hydrology
1/285
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
286 Terms
What drives the hydrologic cycle?
Solar Energy
Let’s say three different regions, a city, a farmland and a dessert has same acreage (and each of them are a watershed of their own). Now, if a rainfall event with P mm precipitation occurs in these three locations, which one would have the maximum runoff?
The City
The Farmland
The Desert
The City
Let’s assume that in a certain watershed, 1/3rd of annual rainfall contributes to surface runoff, evapotranspiration, and groundwater recharge each. What type of climatic condition you would say the watershed is in?
Humid
Arid
Semi Humid
Semi Arid
Humid
The fraction of precipitation that leaves a watershed as streamflow is called:
Runoff Ratio
What is the approximate change in runoff when an area changes from natural ground cover to 35%-50% impervious surface? (refer to the approximate percentages based on the lecture slides)
+20%
What is the approximate change in shallow infiltration when an area changes from natural ground cover to 75%-100% impervious surface? (refer to the approximate percentages based on the lecture slides)
-15%
What is the approximate change in runoff when a town returns an abandoned industrial area back to a park with native vegetation, changing the neighborhood from 75%-100% impervious surface back to 35%-50% impervious surface? (refer to the approximate percentages based on the lecture slides)
-25%
What is the order of difference in residence time between water in a river channel and in swamps?
Years
Mark if the statement is true or false:
The actual evapotranspiration is always greater than the potential evapotranspiration.
False
What could be the most likely cause that a site has a higher actual evapotranspiration compared to the precipitation:
Irrigation
Groundwater recharge is possible during the winter months, even-though there is not much rainfall because the snowmelt infiltrates the soil in pervious regions. (T/F)
True
If Hurricane Harvey occurred during 1996, how less would have been the depth of resulting runoff (flood depth) compared to 2017?
0.75 inches
0.25 inches
1.50 inches
2.75 inches
2.75 inches
Estimate the relative change in runoff for the New River (runoff ratio w = 0.10), if climate change results in a 15% increase in precipitation and a 15% decrease in evaporation.
3.85
True or False: The number of floods, and associated human and economic losses in the US are decreasing due to climate change and urbanization.
False
Increasing the elevation to the pour point for grid cells completely surrounded by higher terrain is called
pit filling
Which of the following can distinguish a drainage basin?
Wind patterns
Groundwater flows
Topography
Vegetation
Topography
How many HUC-8 regions is Blacksburg a part of?
2
Which of the following statements is True?
Higher flow accumulation values are ridge tops
Lower flow accumulation values are valleys & stream channels
Flow direction is only calculated for the cells with the steepest descent
Flow direction is calculated as the direction of steepest downward descent
Flow direction is calculated as the direction of steepest downward descent
Which of the following statements is false?
Water flows along the steepest descent
Streamlines flow towards drainage divides and intersect them
Water flows perpendicular to elevation contour lines
Topographic maps show lines of equal elevation
Streamlines flow towards drainage divides and intersect them
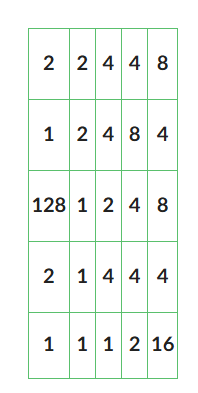
According to the following eight direction pour point model, what cell does the water flow out of? Identify the cell as (row, column) with the bottom left corner being (1,1) and the top right corner being (5,5).
(1,4)
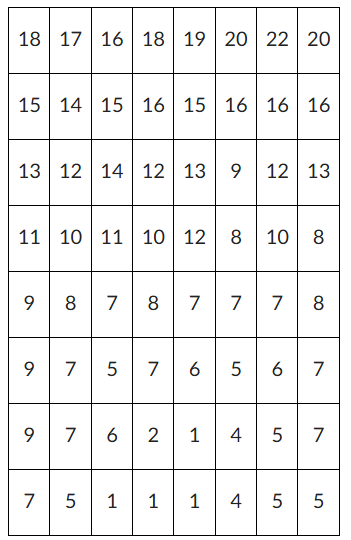
Use the following DEM elevation map for this question. Elevations are given in meters (m) and the map has a 30m resolution (each square is 30m by 30m). What is the slope of cell (5,2) to the cell that it drains to? Identify the cells as (row, column) with the bottom left corner being (1,1) and the top right corner being (8,8). Hint: Cell (5,2) has an elevation of 10m. (If the image does not show up, try clicking the link next to it).
0.071
According to the Strahler Stream Order, what order stream is created when a 2nd order and 3rd order stream meet?
3rd
A ________________ based on flow accumulation or grid order is needed to define a stream network.
threshold
Why is it a fundamental rule in topographic mapping that contour lines do not intersect?
It ensures that one point doesn’t have multiple elevations at the same time.
In the Strahler stream order system, when two streams of the same order come together, what is the order of the resulting stream?
It increases by 1
Which of the following methods is NOT commonly used to determine the boundary of a watershed?
Topographic maps
Flow accumulation
Groundwater Mapping
Aerial photography
Groundwater Mapping
Flow distance from each cell of the watershed to the outlet is defined as,
flow length
Which of these spatial methods would you expect to produce more accurate estimates for rainfall interpolated from point gages?
Inverse Distance Weighting Method
Both have the same level of accuracy
Artimetic Mean Method
Inverse Distance Weighting Method
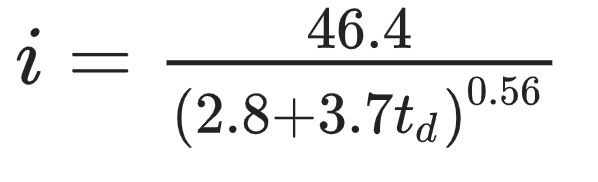
The IDF curve for 10-year storms in Raintown, Waterstate is given by
where i is the average intensity in inches/hr and td is the duration in minutes. Assuming that the maximum rainfall intensity occurs at 50% of the rainfall duration, estimate the triangular hyetograph for a 70-min storm. At what time (t ; measured in minutes from beginning of storm) does the peak rainfall intensity occur?
35

The IDF curve for 10-year storms in Raintown, Waterstate is given by
where i is the average intensity in inches/hr and t is the duration in minutes. Assuming that the maximum rainfall intensity occurs at 50% of the rainfall duration, estimate the triangular hyetograph for a 70-min storm. What is the peak intensity (i ) in inches/hr of the triangular hyetograph? Give answer rounded to one decimal
place.
4.1
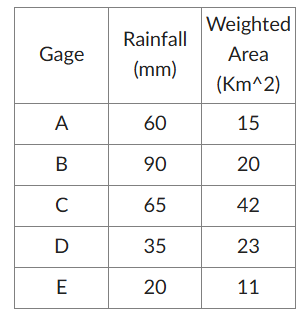
Calculate the spatially averaged rainfall for a watershed if there are five gages located inside the watershed using the Thiessen Polygon method. The area-weighted Thiessen polygon representative areas corresponding to each of the five rain gages and recorded rainfall are as follows:
58
Assuming all other factors stay the same, when the wind speed increases, the pan coefficient of evaporation ________________
stays the same
is negative
decreases
increases
decreases
Select the correct statement:
Rainfall is uniform over across space and time in a watershed
On average, snow/snow melt events deliver more volume to soils compared to rain only events
Accurate ET modeling is more important for event based modeling than continuous modeling
NRCS Type II distributions are applied over a minority percent coverage over the US
On average, snow/snow melt events deliver more volume to soils compared to rain only event
Answer true or false:
A non-exceedance probability of 90% means that there is a 10% chance that a rainfall event of a magnitude would occur in any given year and this corresponds to an event of 10-year return period
True
One of the disadvantages of using the water balance method to estimate evaporation is that it _____________________.
combines measurement uncertainties
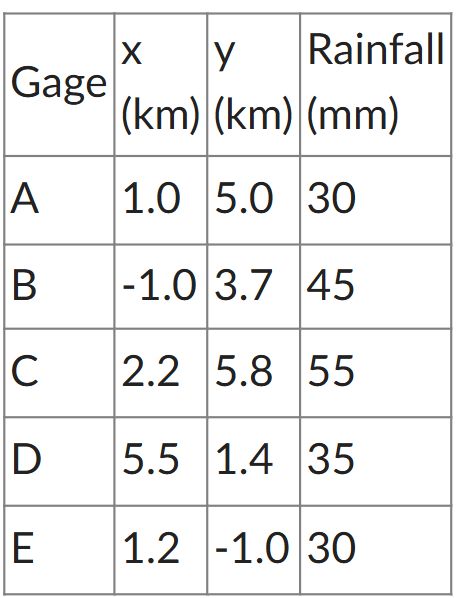
Calculate the spatially interpolated rainfall for a point P located at (1, 1) using the inverse distance weighting method using five gages. The coordinates of the five rain gages and recorded rainfall are as follows:
35
Which of the following does NOT impact interception loss.
Precipitation Depth
Forest Cover
Soil type
Canopy density
Soil type
When a soil is saturated then the water content is equal to the ___________
Porosity
Interception losses are ultimately _____________________.
evaporated
As the water content in the soil increases the absolute value of the pressure head ___________
decreases
If the infiltration capacity is higher than rainfall intensity, then the rate of infiltration will be equal to ___________________.
the rainfall intensity
By what percentage would the effective saturation increase if the moisture content of the soil changes from 0.3 to 0.46? Assume that the porosity is equal to 0.75 and the residual moisture content is equal to 0.07. Report the value in nearest integers.
70
Which of the following statements is false?
Horton model assumes infinite depth of vadose zone
Depression storage can reduce the onset time of runoff in a watershed
Green-Ampt method assumes a sharp wetting front
The pressure head in the saturated zone is hydrostatic
Depression storage can reduce the onset time of runoff in a watershed
Which of the following is not a parameter in Green-Ampt method calculations?
suction head
Datum head
Interception storage
porosity
Interception storage
Which of the following is false about the flow through soils?
The infiltration rate is affected by vegetation
The flow rate through porous media is inversely proportional to the area of medium
The difference between tension heads between wetting and drying is called hysteresis
Horton model assumes that infiltration tends to decrease in an exponential manner
The flow rate through porous media is inversely proportional to the area of medium
According to Darcy's Law, how will the flow change if the length and the hydraulic conductivity both increase?
depends
As the moisture content in a soil increases, the hydraulic conductivity, K:
increases
Which of the following is true:
The Horton's method assumes that the soil has a fixed depth up to the water table.
The infiltration rate in Hortons method increases exponentially with time.
The Green Ampt method assumes a sharp wetting front dividing the saturated and unsaturated soil.
Sorptivity is the rate at which water is drawn out of a soil
The Green Ampt method assumes a sharp wetting front dividing the saturated and unsaturated soil.
Of the infiltration models, which is a fully empirical model?
Green-Ampt Model
NRCS Curve Number Method
Horton's Equation
Philip's Equation
NRCS Curve Number Method
If the antecedent runoff condition for a watershed has been Dry recently, would you expect the runoff, Q, to increase or decrease compared to moderate conditions?
decrease
According to the NRCS Curve Number Method, if a dirt road is soil group C and is in antecedent runoff condition III (wet), what would be the initial abstraction with a rainfall depth of 0.3 in? Enter you answer in three decimal places.
0.129
According to the NRCS Curve Number Method, if a dirt road is soil group C and is in antecedent runoff condition III (wet), what would be the depth of the runoff (Q) with a rainfall depth of 0.3 in and an initial abstraction of 0.128? Enter you answer in three decimal places.
0.036
Would the runoff calculated in question 3 and 4 be considered accurate (using the NRCS Curve Number Method)?
depends on several factors
What is the lag time of a hydrograph?
excess precipitation centroid to peak discharge
How is time of concentration measured on a hydrograph?
end of excess precipitation event to the inflection point of the recession limb
Using the constant slop method for a given storm hydrograph, does the baseflow increase or decrease during the storm?
Increases
If a given area's land cover increases the impervious area and all other factors remain the same, how would the lag time change for the same storm?
decrease
What are the main components of a water budget?
Precipitation, evaporation, transpiration, streamflow, groundwater inflow/outflow, soil storage, and human uses
What does residence time represent?
The average time water spends in a subsystem of the hydrologic cycle.
What is the residence time of atmospheric water?
Approximately 8.2 days
Which water reservoir has the longest residence time?
Ice caps, glaciers, and permafrosts (1,000 to 10,000 years)
How does rapid development affect flood risk
Increases runoff and decreases subsurface storage, raising flood risk
What assumptions are made in long-term water balance models?
Groundwater discharge and change in storage are negligible
What does the steady-state assumption imply?
No change in storage over time
Why is the runoff ratio limited?
It varies with soil moisture, precipitation rate, and interception.
What is a watershed?
A region draining into a river, river system, or body of water; defined by a drainage point and its upstream area.
catchment
The surface water portion of a watershed that drains to a single outlet
drainage divide
A topographic barrier (e.g., ridge or hill) that separates adjacent drainage basins
drainage area
horizontal projection of the area contributing flow to a point in a stream
What does HUC stand for?
Hydrologic Unit Code – a system for classifying watershed scales
List the HUC levels from largest to smallest.
HUC2 (region) → HUC4 (subregion) → HUC6 (basin) → HUC8 (subbasin) → HUC10 (watershed) → HUC12 (sub-watershed)
Are watersheds nested?
Yes, smaller watersheds are nested within larger ones
Classification where first-order streams have no tributaries; stream order increases at confluence
Should be in high-flow pathways and converted to grid layer
Assumption in DEM-based delineation
Water flows downhill and each cell has a defined flow path