Urban Environments (Geography IB)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Urban
An area of habitation that provides services for payment to the surrounding countryside. Offers a variety of services to the public, can include manufacturing, or breadth of shops available for consumers
Rural
Dwelling or group of dwellings which solely function as housing for farm workers. Lacks public services
Settlement
All types of places where people live
Site
Physical location of the settlement on a global scale.
Site factors include terrain, climate, vegetation etc
Situation
Location of a place relative to its surroundings.
Hinterland
The area surrounding an urban place
Primary industry
Obtain natural resources sourced directly from earth
Agriculture, mining, forestry
Secondary industry
Converts raw materials provided by primary industries into products for consumers.
Manufacturing processes → processing and fabricating
Tertiary industry
Provides services
Health, banking, accounting and restaurants
Quaternary industry
Provide knowledge-based services such as information technology, information generation and sharing, research and development, education and design
Threshold population
Amount of people needed for a settlement to be viable
Urban hierarchy
A reflection of the different sized settlements which reflects the ranges and threshold populations of goods and services that people demand within the area
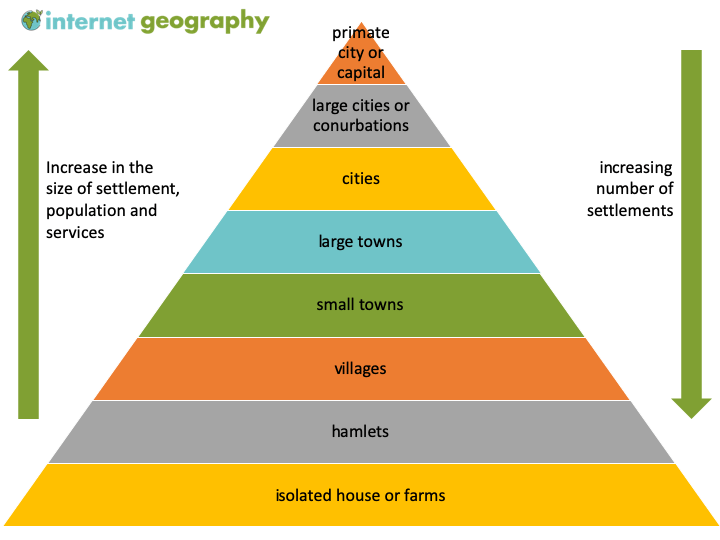
High order goods (low frequency)
Goods purchased less frequently. Generally expensive goods
Low order goods (high frequency)
Goods and services that people demand locally, therefore have a short range
Primate city
The largest city in a country, which has a population of half or a third of the nations entire population
Bid-rent theory
Retailers are able to pay a high rent cost, but are only willing to do so when in a highly accessible location. As a means of making profit, being in an accessible location with high foot traffic is important for retailers
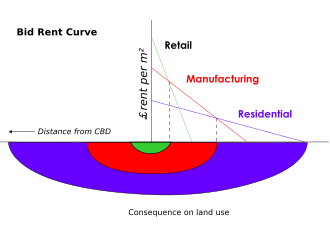
Distance decay
Willingness to travel diminishes as distance increases
Urban growth
Shanty housing
Settlement of impoverished people who live in poor housing conditions
Houses constructed with cheap materials (corrugated iron, fabric or wood)
Found in abandoned areas (near train stations, rivers)
Urbanisation
Measurement of the proportion of the population living in urban areas at a given time
Urban growth
Raw increase in the quantity of people living in urban places
Centripetal movement (inward)
refers to the movement of people to urban areas. Includes rural-urban migration, gentrification and re-urbanisation
Centrifugal movement (outward)
refers to the movement of people out of urban areas. Includes urban sprawl, suburbanisation and counter urbanisation
Gentrification
middle class residents chose to move to run down inner city areas for the intention of renovating old infrastructure. Old building are then restored to their original quality, therefore providing them with considerable profit.
Example: Port Melbourne, New York
Rural-urban migration
Movement of people from rural areas to urban areas.
Examples: China, Papua New Guinea
Re-urbanisation
when people move back into inner city areas where populations had previously declined due to a range of social, economic and environmental issues
Examples: Docklands
Counter urbanisation
Suburbanisation
Overall movement and resettlement of people from inner city locations to vast new areas of housing further from the CBD
Urban sprawl
Rapid expansion of the geographic extent of cities and towns
Exurbanisation
Affluent people move from the city to rural places
Green infrastructure
Structures which work with nature to bring environmental benefits to the population
Examples: Central Park NY, Melbourne Botanical gardens
Grey infrastructure
Determine a city’s layout or urban morphology
Examples: Princes Highway in Melbourne, Pacific Coast Highway California
Deindustrialisation
The long-term, absolute decline in employment in the manufacturing sectors of an economy. It refers to a loss of jobs rather than a decline in productivity
Causes of deindustrialisation
Globalisation
Consumer preference
Technological advancements
Government policies
Urban microclimate
climate of any small area that is different to it's surrounding area
Urban heat island
a type of urban microclimates in which an urban area becomes warmer than the surrounding area
Traffic congestion
When the density of cars on a road excess the carrying capacity of the road. This is evident in slower travel speed for vehicles, longer travel times and queues of vehicles
Factors of traffic congestion
More cars on the road
Road works → detour
Peak hour
Accidents / crashes
Weather
Resilient city
Capacity of people, communities, businesses and systems within a city to survive, adapt and thrive no matter what kind of chronic stresses and acute shocks they experience
Eco city
a human settlement modeled on the self-sustaining resilient structure and function of natural ecosystems