Build a Nephron - Distal Convoluted Tubule
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is the ultrastructure of the classic distal tubule
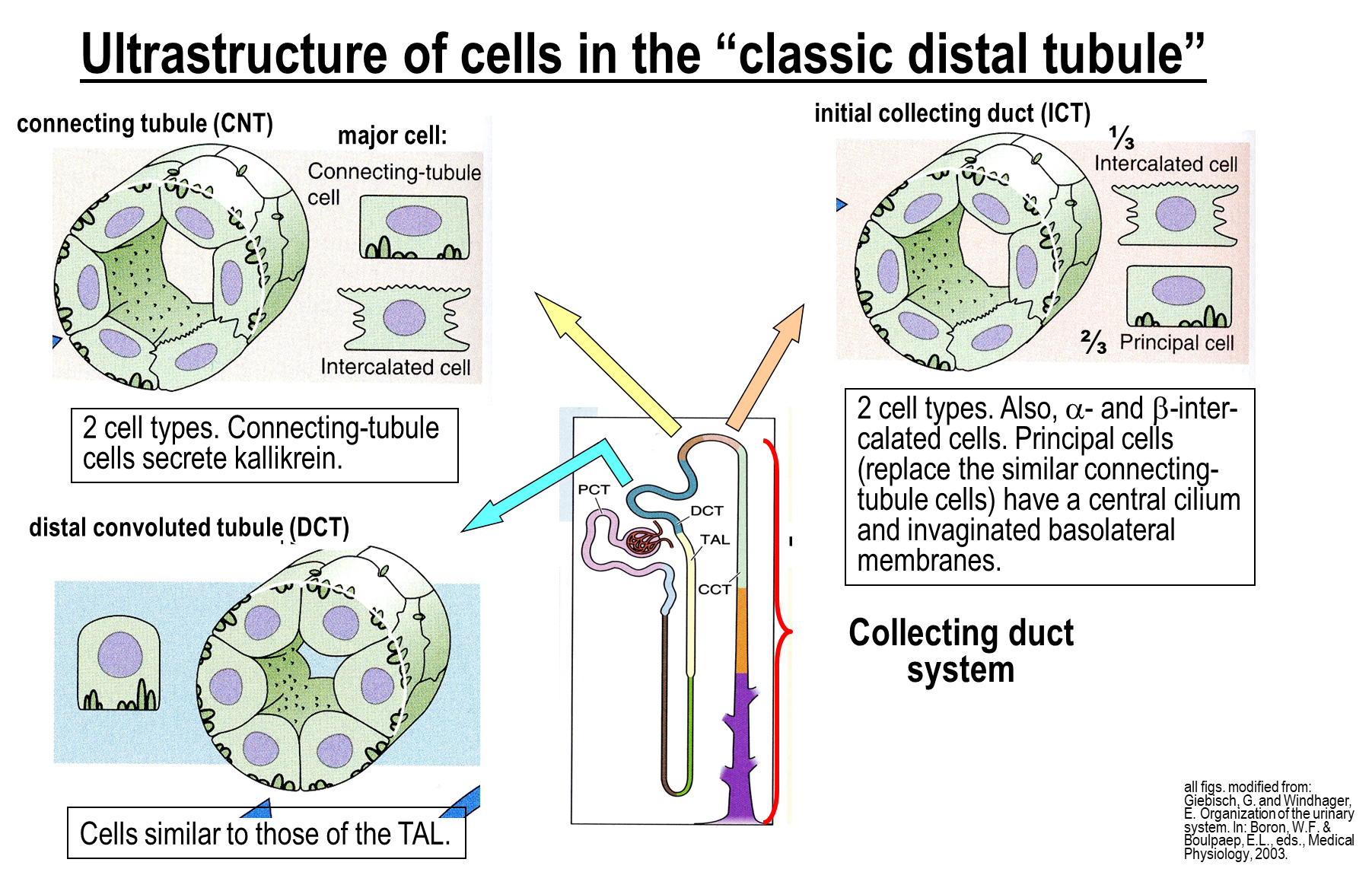
The Classic Distal Tubule is comprised of three major segments
1) Distal Convoluted Tubule
→ basically the same structure as the thick ascending limb
2) Connecting Tubule which contains two new cell types
→ connecting tubule cells
→ intercalated cells - subdivided into beta and alpha subtypes
3) Initial Collecting Duct
→ connecting tubule cells are replaced by principal cells
→ also contains intercalated cells - subdivided into beta and alpha subtypes
What is the ultrastructure of the collecting duct system
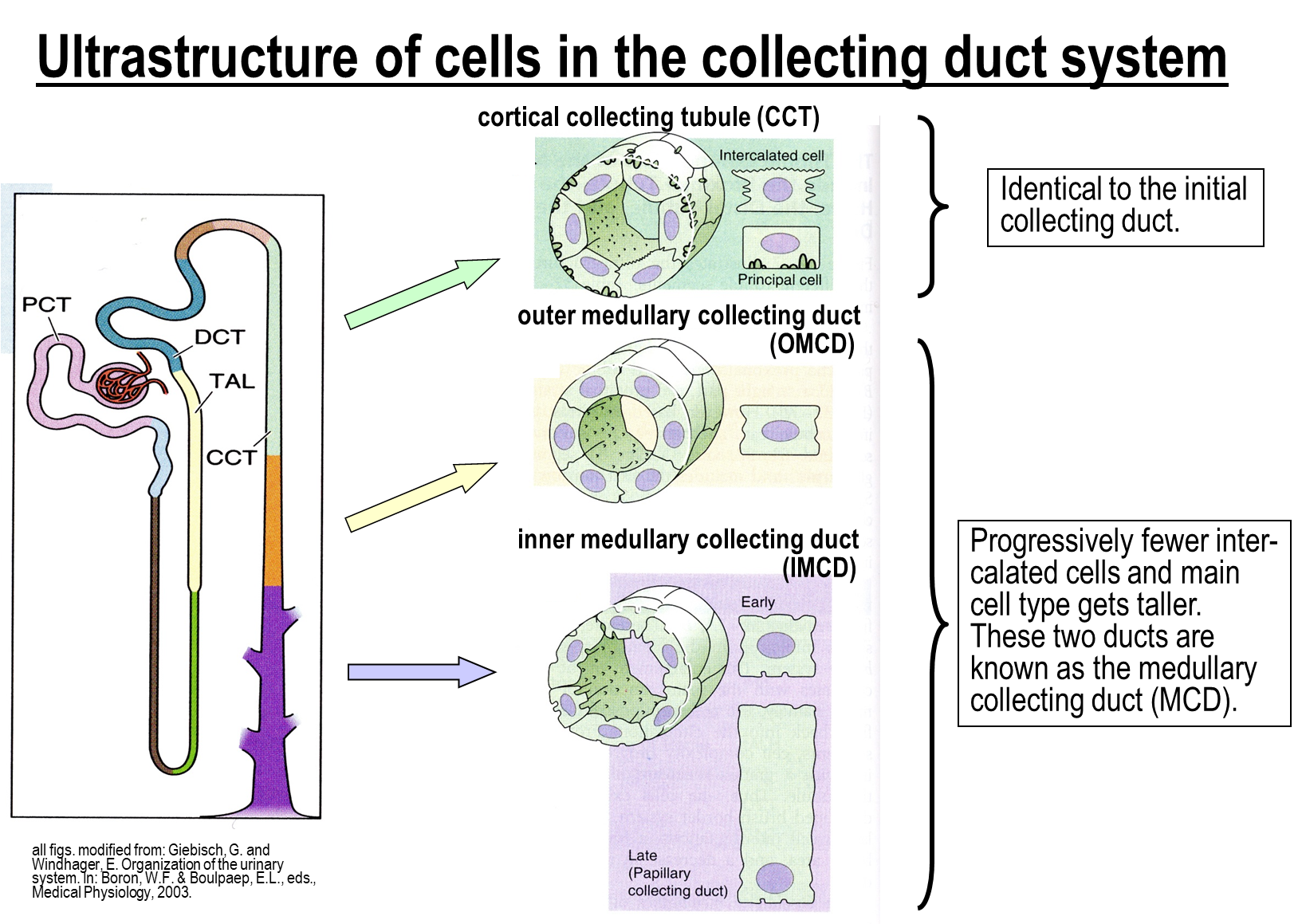
The collecting duct system is subdivided into three major regions:
1) Cortical Collecting Tubule
→ comprised of intercalated cells and principal cells, similar to the initial collecting duct
2) Outer Medullary Collecting Duct and Inner Medullary Collecting Duct
→ comprised of the same cell type, but the cell will become taller and tighter together as you move from outer to inner
What are the sodium reabsorption at the distal convoluted tubule
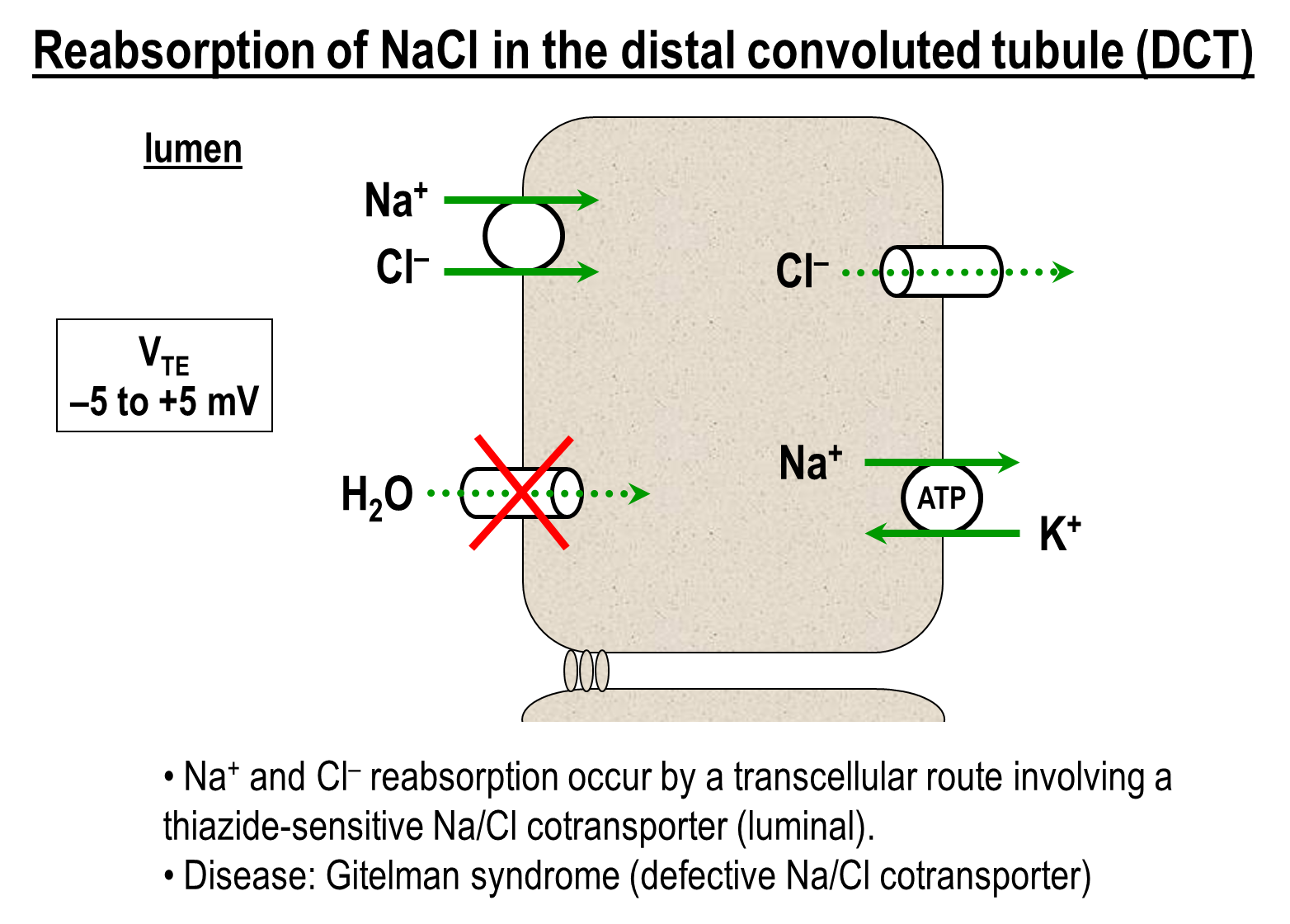
1) Thiazide sensitive sodium chloride transporter on the apical surface
→ can be inhibited by thiazide diuretics leading to decreased by a class of thiazide diuretics
2) Basolateral Transporters
→ Sodium Potassium ATPase
→ Chloride Channel
What is the mechanism of sodium and chloride reabsorption in the cortical collecting tubule?
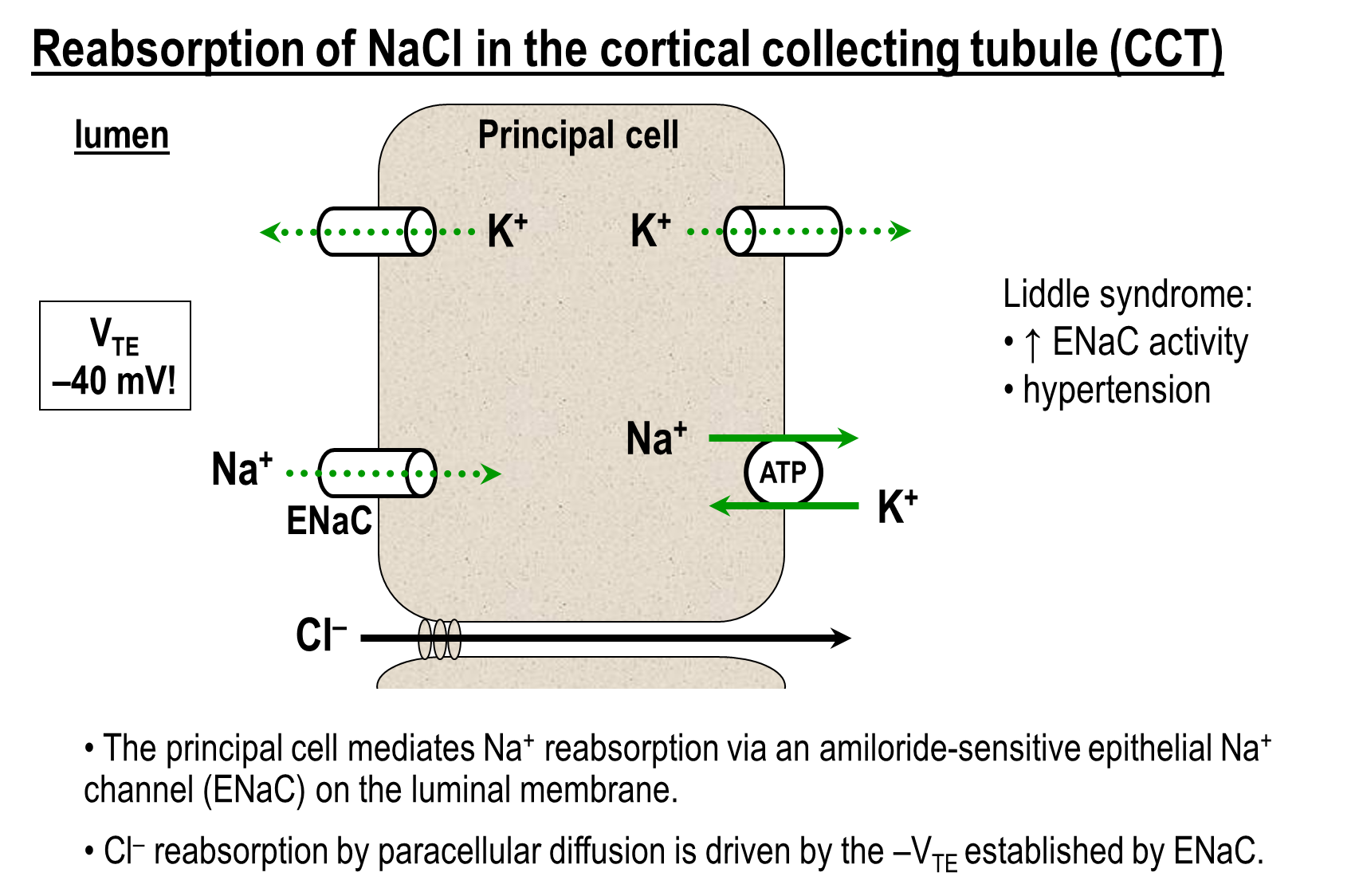
The cortical collecting tubule can reabsorb sodium via the Epithelial Sodium Channel (ENaC)
1) ENaC on the principal cells is constitutively active and its transport creates a negative transepithelial potential
→ this negative transepithelial potential will stimulate proton and potassium secretion into the lumen
→ negative potential will also draw chloride through the paracellular route
2) Chloride reabsorption via the chloride bicarbonate exchange on the beta intercalated cells
What is Liddle Syndrome
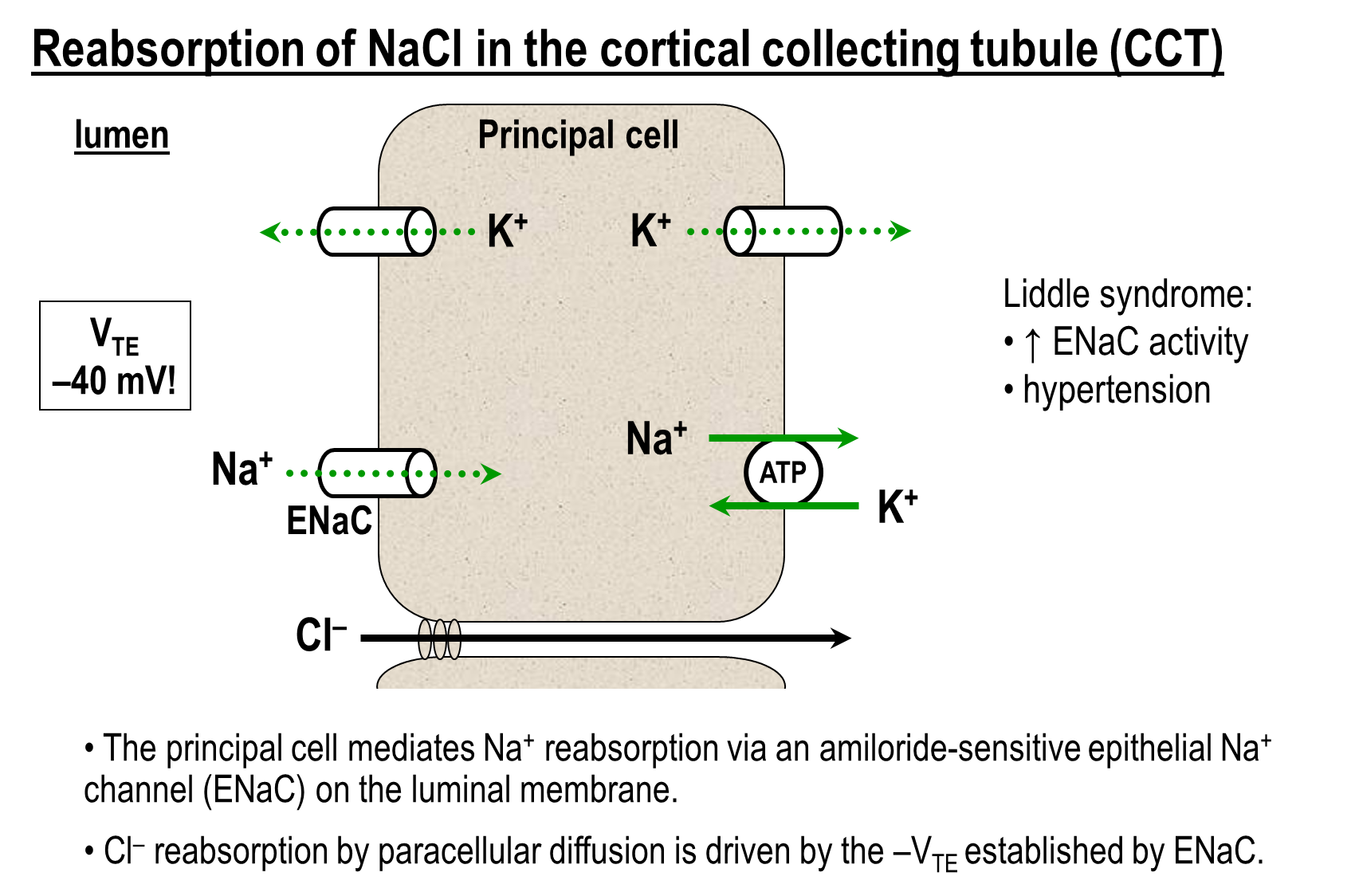
Liddle Syndrome is increased ENaC activity
→ this leads to increased sodium chloride reabsorption at the cortical collecting tubule
→ patients will experience hypertension and are extremely sensitive to salt levels
What is Gitelman Syndrome?
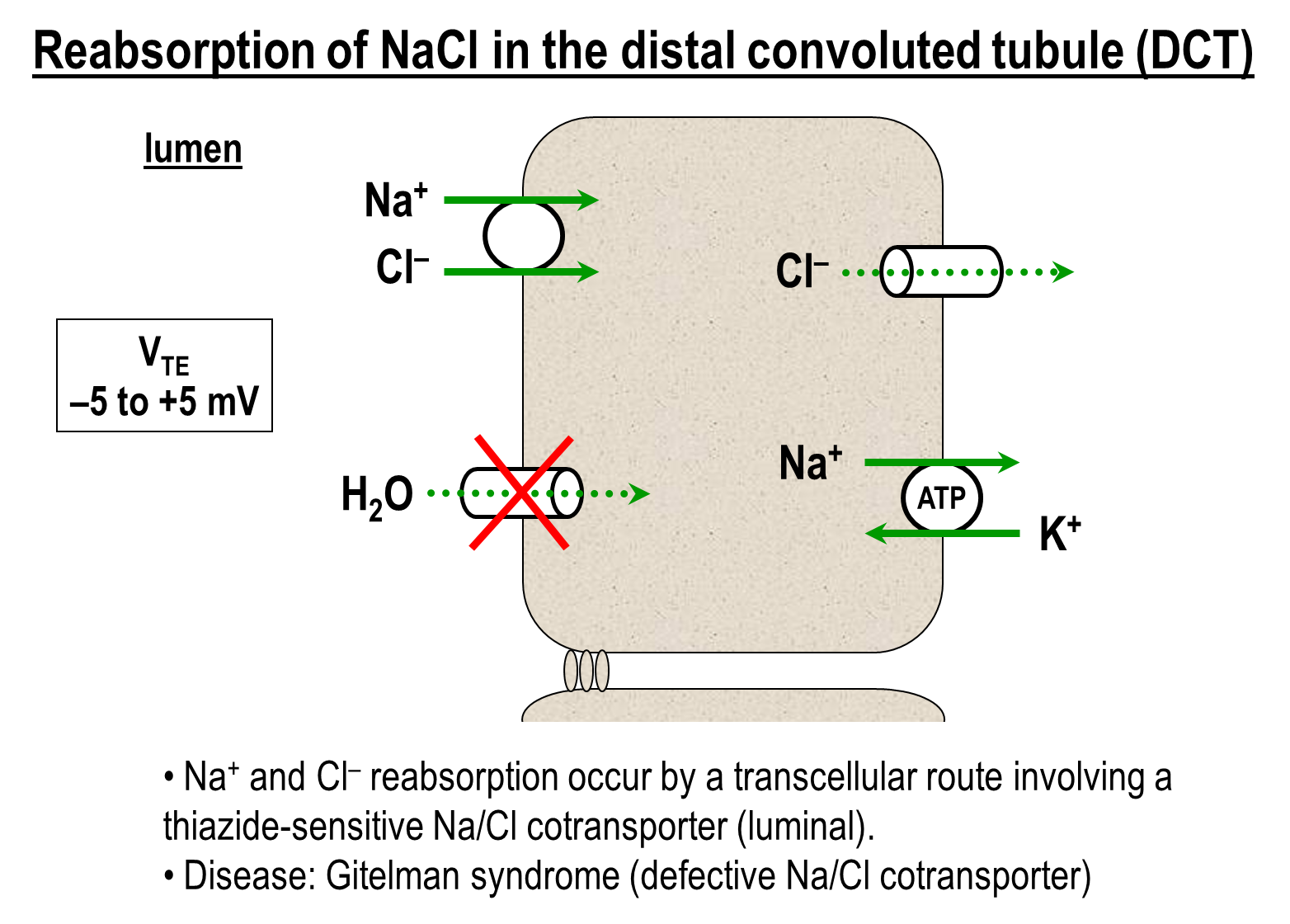
Gitelman Syndrome is a defective Sodium Chloride cotransporter found in the distal convoluted tubule
→ leads to decreased sodium chloride reabsorption across the DCT
How is Sodium Reabsorption regulated in the distal tubule?
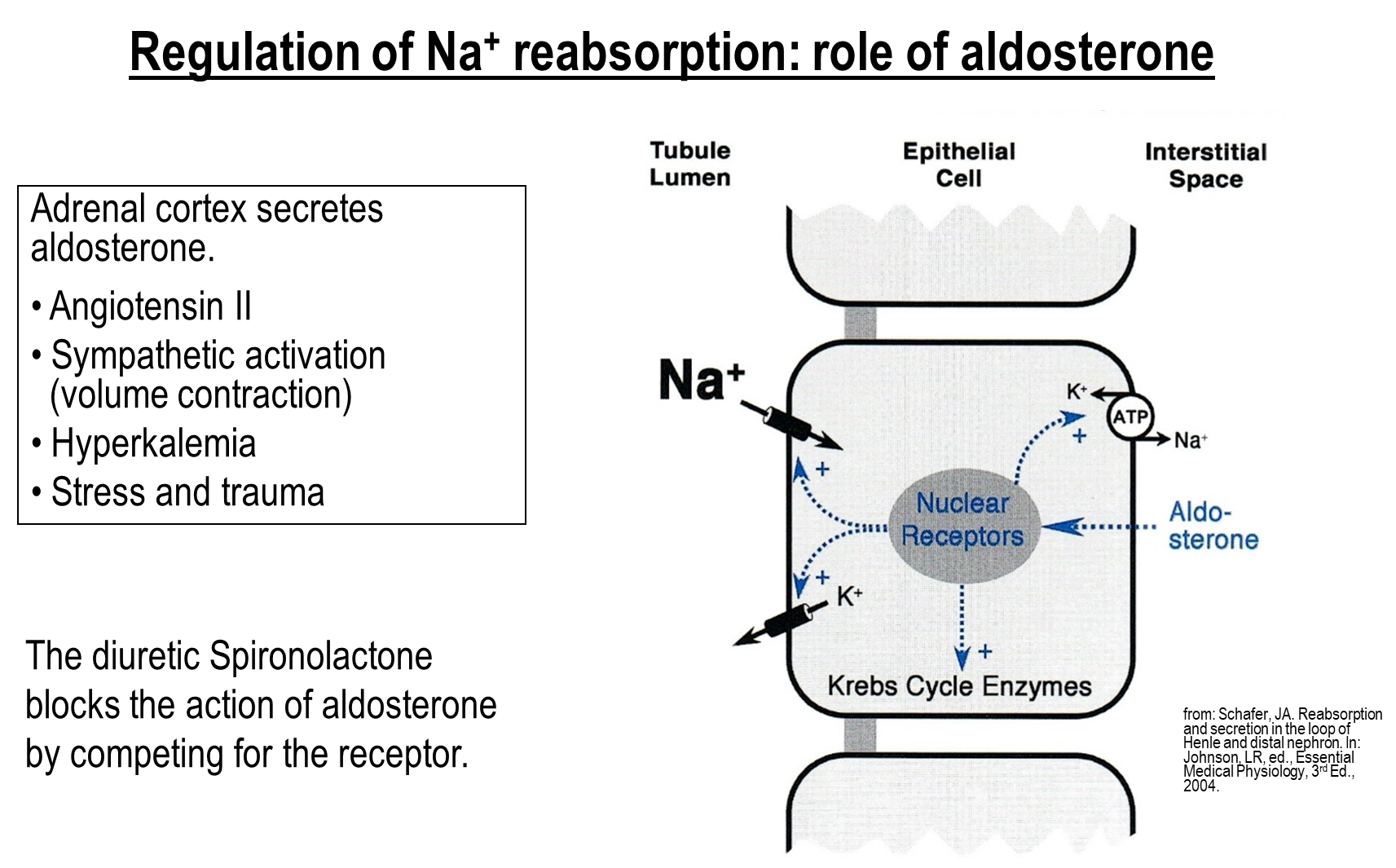
Aldosterone released from the adrenal cortex in response to angiotensin II, sympathetic activation, or hyperkalemia is responsible for sodium reabsorption regulation in the DCT
1) Aldosterone crosses the cell membrane and binds to nuclear receptors increasing activity of ENaC and the apical potassium channel
→ also stimulates the sodium potassium pump on the basolateral membrane
2) Aldosterone also upregulates Kreb Cycle Enzymes leading to increased ATP production
can be inhibited by Spironolactone
How does water reabsorption occur in the distal
Water Reabsorption in the Distal Nephron occurs passively as a result of both increased water permeability and some osmotic driving force
1) Anti-Diuretic Hormone is the main controller of this process
→ when ADH is low, water permeability is low and less water is being reabsorbed from the distal convoluted tubules
→ when ADH is high, water permeability is high more water is being reabsorbed
How is Potassium Reabsorbed in the Cortical Collecting Tubule?
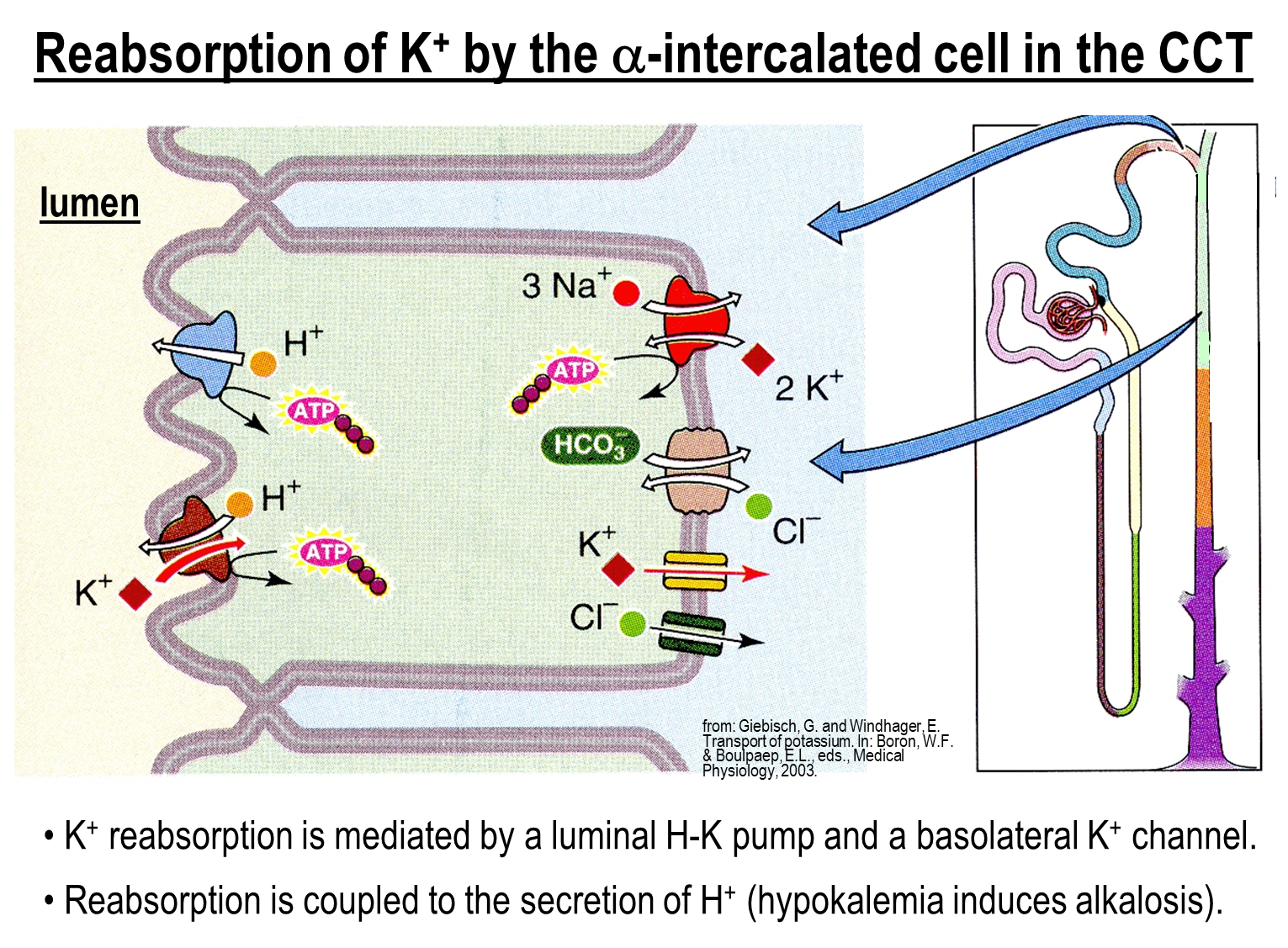
Potassium is secreted into the urine in the cortical collecting tubule due to the effect of ENaC generating a negative transepithelial potential via the apical potassium channel
1) However, potassium can be reabsorbed at the alpha intercalated cells via the Hydrogen Potassium Pump (exchanger)
→ pumps potassium across the apical membrane in exchange for protons out into the lumen
→ aids in reabsorption of potassium when potassium levels are low
What is Acid-Base Secretion at the medullary collecting ducts?
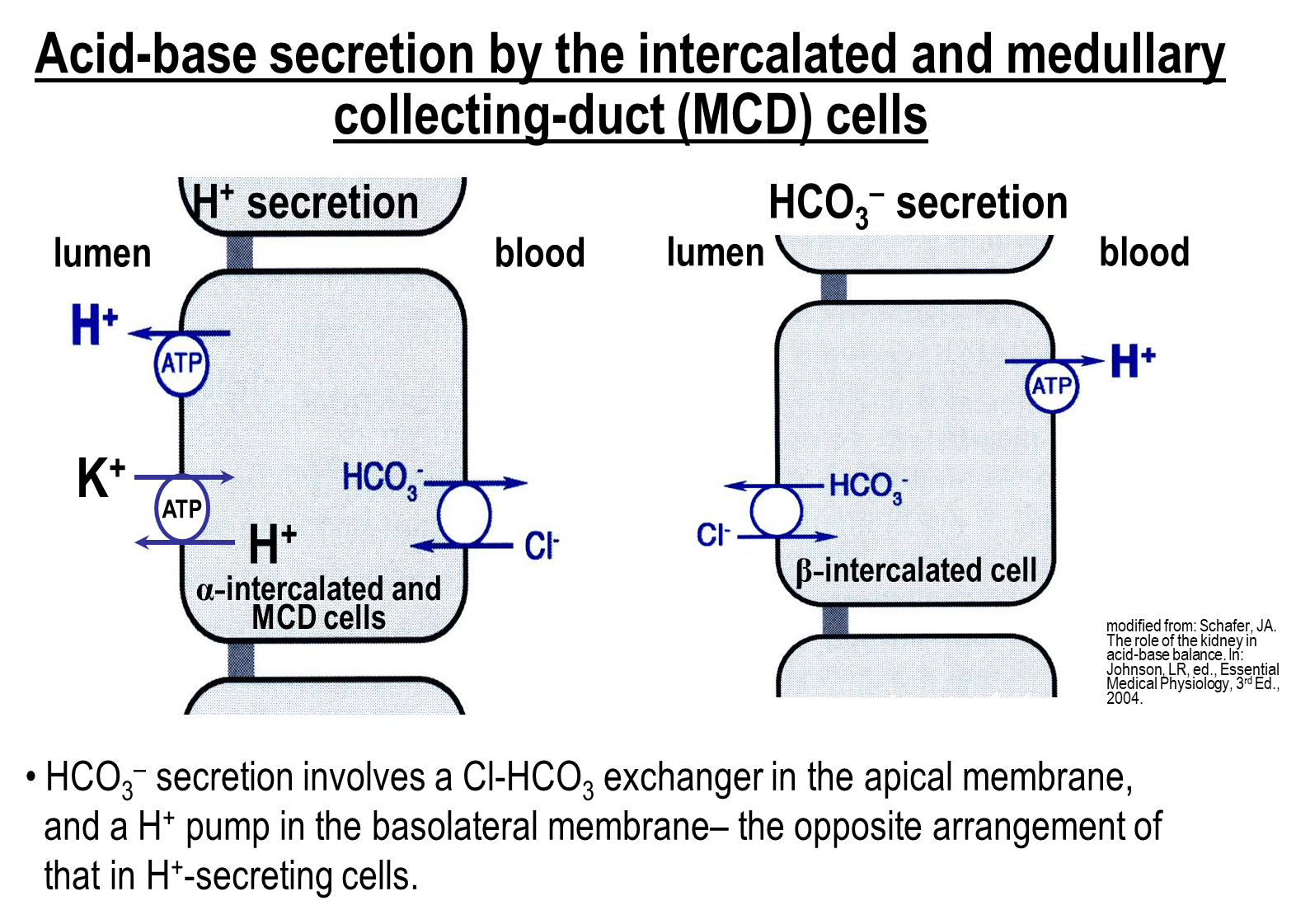
Acid Base Secretion into the lumen of the nephron occurs at the medullary collecting ducts
1) Acid secretion occurs at the alpha-intercalated cells
→ secrete protons via the proton pump and the Hydrogen Potassium Exchanger
→ both these transport mechanisms drive protons into the lumen
→ because of this we also need a chloride bicarbonate exchanger on the basolateral end in order to acid base balance
2) Bicarbonate secretion occurs at the beta-intercalated cells is responsible for bicarbonate secretion
→ contains a proton pump on the basolateral side
→ contains a chloride bicarbonate exchanger on the apical side
How does reabsorption of calcium occur in the distal convoluted tubule
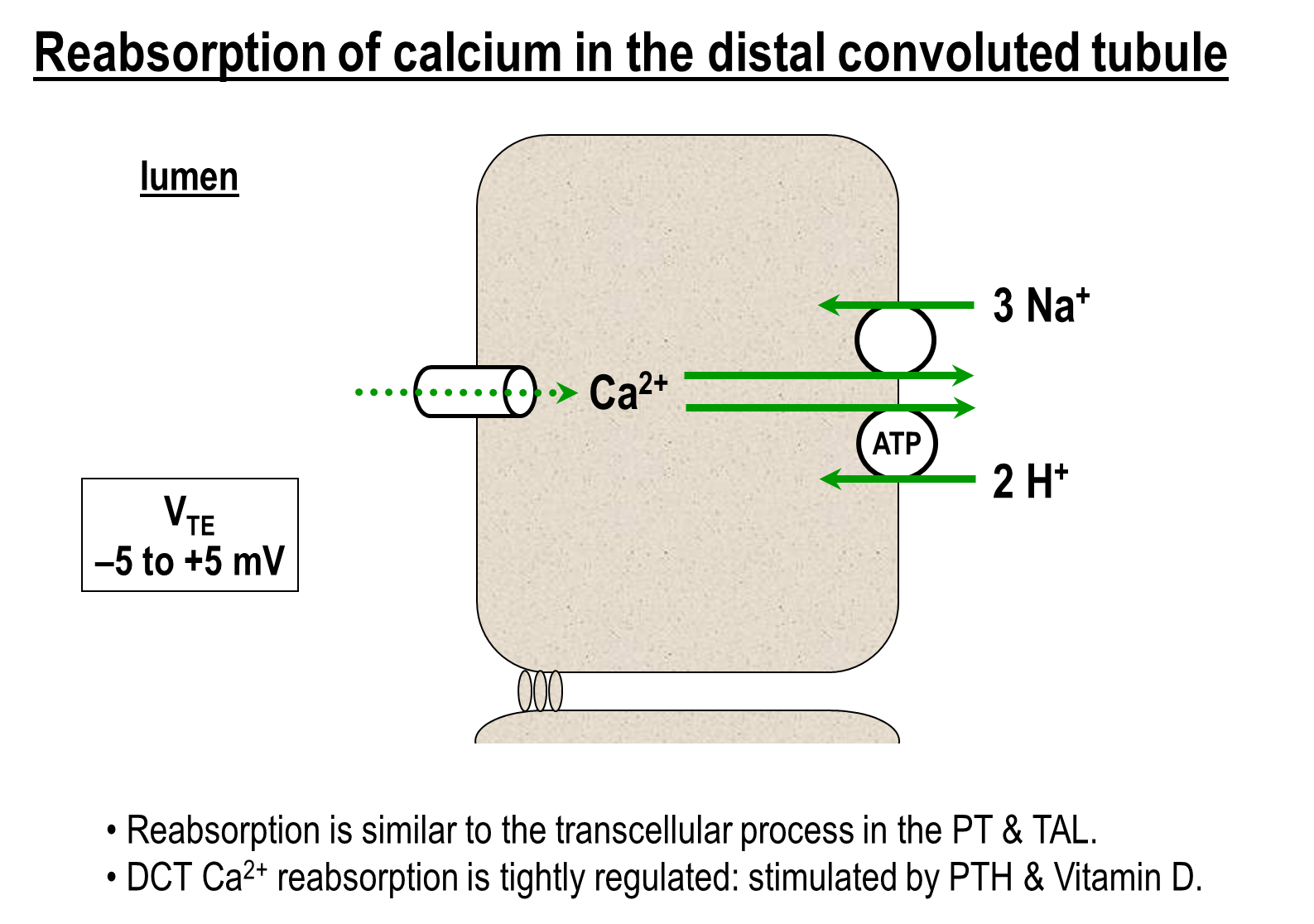
The majority of calcium is regulated and occurs transcellularly
1) Calcium Channel on the Apical Surface
2) Basolateral End
→ Calcium Sodium Exchanger - one calcium for 3 sodium in
→ Calcium Proton Exchanger (ATPase)
3) This process is regulated by parathyroid hormone and vitamin D
→ parathyroid hormone directly stimulate the calcium channel on the apical surface
→ Vitamin D will increase expression of calbindin, an intracellular calcium buffer that will bind to an decrease calcium concentration inside the cell. This leads to an increased driving force through the apical calcium channel
What are the effects of the three common diuretics on potassium and calcium reabsorption?
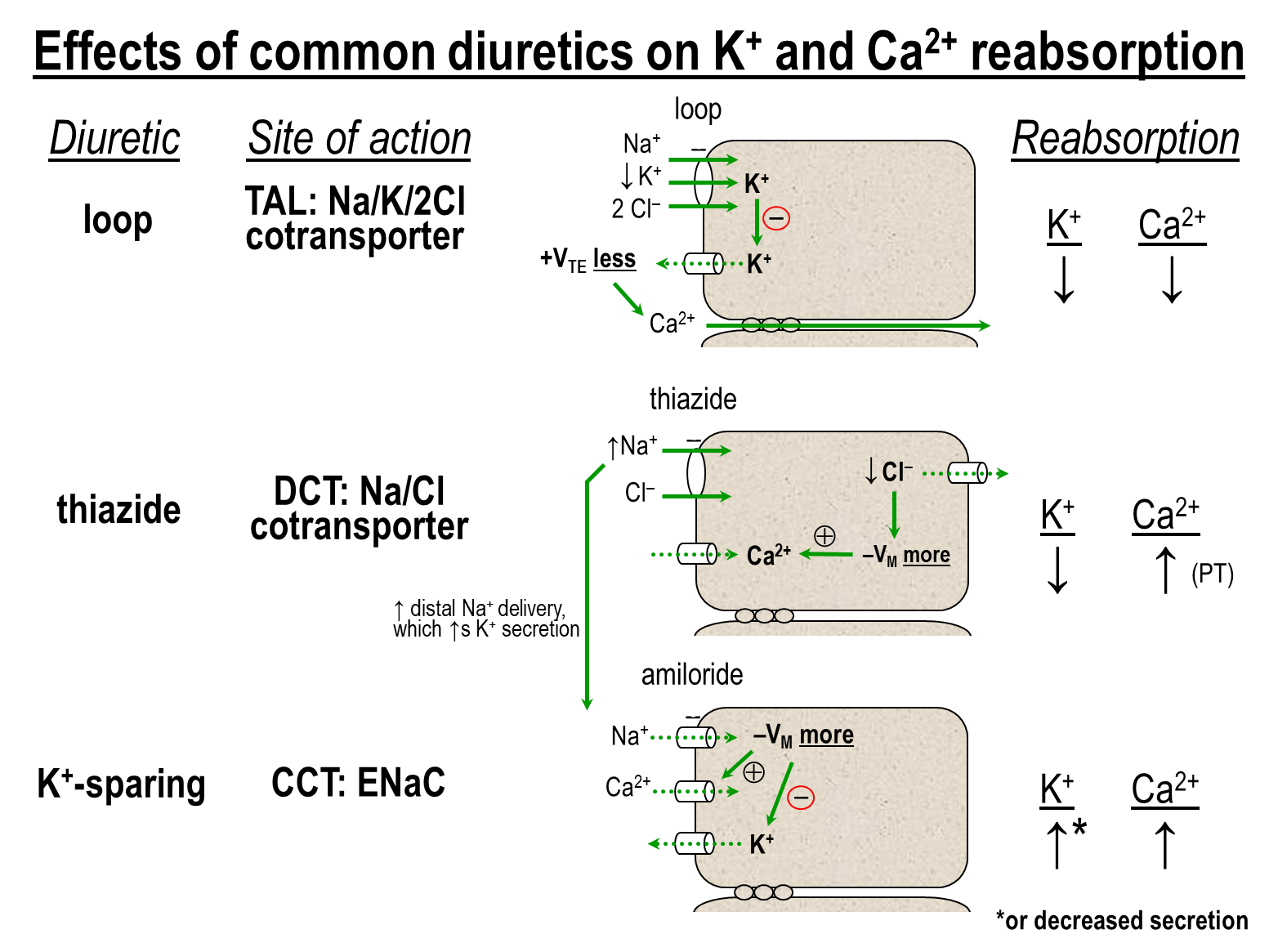
1) Loop
→ binds to and inhibits the Na/K/2Cl cotransporter leading to decreased sodium potassium and chloride levels
→ also decreases potassium secretion into the lumen via the apical channel leading to decreased paracellular reabsorption of cations
2) Thiazide
→ blocks the Sodium Chloride cotransporter at the distal convoluted tubule
→ leads to less sodium being reabsorbed at the DCT, and more sodium is then delivered to areas of the nephron that contain ENaC
→ this will promote further potassium secretion at the Cortical Collecting Tubule
→ thiazides will increase calcium reabsorption
3) Potassium Sparing
→ Blocks the ENaC at the Cortical Collecting Tubule
→ leads to less sodium being reabsorbed and a less negative transepithelial lumen potential
→ leads to a decrease in potassium secretion
→ increase calcium reabsorption