Patient Assessment II: Abdominal/GI history + PE
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
what is included in the upper GI tract
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach
what is included in the lower GI tract
SI, LI, rectum, anus
main fxs of GI system
assimiliate nutrients and eliminate wastes
located in mouth - produce digestive juices
salivary glands
located in RUQ - produces bile which helps digestion
liver
located in RUQ - connects bile ducts, stores bile
gallbladder
located in LUQ - produces digestive enzymes
pancreas
lines abdominal cavity acting as protective cover
peritoneum
fat anchoring the SI
mesentery
what connects the pharynx to the stomach and is located posterior to the trachea
esophagus
what are the 3 sections of the stomach
fundus
body
pylorus
where are most nutrients absorbed in the GI tract
SI (primarily jejunum)
how long does it take for food to travel through the SI
~5hrs
what are the primary functions of the LI
- absorb water and electrolytes from undigested food
- form solid waste
- produces and absorbs certain vitamins
- maintain fluid balance
- bacterial fermentation
- immune function
what are the sections of the LI
cecum
colon (ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid)
rectum
anus
what is the small organ under the liver that stores and releases bile to aid in fat digestion?
gallbladder
what is the exocrine function of the pancreas?
- produces digestive enzymes (amylase, lipase, protease) to breakdown carbs, fats and proteins in SI
- secrete bicarb ions to neutralize stomach acid
what is the endocrine of the pancreas?
produces insulin to regulate blood glucose levels
produces glucagon to raise blood sugar
produces somatostatin - inhibits release of insulin and glucagon
what organ in LUQ has white pulp which filters blood and produces lymphocytes
spleen
kidneys are located in the ______
retroperitoneum
what are the functions of the kidney
- get rid of water soluble waste
- produce renin, erythropoietin, and vit D (calcitrol)
- synthesize prostaglandins
- control pH
what contains the umbilicus
linea alba
what are the branches of the descending aorta
iliac arteries
splenic artery
renal arteries
what are considered structural diseases
IBD (ulcerative colitis, chrons)
colorectal cancer
what are the most common GI symtpoms
- constipation
- diarrhea
- nausea
- vomiting
- abd pain
- heartburn/reflux
- bloating
what are some red flag symptoms with GI complaints?
- unexplained weight loss
- dysphagia
- odynophagia
- profuse and prolonged vomiting
- GI bleeding
- nocturnal diarrhea
- jaundice
- severe pain
what type of pain:
- when hollow organs contract forcefully or distend
- difficult to localize
- gnawing, burning, aching
visceral
what type of pain:
- inflammation of the parietal peritoneum
- steady aching pain, more severe
- localized
- aggravated by coughing or movement
parietal
common clinical presentation of heartburn
burning substernal pain
usually occurs after meals
worse at night with laying down
what are some silent symptoms of heartburn
chronic cough
wheezing
hoarseness
sore throat
halitosis
choking
clinical presentation of upper GI bleed
melena or hematemesis
black or tarry stools
iron deficiency anemia (+/-)
clinical presentation of lower GI bleed
bright red/maroon stool
iron deficiency anemia (+/-)
what can cause dysphagia/odynophagia
structural anomalies
motility disorder
infections/ulcerations
disorders of the urinary tract can cause _______ or ______ pain
abd; back
what are s/s of urinary tract infection/disorder
suprapubic pain
dysuria, urgency, frequency
polyuria/nocturia
urinary incontinence
hematuria
kidney/flank pain
what are some common GI s/s seen with pregnant women?
heartburn
gallstones
urinary stasis/urgency
constipation or flatus
hemorrhoids
what functional abilities of GI tract are often seen in older adults
slow motility
secretion and absorption slows
*may result in food intolerances
for abd exam, you should expose pt from _____ to _____
xyphoid; symphysis of pubis
what organs/areas are included in abdominal exam
mouth/teeth/tongue
stomach
liver/gallbladder
pancreas
SI/LI
rectum/anus
spleen
kidneys
vasculature
bladder and female reproductive organs
what is the order of the abdominal exam
inspection
auscultation
percussion
palpation
special tests
always ____ before palpation/percussion in the abdomen!!!
auscultate
what are you looking at during inspection of abdomen
general appearance
skin (jaundice, rashes etc)
contour (flat round, scaphoid, protuberant)
movement
superficial veins (should not be present)
facies and hands
abdominal muscles
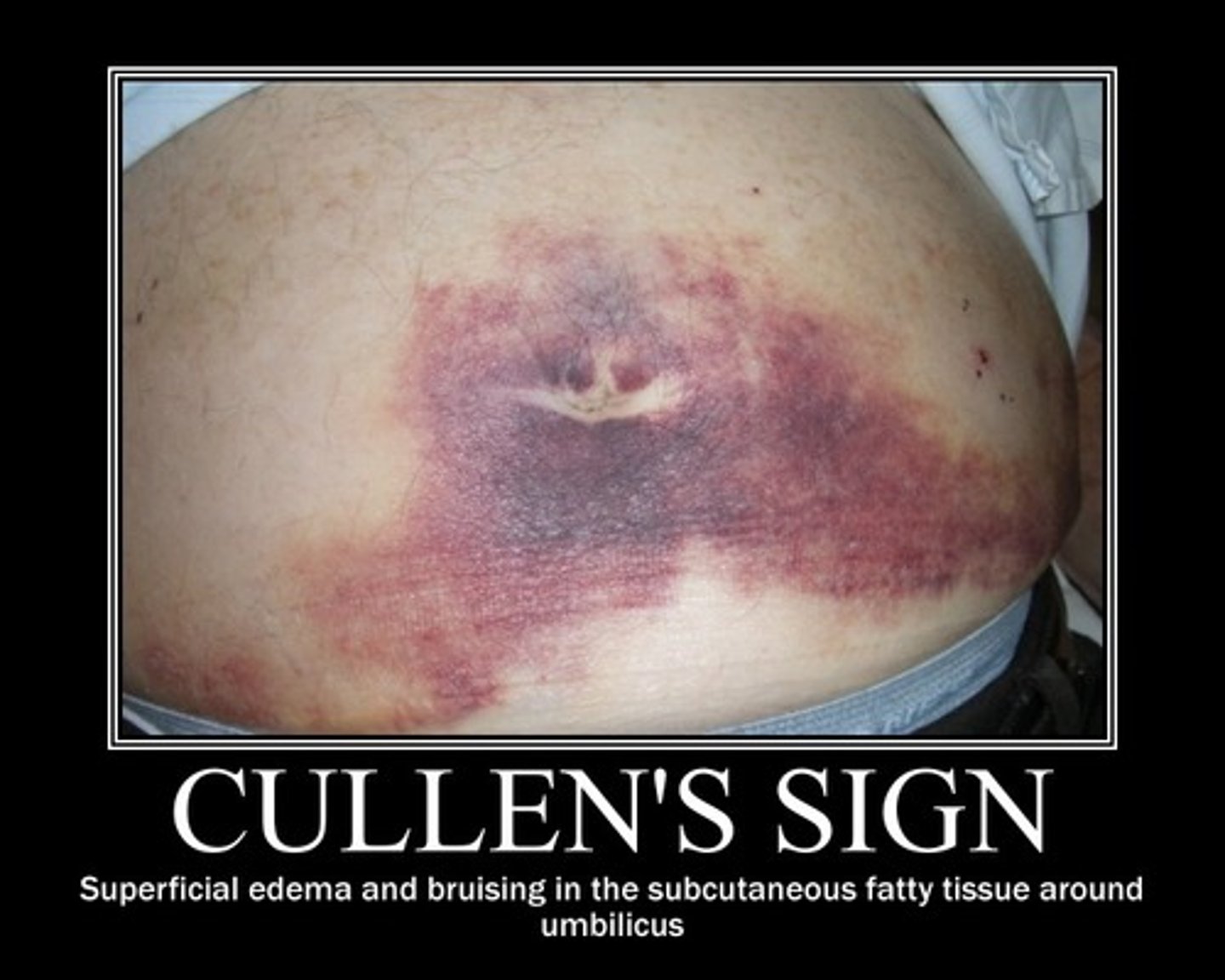
what sign: superficial edema and bruising in subQ fatty tissues around periumbilicus. d/t hemorrhagic pancreatitis
cullens sign
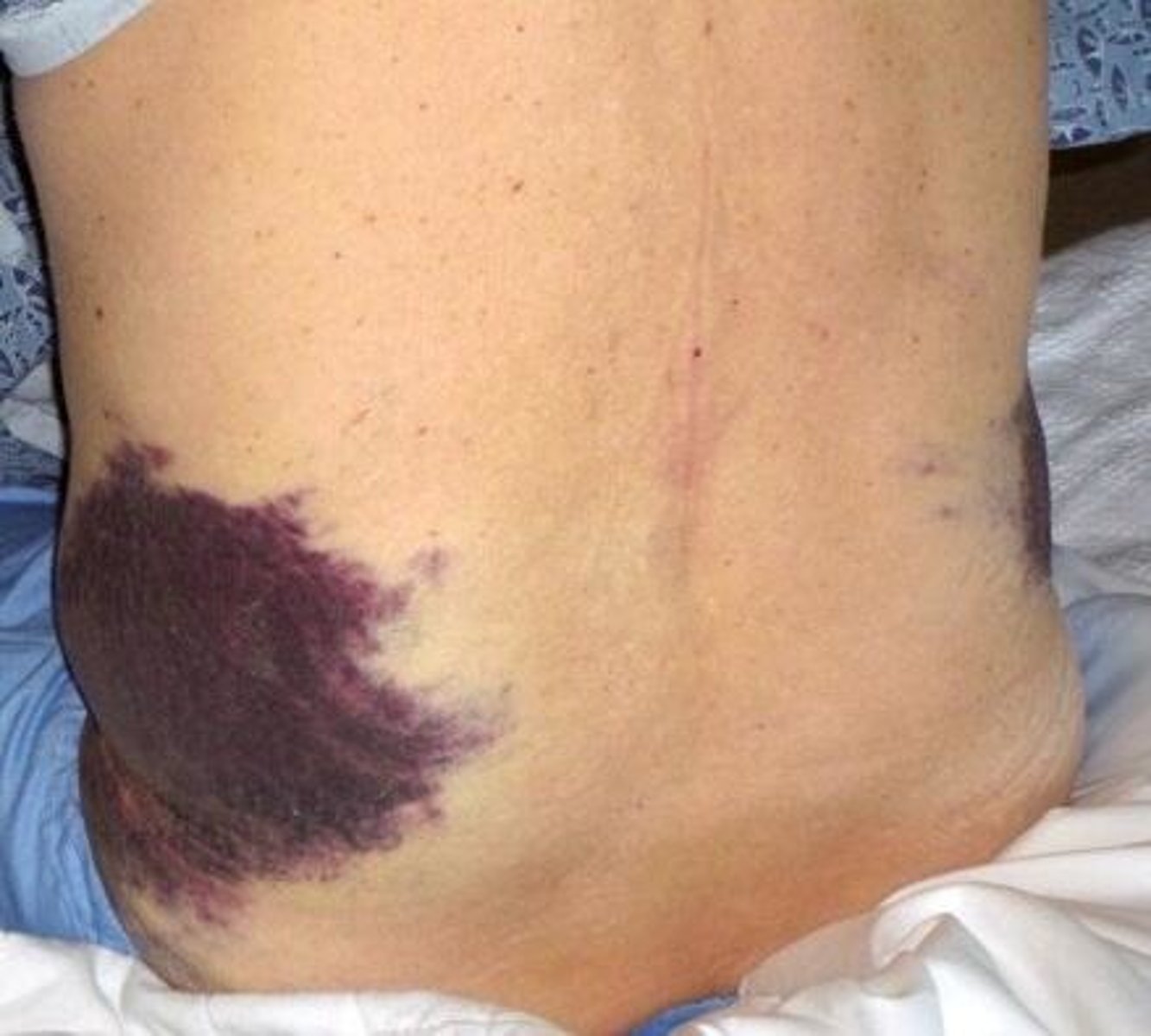
what sign: blueish discoloration of umbilicus from hemoperitoneum often associated with acute necrotizing pancreatitis
grey turners sign
when may you hear inc bowel sounds
gastroenteritis, early intestinal obstruction, hunger
when may you hear high pitched bowel sounds
borborygmi - suggests intestinal fluid and air under pressure as in early obstruction
when may you hear dec bowel sounds
peritonitis, paralytic ileus, constipation
when may you hear absent bowel sounds
typically indicate a surgical emergency
what might be heard d/t inc collateral circulation between portal and systemic venous system
venous hum
what might be heard over aoritc, renal and iliac arteries that indicates turbulent flow
bruits
when percussing what sounds do the following produce:
Gas -
Liquid -
Solid -
gas - tympany
liquid - dullness
solid - more profound dullness
what organ is located in traubes space (6th rib posteriorly, L ant axillary line)
spleen
how do you assess shifting dullness
assess for tympanny, dullness while pt is supine, then have them roll to the side
what is the fluid wave test
pt places hand in center of abd, provider taps one side of the abd and notes if they can feel a "wave" on the other side
what are bulging flanks a sign of
ascites
what type of palpation relaxes pt, elicits tenderness/muscle stiffness
light
what type of palpation is required to assess for masses, guarding and rebound tenderness
deep
what organs should not normally be palpable
spleen, kidneys, bladder
what area of hand should you use to palpate the abd
flat part or pads of fingers (not tips)
when should you palpate the painful area
LAST
what are you palpating for with deep palpation
bulges, masses
liver
gallbladder
spleen
kidneys
aortic pulsation
what masses would be considered physiologic
pregnant, uterus
what masses would be considered neoplastic
tumors, firm, nodular
what masses would be considered vascular
pulsatile
what masses would be considered inflammatory
associated with tenderness (diverticulitis or appendicitis)
what is the normal percussable span of the liver in mid clavicular line? sternal line?
6-12cm; 4-8cm
a normal liver may be palpable ______ below the costal margin in midclavicular area
3cm
an enlarging spleen will migrate from _____ to _____
LUQ; RUQ
what can pain with percussion over CVA be associated with?
kidney infection, stone, inflammation or injury
what is a red flag when palpating aorta
>5cm and pain
what is normal aorta size?
3cm
what special test? and when is it used?
straighten and stiffen fingers of one hand and make a jabbing movement toward organ to displace fluid
ballotte; used for ascites
what sign:
+ in appendicitis
press deeply in LLQ and will ilicit pain in RLQ
rovsings
what sign:
+ in appendicitis
pt supine, place hand above R knee and as pt to raise leg against your hand
psoas sign
what sign:
+ in appendicitis
examiner flexes pts right hip and interanlly rotates
obturator
what sign:
+ in appendicitis
palpate this point which is 1.5-2 inches from ASIS
mcburneys point
what test:
assesses for peritoneal inflammation
over area of pain or suspected pain push gently, then firmly, then abruptly let go
rebound tenderness
what sign:
test for inflammation of gallbladder
pt lies supine, ask pt to take a deep breath, if there is pain = positive
murphys sign
what special test should be done on all pts with abd pain
digital rectal exam