Physics multiple choice exam
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Current
current is the flow of charge in a circuit measured in amps (A)
Potential
the amount of energy per unit of charge measured in volts (V)
Energy
can be determined using potential and current measured in joules (J)
Electrical resistance
a measure of the opposition of the flow of current in a circuit
Resistance (definition)
it is defined by Ohm’s law and is measured in units of volts/amps of Ohms (omega symbol)
Resistance (what affects it?)
length, thickness of material, temperature of substance
Power
describes the rate of energy usage, measured in watts (W)
Kirchhoff’s Current law
the current flowing into a node must be equal to the current flowing out of it. (current is the same in series)
Kirchhoff’s Voltage law
the sum of the voltage differences around any closed loop in a circuit must be zero (voltage in parallel is the same)
how do you add resistors in series?
add them together
how do you add resistors in parallel
add the inverses
Magnetic force
similar magnetic poles repel each other with force, even at a distance. dissimilar magnetic forces attract each other with a force, even at a distance
magnetic fields
field lines are always drawn from north to south
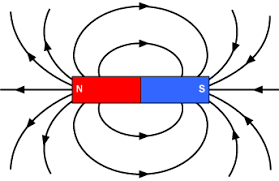
Straight Conductor
magnetic fields make a circle around the rod
Solenoid
the magnetic field moves towards the positive charge
Right hand rule #1
thumb in the direction of the current fingers indicating the direction of the magnetic field (straight conductor)
Right hand rule #2
fingers wrap in direction of current thumb indicating the direction of the field (solenoid)
Right hand rule #3
palm points in the direction of the magnetic force, fingers point in the direction of the magnetic field, thumb points in direction of the current
Faraday’s law
it states that any change in the magnetic field near a conductor induces a voltage in the conductor, causing an induced electrical current
Len’s law
if a magnetic field induces a current in a coil, the electric current is in such a direction that it’s own magnetic field opposes the change that produced it
things that cause a higher voltage
a larger magnet strength, number of loops, speed of magnet
things that cause a lower voltage
a larger area of loops
step down transformer
current goes up voltage goes down
step up transformer
current goes down, voltage goes up
characteristics of waves
amplitude, period, wavelength, frequency, speed
transverse waves
moves perpendicular to movement ex: baseball game wave
longitudinal waves
moves parallel to movement ex: sound waves, earthquakes
torsional waves
spins one way then the other ex: swings
what is the speed of a wave dependent on?
the medium it travels through, the speed of a sound wave in air, air temperature
how are sonic booms created?
a barrier is created when moving faster than the speed of sound out of pressure waves, when broken it creates a sonic boom
Mach #
>1 = subsonic, between 1 and 5 = supersonic <5 = hypersonic
what is the Mach # dependent on
air temperature, object speed, speed of sound
Doppler effect
the perceived change in frequency of a sound as it moves towards or away from an observer
Principle of superposition
when waves interact we add their amplitudes to determine the resultant wave
constructive interferance
the process of forming a wave with a larger amplitude when two or more waves combine
destructive interference
the process of forming a wave with a smaller amplitude when two or more waves combine
standing waves
created when waves with the same frequency, velocity and wavelengths interfere
fixed end reflections
when a wave reflects off of a boundary that is more dense it’s reflection is ½ wavelengths out of phase with the original wave
free end reflections
when a wave reflects off of a boundary that is less dense it’s reflections is in phase with the original wave
resonance on strings
number of nodes between fixed ends and overtone are equal to frequency #, harmonic is one more than frequency #, wavelengths is number of total node x 0.5
resonance in tubes (closed end)
harmonic × ¼ is the # of waves, overtone is # of node not on the end
resonance in tubes (open end)
harmonic x ½ is # of waves, overtone is # of nodes - 1
kinematics
the study of motion
Distance
the total length of the path travelled
Position
the location of an object with respect to a reference point
Displacement
the change in an object’s position
Scalar measurements
they have a magnitude and a unit
Vector measurements
they have a magnitude, unit and direction
position time graph slope
the velocity of the object
Acceleration
the change in velocity per unit of time
position time graph for an accelerating object
curved line of motion
slope of tangent to curved line (position-time graph)
instantaneous values of velocity
velocity time graph slope
acceleration
area under the line in a velocity time graph
displacement
straight, horizontal line on velocity time graph
constant velocity, no acceleration
straight upward slope on velocity time graph
increasing velocity, constant positive acceleration(straight horizontal line on acceleration graph)
straight downward slope on velocity time graph
decreasing velocity, constant negative acceleration(straight horizontal line on acceleration graph)
area under acceleration graph
velocity
Projectile
any object that moves along a 2 dimensional trajectory under the influence of gravity only
what angle is a projectile hit at if it goes it’s maximum horizontal displacement
45 degrees
4 fundamental forces
electromagnetic, gravity, weak nuclear, strong nuclear
Newton’s first law
all objects will remain at rest or at a constant velocity until acted upon by an unbalanced force
Newton’s second law
when an unbalanced force is applied to an object, the object will accelerate (F = ma)
Newton’’s third law
for every action force there is an equal opposite reaction
gravity
it acts through the mass of an object
Normal force
it is a part of an action-reaction pair. when an object presses on a surface, the normal force in the reaction force that presses back, it is alway perpendicular to the surface
coefficient of friction
a measure of the attraction between two materials
Friction
depends on the nature of 2 surfaces in contact and the magnitude of the normal force
Energy flow diagrams
Define a system, determine critical instances
Work
the transfer of energy from on form to another
kinetic energy
the energy of motion (Ek = 1/2mv squared)
Gravitational potential energy
stored in an object due to it’s height (Eg = mgh)
elastic potential energy
springs, rubber bands
nuclear potential energy
stored in the nucleus of an atom
electric potential energy
positive and negative charges
magnetic potentila energy
magnetic poles
chemical potential energy
stored in chemical bonds
radient potential energy
stored in light
Law of conservation of energy
energy cannot be created or destroyed only transformed
Efficiency
the completeness of energy transfer, usually expressed as a percent Eout divided by Ein
what type of friction is usually greater?
static friction