PULM/HEME EXAM 1 🫁
1/449
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
450 Terms
Voltage (V)
Difference in charge between inside and outside of the cell (membrane potential, Vm).
Membrane Potential (Vm)
Voltage across the cell membrane.
Current (I)
Flow of electric charge over time.
Conductance (g)
How easily ions flow (ease of current flow).
Resistance (R)
Opposition to ion flow.
Nernst Potential (Eion)
Voltage at which only that ion is at equilibrium (no net flow).
Balance of chemical gradient vs electrical gradient for that ion.
Electrochemical Gradient
Combination of voltage difference (electric) + concentration difference (chemical)
0 mV
When all Na+ channels are open
Depolarization
Membrane potential becomes less negative (moves toward +).
Often caused by Na⁺ or Ca²⁺ flowing in.
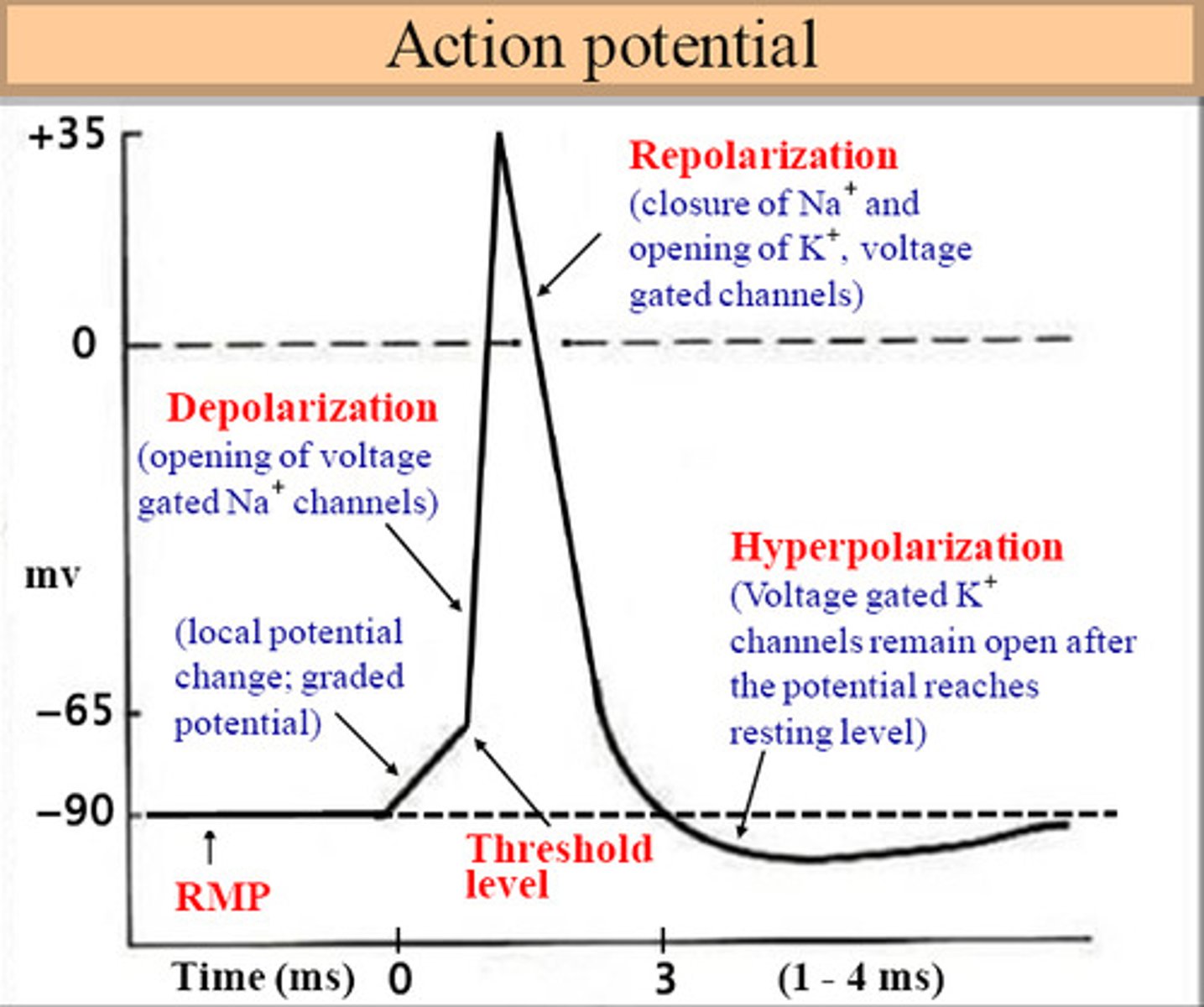
Hyperpolarization
Membrane potential becomes more negative.
Often caused by K⁺ flowing out.
Na⁺/K⁺ pump
Exchanges 3 Na⁺ out for 2 K⁺ in; uses energy.
The three main types of channels are __________, __________, and __________.
voltage-gated, ligand-activated, inward rectifier.
In most neuronal cells, the relative permeabilities are __________ >> __________ > __________ >> __________.
K⁺ >> Cl⁻ > Na⁺ >> Ca²⁺.
Refractory period
Period after an action potential when it is harder to generate another one because potassium channels remain open.
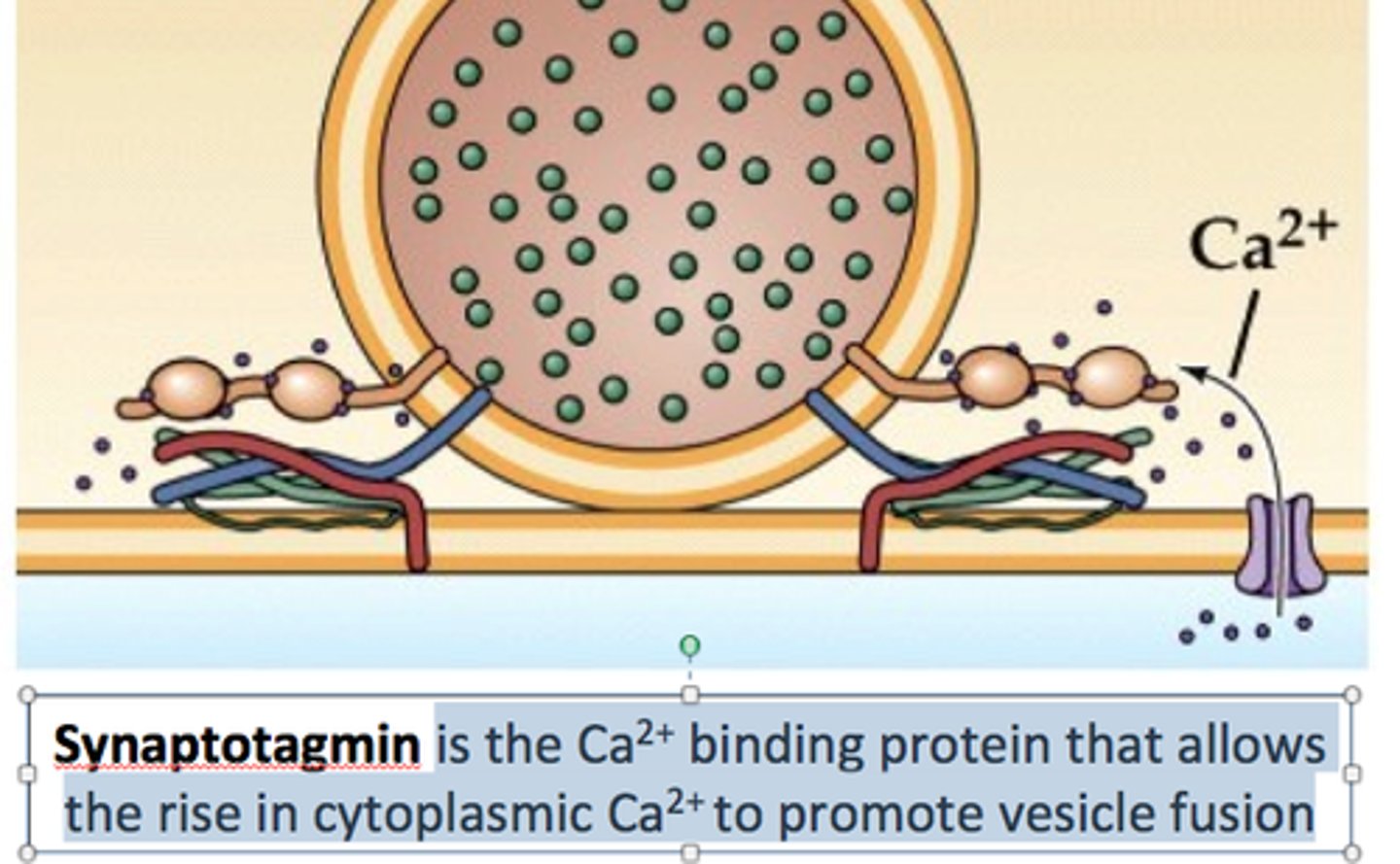
SNARE mechanism steps
Docking, priming (ATP use), calcium-triggered fusion.
Synaptotagmin
A specialized protein that responds to calcium ions to trigger vesicular exocytosis.
The sympathetic nervous system has a __________ origin.
Thoracic lumbar.
The parasympathetic nervous system has a __________ origin.
Craniosacral.
Sympathetic ganglia include __________ and __________ ganglia.
Paravertebral, prevertebral.
Key Cranial Nerves of ANS
3,7,9,10
Parasymphateic ganglia include __________ and __________ ganglia.
Peripheral; terminal
Parasympathetic postganglionic neurotransmitter
Acetylcholine
Sympathetic postganglionic neurotransmitter
Norepinephrine
Differences between ANS divisions - Parasympathetic outflow
Cranio-sacral (CIII, VII, IX, X; S2 to S4).
Differences between ANS divisions - Sympathetic outflow
Thoraco-lumbar (T1 to T12; L1 to L3).
Parasympathetic ganglia are __________; sympathetic ganglia are __________.
Peripheral or terminal, paravertebral or prevertebral.
Parasympathetic preganglionic fibers are __________ and postganglionic fibers are __________.
Long (myelinated), short (non-myelinated).
Sympathetic preganglionic fibers are __________ and postganglionic fibers are __________.
Short (myelinated), long (non-myelinated).
Parasympathetic stimulation is usually __________; sympathetic stimulation is usually __________.
Localized, generalized.
Sympathetic postganglionic neurotransmitter is usually __________.
Norepinephrine.
**Exception: Sympathetic preganglionic neurons synapse on chromaffin cells, which release epinephrine/norepinephrine.
Parasympathetic postganglionic neurotransmitter is __________.
Acetylcholine.
Sympathetic postganglionic neurons release acetylcholine where?
Sweat glands
Sympathetic preganglionic neurons synapse on chromaffin cells, which release ________
epinephrine/norepinephrine.
Parasympathetic functions include decreases in __________, __________, __________, and __________, and increases in __________ and __________.
Cardiac output, respiration, mental activity, blood glucose; gut motility, pupil constriction.
Sympathetic functions include increases in __________, __________, __________, __________, __________, and __________.
Mental activity, respiratory rate, heart rate, arterial blood pressure, blood glucose and free fatty acids, blood flow.
Single innervation examples
Peripheral blood vessels, spleen, sweat glands, piloerector muscles (sympathetic only).
No innervation examples
Blood vessels with ACh, histamine, angiotensin receptors.
Adrenergic receptor α1
Most postsynaptic, excitatory.
Adrenergic receptor α2
Many presynaptic, inhibitory.
Adrenergic receptor β1
Heart, gut, excitatory.
Adrenergic receptor β2
Remainder, inhibitory.
Adrenergic receptor β3
Fat cells, excitatory.
Chronotropy
heart rate (pace of the SA node)
Inotropy
force of contraction
Parasympathetic vs Sympathetic Heart Control
Parasympathetic: Controls chronotropy
Sympathetic: Controls chronotropy and inotropy
Sympathetic postganglionic nerves to the heart come from which ganglia?
Stellate and inferior cervical ganglia.
Sympathetic heart effects include positive __________ and __________ effects.
Chronotropic, inotropic.
Result: Faster heart rate and more forceful contractions
Parasympathetic postganglionic fibers to the heart terminate in which structures?
SA node, atria, AV node.
The parasympathetic nervous system has no innervation of the __________.
Ventricular muscle.
baroreceptors
detect changes in blood pressure
Baroreceptor reflex - low BP
↑ Sympathetic tone (↑ HR, ↑ contractility, vasoconstriction); ↓ parasympathetic tone.
Baroreceptor reflex - high BP
Opposite of low BP response.
BP drops
Heart rate ↑ (positive chronotropy)
Heart contraction ↑ (positive inotropy)
Vessels constrict ↑ TPVR
Parasympathetic ↓
BP rises (opposite)
Heart rate ↓
Heart contraction ↓
Vessels dilate ↓ TPVR
Parasympathetic ↑
Parasympathetic tone in lung
Bronchoconstriction (M3), more mucus (harder to breathe)
Sympathetic tone in lung
Bronchorelaxation (β2), possibly by suppressing parasympathetic tone.
Sympathetic GI effect
↓ tone, motility, secretion
↑ sphincter activity (keeps things "closed" no time to shit!)
Parasympathetic GI effect
↑ tone, motility, secretion.
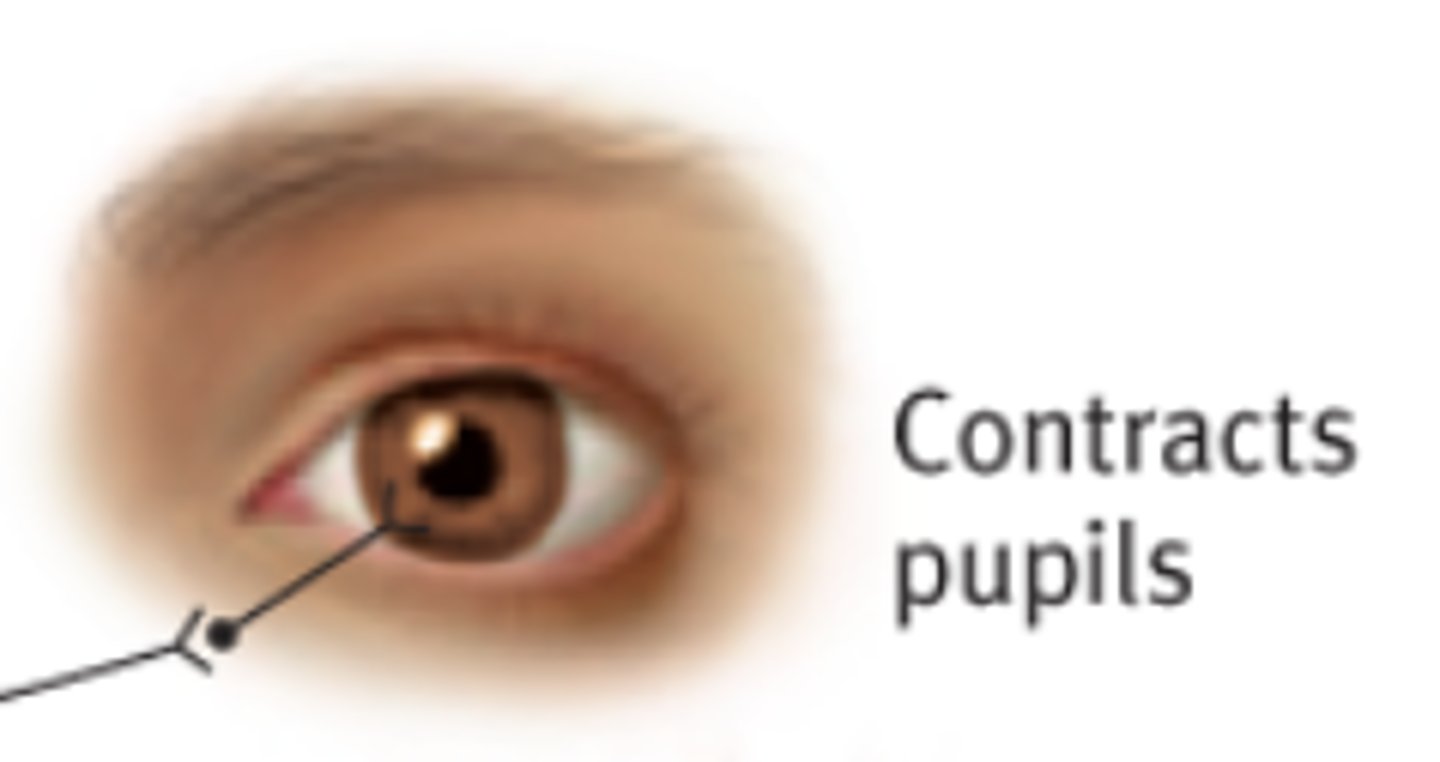
Parasympathetic eye effect
Pupil constriction (miosis) via circular muscle contraction.
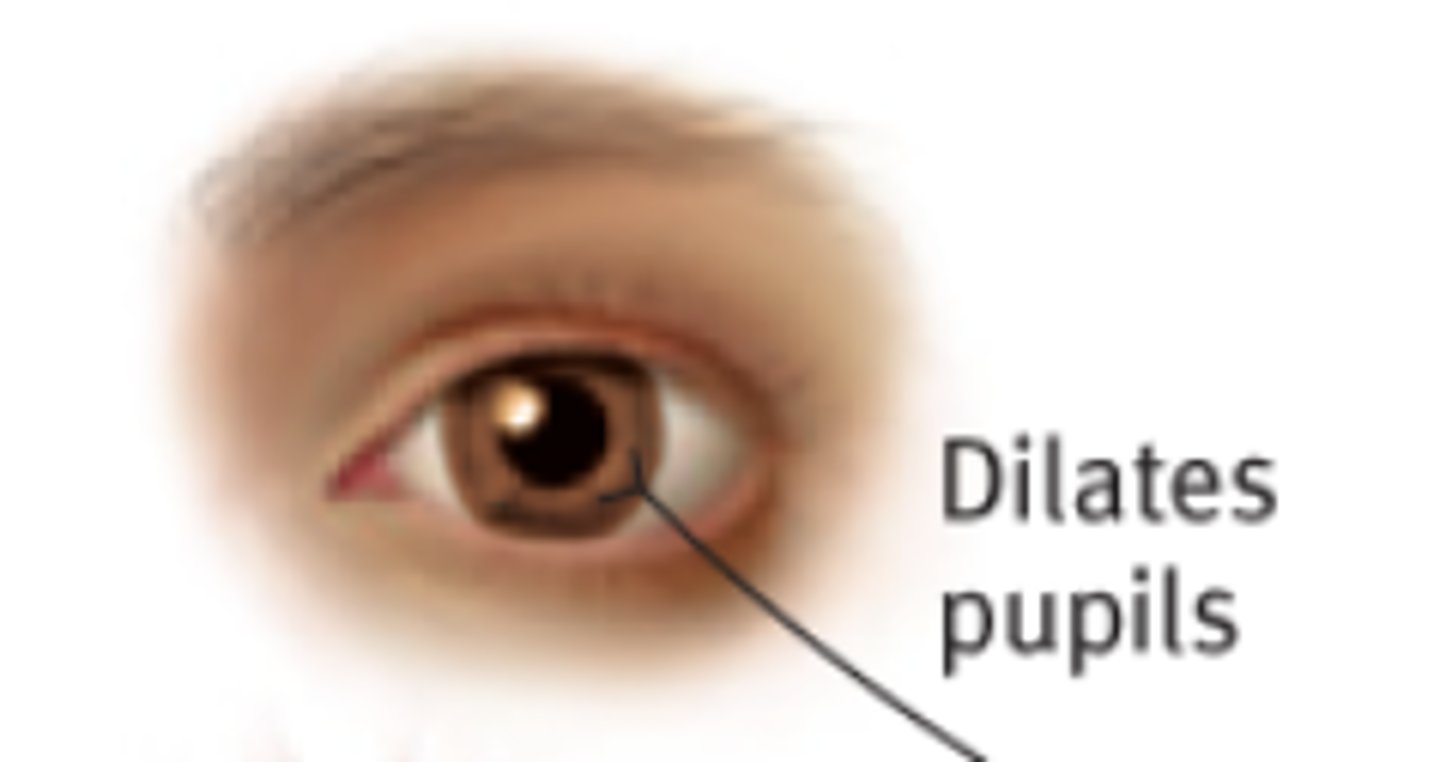
Sympathetic eye effect
Pupil dilation (mydriasis) via radial muscle contraction.
Enteric Nervous System (ENS)
the gut's own "brain"
Integrates parasympathetic and sympathetic input and local reflexes
Uses multiple chemical mediators to coordinate activity
How does sympathetic function work in the ENS?
Sympathetic mainly works by modulating parasympathetic activity → slows or inhibits gut functions indirectly
Radial (dilator) muscle →
sympathetic stimulation → muscle contracts → pupil gets bigger (mydriasis)
Circular (sphincter) muscle →
parasympathetic stimulation → muscle contracts → pupil gets smaller (miosis)
Like your going to sleep!
excitatory post synaptic potential
the neuron is more likely to fire action potential this is a signal from the previous neuron that just fired an action potential
Parasympathetic lens effect
Ciliary muscle contraction → lens thickens → near vision.
Ligaments pull → lens is flat →
good for seeing far away (sympathetic)
They are strong enough to pull the lens so much that it becomes flat, as you can older this elasticity decreases and you need glasses to see far away.
If you want to see something close
Ciliary muscle contracts
Ligaments loosen
Lens becomes thicker/rounder → focuses near objects

What neurotransmitter is active at all sites of cholinergic transmission?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Is acetylcholine a good CNS agent? Why or why not?
No, it's a poor CNS agent because it is a charged quaternary nitrogen compound and is broken down by plasma butyrylcholinesterase.
What are the two main types of acetylcholine receptors?
Muscarinic and Nicotinic receptors
How is acetylcholine (ACh) synthesized?
In a single step from choline by adding Acetyl CoA.
What enzyme catalyzes ACh synthesis?
Choline Acetyltransferase (ChAT)
Where does choline for ACh synthesis come from?
Acetylcholinesterase activity
Phosphatidylcholine
Phosphorylcholine
Where does Acetyl CoA for ACh synthesis come from?
Glycolysis
Is ChAT the rate-limiting step in ACh synthesis?
No, choline uptake is the limiting factor.
What do the Gα subunits of muscarinic (M) receptors mainly target?
Adenylyl cyclase (AC) and Phospholipase C (PLC)
Which muscarinic receptors are associated with Gαi?
M2 and M4
What is the effect of M2 & M4 activation via Gαi?
Decreases Adenylyl Cyclase (AC) activity.
What secondary effects can occur from M2 & M4 activation?
Effects via the βγ subunits
Which muscarinic receptors are associated with Gαq?
M1, M3, and M5
What is the effect of M1, M3 & M5 activation via Gαq?
Increases Phospholipase C (PLC) activity
What type of channels are nicotinic receptors?
Direct ligand-gated cation channels
How many acetylcholine (ACh) molecules are required to activate nicotinic receptors?
Two ACh molecules
Which ions pass through nicotinic receptors?
Sodium (Na⁺) and Potassium (K⁺)
What is the net effect of ion passage through nicotinic receptors?
Inward sodium current → depolarization
How fast is ACh binding and release at nicotinic receptors?
Very rapid; effects are transient (<10 ms)
What is the structural composition of nicotinic receptors?
Five subunits, 35-50% homologous; all have two α subunits
Which subunits are responsible for ACh binding?
The α subunits
What happens with long-term exposure to ACh at nicotinic receptors?
Development of a high-affinity receptor in a closed "desensitized" state.
Fast EPSP
Quick depolarization of a neuron via nicotinic receptors and acetylcholine; starts immediately and lasts milliseconds.
Slow EPSP
Gradual increase in neuron excitability via M1 muscarinic receptors and acetylcholine; starts ~1 second after stimulation and lasts up to 30 seconds.
IPSP
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential that hyperpolarizes the neuron, making it less likely to fire; mediated by M2 muscarinic, α-adrenergic, or dopaminergic receptors.
Late slow EPSP
Very long-lasting excitatory effect mediated by peptide neurotransmitters (e.g., Substance P, LHRH); starts after 10-30 seconds and lasts several minutes; regulates long-term neuronal response to repeated stimulation.
Effect of the M2 receptor on the AV node
Decrease conduction velocity
Effect of the M2 receptor on the atrium
Decrease refractory period and contractile force
Effect of the M2 receptor on the ventricle
Decrease in contractility
M3 Receptor Target and Effect
Smooth Muscle Contraction via the Gq pathway
Receptors on the Autonomic Gangila
M1 and Nicotinic Neuron (Obviously it's on the Gangila)
Nicotinic Nm Receptor Location
Skeletal muscle at neuromuscular junction (NMJ