Organization and Management Exam 3: Cedarville University
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Organizational Structure
Vertical and horizontal configuration of departments, authority, and jobs within a company
Organizational Process
Collection of activities that transform inputs into outputs that customers value
Departmentalization
Method of subdividing work and workers into separate organizational units responsible for completing particular tasks
Methods of Departmentalization
Functional, product, customer, geographic, matrix
Functional Departmentalization
Typically young or small orgs - units are responsible for particular business functions
Product Departmentalization
Units are responsible for producing particular products or services
Customer Departmentalization
Units are responsible for particular kinds of customers
Geographic Departmentalization
Units are responsible for doing business in particular geographic areas
Matrix Departmentalization
Hybrid organizational structure (2+)
Centralization
Most of the authority is located at the upper levels of the organization. Managers make most decisions, even the relatively small ones
Decentralization
A significant amount of authority rests in the lower levels of the organization. Workers closest to problems are authorized to make decisions
Product Departmentalization Disadvantages
-Duplication
-Coordination across different product departments
Standardization
Solving problems by consistently applying the same rules, procedures, and processes
Authority
The right to give commands, take action, and make decisions to achieve organizational objectives
Chain of Command
Vertical line of authority that clarifies who reports to whom throughout the organization
Unity of Command
Principle that workers should only report to one boss/manager
(does not apply in matrix organization)
Delegation of Authority
Assignment of authority and responsibility to a subordinate to complete a manager's tasks
Line Function
Activities related directly to creating or selling the company's products
Organizational Processes
-Intraorganizational (within)
-Interorganizational (between)
Mechanistic Organizations
Stable, unchanging business environments
Structure
Characterized by specific jobs and responsibilities
Organic Organizations
Increasingly dynamic environments
Reengineering
Fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business
Modular Organizations
Outsource non core business activities to outside companies
Virtual Organizations
Network of independent companies that work together
(Temporary/Task oriented)
Work Teams
Small number of people with complementary skills who hold themselves mutually accountable for pursuing a common purpose, achieving performance goals, and improving interdependency
Advantages of Teams
-Focus on specific customers can increase customer satisfaction
-Improve product and service quality
-Increase speed and efficiency in product development
-Increase job satisfaction (Cross Training)
-Share benefits of group decision making (Multiple Perspectives)
Disadvantages of Teams
-Initial high turnover
-Social loafing
Disadvantages of Group Decision Making
-Groupthink: Members of highly cohesive teams feel the pressure not to disagree with each other
-Member Domination: One or two people dominate group discussions
Autonomy
The degree to which workers have the discretion, freedom, and independence to decide how and when to accomplish their jobs
Kinds of Teams Based on Autonomy
-Traditional Work Groups/Teams
-Employment Involvement
-Semi-autonomous Work Teams
-Self Managing Teams
-Self Designing Teams
Special Kinds of Teams
-Cross-functional Teams
-Virtual teams
-Project teams
Work Team Characteristics
-Norms
-Cohesiveness
-Size
-Conflict
If standardization is important, organization MAY want to stay centralized
True
One of the disadvantages associated with product departmentalization is costly...
Duplication
Social loafing is defined as a team member failing to perform because of a lack of laziness
False
Team Norms
Informally agreed-on standards that regulate team behavior
Team Cohesiveness
Extent to which members are attracted to the team and motivated to remain in it
Team Size
-6-9 members
-Should be small enough for members to get to know each other and feel comfortable contributing
Greater Team Size
Opposes the risk of domination
Team Conflict
Arises from disagreement over team goals
Types of Conflict
Cognitive (c-type): Focuses on problem related differences of opinion (Functional/Constructive)
Types of Conflict
Affective (a-type): Emotional reactions that occur due to personal disagreement (Dysfunctional/Destructive)
Enhancing Work Team Effectiveness
- Setting Team Goals & Priorities
- Setting Specific Team Goals
- Setting Challenging Goals
- Setting Stretch Goals
Types of Employee Compensation
Skill-Based Pay: employees are paid for learning additional skills or knowledge.
Types of Employee Compensation
Gainsharing: companies share the financial value of performance gains with their workers.
Types of Employee Compensation
Non-financial Rewards: most effective when teams or team-based interventions are first introduced.
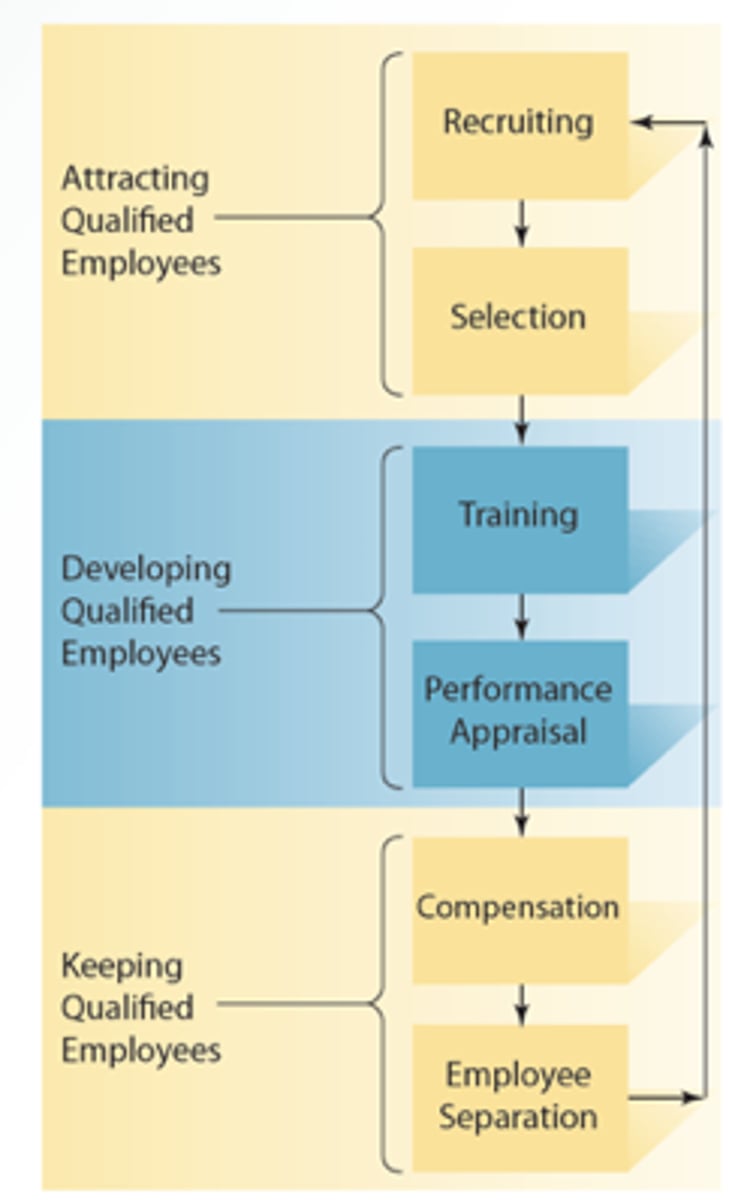
Human Resource Management
Process of finding, developing, and keeping the right people to form a qualified work force
Adverse Impact
Unintentional discrimination that occurs when members of a particular race, sex, or ethnic group are unintentionally harmed or disadvantaged because they are hired, promoted, or trained (or any other employment decision) at substantially lower rates than others
Disperate Treatment
Intentional discrimination that occurs when people are purposely not given the same hiring, promotion, or membership opportunities because of their race, color, sex, ethnic group, national origin, or religious beliefs
Sexual Harassment
Form of discrimination in which unwelcome sexual advances, requests for sexual favors, or other verbal or physical conduct of a sexual nature occurs
Quid pro quo
This for that
Recruiting
Process of developing a pool of qualified job applicants
Job Analysis
Purposeful, systematic process for collecting information on the important work-related aspects of a job
Job Description
Responsibilities of an employee
Job Specification
Qualifications needed to successfully perform a job
Internal Recruiting
Process of developing a pool of qualified job applicants from people from within the company
(Job posting, word of mouth, direct approach)
External Recruiting
Process of developing a pool of qualified job applicants from outside the company
(Advertising, employee referrals, walk-ins, internet job sites, social media, etc)
Selection
Process of gathering information about job applicants to decide who should be offered a job
Validation
Process of determining how well a selection test or procedure predicts future job performance
Topics to Avoid in an Interview
-Children
-Age
-Disabilities
-Physical Characteristics
-Citizenship/arrested
Unstructured Interviews
Interviews in which interviewers are free to ask the applicants anything they want
Structured Interviews
All applicants are to ask the same set of standardized questions
Training
Providing opportunities for employees to develop the job-specific skills, experience, and knowledge they need to do their jobs or improve their performance
Needs Assessment
Process of identifying and prioritizing the learning needs of employees
Performance
Process of assessing how well employees are doing their jobs
Compensations
Financial and non financial rewards given to employees in exchange for their work
Job Evaluation
Determines the worth of each job in a company
(Helps to set pay structures)
Pay-Level
Decisions related to paying workers below, above, or at current market wages
Pay Variability
Decisions related to linking pay to organizational performance
Pay Structure
Decisions related to employees receiving different levels of pay
Employee Separation
Involuntary or voluntary loss of an employee
Downsizing/Layoffs
Planned elimination of jobs
Retirement
Early retirement/Phased retirement
Employee Turnover
Employees choose to leave the company
Diversity
Variety of demographic, cultural, and personal differences among an organization's employees and customers
Affirmative Action
Refers to purposeful steps taken by an organization to create employment opportunities for minorities and women... eliminating unlawful discrimination
Affirmative Action
Required by law for private employers with 50 or more employees and federal contracts of $50,000 or more
Purpose for Affirmative Action
Create a positive work environment where no one is advantaged or disadvantaged
Diversity is NOT Affirmative Action
True, they are related but not the same
Surface Level Diversity
Differences that are observable, typically unchangeable, and easy to measure
Deep-Level Diversity
Differences are communicated through verbal and nonverbal behaviors and learned only through extended interaction with others
Studies show that getting to know and understand each other reduces prejudice and conflict
True
Social Integration
Degree to which group members are psychologically attracted to working with each other to accomplish a common objective
Personality
Relatively stable set of behaviors, attitudes, and emotions
Big Five Personality Dimensions
-Extraversion (Extroversion)
-Emotional Stability
-Agreeableness
-Conscientiousness
-Openness to Experience
Skills-Based Diversity Training
Teaches employees the practical skills they need for managing a diverse work force
Awareness Training
Designed to raise employees' awareness of diversity issues and to challenge underlying assumptions or stereotypes we may have about others
Diversity Audits
Formal assessments that...
-Measure employee and management attitudes
-Investigate the extent to which people are advantaged or disadvantaged with respect to hiring and promotions
-Review companies' diversity-related policies and procedures
Diversity Pairing
People of different cultural backgrounds, sexes, or races/ethnicities are paired for mentoring
What does Scripture say?
-Be proactive
-Carefully and faithfully following and enforcing federal and state laws
-Treat differences as important but not special
-Finding the common ground
CH11 Common Theme
Human Resource Chart
Human Resource Management Process