12- Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
what is the oxidation number of uncharged atoms all by themselves or only bonded to other atoms of the same element?
ex. H2, Na, Cl2, Al
0
what is the oxidation number of monoatomic ions?
ex. K+, S2-, Mg2+, Al3+
oxidation number is equal to the ion's charge
what is the oxidation number of a nonmetal?
-usually negative
-fluorine is always -1. Other halogens are usually -1, but can be positive if bonded to O
-oxygen is usually -2, except in peroxides (like H2O2) where it's -1
-hydrogen is +1 when bonded to nonmetals and -1 when bonded to metals
what should the combined oxidation numbers of all the atoms in your compound add up to?
it should add up to your compound's total charge
what are the oxidation states of Zn, Cd, and Ag?
Zn: +2
Cd: +2
Ag: +1
when assigning oxidation numbers, the last element assigned gets whatever number balances the charge for the entire compound
in a voltaic cell, the anode/cathode experiences oxidation/reduction
anode: oxidation
cathode: reduction
in order for this to be spontaneous, the anode must be at a higher energy than the cathode so that it's more willing to give up its e-
a voltaic cell's ability to provide energy
electromotive force (emf)
aka electrode potential (Ecell)
when ΔG-, Ecell is +
cells that push electrons energetically uphill, from oxidant to reductant, in the opposite direction from which they would normally go
electrolytic cell
-you provide an external electric current that pushes electrons uphill, from the former oxidant to the former reductant
-this is NOT spontaneous, +ΔG and -Ecell
pushing electrons uphill
electrolysis
in an electrolytic cell, the anode is positive/negative and the cathode is positive/negative
anode: positive
cathode: negative
the flow in both cells is the e-from anode to cathode
in electrolytic cells, cations flow towards the cathode and anions flow toward the anode
what are the two ways of accomplishing a free flow of electrons for electrolysis?
1. melt reactants (molten)
2. dissolve ions in solution (aqueous)
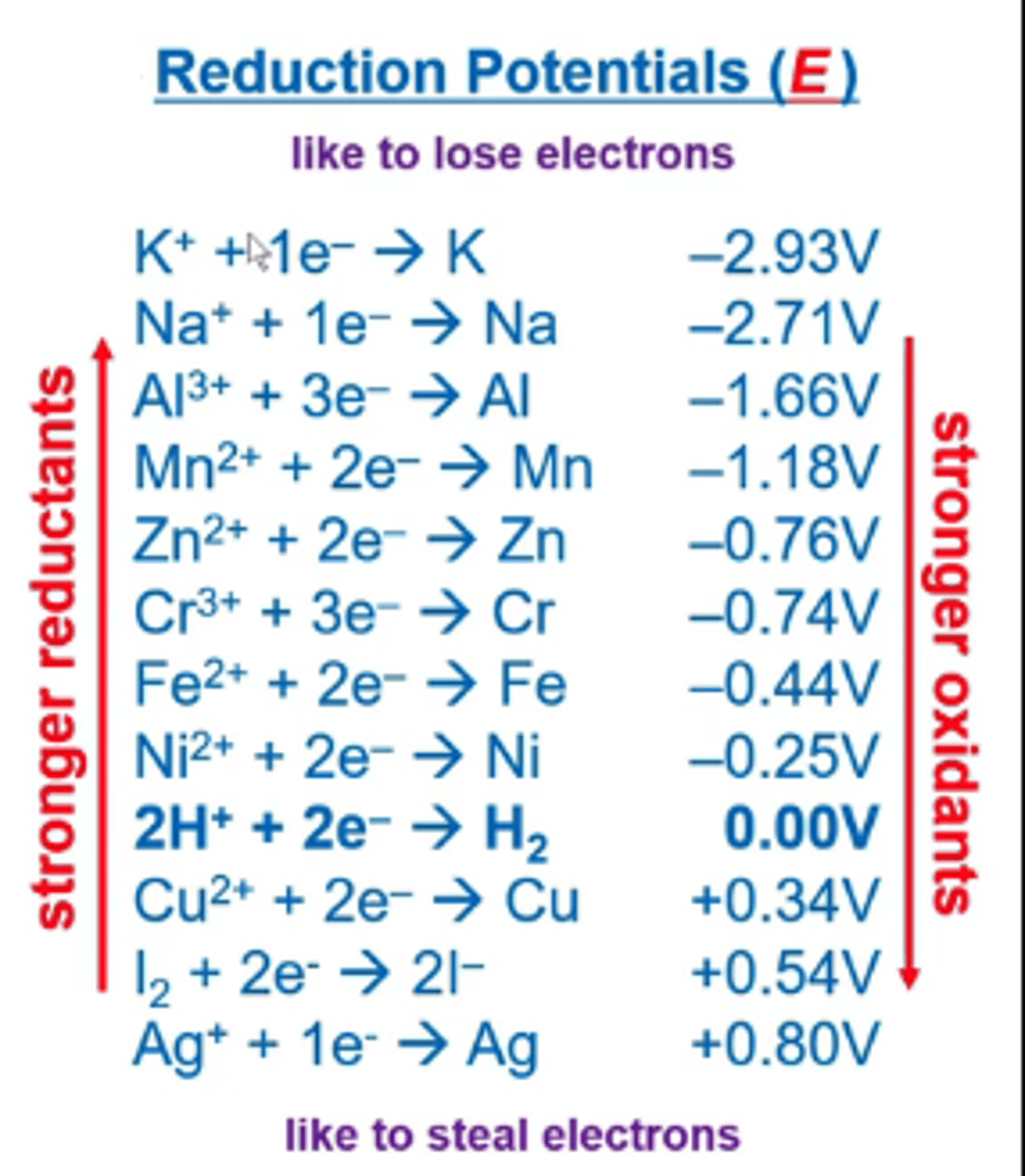
what is the equation to calculate an electrochemical cell's Ecell
look up the E value (aka reduction potential) for the reduction reaction in your cell. That's the reaction occurring at the cathode.
look up the E value (aka oxidation potential) for the oxidation reaction in your cell. That's the reaction occurring at the anode,
Ecell = Ereduction + Eoxidation
you do have to reverse the sign for the Eoxidation reaction
what is the nernst equation, used to convert Ecell into Enaught cell?
Ecell = Enaught cell - (0.0592/n) * log(Q)
n: #mols of e- transferred in the redox rxn
Q: reaction quotient (ratio of products/reactants)
if you change conc. so as to shift a spontaneous reaction to the right, then it will increase Ecell and vice versa
to perform calculations regarding current, time, electrons transferred, what equation do you use?
F=100,000
1C = 1 amp x 1 s
