Hemorrhage and Thrombosis
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
hemorrhage and thrombosIS
failure of hemostatis leads to _________ or ________________
hemorrhage
_________________: Extravascular loss of blood
thrombosis
_____________: Inappropriate formation of intravascular clots
(pulmonary) hemorrhage
What?
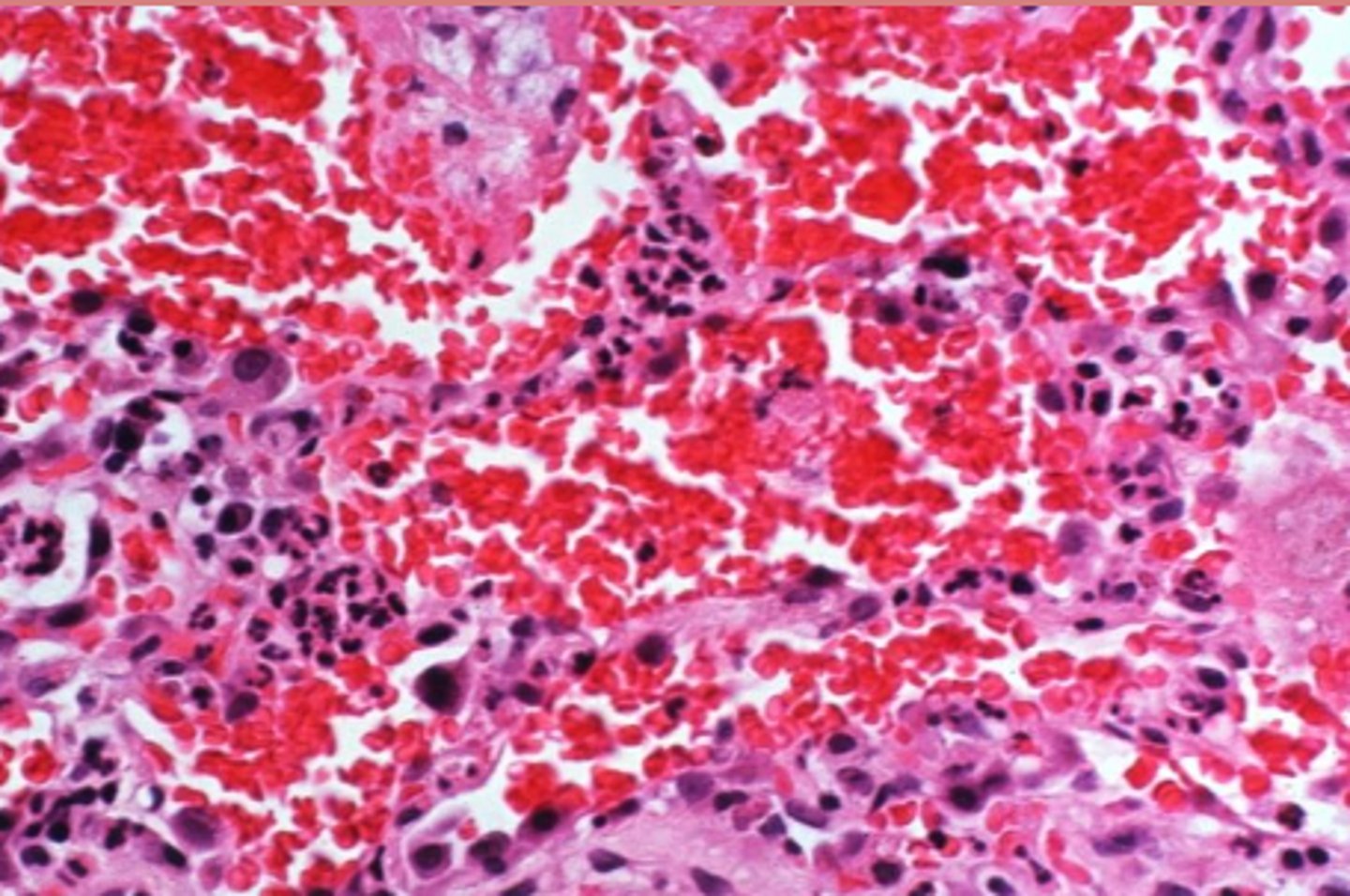
(pulmonary intravascular) thrombosis
what?
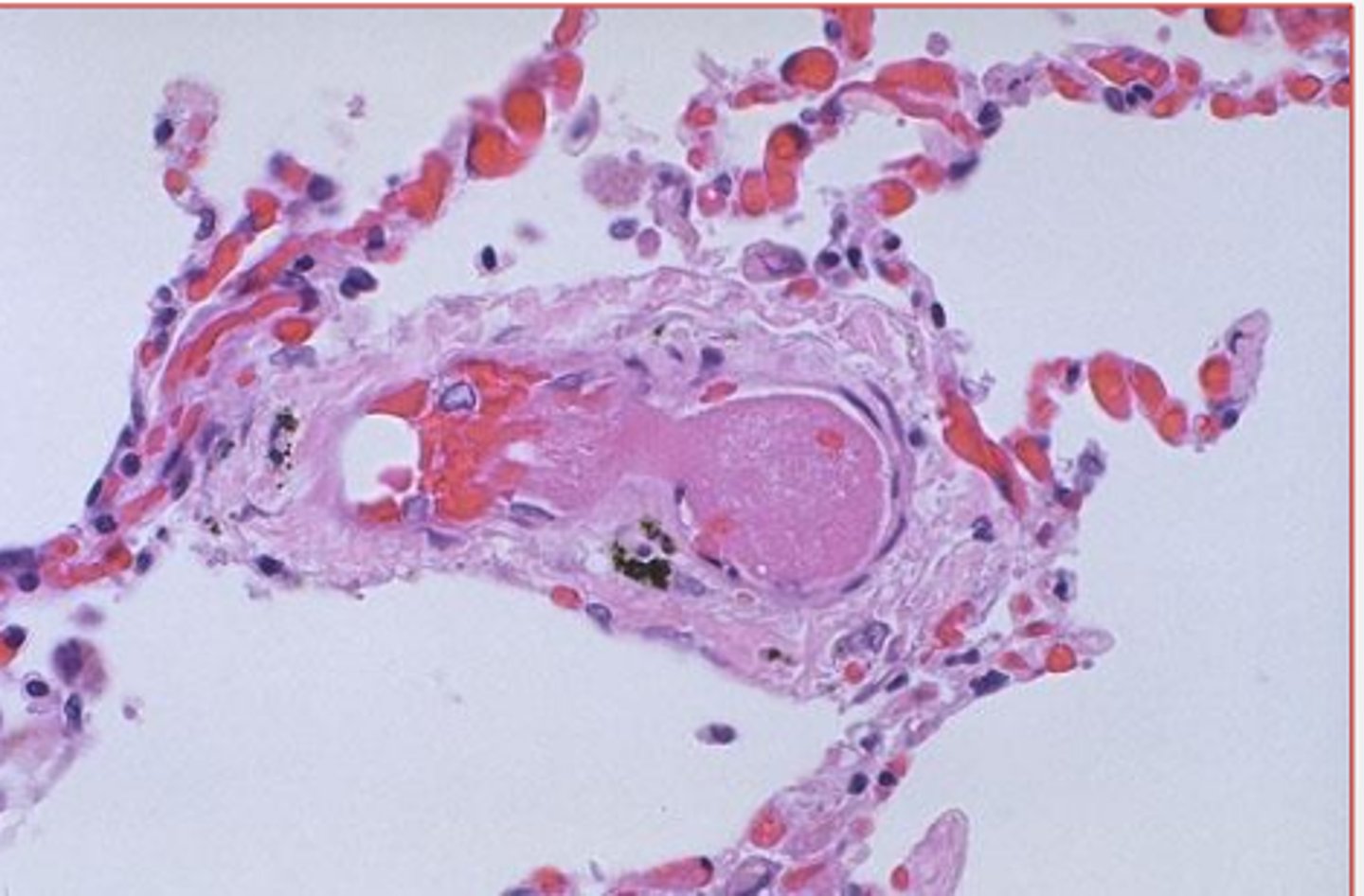
rhexis
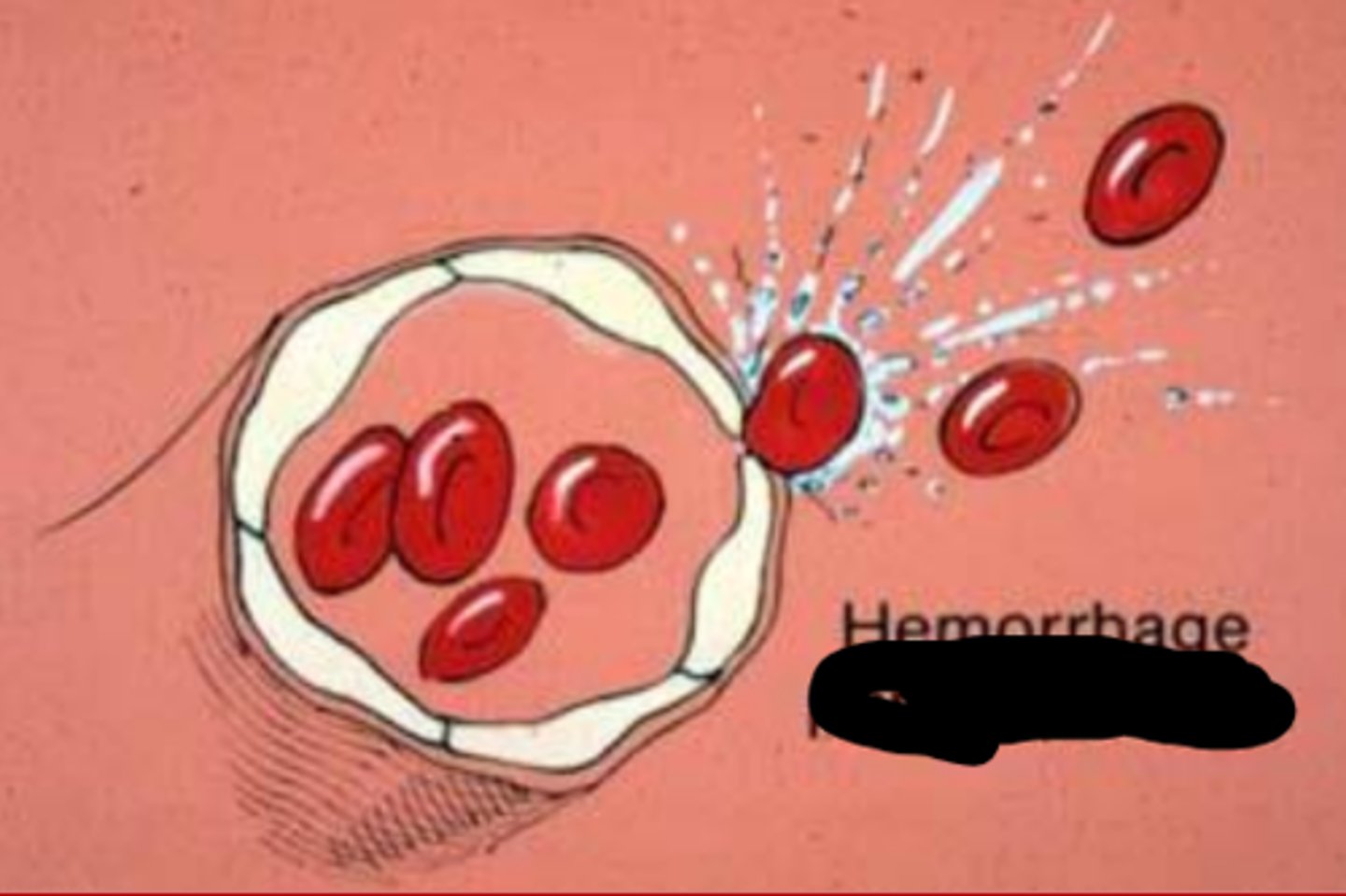
Hemorrhage by "breaking forth, bursting"
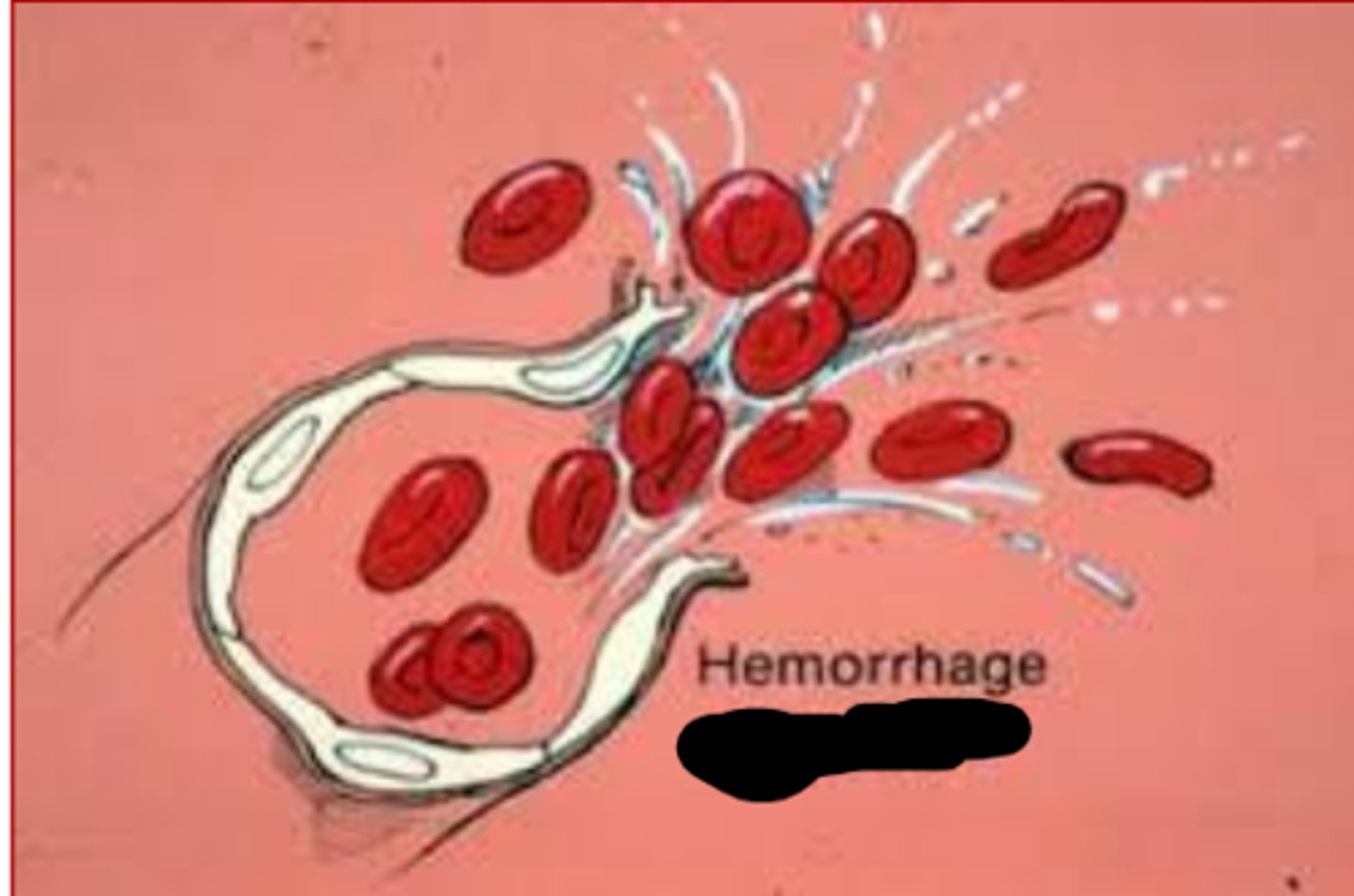
diapedesis
Hemorrhage by "leaping through" or squeezing out of vessels
cause, location, severity
WHat determines what a hemorrhage looks like
petechia
If blood spots are roughly 1-2 mm they are called _____________
purpura
If blood spots are roughly 3 mm - 1 cm they are called _____________
ecchymosis
If blood spots are roughly 1-3 cm they are called _____________
petechia
what type of blood spot on this kidney?
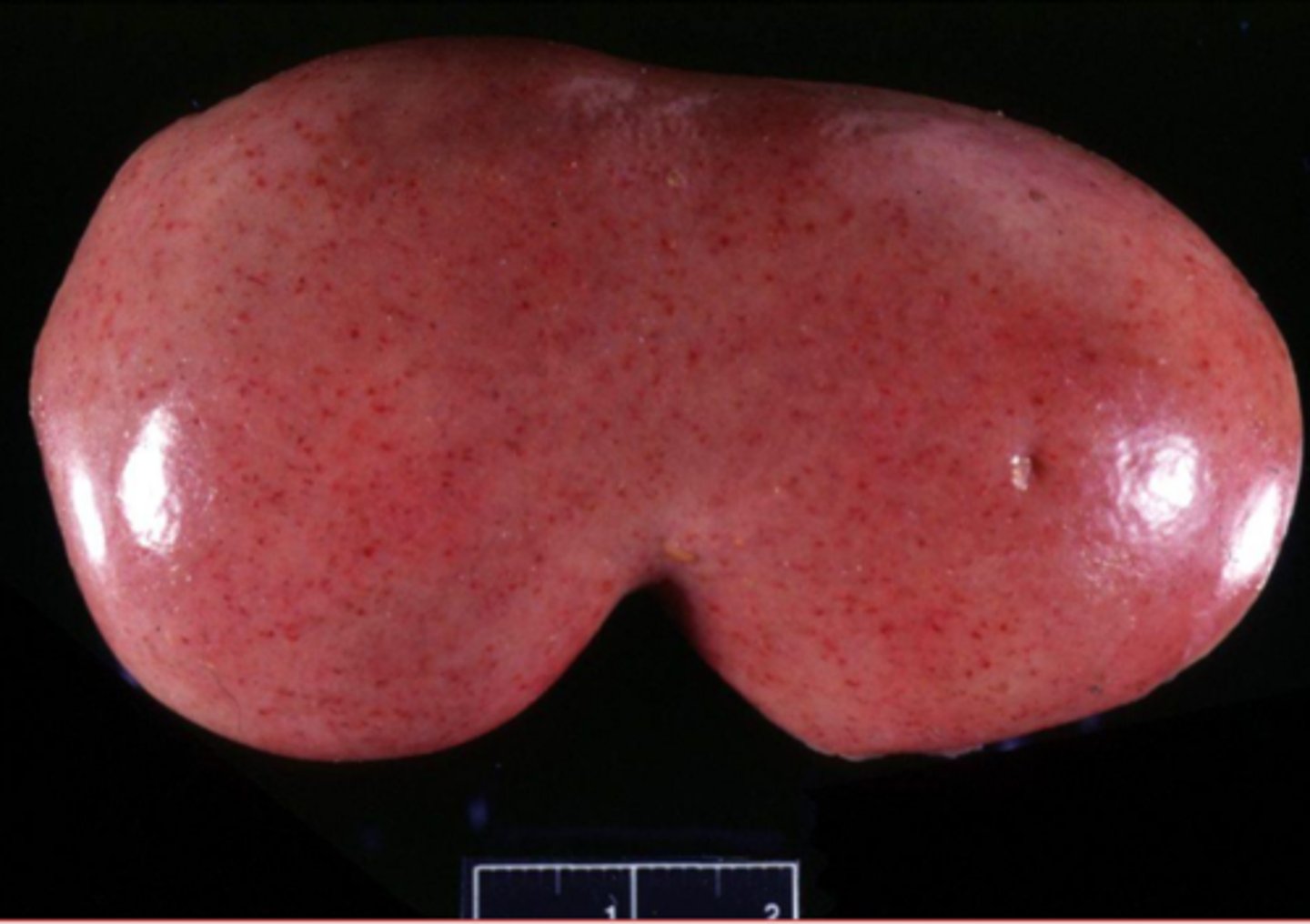
ecchymosis
What type of blood spot on this kidney?
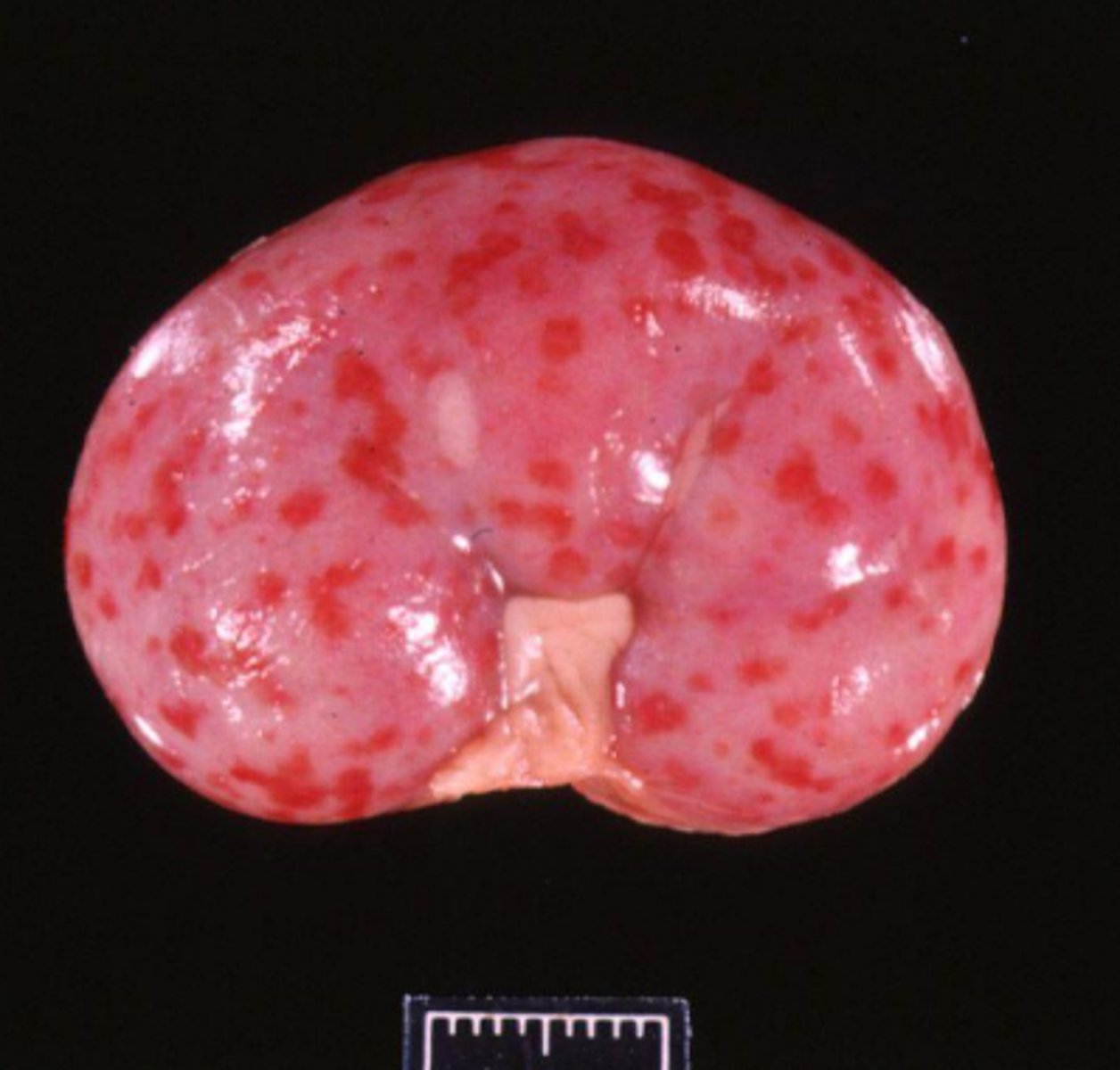
suffusive hemorrhage
________________Larger continuous areas of hemorrhage
hematoma
______________: focal, confined hemorrhage
hemo-
what prefix do we tend to use to describe a blood filled cavity?
until extravascular pressure matches the pressure in the vessel
How long do hematomas continue to grow?
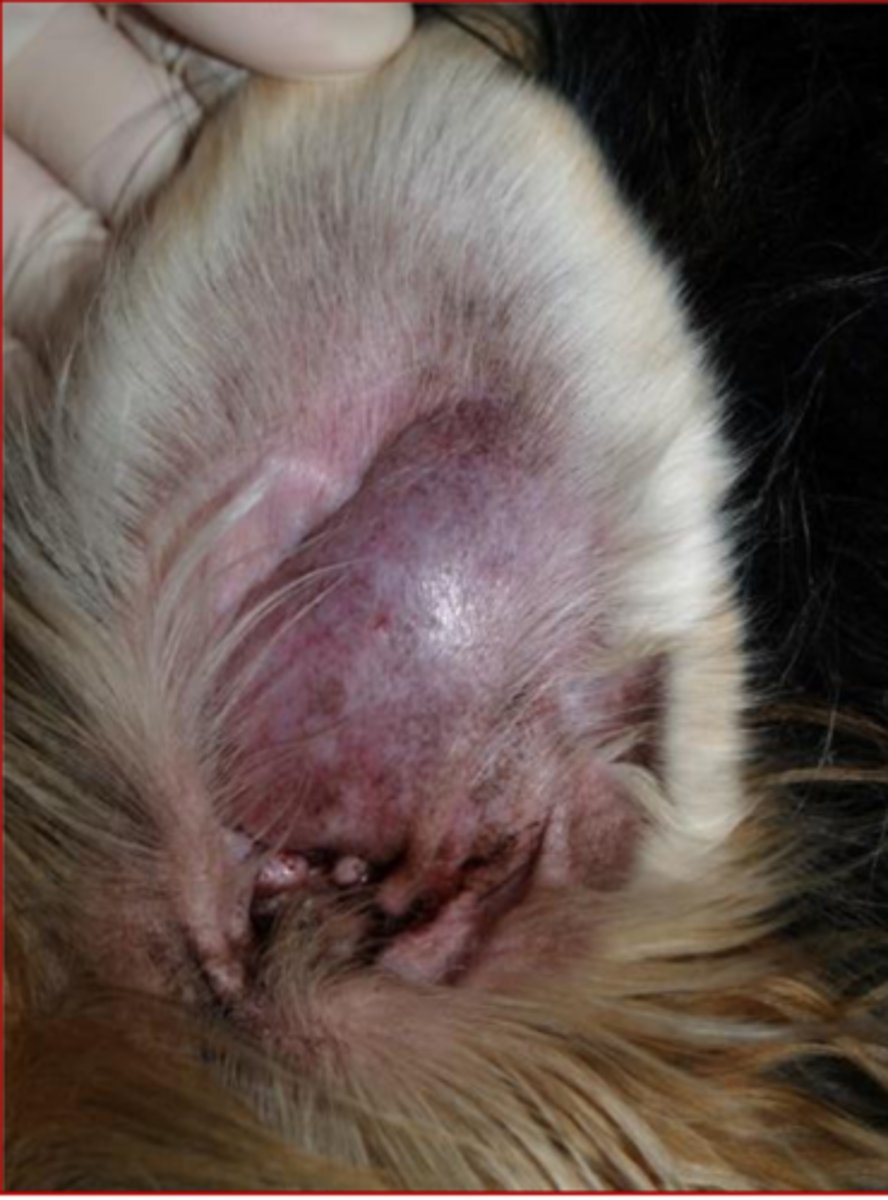
aural hematoma
What?
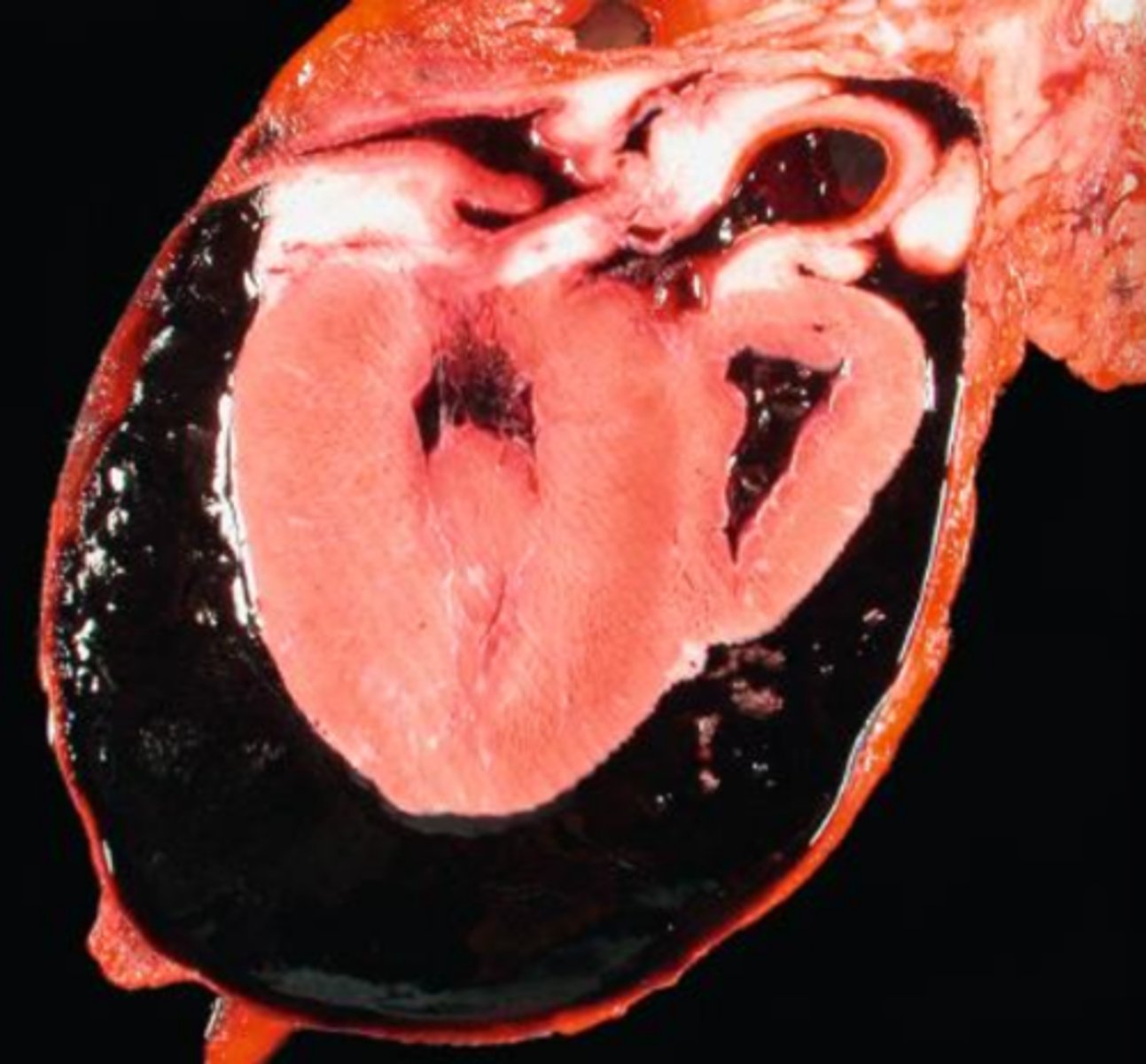
hemothorax
what?
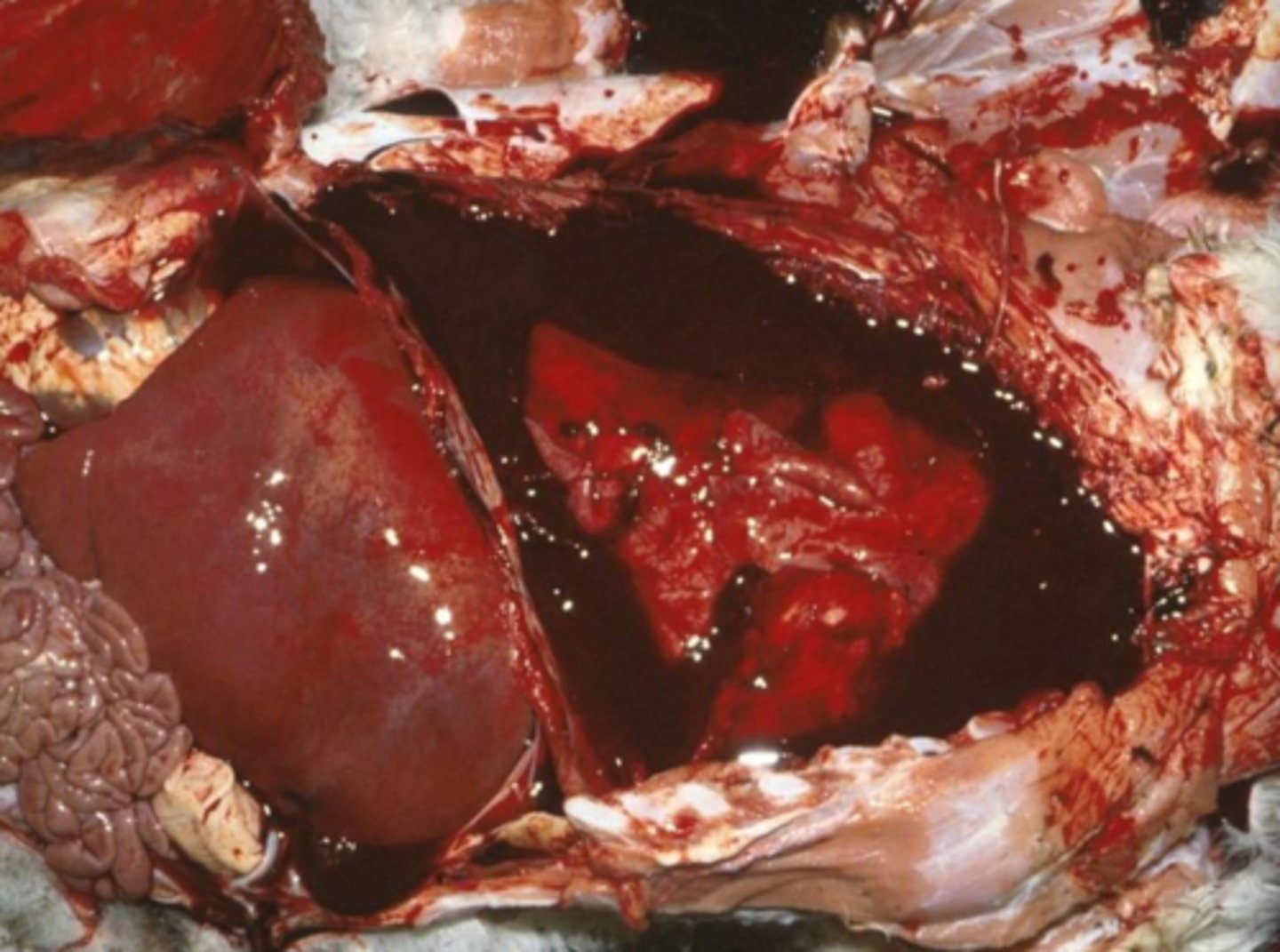
hemopericardium
What?
petechiae and ecchymoses
hemorrhage by diapedesis results in _______ and ______________
cutaneous petechiae and ecchymoses
what?
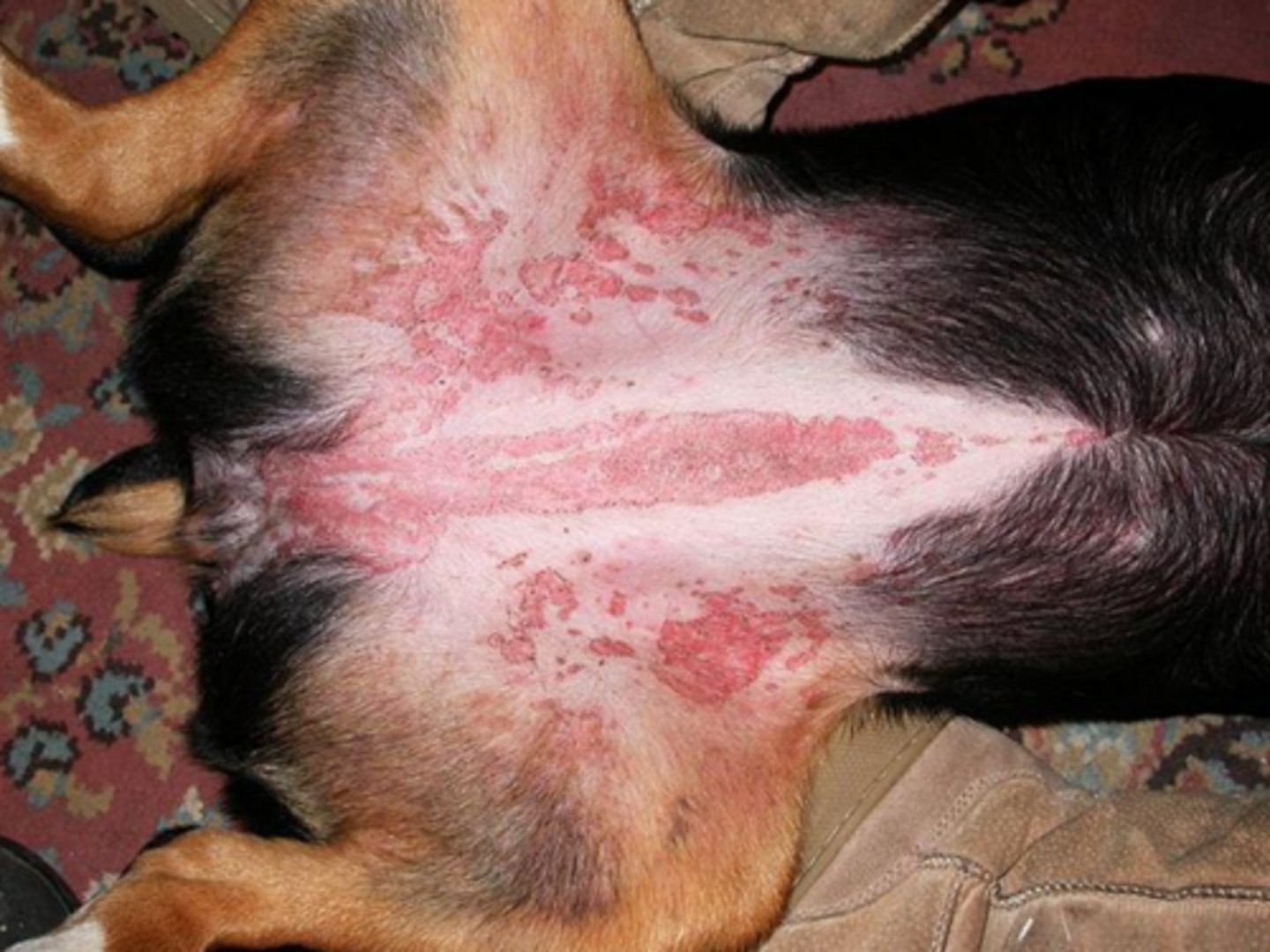
minor defects (endothelial damage); defects of primary hemostasis (platelet defects, von Wilebrand disease)
What can cause hemorrhage by dispedesis?
trauma, extensive damage by infectious damage
what can cause hemorrhage by rhexis?
endothelial cells, coagulation factors, platelets
Abnormal function of what leads to hemorrhage? (3)
Trauma, inflammation, Infectious Disease, Genetic Disorders, Nutritional Disorders
What are some causes of hemorrhage in the blood vessels?
trauma
_____________: hemorrhage due to Physical disruption of blood vessel wall
type III hypersensitivity, feline infectious peritonitis, (FIP is Type IV)
If blood vessels begin to lead rbcs due to inflammation, what type of reaction are we looking at? WHat are specific examples?
Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Virus,
Vasculitis and hemorrhage due to endothelial injury
what is an example of infectious disease based hemorrhage?
Why is hemorrhage caused by this?
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, Dermatosparaxis
fragile skin and blood vessels; more likely to break and bleed
what are some examples of hemorrhage from genetic disease?
Why does this lead to hemorrhage?
ehlers-danlos syndrome
What
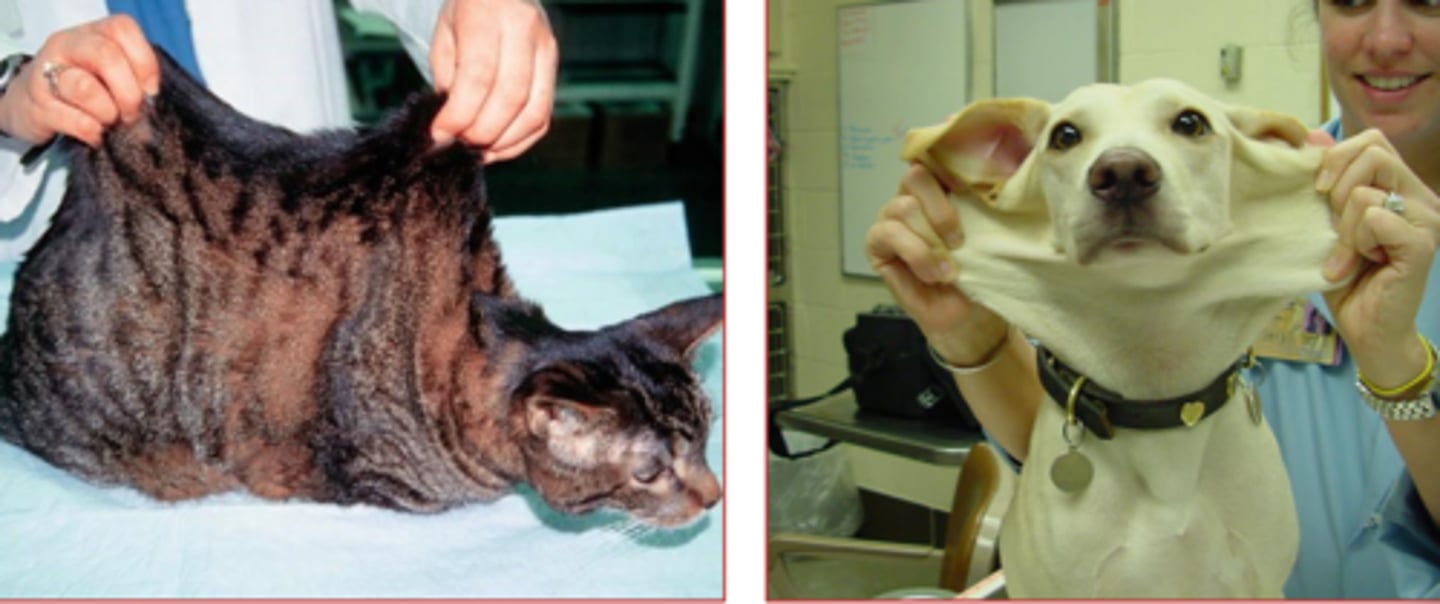
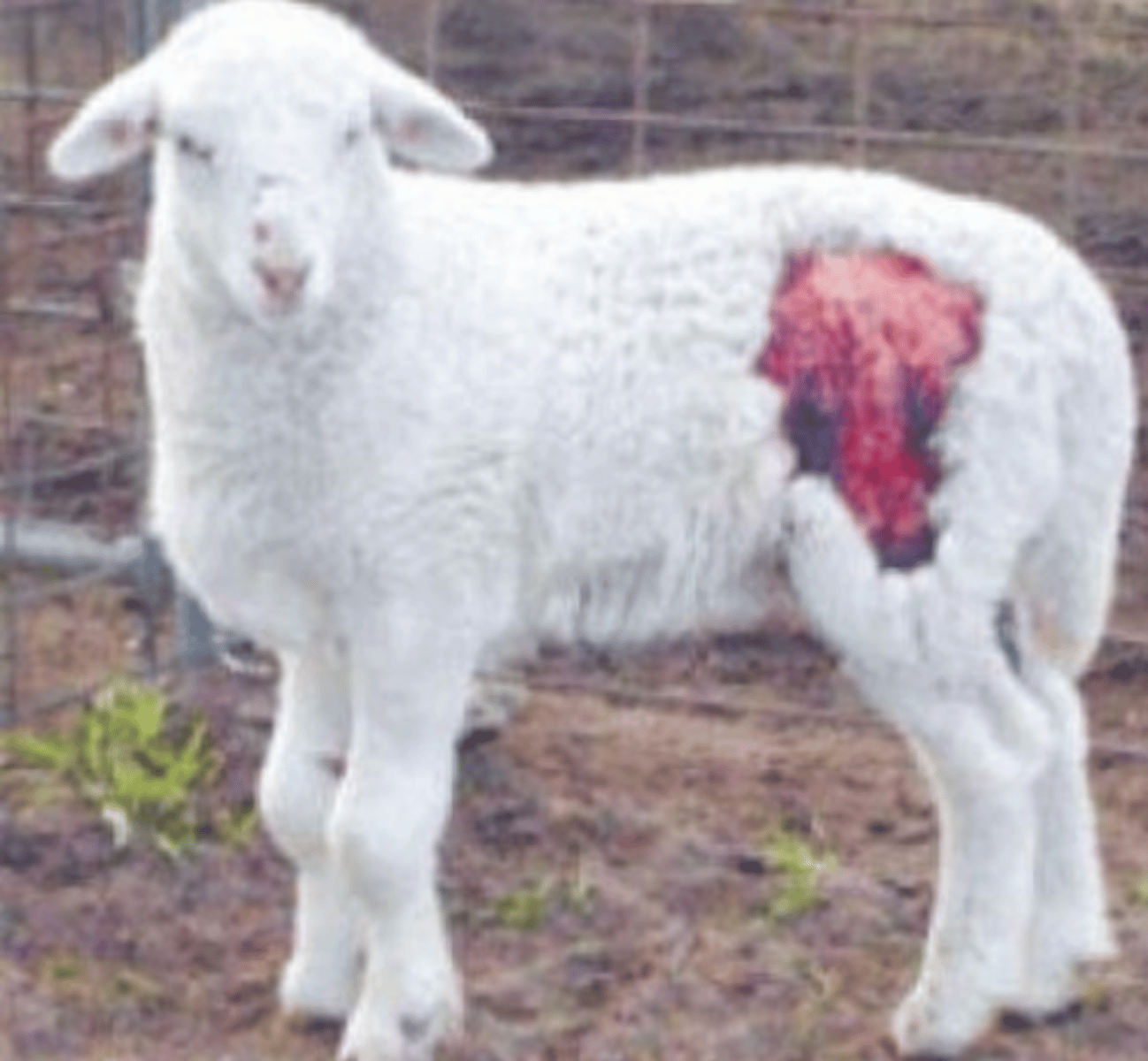
dermatosporaxis
disease of collagen molecule, in which the NT domain persists instead of cleaving, that causes skin to have consistency of wet blotting paper.

Vitamin C deficiency/scurvy
what is the most notable nutritional disorder that causes hemorrhage?
ascorbic acid (vit C), proline, lysine, hydroxyproline, hydroxylysine, collagen cross-links
__________________ serves as an enzyme cofactor that is required for the hydroxylation of ________- and ____________. without __________ and _____________, there is impaired formation of the ___________ so we can't form clots.
deficient and defective collagen synthesis
What is the reason scurvy causes hemorrhage in SIMPLE terms
true
true/false: Vit C also required for synthesis of dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, carnitine, for wound healing, conversion of cholesterol into bile acids, as an antioxidant, etc...
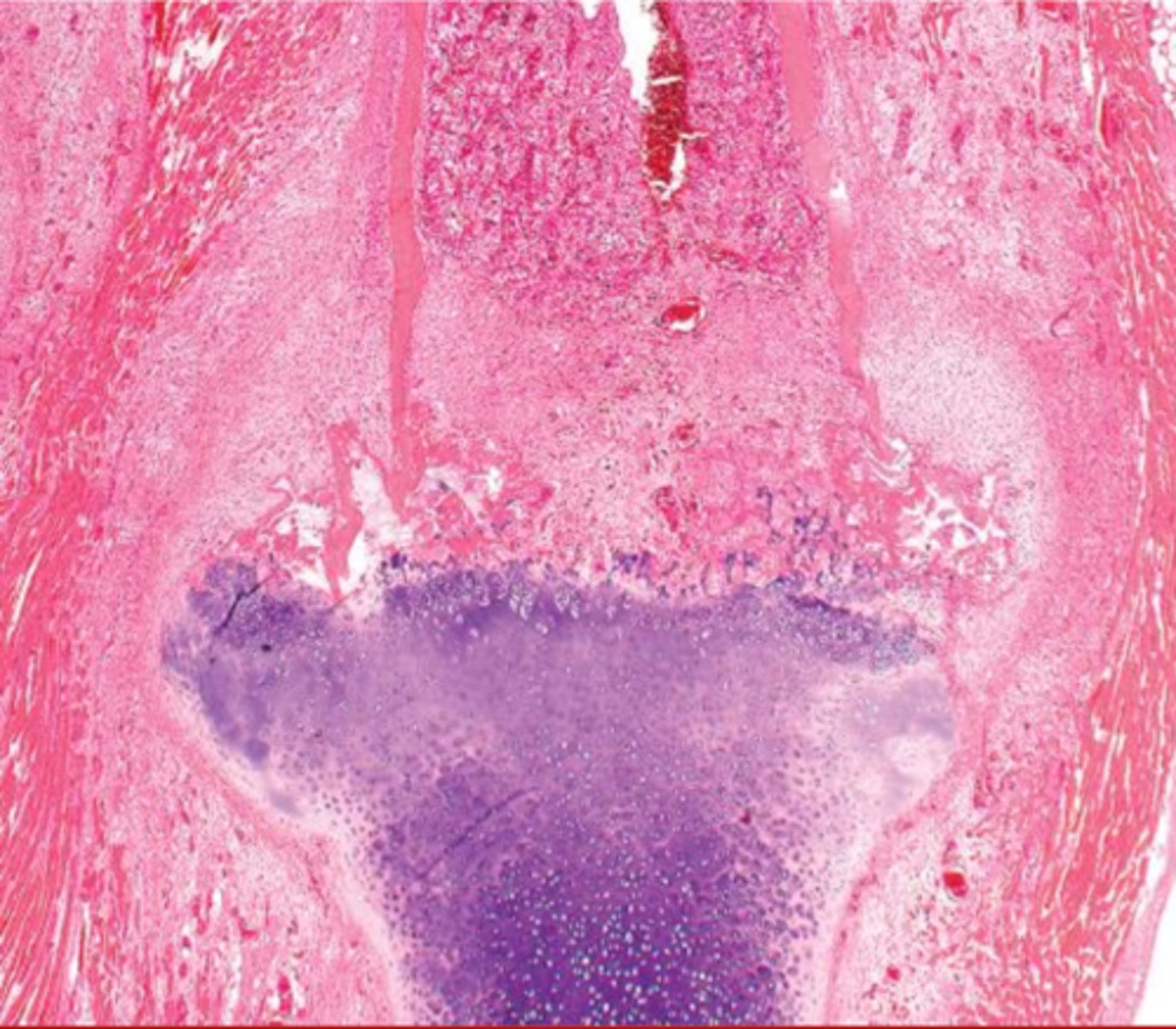
loose teeth, fragile vessels
why does scurvy lead to hemorrhage specifically around the teeth or joint capsules?
the defective collagen leads to really disorganized and messy areas like this
why does scurvy look like this?
decreased numbers, abnormal function
what two things lead to hemorrhage because of platelet issues?
thrombocytopenia
_______________________: decreased numbers of platelets
decreased production, increased destruction, increased use, (also sequestration but she didn't say that)
what leads to a thrombocytopenia?
megakaryocyte damage/destruction; radiation injury, estrogen toxicity, cytotoxic drugs, viral disease (parvo)
What causes decreased platelet production? (One general reason, 4 specific reasons, 1 SUPER specific reason)
immune mediated, drug reaction, viral diseases (equine infectious anemia)
what causes increased destruction of platelets?
diffuse endothelial damage, generalized platelet activation (DIC)
what are some examples of increased platelet use?
thrombocytopathy
______________________ = decreased function of platelets
- deficient in surface receptors, von willebrand disease
- NSAIDs (aspirin), Renal failure (uremia)
give two examples of a hereditary thrombocytopathy
and two of an acquired thrombocytopathy
hemophilia A - deficient in factor VIII
hemophilia B - deficient in factor IX
what are the X-linked hemophilia?
liver disease, vitamin K deficiency
what are some general issues that can cause decreased coagulation factor production
decreased synthesis
why can liver disease cause fewer coag factors?
moldy sweet clover, warfarin, sulfaquinoxaline
what are some vitamin K deficiency causes?
- dicumarol in _________________--
- anti-coagulant rodenticides like ______________
- _________________
DIC
whats the main example of hemorrhage due to increased use of coag factors?
disseminated intravascular coagulation
hemorrhage can occur with decreased platelets or abnormal platelet function. Decreased platelet numbers due to increased use is associated with ___________
liver issues
hemorrhage due to decreased coagulation factors is associated with ___________
bone marrow issues
decreased platelet numbers due to decreased platelet production is associated with _________________
immune mediated disease
decreased platelet numbers due to increased platelet destruction is associated with _______________
physiological
What type of thrombus is Part of normal hemostasis; rapidly resolved
pathological
what type of thrombus is persistent or inappropriate
vascular injury, altered blood flow, hypercoagulability
what are the three things in virchow's triad that lead to thrombosis?
endothelial injury/vascular injury
which corner of Virchow's triad is most important to vet med?
increased procoagulants, decreased anticoagulants
what two things are stimulated by alterations to the endothelium?
subendothelial collagen, Tissue Factor, platelet
After endothelial injury:::::: these four things happen
Exposure of________________
Release of _____________
____________ adherence and activation
Local depletion of Prostacyclin and Tissue Plasminogen Activator
stasis, turbulence
abnormal blood flow increases risk of thrombosis. What are the two abnormalities?
true
true/false: in normal laminar blood flow the Cells flow centrally in the blood vessel separated from the endothelium by a thin layer of plasma
heart failure,
vascular obstruction/dilation
if there is a stasis systemically, it's likely from ___________
if there is one locally its probably _______________
acumulation of activated coag factors, platelets contacting the endothelium
what two things do slow flow rates favor?
where vessels branch, narrowing of vessel lumens, site of venous/lymphatic valves
where is turbulence greatest/most likely?
mixes up the blood, increases coag factor interaction with other factors AND with endothelium
how does turbulence put you more at risk or a thrombosis?
true! (decrease degradation)
true/false: Hypercoagulability reflects an increase OR DECREASE in the concentration of activated hemostatic proteins
inflammation
what is the most common cause of hypercoagulability?
attached to the vessel/heart wall
key point about thrombi: they are ALWAYS _________________________
endothelial damage
arterial thrombi are usually initiated by ________________--
platelets and fibrin
arterial thrombi are primarily made of _______________________
DULL, tan/red/gray, +/- vessel occlusion, tail extends downstream, laminated appearance
The shape and appearance of arterial thrombi are due to the rapid blood flow there... describe the appearance:
lines of Zahn, arterial thrombi
______________________: Alternating layers of platelets, interspersed by fibrin intermixed with erythrocytes and leukocytes
These are more often found in [arterial/venous] thrombi
stasis
venous thrombi most often occur in areas of ____________
incorporate RBCs, platelets, fibrin, WBCs
because the blood is moving slowly or is still, thrombi in veins typically include lots more things and are composed of __________________________ (4)
gelatinous, soft, glistening, dark reed, occlusive, often extend upstream
describe the appearance of a veinous thrombi
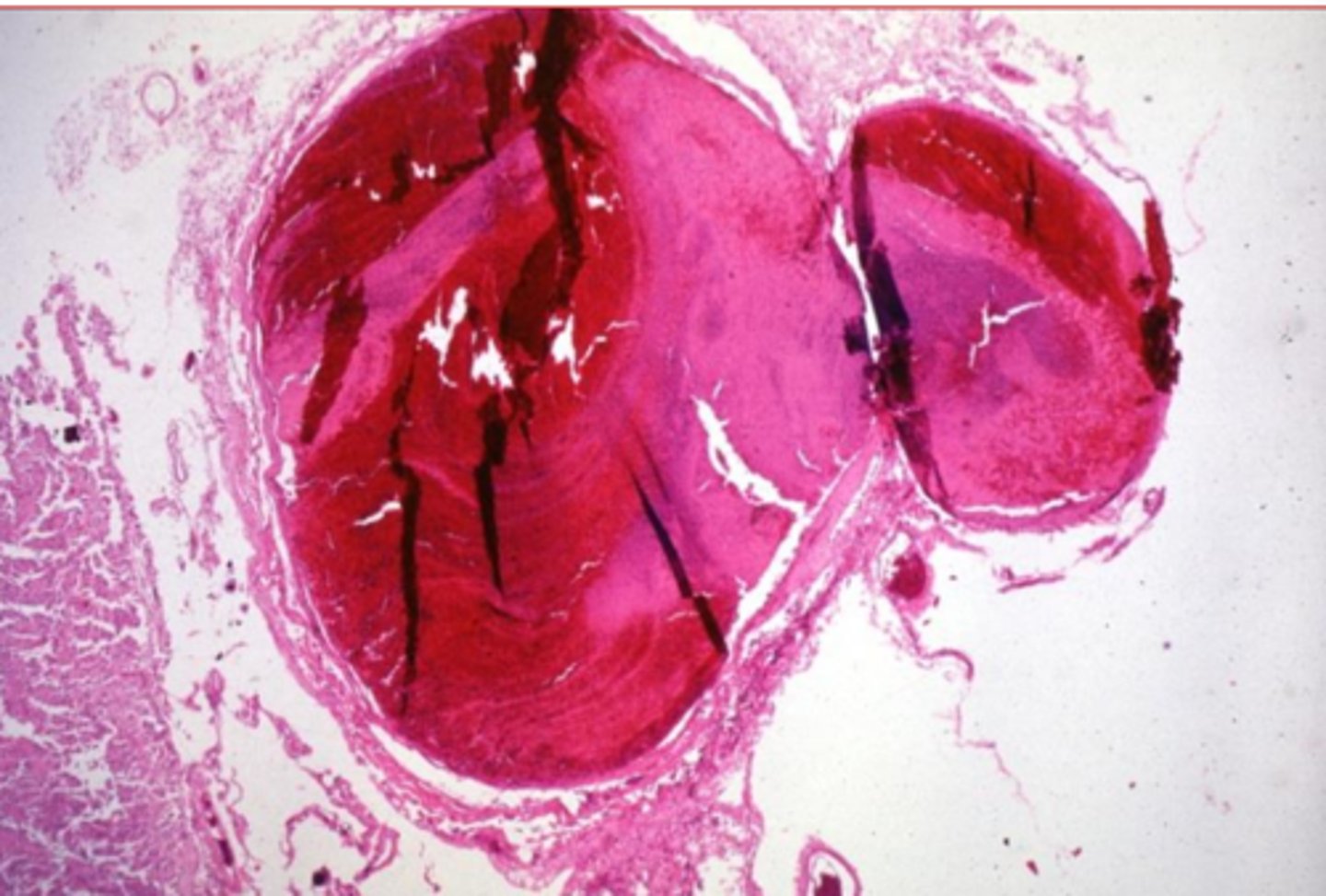
arterial thrombi
What is this?
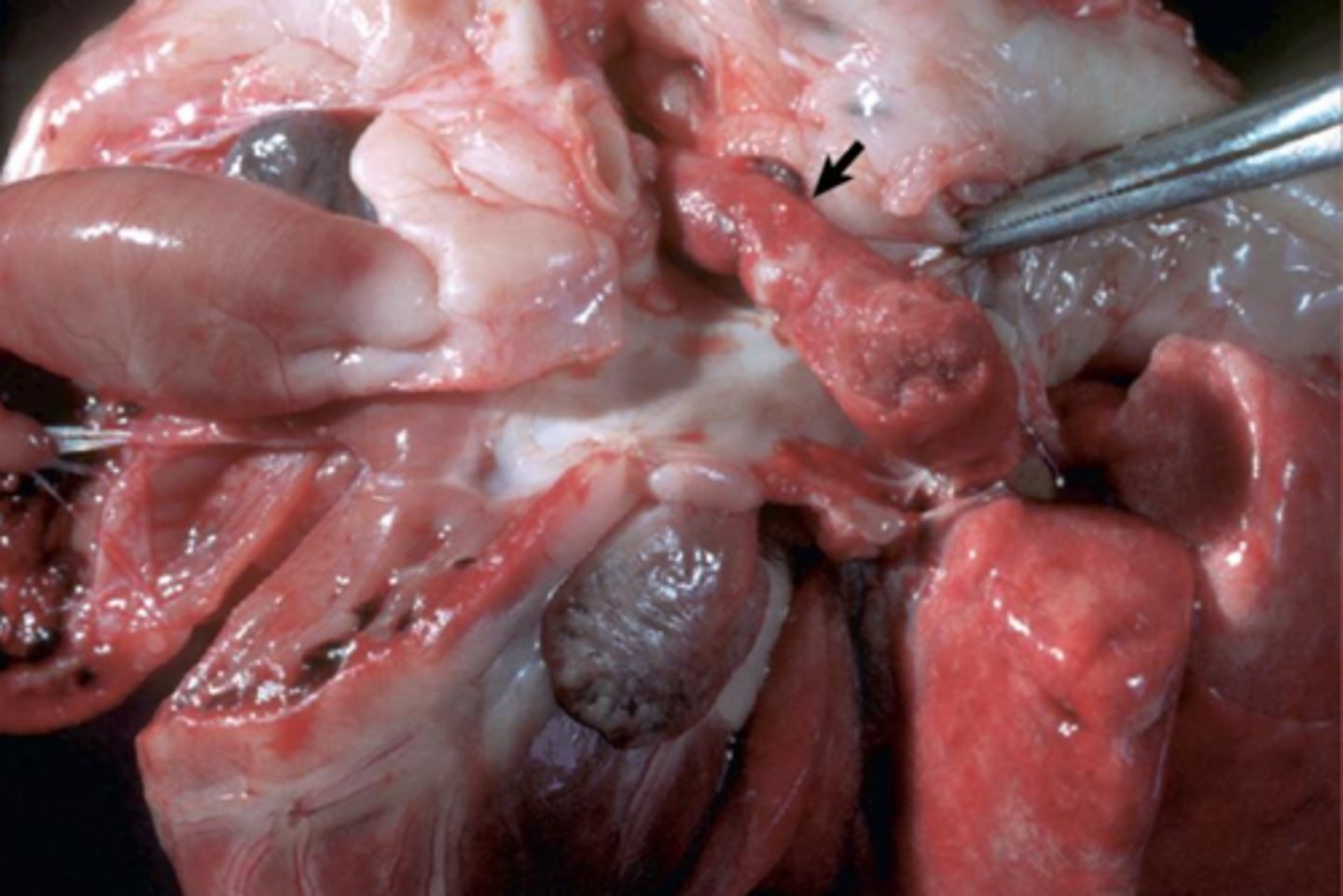
veinous thrombi
what is this
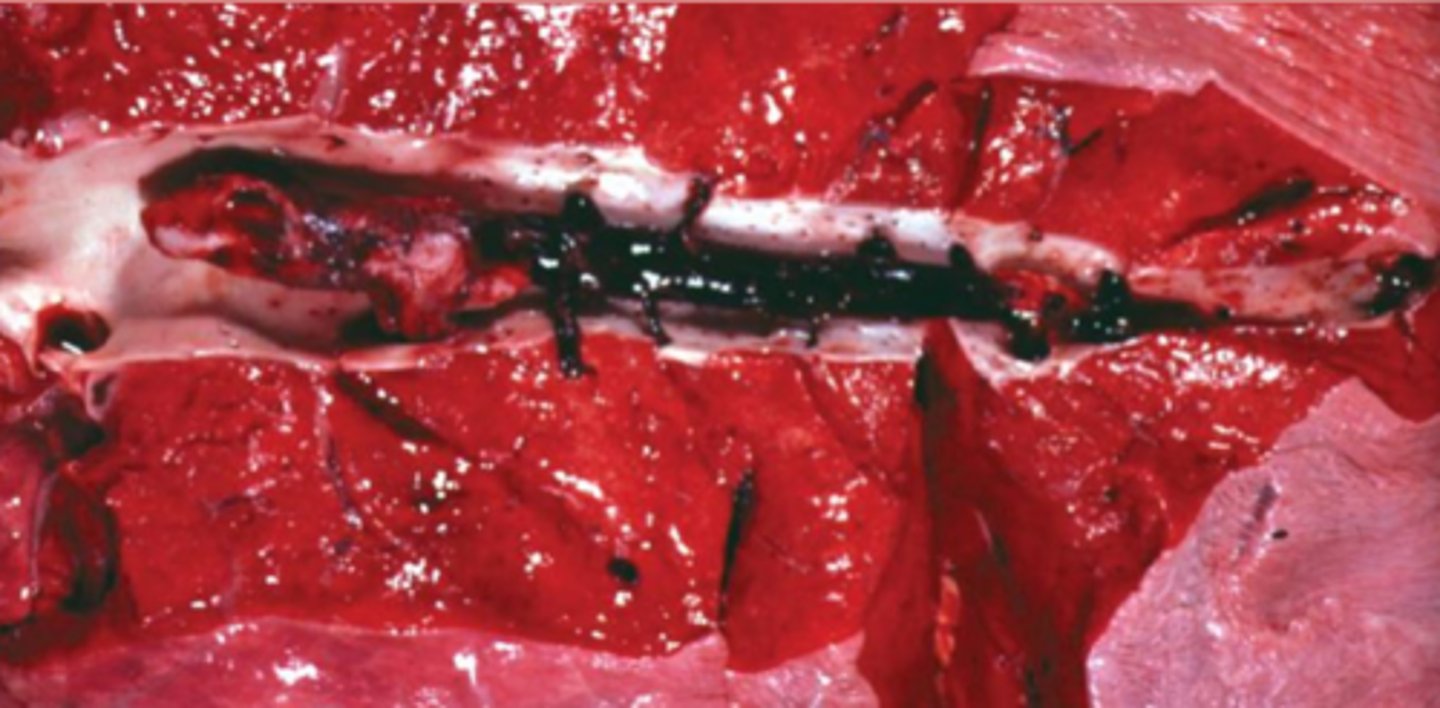
arterial thrombi
what is this
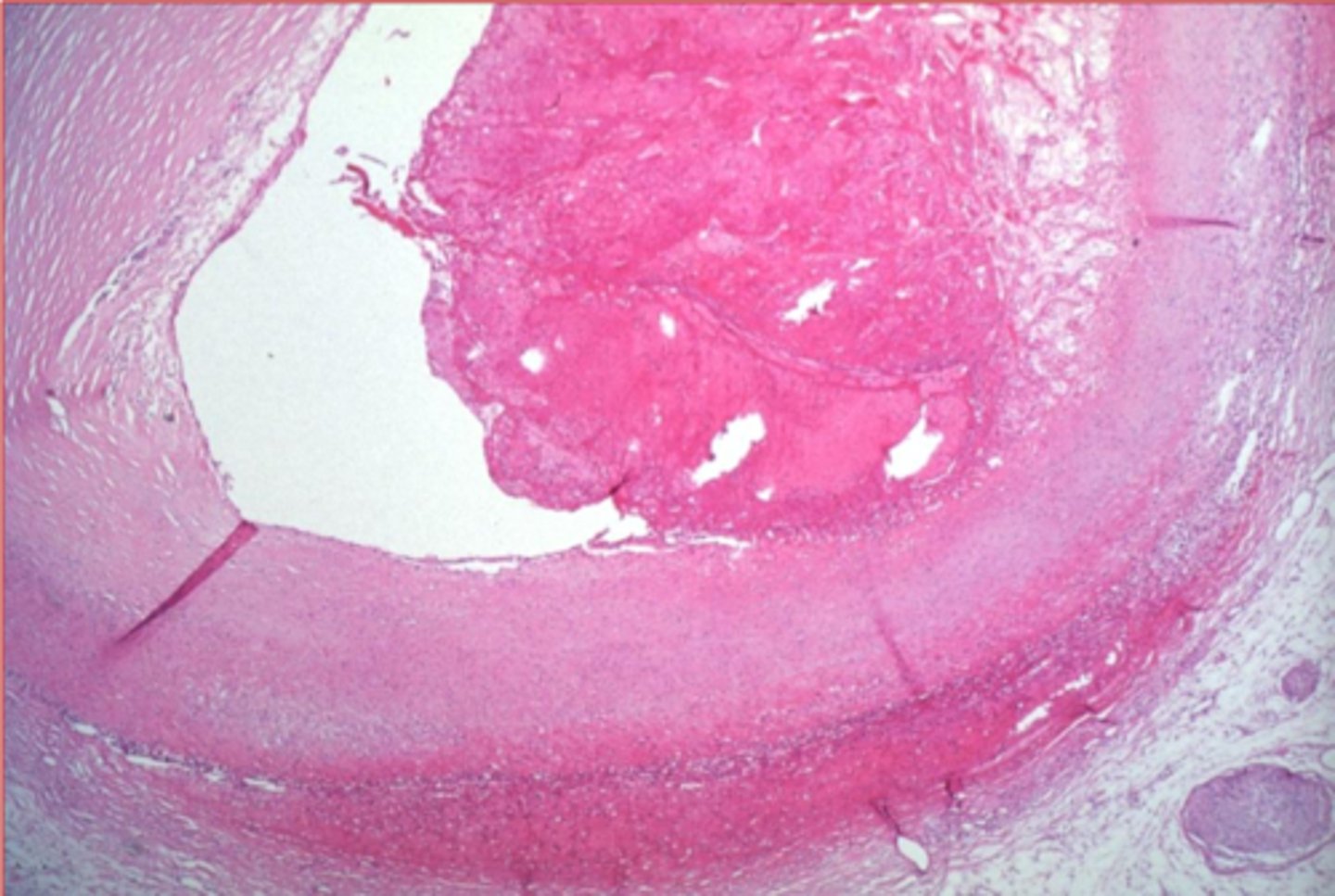
lines of zahn
what is this?
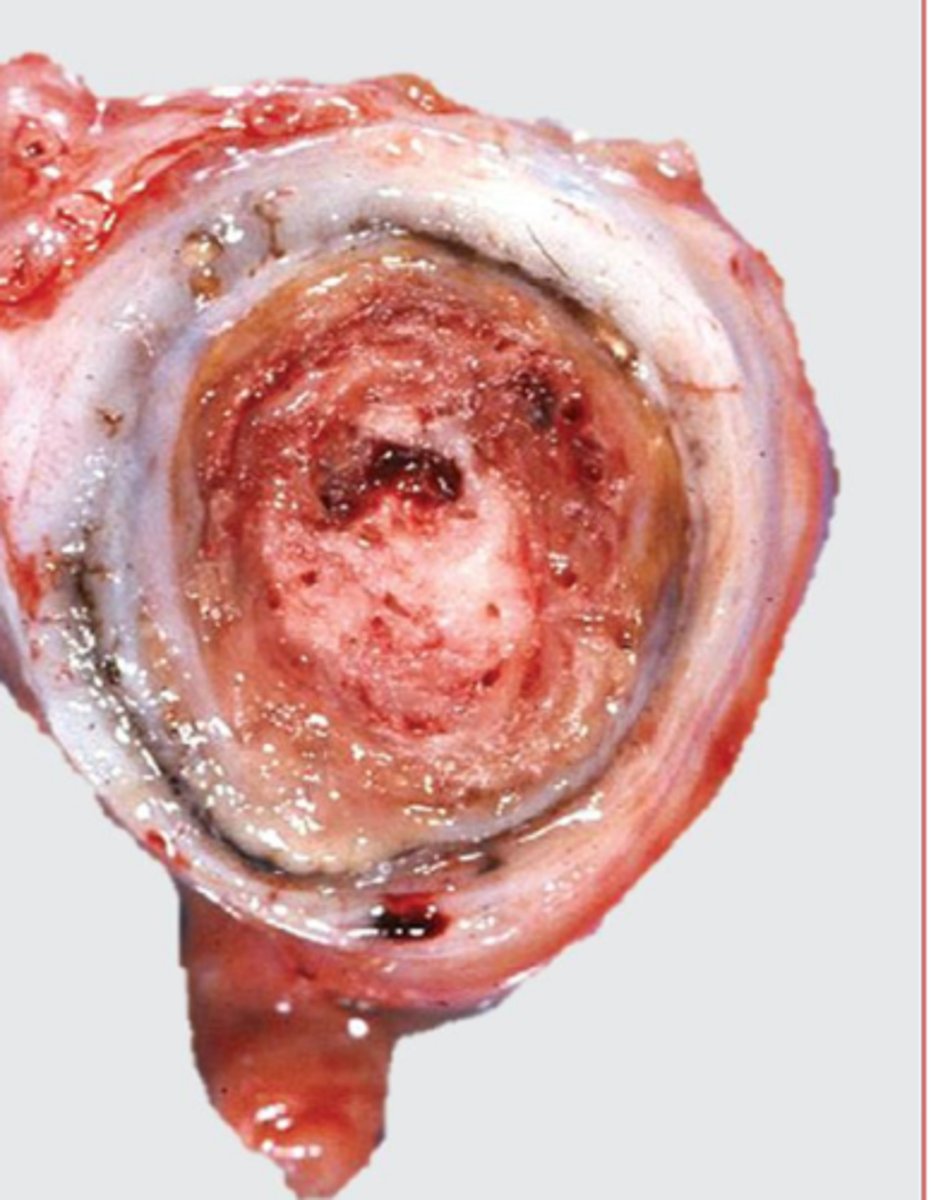
veinous thrombi
what is this?
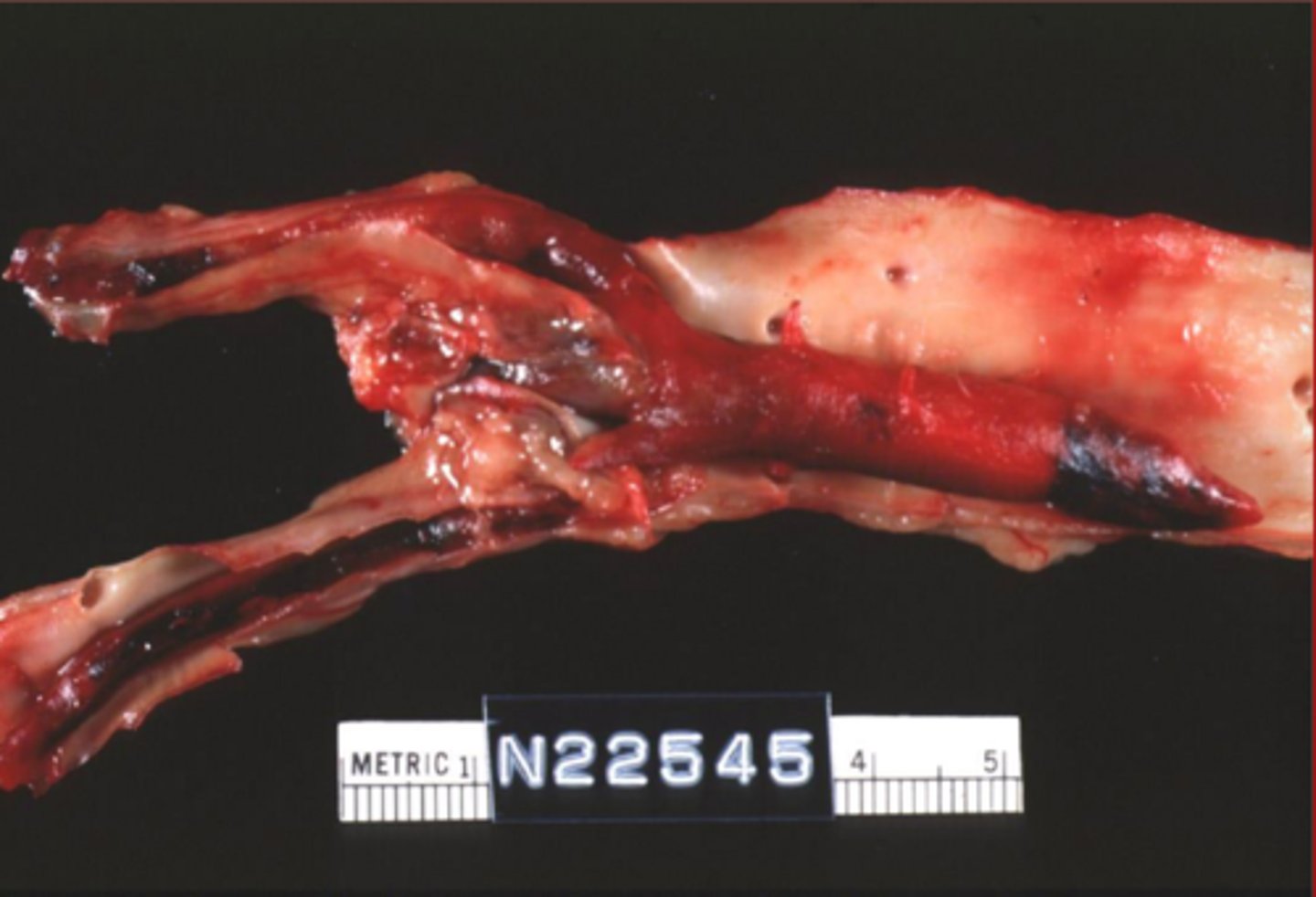
arterial
arterial or veinous thrombi?
softer, NO POINT OF ATTACHMENT, no associated lesions, dark red (currant jelly) or yellow (chicken fat)
what are some characteristics of postmeortem clots?
location, ability to disrupt perfusion
significance of a thrombus is determined by its ____________ and ___________________ in a dependant tissue