CHEM 3BL Final Mechanisms + Reagent/Step Purposes
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
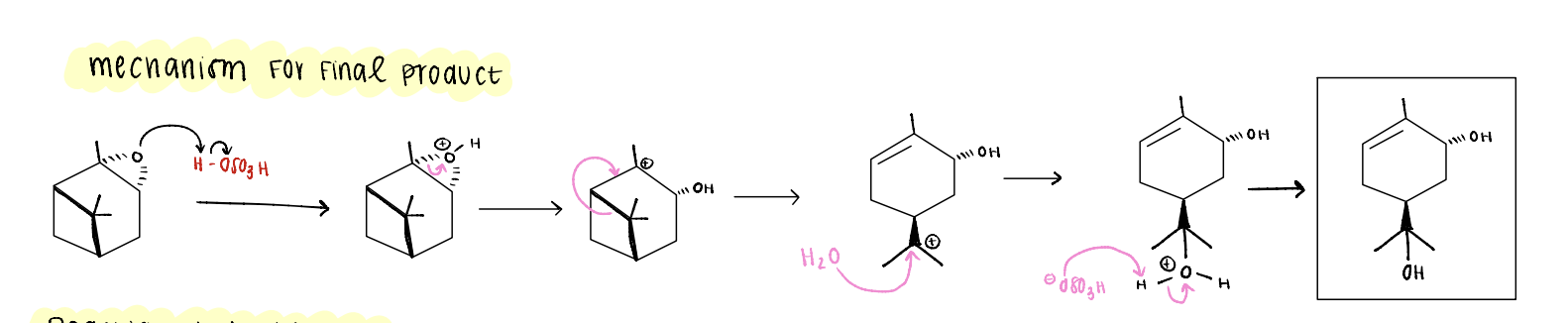
alpha pinene oxide mechanism for final product
epoxide ring gets protonated, opens, creates a carbocation.
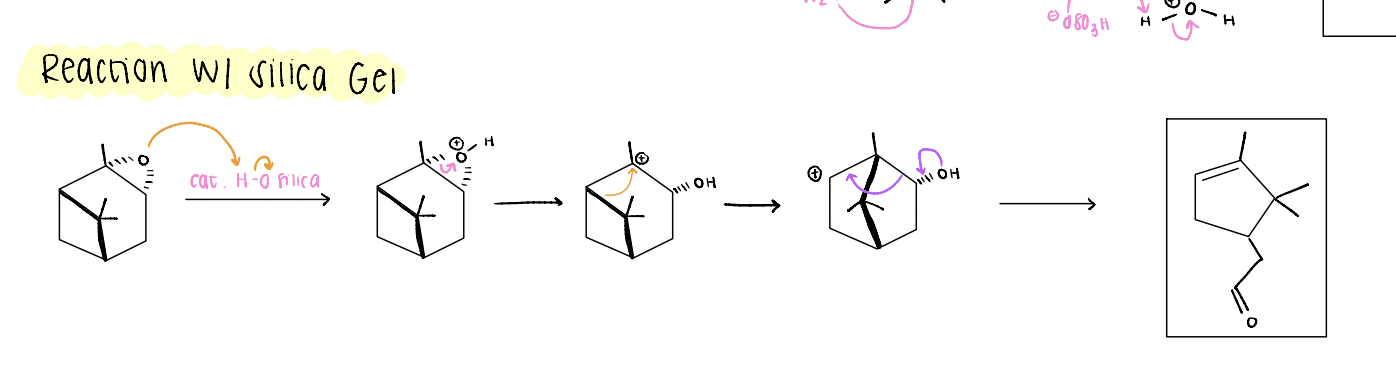
alpha pinene oxide reaction with silica gel
2 alkyl shifts
steps for recrystallization
1) dissolve in minimum amt of hot solvent
2) cool to room temp, then in an ice bath
3) isolate crystals, wash, and dry
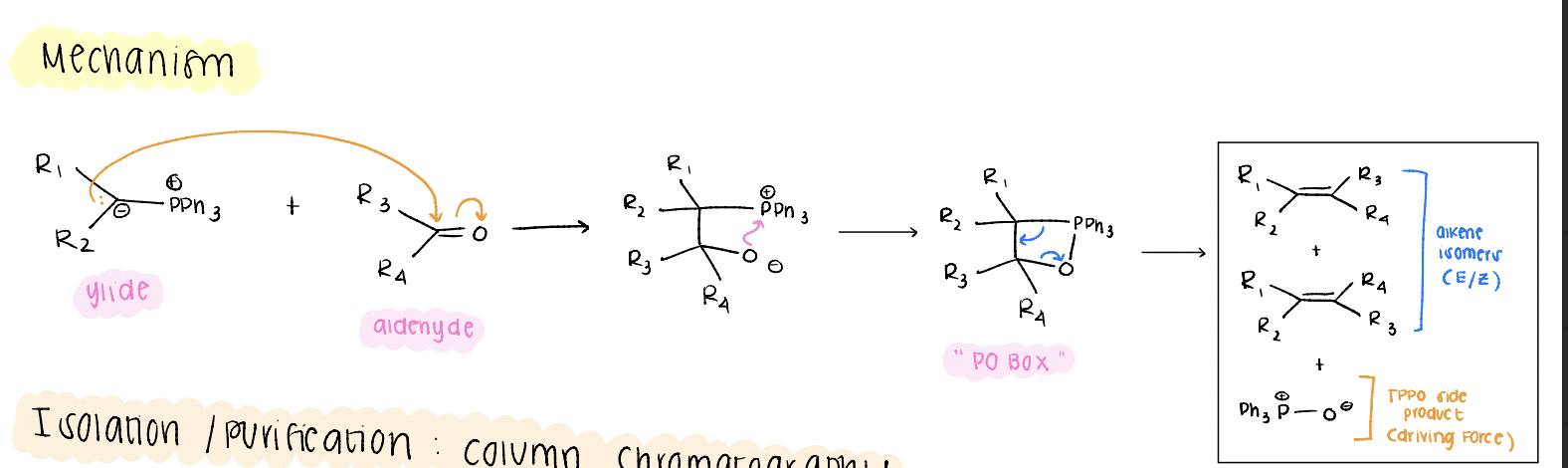
wittig mechanism (ylide + aldehyde, p-o box bs)
lone pair on carbanion attacks aldehyde, o- attacks the phosphate to create the p-o box, break and create a bond simultaneously for the final alkene.
coupling constant hz ranges
trans: 12-18 hz
cis: 6-12 hz
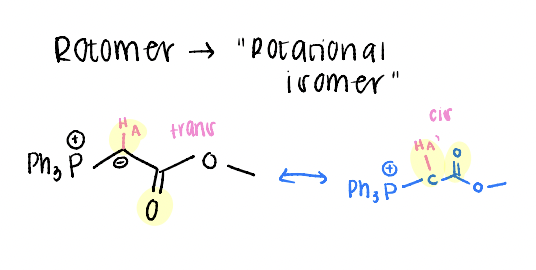
rotamer
“rotational isomer”
what creates small coupling?
if there are 2 hydrogens separated by 4 bonds & one of the bonds in a pi bond
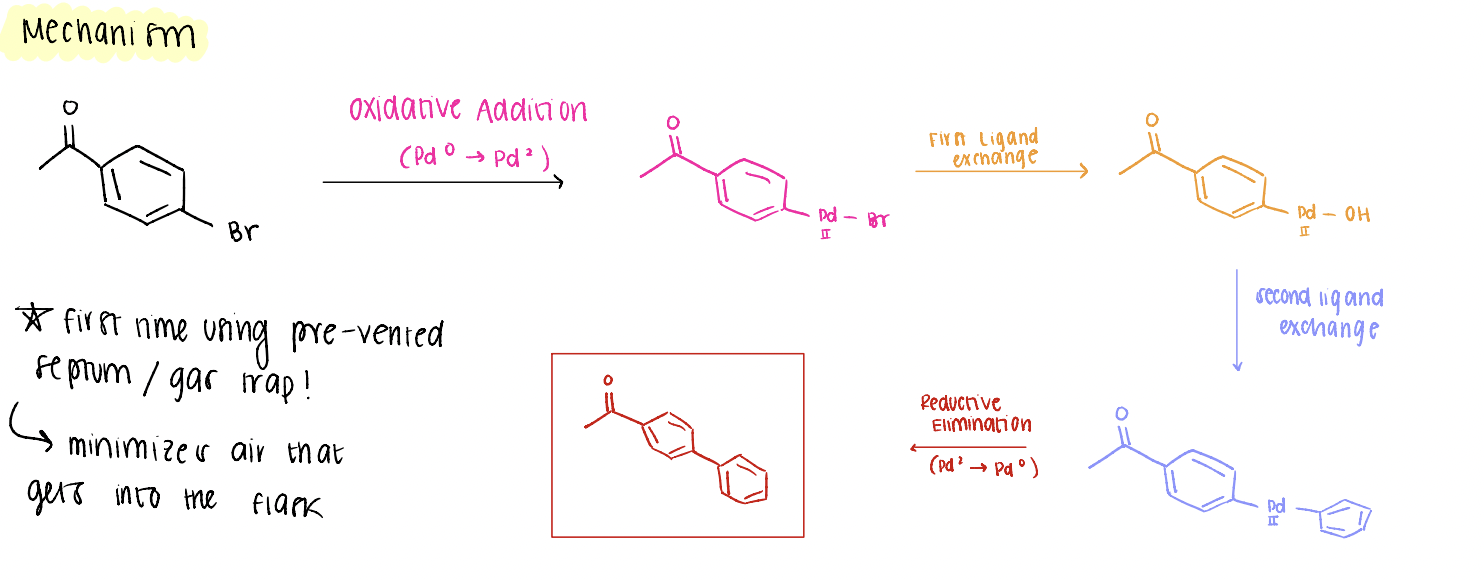
suzuki mechanism
reaction between an aryl halide + boronic acid (oxidative addition, 2 ligand exchanges, reductive elimination) to form new carbon carbon bonds!
advantages of suzuki vs. grignards
1) can run in H2O
2) No side reactions
3) catalytic metal is regenerated
purpose of using a gas trap
minimizes air that gets into the flask. vapors return to flask as condensate so you can heat for large amounts of time.
purpose of Pd
generates active catalyst
purpose of Bu4NBr
phase transfer agent: helps aid 4-bromoacetphenone into the aqueous phase (into water)
purpose of K2CO3
generates base (-OH) from solvent
purpose of H2O in suzuki reaction
solvent
what does filtering then washing the solid with water do?
physically separates solid from liquid, washing with water washes away ionic impurities.
what does centrifuging do?
spinning really fast helps sink heavier materials to the bottom of the tube for ease of separation.
what does boiling then adding water dropwise do?
boiling the supernatant increases the concentration of liquid and helps the product precipitate out. because the product is insoluble in water, adding water helps the product further crystallize.
HOW does Bu4NBr aid as a phase transfer agent?
when it dissociates into N+ and Br-, N+ does ion-dipole interactions with water. the nonpolar butyls interact with the nonpolar phenyls on 4-bromoacetophenone through ID-ID interactions.
oxidative addition
Pd(0) -→ Pd(2) *think: you’re ADDING Hs onto Pd!
reductive elimination
Pd(2) —> Pd(0) *ELIMINATING Hs from Pd
ligand exchange for suzuki
changing what is attached to Pd (ex: Br → OH, OH → phenyl)
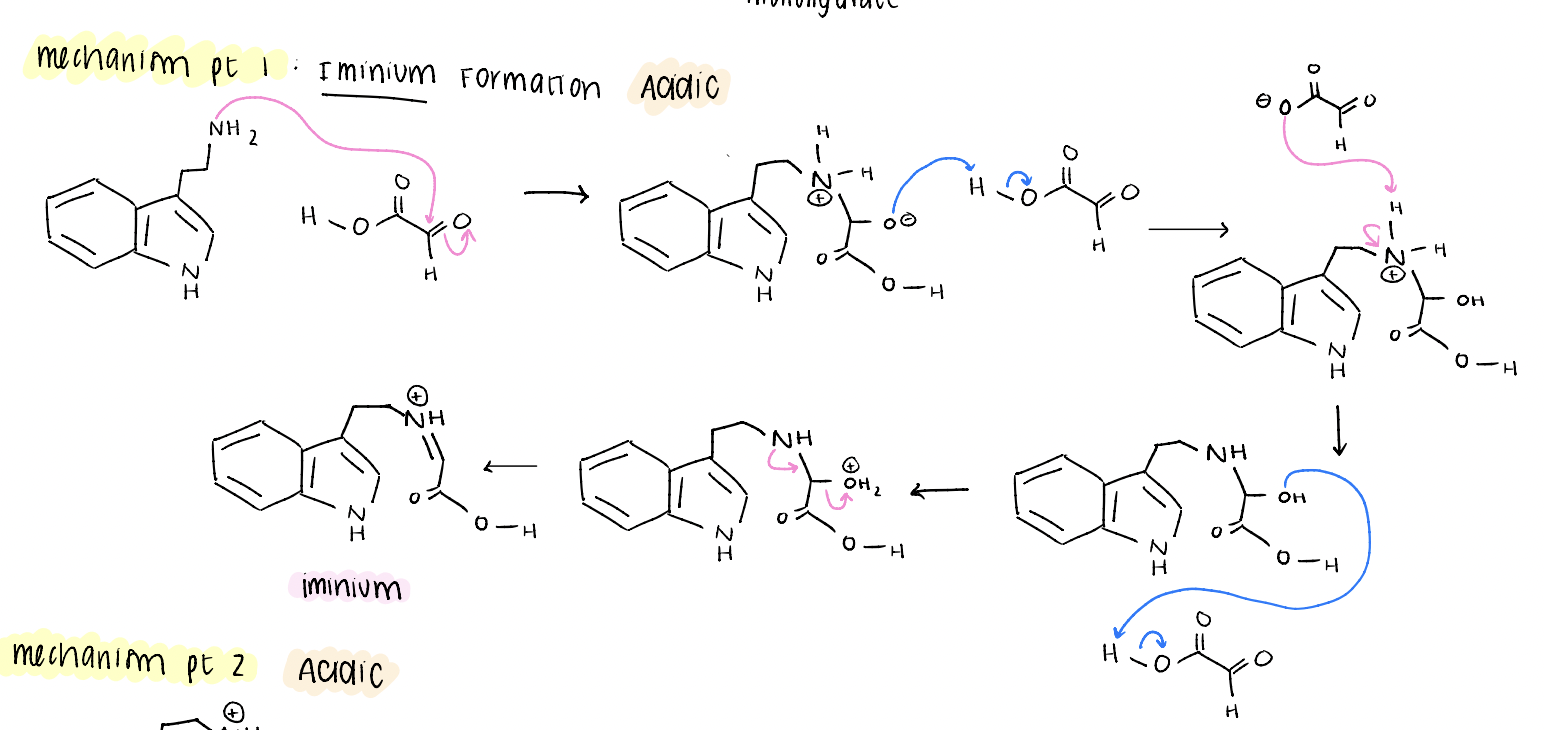
tetrahydrobeta carboline mechanism pt 1
iminium formation (acidic conditions)
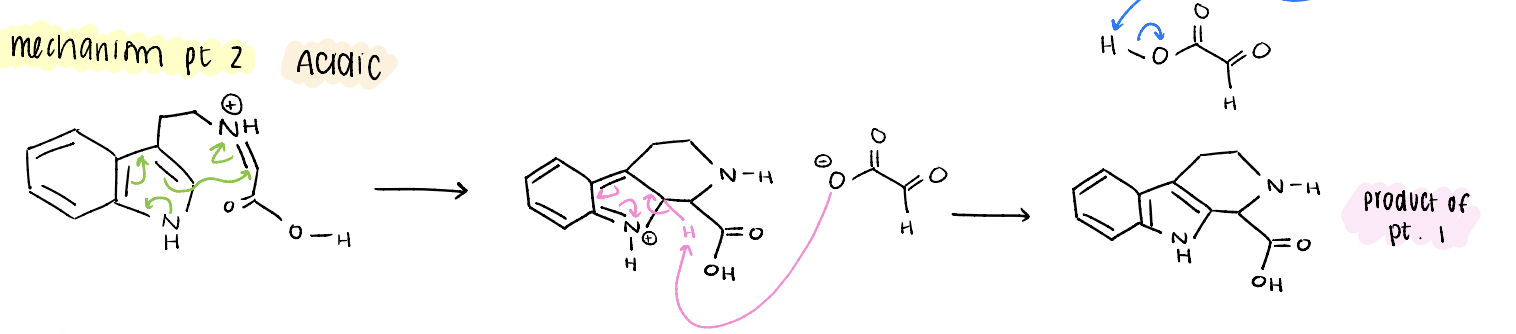
tetrahydrobeta carboline mechanism pt 2
EAS reaction (acidic)
tetrahydrobeta carboline mechanism pt 3
decarboxylation, neutralize ammoniums, enamine → imine, restore aromaticity, product!
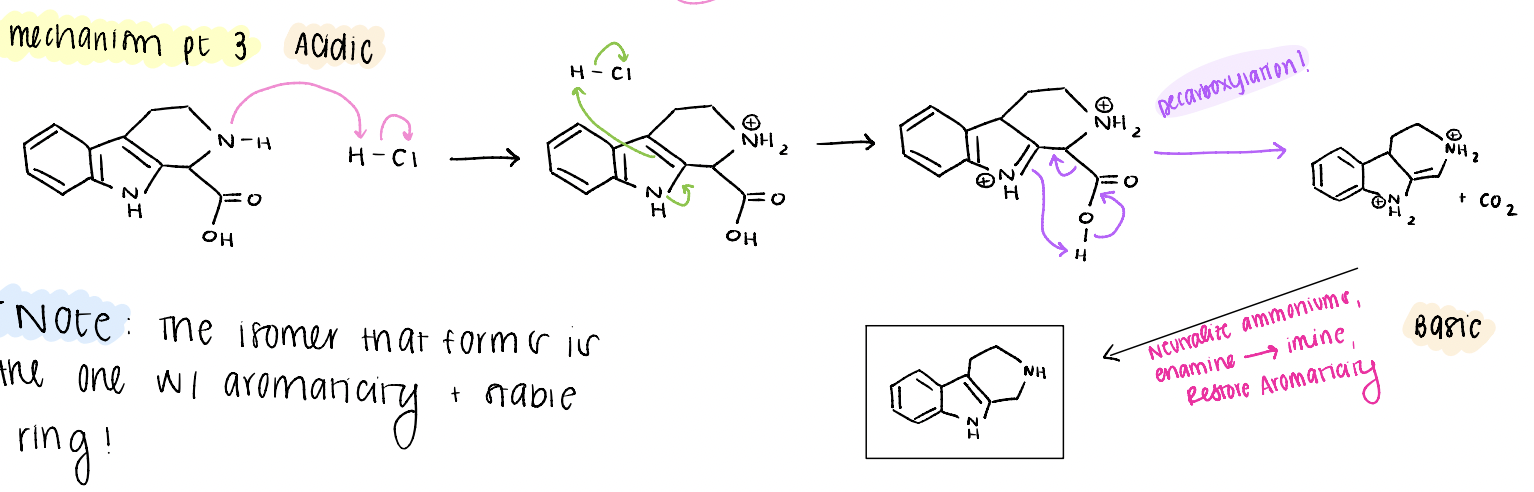
what determines what product is observed? (tetrahydrobeta carboline)
choose the one that doesn’t break aromaticity and has the most stable ring!
aldol condensation mechanism
make enolate nucleophile, attack, protonate O-, E1CB mechanism
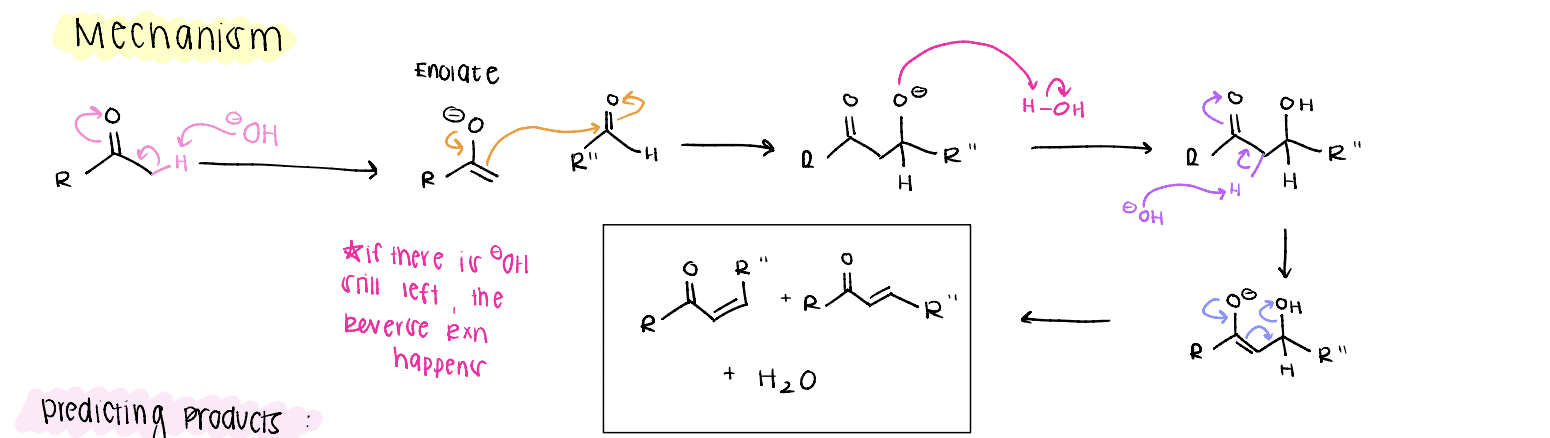
what happens if the ketone (acetone nucleophile) is in excess?
mono-addition product is major
what happens if the aldehyde (electrophile) is in excess?
di-addition product is major
why can only acetone be an enolate nuclephile?
between acetone and the aldehyde, acetone is the only one with enough alpha Hs
purpose of NaHCO3 wash (aldol condensation)
1) converts -OH to H2O
2) produces CO32- (less nuc. base) which prevents the reverse reaction from happening!
what drives the aldol condensation reaction forward?
the mixture gets cloudy from the product precipitating out
what does washing with water until the pH is neutral do for the aldol condensation purification process?
washes away CO32-
how do we know if recrystallization is necessary?
it is not necessary if the Rf values between the recrystallized product and crude product are about the same and visualize the same.
chemoselectivity
multiple functional groups, but only some react
chemoselectivity of transfer hydrogenation mechanism overview
oxidative addition, migratory insertion (Pd inserts itself onto the alkene), then reductive elimination
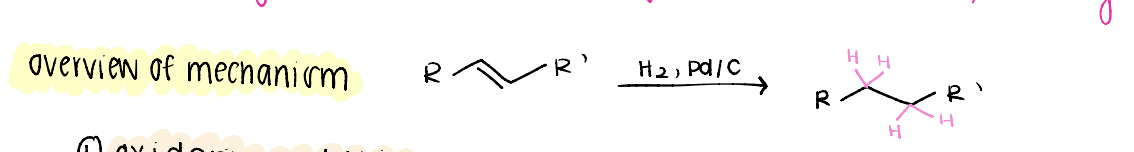
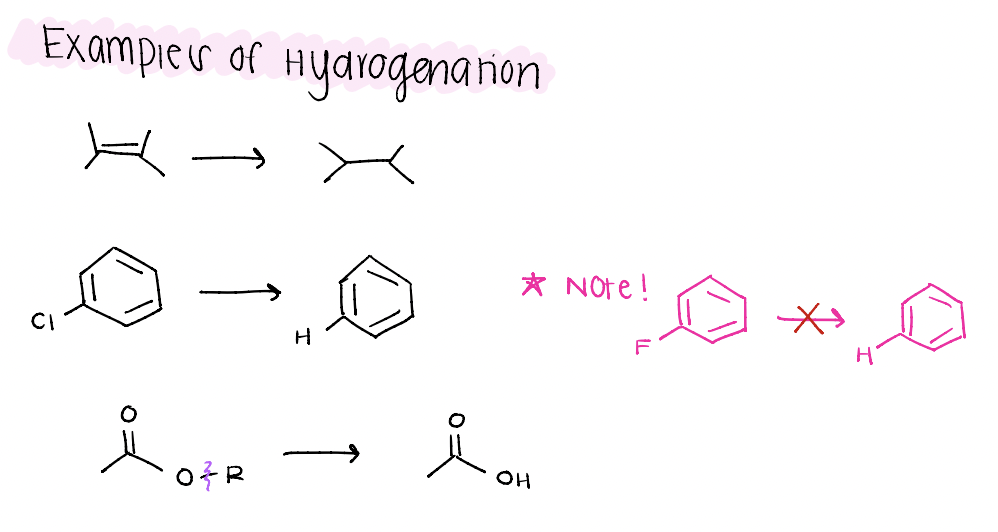
what are some examples of what can happen with hydrogenation?
what does adding HCL + ether do for the purification process for hydrogenation?
protonates carboxylate and moves the product into the organic layer
how do we dry the ether with Na2SO4
sodium sulfate does ion dipole interactions with water and forms clumps, taking water out of the ether
chemoselectivity possible reductions

azo dye mechanism
coupling reagent + diazonium salt EAS
activate nuc. —> attack N triple bond —> restore aromaticity -→ protonate O-
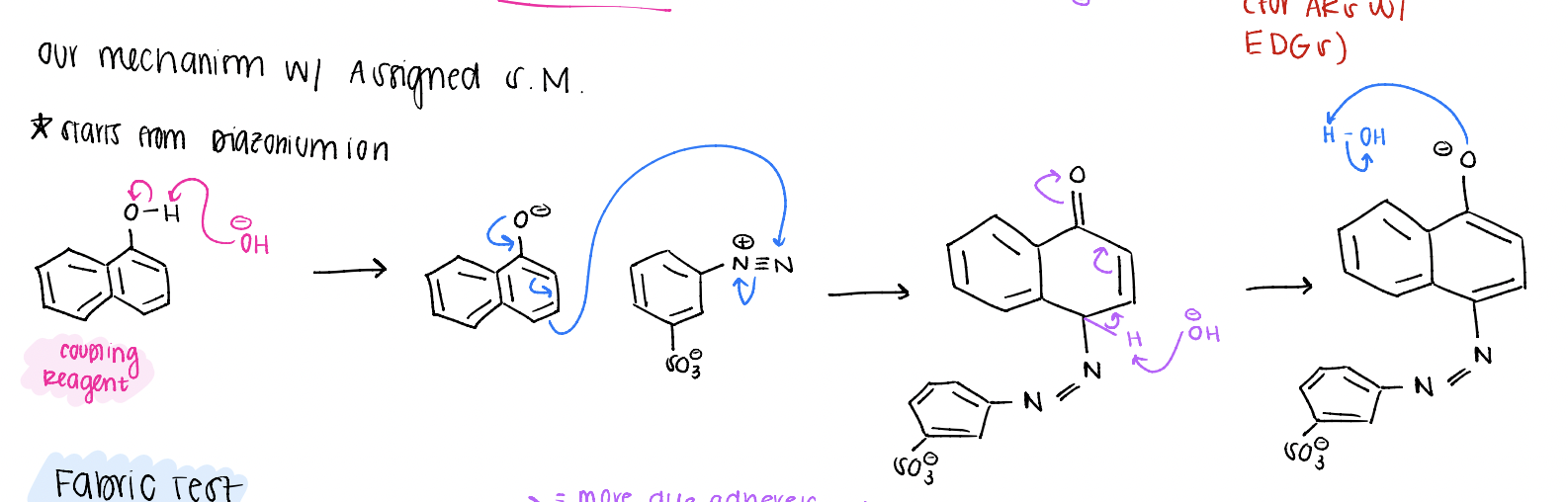
positions on an aromatic ring in relation to R group
ortho (1 carbon away), meta (2 carbons away), para (3 carbons away)
what determines how dark a dye will appear on a fabric?
if a fabric has BOTH H-bond donors and acceptors, the dye will appear DARKER on these fabrics and lighter on fabrics with only one or the other, or neither.
why do more conjugated pi systems have higher wavelengths?
more conjugated pi systems → smaller HOMO-LUMO gap -→ absorbs lower energy photons → higher wavelength (ex: red)
hydrogenation
reduction of an alkene
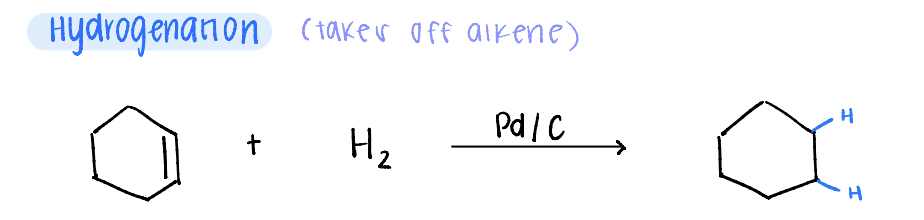
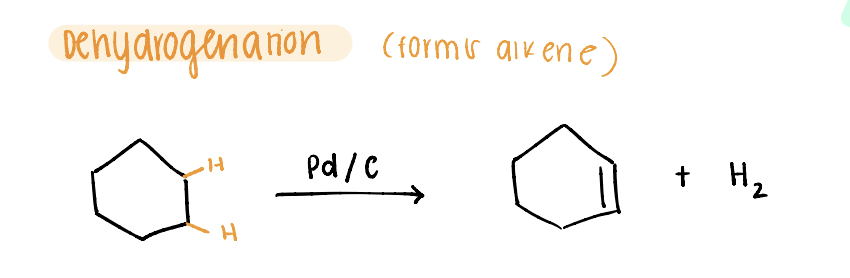
DEhydrogenation
FORMS alkene
carvone to carvacrol mechanism
*the goal is to get to an aromatic product!
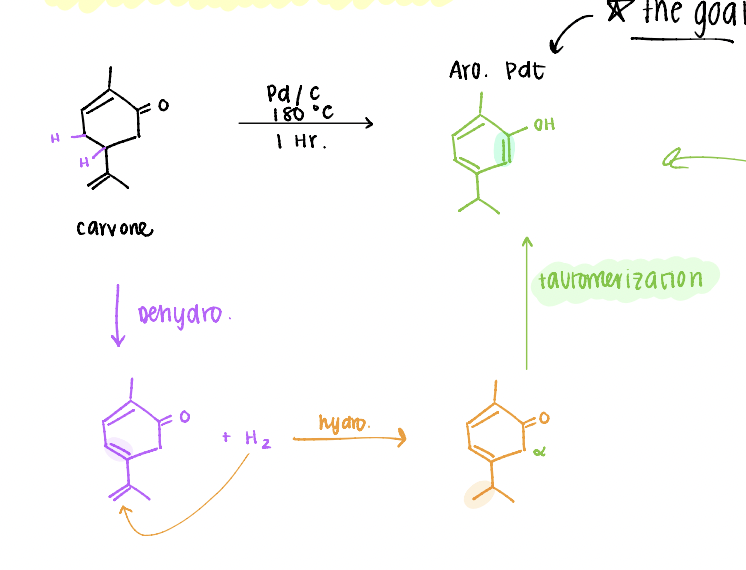
purification method for carvacrol reaction
liquid-liquid extraction: separates products based on REACTIVITY
extraction process for carvacrol
(pretend that bottom alkene on the desired product isn’t there…)
our desired product is the only one that loses its H because it is more acidic! (due to resonance stabilization)
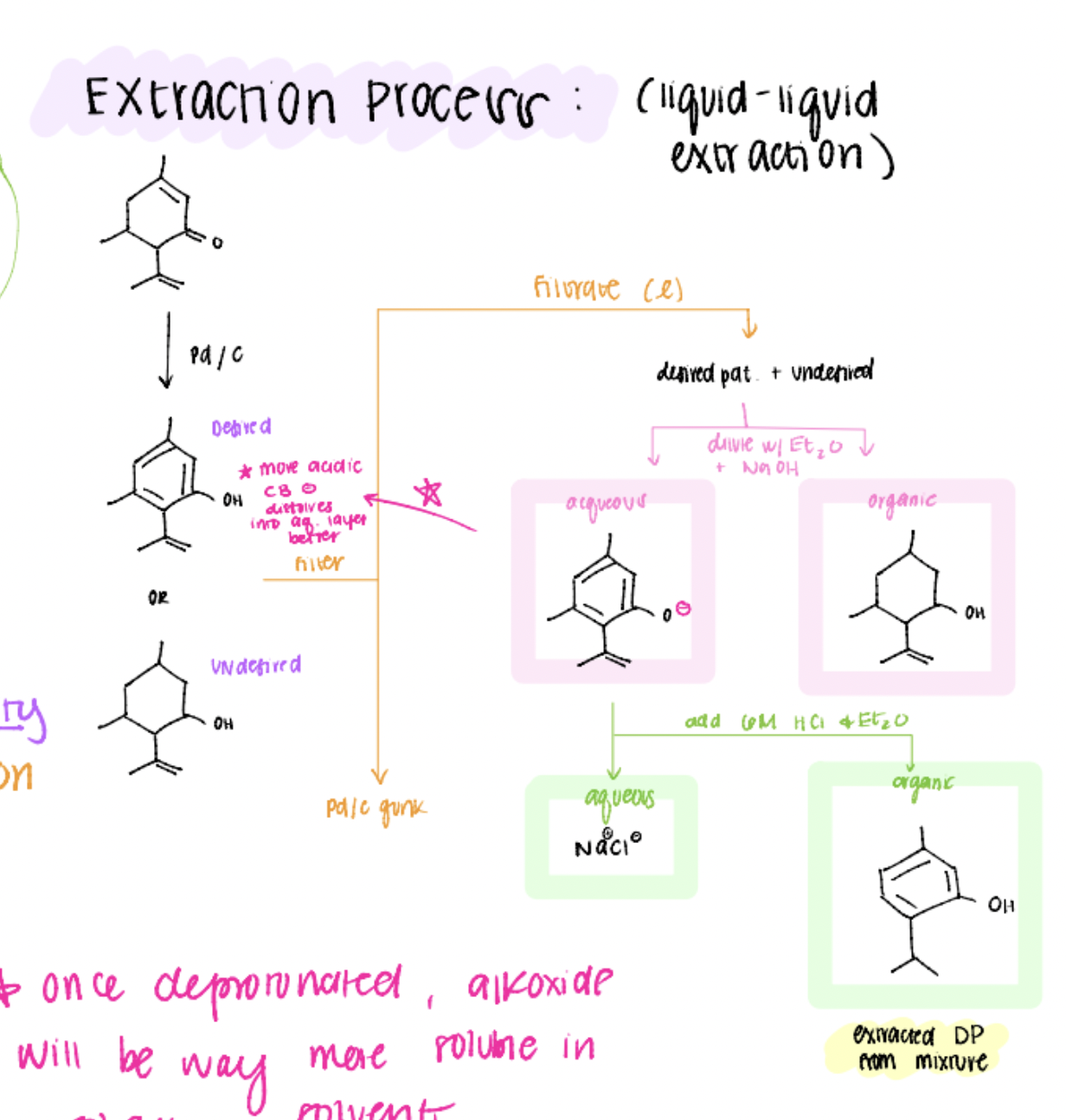
carvacrol extraction process flow chart
what is the purpose of co-spotting? (lab I)
to compare an unknown compound or reaction mixture to a known standard or reactant on the same plate. This allows for easier identification of components, especially when their Rf values are similar
Why is it important to achieve a pH of 12?
basic conditions are necessary to form the final neutral aromatic product
During Lab B, Hermione Student attempted to purify their crude product via recrystallization. They first dissolved their crude solid in 0.5 mL of hot ethyl acetate, but when they cooled their solution, no crystals were obtained. What happened?
Hermione likely did not obtain as much crude product as the textbook expected, and so accidentally used too much solvent.
After successfully reattempting their recrystallization, Hermione spotted their starting material, crude product, and recrystallized product on a TLC plate and developed the plate in 90:10 hexane:ethyl acetate. When Hermione visualized their plate under UV light, they didn't see any spots! What happened?
None of these substances have conjugated pi systems, so they are invisible under UV light.
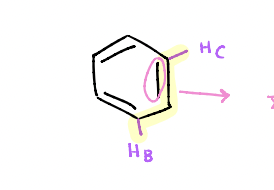
Which of the following alkene protons ( HA or HB) will have a higher chemical shift value and why?
Proton B will have a higher chemical shift value because it is a conjugated alkene proton
Why is the long glass tube (the "condenser") attached to the top of the round bottom flask?
so vaporized solvent can condense and be returned to the reaction mixture
Why is the red rubber septum added to the top of the condenser?
so oxygen in the air does not oxidize the palladium catalyst
Why isn't a boiling stick necessary for this experiment?
the magnetic stir bar is sufficient to prevent large bubbles from forming
After the reaction is complete, A Student added the resulting solids and approximately 3 mL of acetone to a centrifuge tube and centrifuged the mixture. They then discarded the supernatant. Why is this a bad idea?
The desired product is dissolved in the acetone.
After centrifuging, you will pipette the supernatant into a large test tube and gradually add water until crystals begin to form. Adding water encourages the product to crystallize because:
The product is less soluble in water than in acetone.
At the end of Exp 23 (Lab E), you will prepare and develop two separate TLC plates, one using 80:20 hexane:ethyl acetate as the mobile phase, and the other using 90:10 hexane:ethyl acetate.
Which mobile phase is more polar?
80:20 hexane:ethyl acetate
What do you predict will be the difference between these two plates?
All of the spots on the 80:20 plate will have larger Rf values.
In Lab G, many of the possible products contain a carboxylic acid. Depending on the pH, carboxylic acids can exist in equilibrium with their conjugate base carboxylate, as shown below. Imagine you reach the end of Lab G and don't see any crystals in your methanol solution. What is a possible explanation for this?
the carboxylate anion is soluble in methanol
In this scenario, the lab textbook recommends that you evaporate off the methanol and add 4.5 mL of 1M HCl and 3 mL of ether to what remains. Where is your product now?
in the organic (ether) layer. the HCl protonates the carboxylate and the neutral molecule is water insoluble
The NaOH reagent (base)in Q1 (in Lab I ) is required to deprotonate the substituted carbon and restore aromaticity ( EAS mechanism last step: refer to lab lecture). What additional purpose does NaOH serve?
deprotonating the alcohol makes 1-naphthol a better nucleophile
In addition to NaOH, Lab I also utilizes HCl. A video showing this portion of the experimental procedure is available hereLinks to an external site.. Why is the HCl dispensed into a flask filled with ice?
Diazonium salts can decompose when heated and explode when dry.