4. Dietary, physical, & chemical diseases of skin & ears in respective pig categories
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What treatment is used for dietary-related skin disease in swine?
Adjusting nutrition
What are examples of dietary related skin diseases?
Zinc deficiency
Iron and copper deficiency
Fat deficiency
Selenium deficiency
Salt deficiency
Vitamins B1, B2, B3, A
What is the pathogenesis of zinc deficiency in swine?
Diets high in phytic acid bind to zinc and form insoluble complexes, reducing zinc absorption
High levels of calcium can also decrease zinc bioavailability
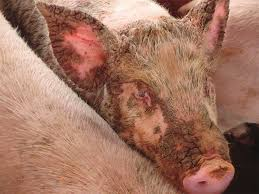
What is parakeratosis in growing pigs?
A condition where red patches of skin become dry, crack, form a crust, and are accompanied by alopecia and diarrhoea
What does zinc deficiency in adults cause?
Reproduction failure
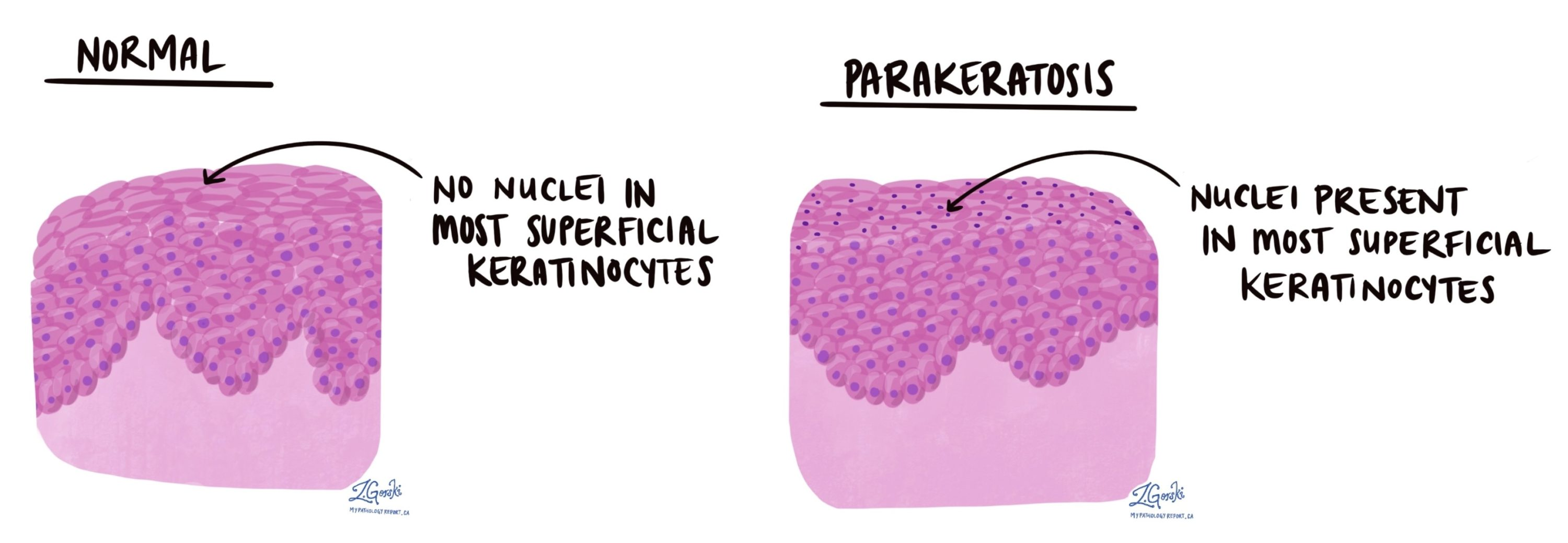
What is the difference between parakeratosis and hyperkeratosis?
Parakeratosis is a disorder of keratinisation where cells retain their nuclei
Hyperkeratosis is the excessive thickening of the stratum corneum due to increased keratin production
What are the clinical signs of iron and copper deficiency in newborn piglets?
Pale skin and mucous membranes, dull bristled hair, alopecia, decreased mobility, rapid breathing, and huddling
What is the treatment for iron and copper deficiency in piglets?
200 mg iron dextran injection (2 ml) IM at days 3-5
OR orally on days 7, 10, and 15
What is the main essential fatty acid for pigs?
Linoleic acid is needed for production of essential long-chain FAs.
What is the main consequence of fat deficiency in growing pigs?
Hair loss, scaly dermatitis, skin necrosis on the neck and shoulders, and an unthrifty appearance
What are the clinical signs of fat deficiency in sows and piglets?
Dry skin, weight loss during lactation, poor growth in piglets
What are the clinical signs of selenium deficiency in swine?
Skin lesions including alopecia
What are the symptoms of salt deficiency in growing pigs?
Poor growth, decreased feed and water intake, and poor hair and skin
What are the symptoms of vitamin B1 (thiamine) deficiency in swine?
Excessive alopecia
Skin ulceration and dermatitis
Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth
Transverse hoof cracking
Bleeding foot pads causing lameness
Infertility and anoestrus in sows
What are the symptoms of vitamin B2 (riboflavin) deficiency in growing pigs?
Slow gain, poor appetite, rough coat, skin exudates, cataracts, poor growth

What are the symptoms of vitamin B2 (riboflavin) deficiency in adult pigs?
Impaired reproduction, post-pubertal gilts fail to cycle but show no other clinical signs, anorexia, farrow dead piglets 4-16 days premature → have little hair, are often partially resorbed, may have enlarged forelegs
What are the clinical signs of vitamin B3 (niacin) deficiency in young and older pigs?
Young pigs: poor growth, diarrhoea
Older pigs: dermatitis on ears, rough skin, paralysis, inflammatory lesions on the dorsum, decreased body weight, severe stomatitis (black tongue)
What are the symptoms of vitamin A (retinol) deficiency in pigs?
Dry coat, split hairs, seborrheic dermatitis, hyperkeratosis, anophthalmia, and microphthalmia

What are examples of physical skin diseases in swine?
Physical skin injuries
Pressure sores (adults)/skin necrosis (piglets)
Photosensitisation
Sunburn
Frostbite
What causes physical skin injuries in swine?
Fighting, biting, and rubbing against sharp materials such as barbed wire or sharp fences
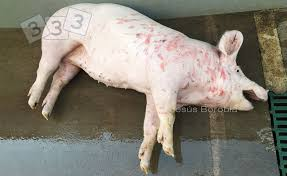
What causes pressure sores in adult sows?
Lying for prolonged periods, especially on the shoulders, leading to tissue damage, interrupted blood flow, and skin infections
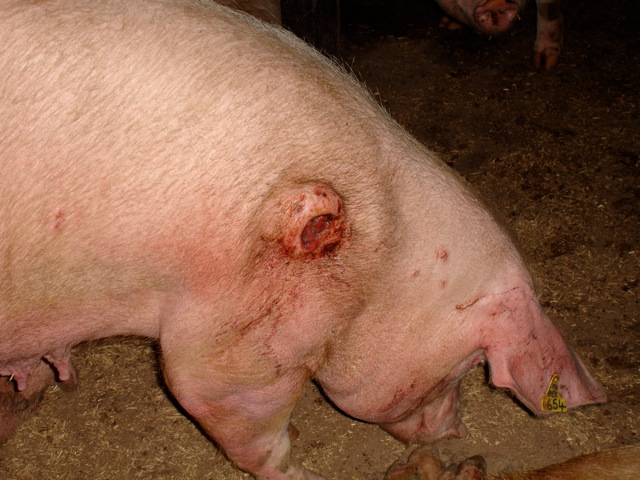
Where do piglets typically get pressure sores?
On concrete floors, often on knees and bony prominences, which may necrotise or become infected, potentially causing bacteraemia
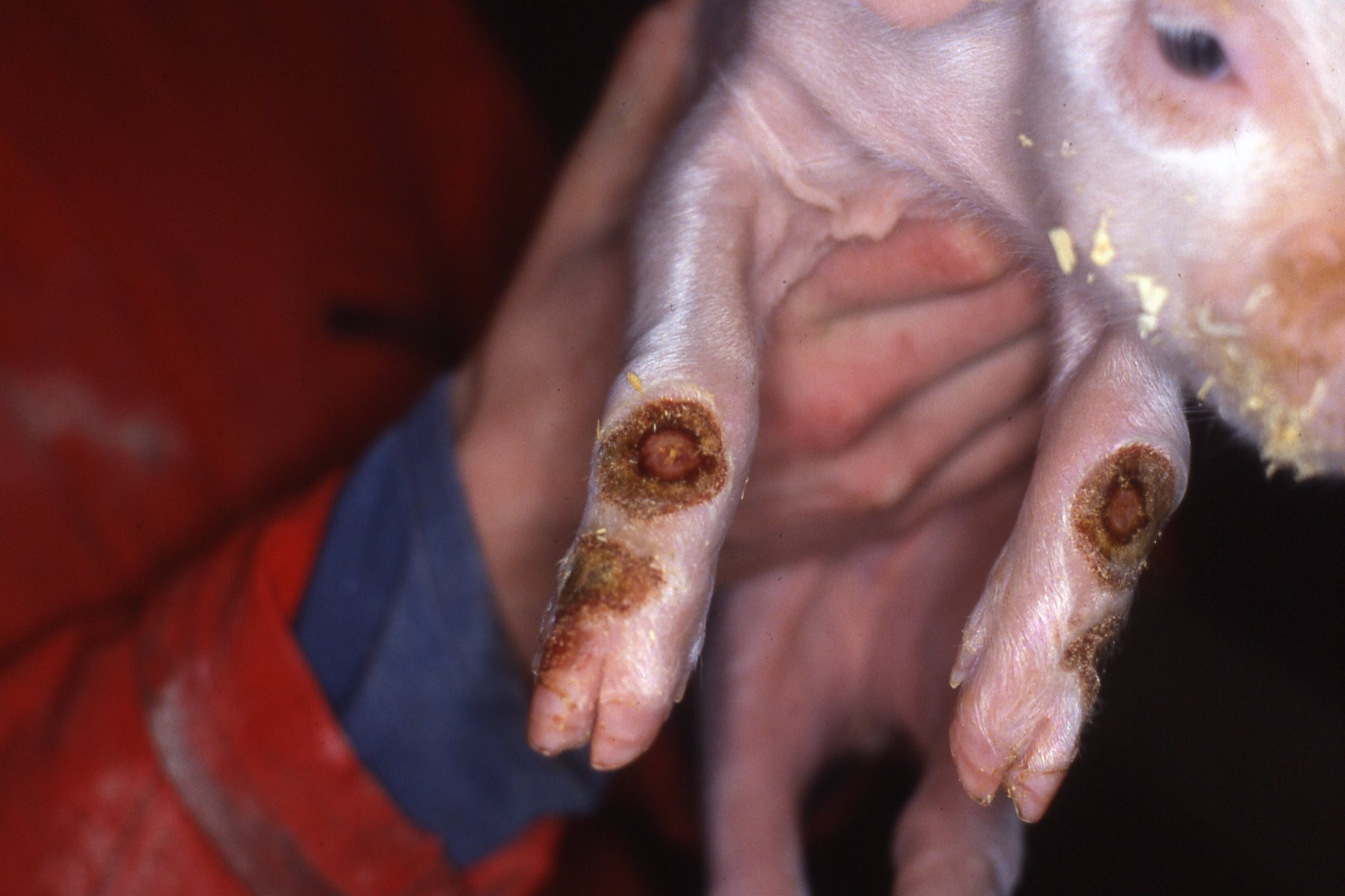
What is photosensitisation in pigs?
A hypersensitivity where the skin reacts excessively to sunlight
What is the aetiology of photosensitisation?
Ingestion of photodynamic agents: alfalfa clover, oats, rape seeds.
Long-term treatment w/ tetracyclines, sulphonamides.
Accumulation of phylloerythrin in plasma due to impaired hepatobiliary excretion.
Possibly hereditary
What are clinical signs of photosensitisation?
Reddening/erythema of skin, oedema, vesicles, necrosis, crusting, ulceration
How is photosensitisation diagnosed?
CS, history of drugs & diet
Liver enzymes – AST, GGT, total bilirubin
USG, liver biopsy
What is the treatment for photosensitisation in swine?
Remove the source of the photodynamic agent, provide systemic antibiotics for secondary bacterial infections, and treat any underlying hepatic disease
What are the clinical signs of sunburn in pigs?
Red, edematous, hot, painful skin that may blister, most commonly affecting ears and back, particularly in white or light-coloured breeds during summer
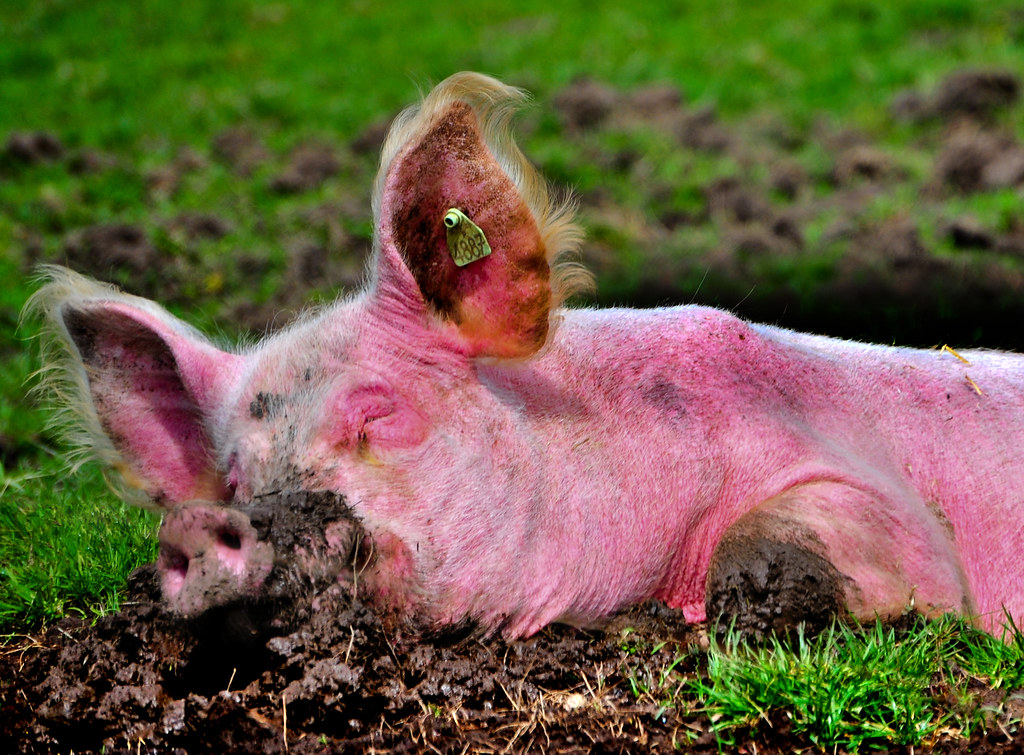

What is the treatment for sunburn?
Wound dressing. Provide shade, avoid prolonged sun exposure
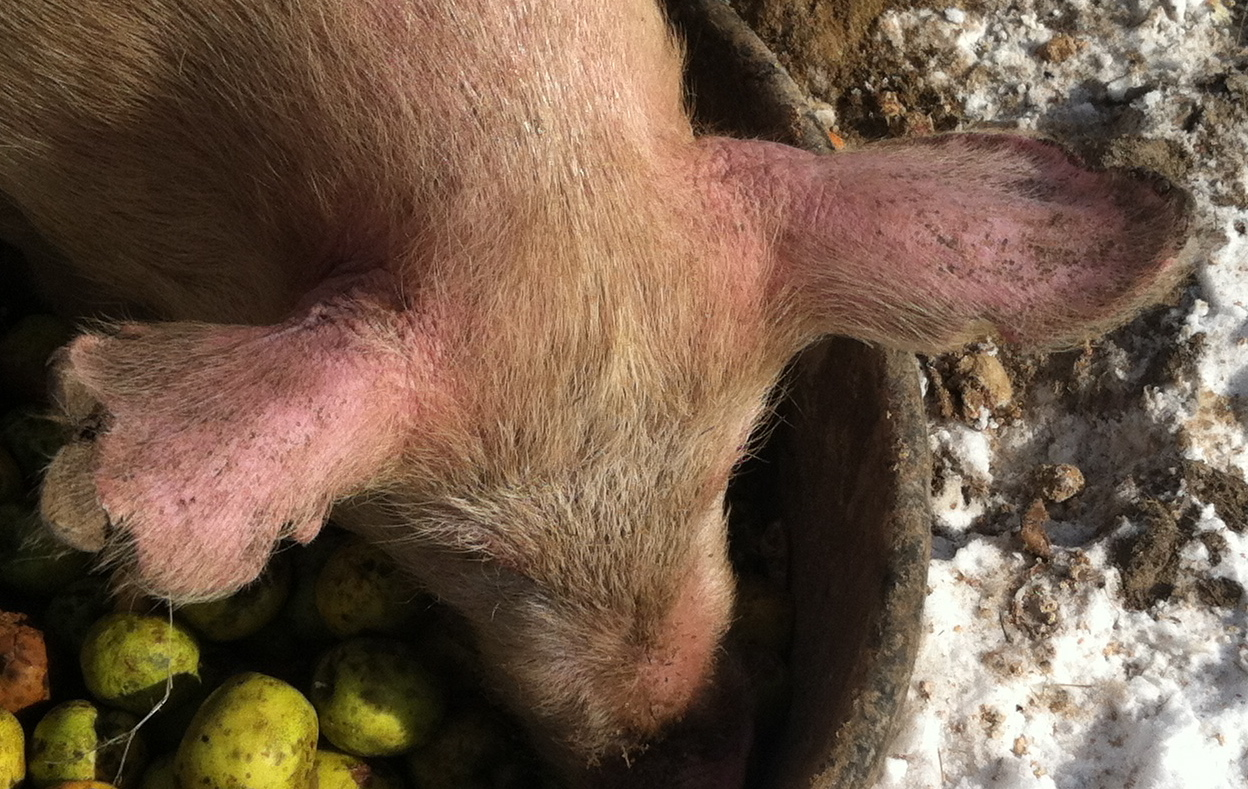
What is frostbite in swine?
A winter problem caused by excessive cold exposure leading to damage to the skin

What are examples of chemical skin diseases?
Primary irritant contact dermatitis
Poisoning
What is primary irritant contact dermatitis in swine?
Skin inflammation caused by exposure to caustics, crude oil, diesel fuel, sprays, plants, urine, vomit, or bedding
What are clinical signs of primary irritant contact dermatitis?
Erythema, ulceration of skin
What is the treatment for primary irritant contact dermatitis?
Remove chemical, disinfection, ATBs for secondary infection
What are the causes of poisoning dermatitis?
Chlorinated naphthalenes (used in insulation/building material - blistering but not used much anymore)
Chronic arsenic poisoning (hypo/hyperpigmentation, keratosis)
Hypervitaminosis A (dry flaky skin)
What are the clinical signs of dermatitis caused by poisoning in swine?
Dry, scaly, thickened skin, corrugated appearance, hair loss, fissure formation, and possible secondary infection
What is the treatment for poisoning-related skin issues in swine?
Correct the underlying cause and use keratolytic agents to remove crusts
What clinical signs are seen in black pigs with Erysipelas?
Raised lesions can be felt by hand