2. Introduction to Electricity w Static Electricity
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
List atomic structures and their charges
The nucleus consist of protons (+), neutrons (neutral charge) and electrons (-), which orbit the nucleus. Protons and electrons have equal but opposite charges, while neutrons have no charge.
Where are electrons located in the atomic structure?
Electrons orbit the nucleus.
What are the two types of electricity?
Static Electricity and Current Electricity
Static Electricity
Static electricity is the build up of electric charge on a surface caused by friction.
Current Electricity
Current Electricity is the flow of electric charge through a conductor, typically involving the movement of electrons in a circuit
Positive charges with positive charges repel/attract?
Repel
Negative charges with negative charges repel/attract?
Repel
Opposite charges repel/attract?
Attract
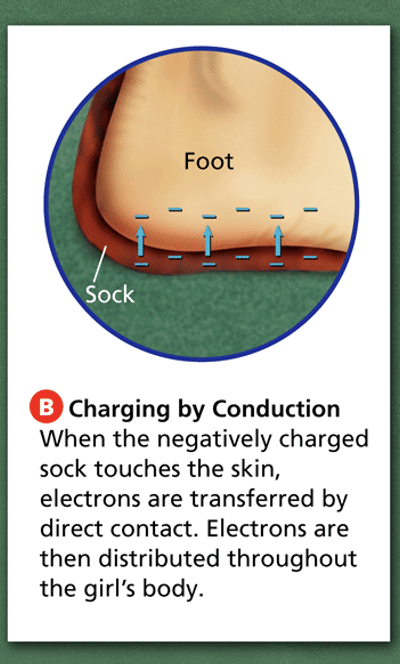
Conduction
The flow of heat of charges through a material which is made by direct contact and electrons flowing.
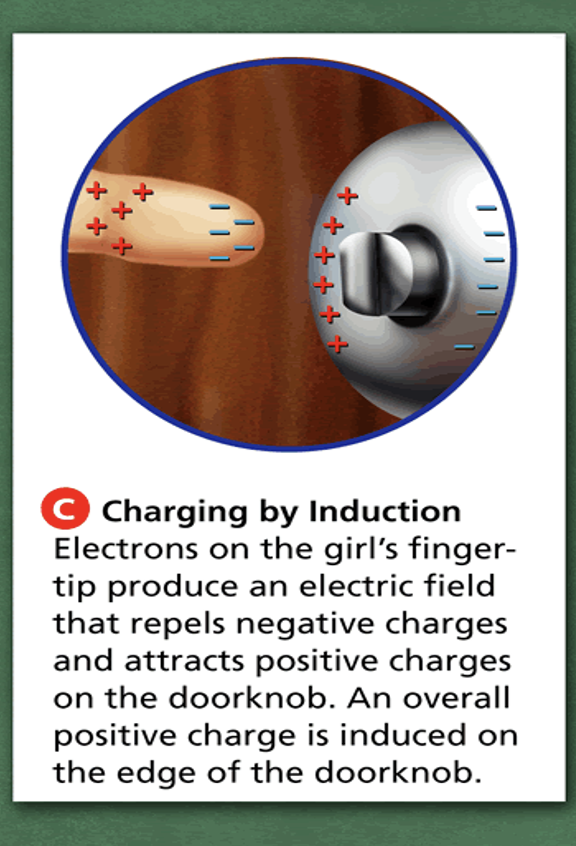
Induction
The process of charging an object without touching it
Friction
A process of two surfaces sliding or trying to slide across eachother in order to remove charges (usually electrons)