Chapter 8: Visual Motion Perception | Quizlet
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Avoiding imminent collision
How do we estimate the time to collision (TTC) of an approaching object?
- Tau (t): Information in the optic flow that could signal TTC without the necessity of estimating either absolute distances or rates.
Biological motion
The pattern of movement of all animals.
Motion-Induced Blindness (MIB)
A moving surface can cause stationary objects to "disappear".
Autokinetic effect
perception of movement of a stationary single point of light in a completely dark room.
- If you fixate on the point of light in the absence of any references, it will appear to move.
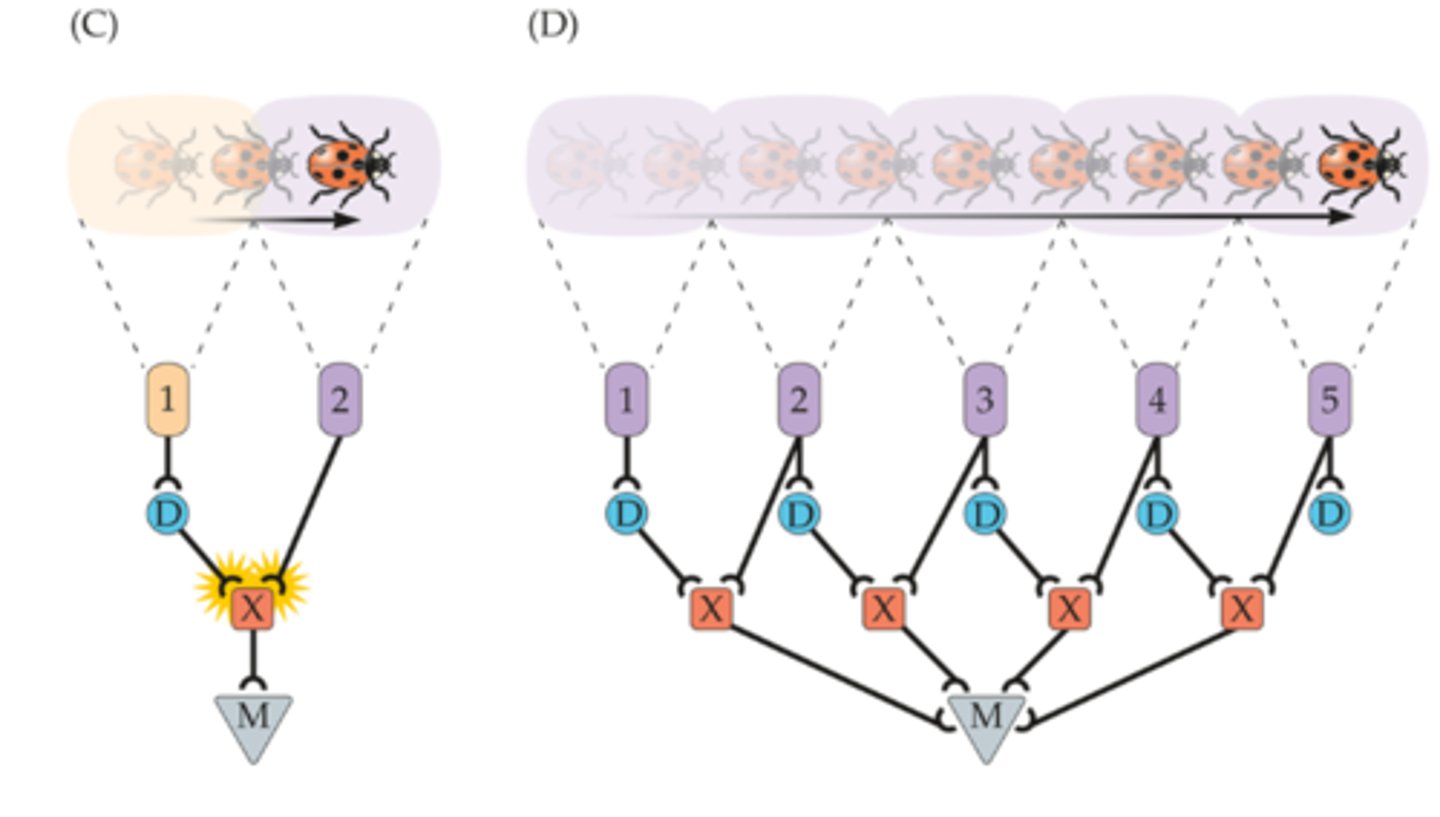
Neural Circuit for motion detection (Reichardt Detector)
Apparent motion
The illusory impression of smooth motion resulting from the rapid alternation of objects that appear in different locations in rapid succession.
Stroboscopic motion
illusion of motion that occurs when a series of images are viewed in rapid succession (cartoons/flipbooks)
Correspondence problem (motion)
The problem faced by the motion detection system of knowing which feature in frame 2 corresponds to which feature in frame 1.
Aperture
An opening that allows only a partial view of an object.
- Aperture problem: The fact that when a moving object is viewed through an aperture (or a receptive field), the direction of motion of a local feature or part of an object may be ambiguous.
First-order motion
The motion of an object that is defined by changes in luminance.
- Luminance-defined object: An object that is delineated by differences in reflected light.
Image-retina system
based on a moving external stimulus that produces successive stimulation of adjacent retinal loci.
Eye movements
Smooth pursuit: Voluntary eye movement in which the eyes move smoothly to follow a moving object.
Saccade: A type of eye movement, made both voluntarily and involuntarily (microsaccade), in which the eyes rapidly change fixation from one object or location to another.
Vergence: A type of eye movement, both voluntary and involuntary, in which the two eyes move in opposite directions.
• Convergent eye movements turn the eyes inward.
• Divergent eye movements turn the eyes outward.
Reflexive: Automatic and involuntary eye movements.
Efference copy (or corollary discharge signal)
When an eye movement is issued, the motor command is copied and sent to other areas of the sensory cortices.
Motion aftereffect (MAE)
The illusion of motion of a stationary object that occurs after prolonged exposure to a moving object.
Interocular transfer
The transfer of an effect (such as adaptation) from one eye to the other.
Middle temporal area (V5)
is a specialized location in the brain for perception of global motion.
Akinetopsia
A rare neurophysiological disorder in which the affected individual has no perception of motion.
Optic array
The collection of light rays that interact with objects in the world in front of a viewer. Term coined by J. J. Gibson (1904-1979).
Optic flow
The changing angular position of points in a perspective image that we experience as we move through the world.
Focus of expansion (FOE)
The point in the center of the horizon from which, when we are in motion, all points in the perspective image seem to emanate.
Two interdependent motion systems
Image-Retina system and Eye-Head system
Eye-head system
incorporates visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive information from the movement of the eyes, the head, and the body to contextualize and perceive movement when the retinal image may be misleading (e.g., when the eyes track a moving object).
Superior colliculus
A structure in the midbrain that is important in initiating and guiding eye movements.
Optokinetic nystagmus
is another reflexive eye movement in which the eyes will involuntarily track a continually moving object, moving smoothly in one direction (e.g., to the right) in pursuit of the object moving in that same direction, and then snap back.
Autokinetic nystagmus
reflexive eye movement in which the eyes will involuntarily track a continually moving object, moving smoothly in one direction.
- Important for image stabilization
- Prevents motion blur
Saccadic suppression
The reduction of visual sensitivity that occurs when we make saccadic eye movements.
Comparator
An area of the visual system that receives one copy of the order issued by the motor system when the eyes move (the other copy goes to the eye muscles).
En progreso (13)
Comenzaste a estudiar estos términos. ¡Sigue así!