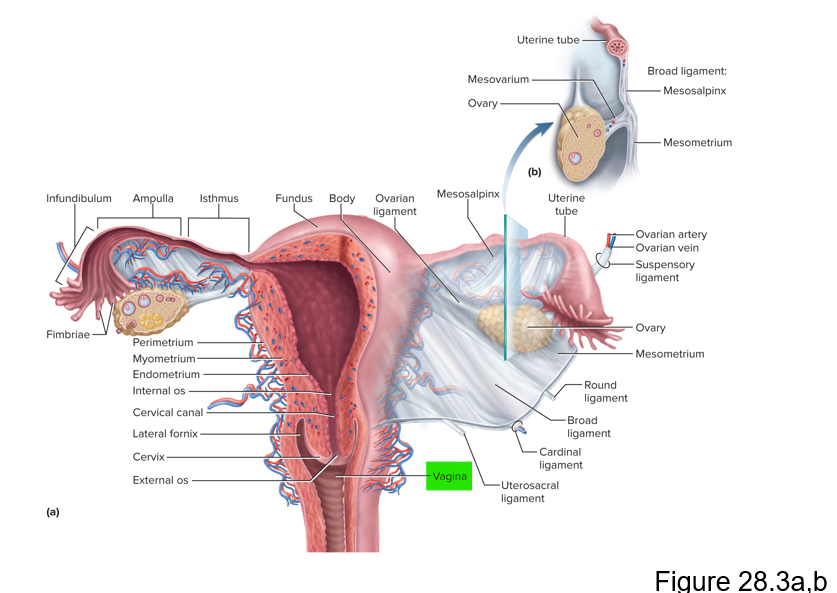
This part of the female reproductive system harbors the fetus, provides a source of nutrition and expels the fetus at the end of its development
Uterus
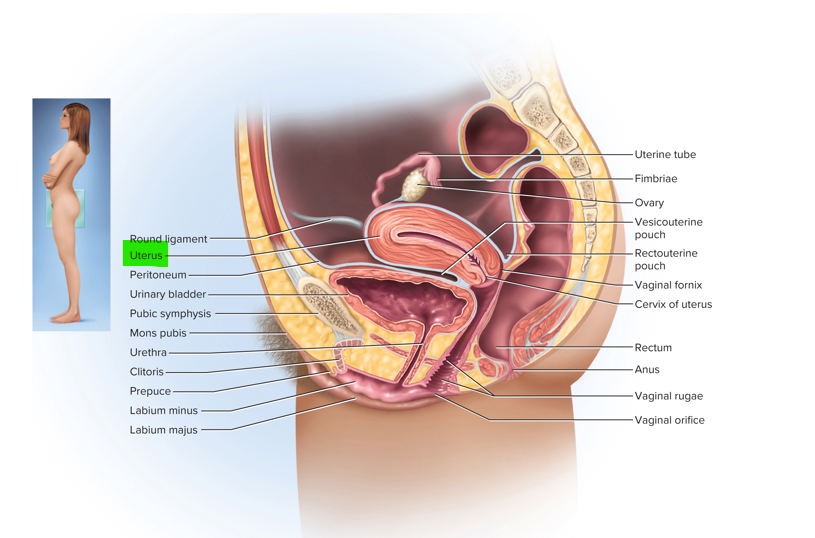
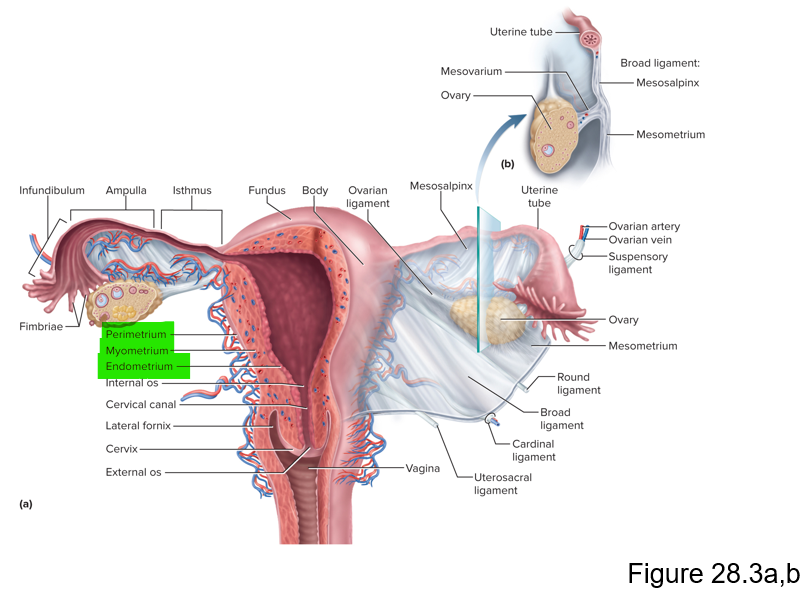
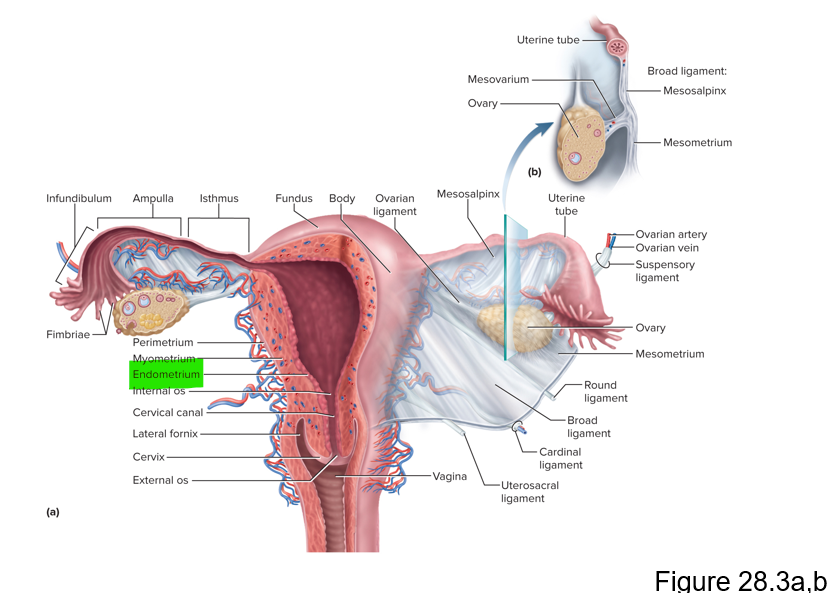
Name the 3 layers of the uterus
Perimetrium, myometrium and endometrium
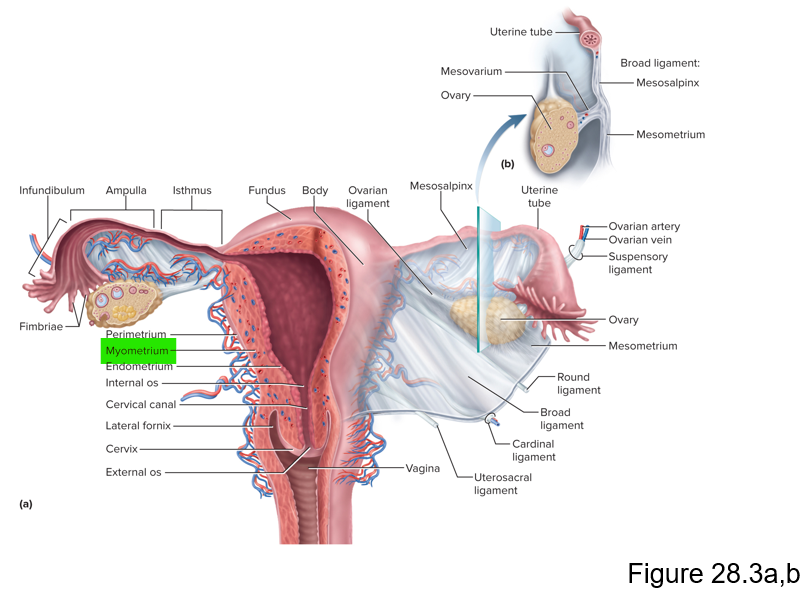
This layer of the uterus is the muscular layer that produces labor contractions and expels the fetus during labor
Myometrium
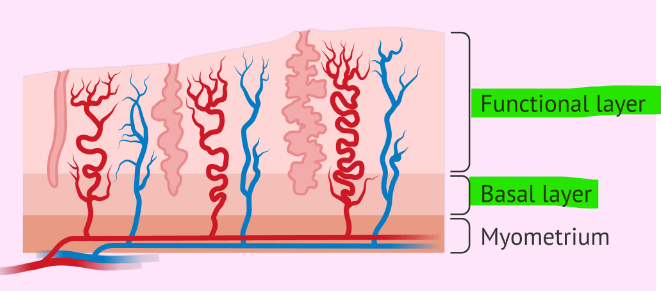
The endometrium of the uterus has 2 layers of inner mucosa; what are they and what is their purpose?
Functional layer - shed each menstrual period; basal layer - deep layer that stays behind and regenerates a new functional layer each menstrual cycle
During pregnancy, this is the site of attachment of the embryo and forms the placenta
Endometrium
This is also known as the birth canal
Vagina