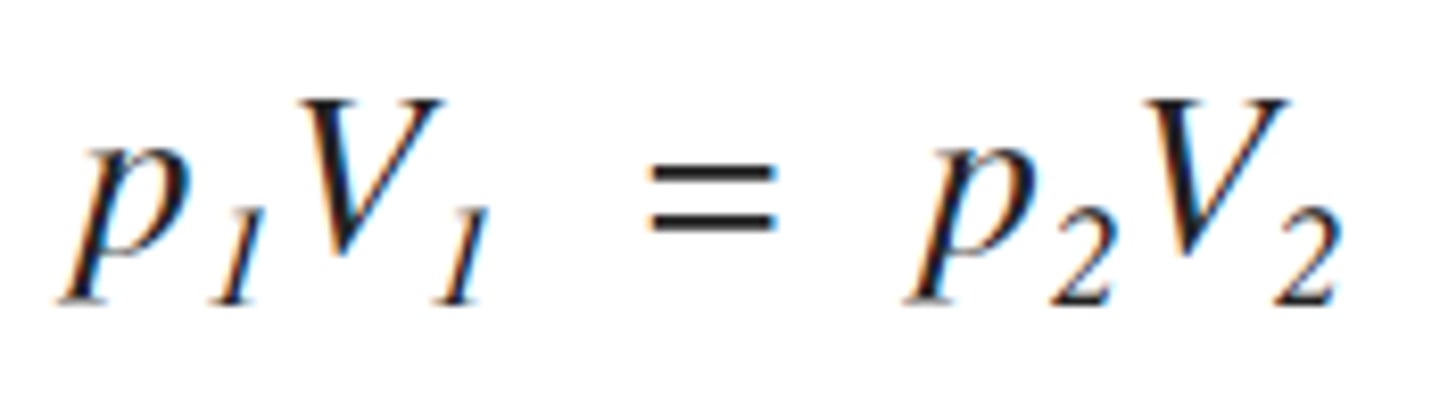Edexcel IGCSE Physics : 5 Solids, Liquids and Gases
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
State the relationship between density, mass and volume

Practical: investigate density using direct measurements of mass and volume

State the relationship between pressure, force and area
pressure[Pa] = force[N]/area[m^2]
How does pressure act at a point in a gas or liquid at rest ?
in a liquid and a gas pressure acts equally in all directions when the liquid/gas is not moving
State the relationship between pressure difference, height, density and gravitational field strength

What happens when a system is heated
heating a system increases its internal energy and causes either an increase in temperature or a change in state
heating a system transfers thermal energy causing a raise in temperature
or the energy may be converted to kinetic energy and cause the particles to move quicker and change state
Describe the changes when a solid melts to form a liquid
when heated the kinetic energy of particles increases
this causes the particles to move and vibrate faster
so they can overcome intermolecular forces of attraction and become a liquid
Describe the changes when a liquid boils to form a gas
when heated the kinetic energy of particles increases
this causes the particles to move and vibrate faster
so they can overcome intermolecular forces of attraction and become a gas
Describe the changes when a liquid evaporates to form a gas
in a liquid some of the molecules at the surface have higher energy than the rest
sometimes they will collide with other molecules and gain enough energy to escape from the liquid
when they escape the remaining molecules have a lower KE and the temperature is lowered
Describe the arrangement and motion of particles in a solid
molecules close together
molecules vibrate over a fixed position
strong intermolecular forces of attraction
regular arrangement of particles
Describe the arrangement and motion of particles in a liquid
molecules close together
molecules arrange randomly
weaker intermolecular forces of attraction than solids
molecules move around each other
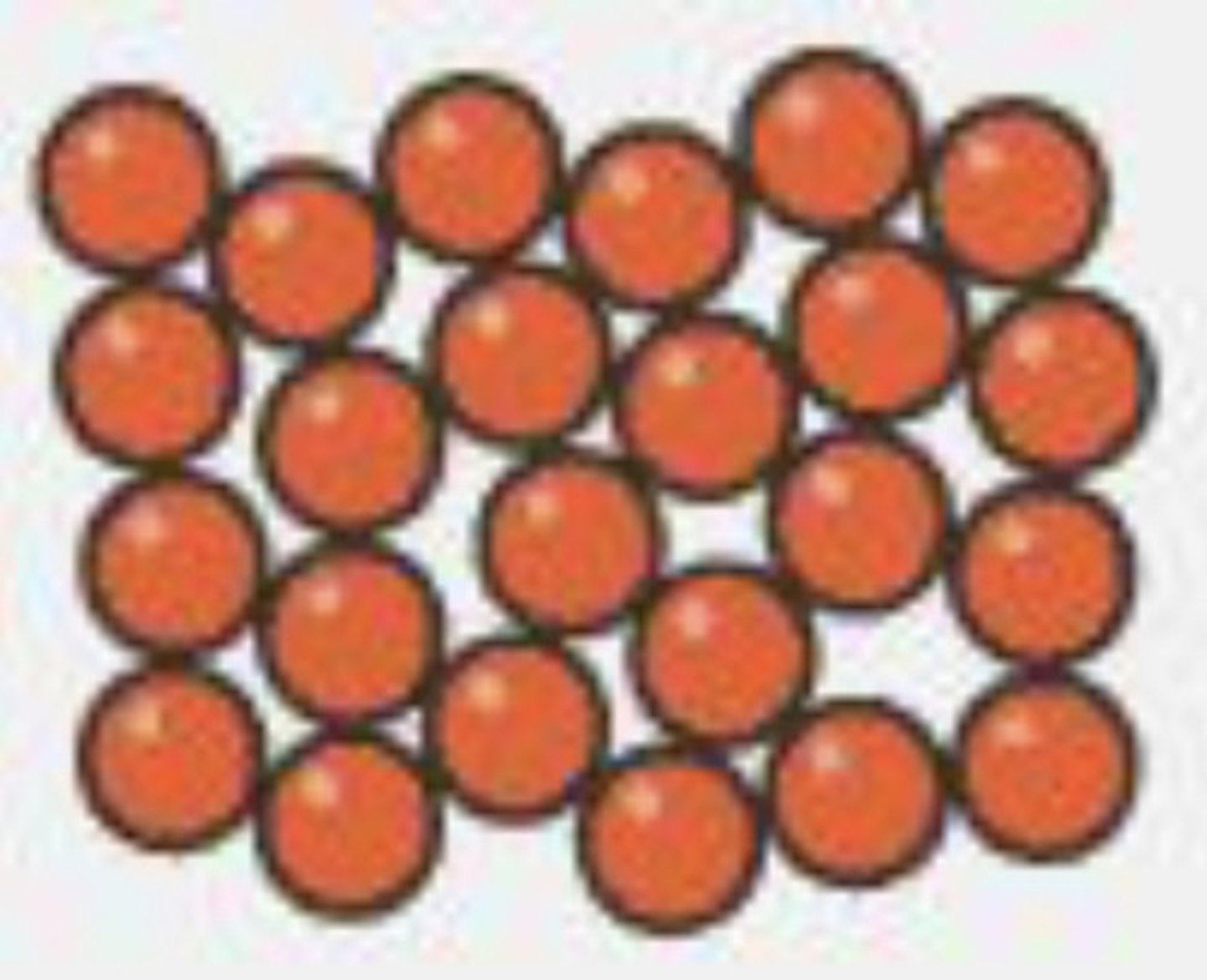

Describe the arrangement and motion of particles in a gas
molecules are far apart from each other in a random arrangement
very weak (negligible) intermolecular forces
molecules move quickly in all directions
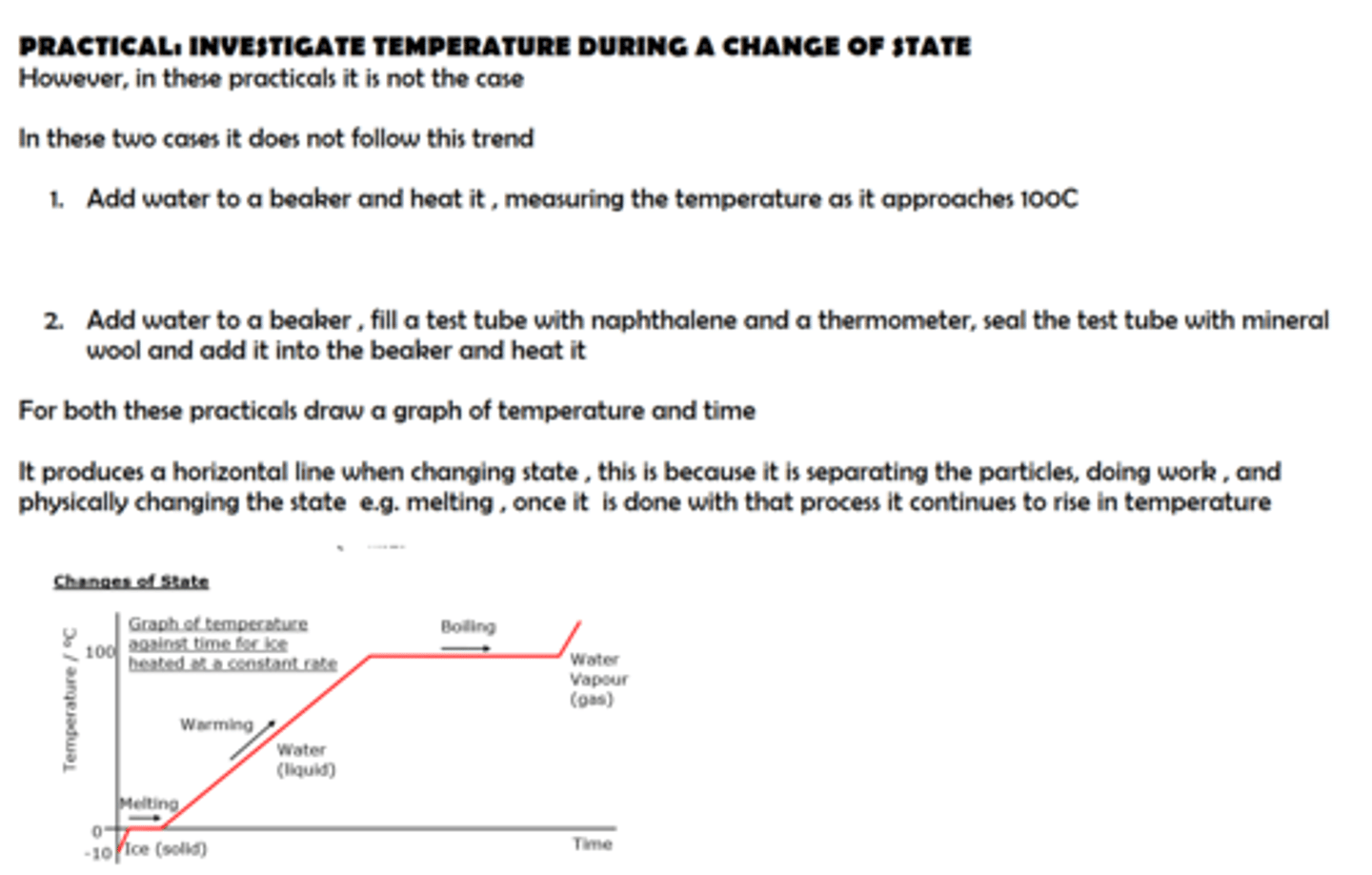
practical : obtain a temperature-time graph to show the constant temperature during a change of state
what is specific heat capacity ?
the amount of energy required to change the temperature of an object by one degree Celsius per kilogram of mass
in (J/kg °C)
State the equation for change in thermal energy
change in thermal energy = mass x specific heat capacity x change in temperature
ΔQ = m x c x ΔT
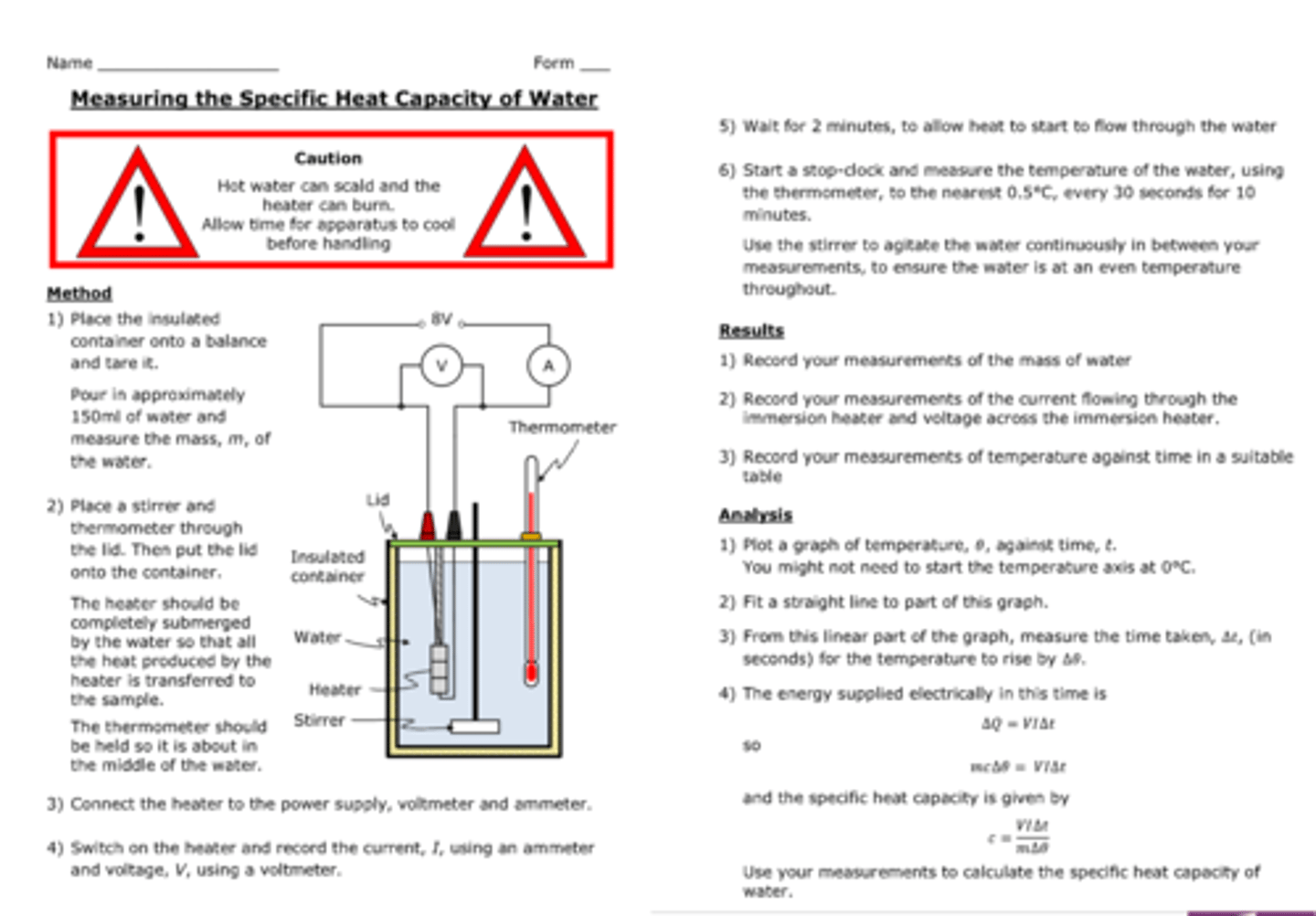
practical : investigate the specific heat capacity of materials including water and some solids
Explain the motion of molecules in a gas
molecules in a gas have a random motion
(Brownian motion)
How does a gas exert pressure on the walls of its container?
molecules in a gas have random motion
when they collide with the walls of the container they exert a force on the
this repeatedly happens exerting a pressure on the container
What is absolute zero ?
when we cool down a gas the particles move slower and the pressure gets smaller
this works up until -273C or 0 kelvin
This is absolute zero as the pressure is zero and the pressure can not get lower than 0 therefore gases can't be colder than -273 C
How do you convert between kelvin and Celsius?
Celsius = K-273
Kelvin = C+273
What is the effect of an increase in temperature in the molecules in a gas ?
an increase in temperature in the molecules in a gas results in an increase in the average speed of gas molecules
How does the Kelvin temperature of a gas relate to its kinetic energy?
the kelvin temperature of a gas is proportional to the average kinetic energy of its molecules
What is the relationship between pressure and volume in a gas at a constant temperature?
at a constant temperature volume increases and pressure decreases
because the molecules collide less frequently with the walls and over a greater area
What is the relationship between pressure and Kelvin temperature at a constant volume ?
the pressure of a gas is proportional to its kelvin temperature
at a constant volume
State the relationship between pressure and Kelvin temperature of a fixed mass of gas at a constant volume
at a constant volume :
pressure 1 [Pa] / Temperature 2 [K] = pressure 2/ Temperature 2
![<p>at a constant volume :<br><br>pressure 1 [Pa] / Temperature 2 [K] = pressure 2/ Temperature 2</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c262bda3-9bba-4e24-843c-993f2df1b479.jpg)
State the relationship between pressure and volume of a fixed mass of gas at a constant temperature
at a constant temperature :
p1V1 = p2V2