module 1 Introduction to Science, the Scientific Method, and Research Studies
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
these flashcards cover lecture 1 - 5 in module 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what are the characteristics of science??
Based on empirical knowledge
Provides rational/natural explanations
Testable
Repeatable & reproducible (and reliable)
Involves observation and experimentation
Generality of principle
what is empirical knowledge??
empirical knowledge is based on evidence
data collection (quantitative and qualitative)
derived from observations or experimentation
what is natural explanations??
very few questions are off limits in science - answers science can provide are limited to the natural world
what does it mean to be testable??
for something to be testable it means there’s a scientific explanation (hypothesis) to a problem which must be testable (through observations and experiments)
it must generate specific expectations (predictions)
what does it mean for something to be repeatable and reproducible??
confirmation is very important
they must be repeatable and reproduced
what does observational and experimentation mean??
experimentation is a controlled setting where there is intervention/manipulation is done to a natural process
what does generality of prinacables mean??
its the establishment that all researchers must follow the same rules and patterns
what is hypothesis vs predictions??
if hypothesis then prediction
example: If competition among trees lowers reproductive output, then
fruit size should be smaller when tree density increase
what are the research processes??
inductive and deductive reasoning
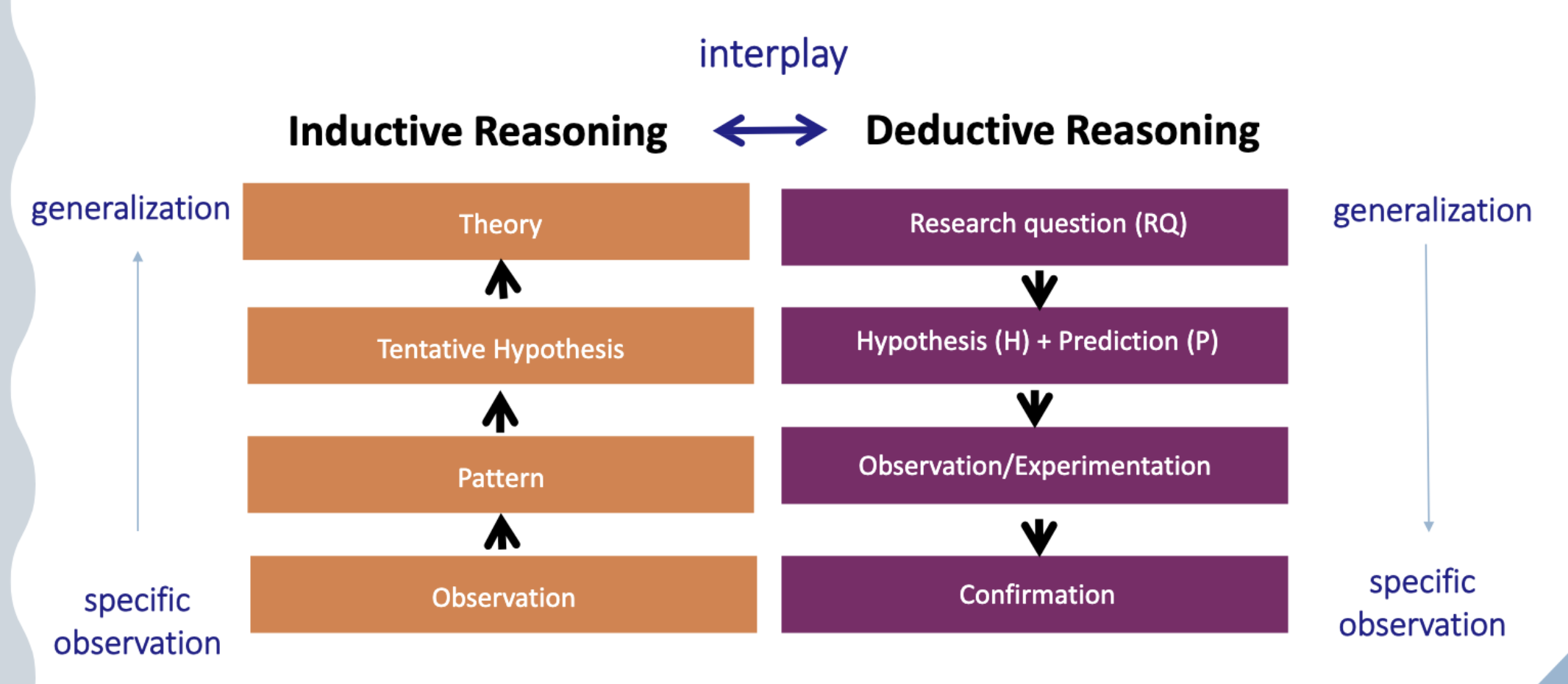
what are the steps of scientific methods??
1. Define/Identify a Problem/Question
2. Formulate a hypothesis (‘potential explanation’)
3. Formulate predictions based on hypothesis
4. Test hypothesis by testing predictions
e.g. make observations or perform experiments and collect
data
5. Analyze data/results
6. Do data support hypothesis?
7. Draw conclusions
8. Communicate results
what is a RH?
RH is a tentative explanation to a research question stated in evidence
stated in advance
based on previous observations
testable
can be falsified but not proven
RH leads to predictions
it implies a relationship between variable
independent variable = predictor
dependent variable = outcome, response
what is the NH??
what is the HA?
its contrary to the null hypothesis
usually corresponds with research hypothesis
what are they types of relationships?
correlation: it implies an association between variables (x and y change together in a systematic way = trend)
causation: indicates that one event (dependent/response
variable) is the result of the occurrence of another event
(independent/predictor variable)