Unit 8: Topic 2 - Energy Flow Through Ecosystems
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
ecosystem
* the sum of all the organisms living in a given area and the abiotic factors they interact with
2
New cards
biotic factors
* living, or once living, components of an environment
3
New cards
abiotic factors
* nonliving (physical and chemical properties of the environment)
4
New cards
1st law of thermodynamics
energy can neither be created nor destroyed, only transferred
5
New cards
2nd law of thermodynamics
exchanges of energy increase the entropy of the universe
6
New cards
ecosystems and energy
* a **net gain** in energy results in energy storage or **growth** of an organism
* a **net loss** of energy results in loss of mass and eventual **death** of an organism
* a **net loss** of energy results in loss of mass and eventual **death** of an organism
7
New cards
metabolic rate
* the total amount of energy an animal uses in a unit of time
* can be measured in calories, heat loss, or by the amount of oxygen consumed (or CO2 produced)
* oxygen is used in cellular respiration and CO2 is produced as a by-product
* an animal’s _____ ________ is related to its body mass
* **smaller** organisms = **higher** _______ ___
* **larger** organisms = **lower** ____________
\*\*\*\*\*this is due to the surface area to volume ratio, a smaller animal has more body surface relative to its volume of metabolizing tissue, so more heat is lost
* can be measured in calories, heat loss, or by the amount of oxygen consumed (or CO2 produced)
* oxygen is used in cellular respiration and CO2 is produced as a by-product
* an animal’s _____ ________ is related to its body mass
* **smaller** organisms = **higher** _______ ___
* **larger** organisms = **lower** ____________
\*\*\*\*\*this is due to the surface area to volume ratio, a smaller animal has more body surface relative to its volume of metabolizing tissue, so more heat is lost
8
New cards
endotherms
* use thermal energy from metabolism to maintain body temperatures
9
New cards
ectotherms
* use external sources (i.e. sun/shade or other organisms) to regulate their body temperature
10
New cards
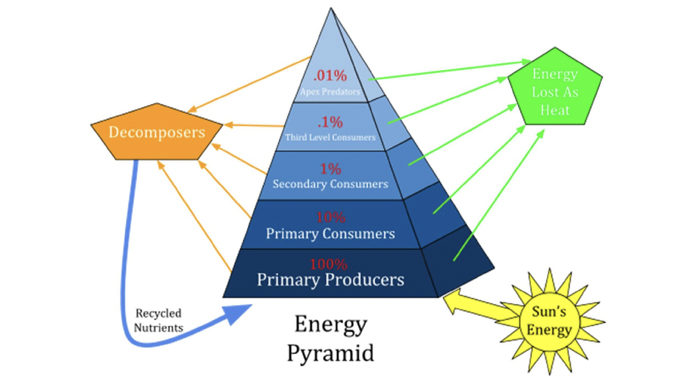
trophic levels
* species can be grouped based upon their main source of nutrition and energy
* energy CANNOT be recycled
* the sun constantly supplies energy to ecosystems
* energy CANNOT be recycled
* the sun constantly supplies energy to ecosystems
11
New cards
primary producers
* tropic levels
* autotrophs
* use light energy to synthesize organic compounds
* plants, algae, photosynthetic plankton
* some organisms are chemosynthetic (produce food using energy created by chemical reactions
* i.e. some bacteria and archaea organisms
* autotrophs
* use light energy to synthesize organic compounds
* plants, algae, photosynthetic plankton
* some organisms are chemosynthetic (produce food using energy created by chemical reactions
* i.e. some bacteria and archaea organisms
12
New cards
heterotrophs
* trophic levels
* rely on autotrophs because they cannot make their own food
* **primary consumers:** herbivores
* **secondary consumers:** carnivores that eat herbivores
* **tertiary consumers:** carnivores that eat other carnivores
* **decomposers:** get energy from detritus (nonliving organic material; leaves, wood, dead organisms)
* include fungi and many prokaryotes
* important for recycling chemical elements
* rely on autotrophs because they cannot make their own food
* **primary consumers:** herbivores
* **secondary consumers:** carnivores that eat herbivores
* **tertiary consumers:** carnivores that eat other carnivores
* **decomposers:** get energy from detritus (nonliving organic material; leaves, wood, dead organisms)
* include fungi and many prokaryotes
* important for recycling chemical elements
13
New cards
trophic structure
* determined by the feeding relationships between organisms
* **food chain**: the transfer of food energy up the trophic levels
* **food web**: linked food chains
* **food chain**: the transfer of food energy up the trophic levels
* **food web**: linked food chains
14
New cards
primary production
* the amount of light energy that is converted to chemical energy
* primary producers set a “spending limit” for the entire ecosystems energy budget
* **Gross primary production (GPP):** total primary production in an ecosystem
* **Net primary production (NPP):** the GPP minus the energy used by the primary producers for respiration (Ra)
* primary producers set a “spending limit” for the entire ecosystems energy budget
* **Gross primary production (GPP):** total primary production in an ecosystem
* **Net primary production (NPP):** the GPP minus the energy used by the primary producers for respiration (Ra)
15
New cards
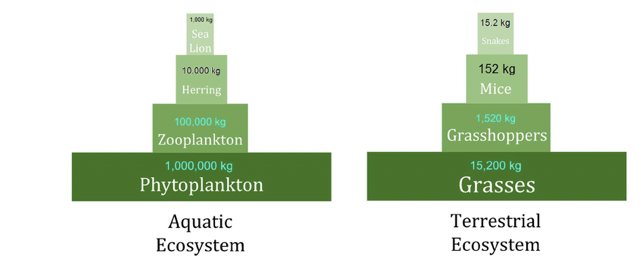
secondary production
* the amount of chemical energy in a consumer’s food that is converted to new biomass
* the transfer of energy between trophic levels is at around 10% efficiency
* the transfer of energy between trophic levels is at around 10% efficiency
16
New cards
matter cycling
* unlike energy, matter cycles through ecosystems
* matter is found in limited amounts, unlike solar energy
* **biogeochemical cycles:** nutrient cycles that contain both biotic and abiotic factors
* water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycle
* matter is found in limited amounts, unlike solar energy
* **biogeochemical cycles:** nutrient cycles that contain both biotic and abiotic factors
* water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycle
17
New cards
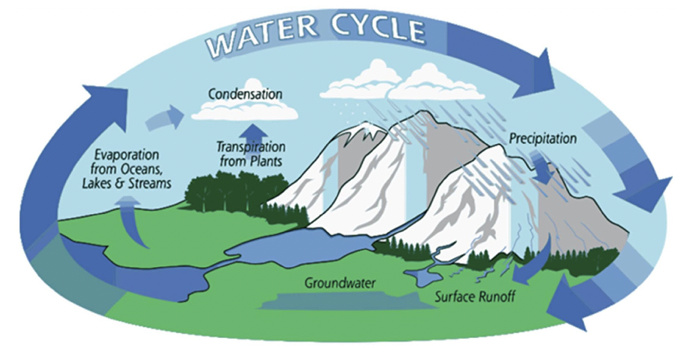
water cycle
* water is essential for all life and influences the rate of ecosystem processes
18
New cards
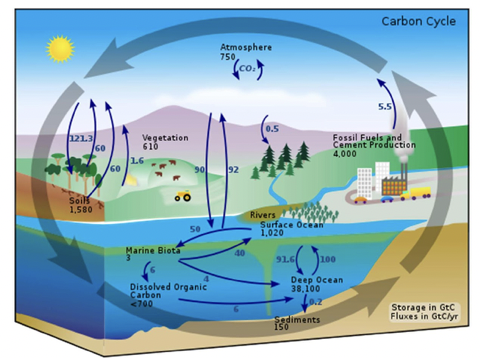
carbon cycle
* carbon is essential for life and required in the formation of organic compounds
19
New cards
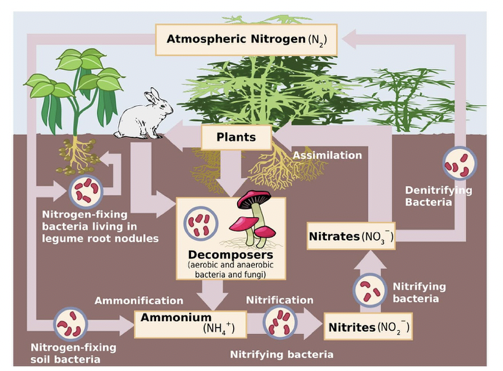
nitrogen cycle
* nitrogen is important for the formation of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids
20
New cards
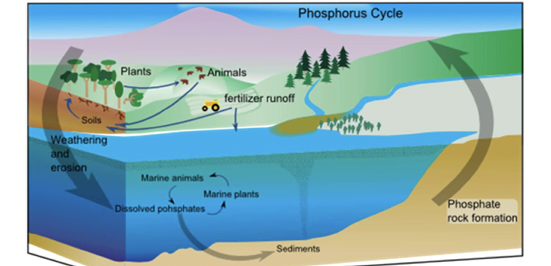
phosphorus cycle
* phosphorous is important for the formation of nucleic acids, phospholipids, and ATP (energy)