Cognitive Exam 2 LTM
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
long-term memory (LTM)
memory systems for storing lots of information for a long period of time
long-term memory “archives” information about past events and knowledge learned
long-term memory interacts with short-term and working memory to provide background and context
long-term memory storage spans moments ago to as far back as you can remember
however, detail often varies with remoteness
either declarative or non-declarative
Types of recall
free
cued
recognitition
ex: seven dwards
STM vs LTM
• short-term memory (STM): memory system for storing small amounts of information for a brief period of time
• long-term memory (LTM): memory systems for storing lots of information for a long period of time
STM and LTM both store information
LTM stores more information than STM
LTM stores information for longer than STM
STM and LTM in relation to Duration
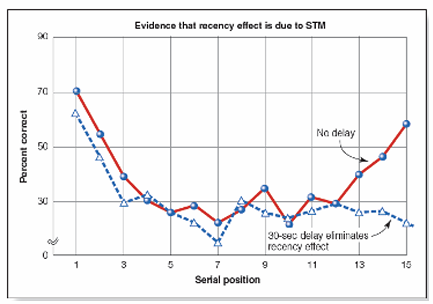
• serial position curve: memory is better for words at the beginning (primacy effect) and end (recency effect) of a list
• primacy effect: better memory for words at the beginning of a list relies on long-term memory
• recency effect: better memory for words at the end of a list relies on short term memory (goes away if memory test is delayed)
Information coding
• visual coding: represent information in the mind as visual images
LTM: This represents how you might visually remember your 3rd grade teacher — her face, classroom, or the way she held a book.
STM: Visual information (like a graph or list) is temporarily held in short-term memory, and people often remember what they just saw — a hallmark of the recency effect.
• auditory coding: represent information in the mind as sounds
LTM: Remembering song lyrics—e.g., Beyoncé’s “Girls” lyrics are stored in long-term memory as a sound pattern
STM: The phonological similarity effect—sets of letters like PGTCDZB are harder to recall than RHXMKWL because they sound more similar, making them easier to confuse in STM
• semantic coding: represent information in the mind in terms of meaning
LTM: You learn classical conditioning by understanding and relating it to Pavlov’s dog experiment, helping you remember it over time.
STM: You remember the word “apple” by thinking, “It’s a fruit I eat for lunch,” not just the sound of the word
• proactive interference: decrease in memory when previously learned material interferes with new learning
switching to words with a different meaning increases memory via a release from proactive interference
STM and LTM: information coding
• short-term memory (STM): memory system for storing small amounts of information for a brief period of time
codes visual, auditory, and semantic information
• long-term memory (LTM): memory systems for storing lots of information for a long period of time
codes visual, auditory, and semantic information
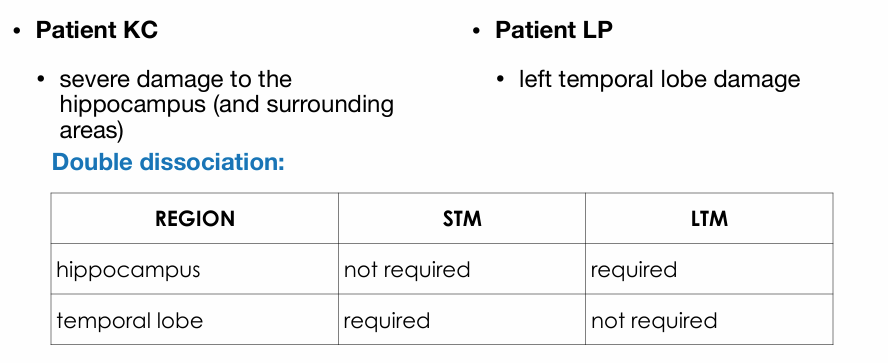
Brain regions: Patients HM and KF
Patient HM
surgery to remove the hippocampus (as part of epilepsy treatment)
STM preserved
LTM impaired
Patient KF
suffered parietal lobe damage (motorbike accident)
STM impaired
LTM preserved

LTM: Declarative→Semantic
long-term, declarative memory for facts
• semantic memory encompasses lexical knowledge
Knowing what the word “photosynthesis” means, how to use it, and that it relates to plants.
• semantic memory has a very large capacity
You remember that the capital of France is Paris, that water freezes at 0°C, and that 2 + 2 = 4. These facts stay with you for years
• semantic memory encompasses general knowledge
You know that whales are mammals, even if you’ve never seen one in real life.
• semantic memory encompasses conceptual knowledge
You understand the concept of “justice” or what makes something a “vehicle,” even if you've never memorized a formal definition
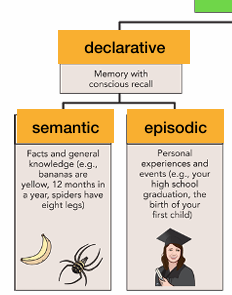
LTM: Declarative→Episodic
long-term, declarative memory for events and experiences
• mental time travel: the experience of traveling back in time to reconnect with personal past experiences
• episodic memory has a very large capacity
remember ppl from class 50 yrs ago
• episodic memories are linked to experiences from a particular place and time
Who: Amy, Sam, Lex, Mel, and Jess What: Summer road trip When: August 2020 Where: PCH in Monterey, CA
• paired associates memory task: study and later remember which words were presented together
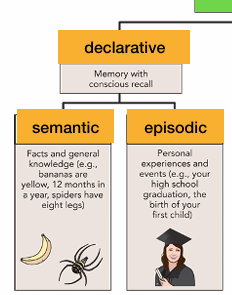
semantic vs episodic
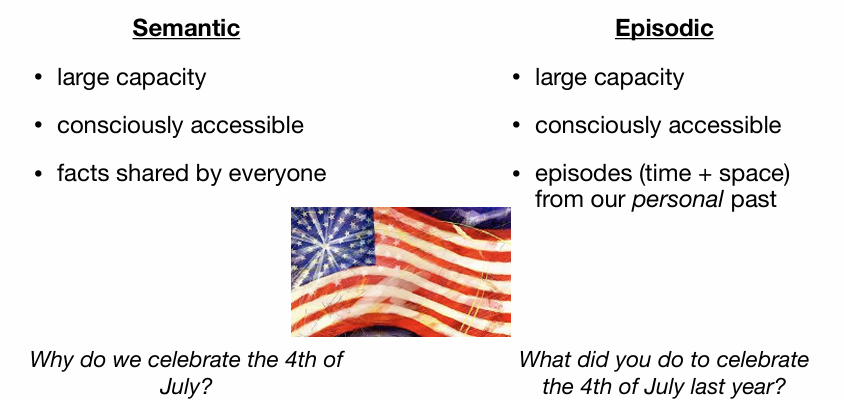
Semantic vs Episodic: Patient KC and LP
Semanticization
• semanticization of remote memories: the loss of episodic details for memories from long ago
• remember/know procedure: test to assess memory for the original experience
Autobiographical memory
long-term, declarative memory for specific experiences from our life
WE ARE THE SUBJECT EVENT
• episodic elements: memory for the event that we personally experienced
• semantic elements: memory for the facts related to an event that we personally experienced
LTM: declarative (explicit)
memory with conscious recall
semantic
episodic
LTM: Non Declarative (implicit)
memories WITHOUT conscious recall
long term memories that you are not aware of
non declarative memory occurs without awareness or intent
procedural
conditioning
priming
Non-declarative: procedural
long-term, non-declarative memory for learned skills
• procedural memory automates our performance
• procedural memory includes the memory for actions when learning a skill
ex: riding bike
• mirror tracing task: learn to trace a star while looking in the mirror
• reverse reading task: learn to read words written backwards
• expert-induced amnesia: well-learned skills are performed automatically and without awareness
ex: playing piano
Non- declarative: priming
exposure to one (primed) stimulus affects the response to another (test) stimulus
ex: semantically related words have primed u to unscramble OCEAN instead of CANOE
ex: we saw picture of HARE and turtle earlier so you write HARE instead of HAIR
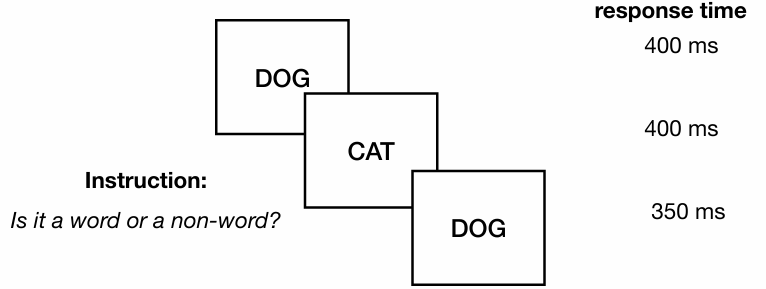
repetition priming
test stimulus is the same as or resembles the priming stimulus
• respond faster when a test stimulus is the same as the priming stimulus
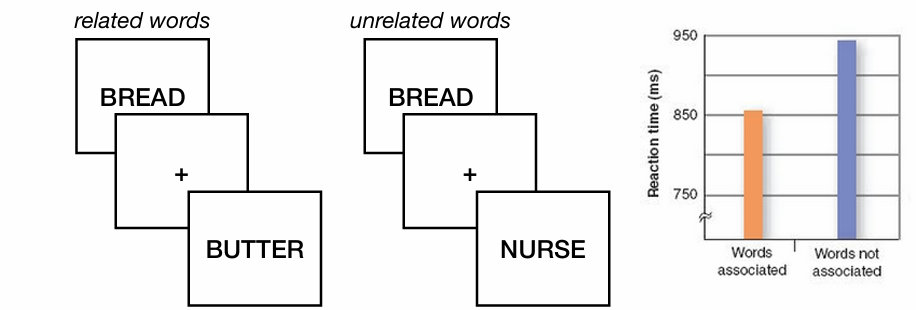
conceptual priming
test stimulus has a similar meaning to the priming stimulus
priming: propaganda effect:
more likely to rate statements read or heard before as being true
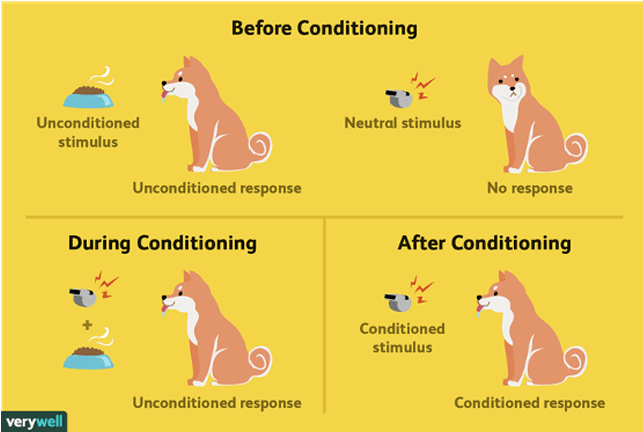
conditioning
when a (neutral) stimulus becomes associated with a (conditioning) stimulus that elicits a particular response
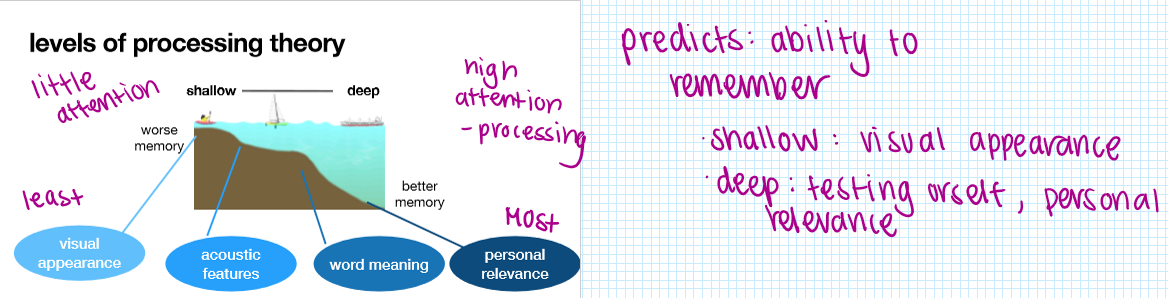
levels of processing theory
memory retrieval depends on how “deeply” information is processed at encoding
how to improve encoding (STM→LTM) REHEARSAL
• maintenance rehearsal: memory is better if you repeat something over and over again
• elaborative rehearsal: memory is better if you relate a stimulus to its meaning or to other information
how to improve encoding (STM→LTM) VISUAL IMAGERY
memory is better if you form pictures in your mind
how to improve encoding (STM→LTM) SELF REFERENCING
memory is better if you relate the stimuli to yourself

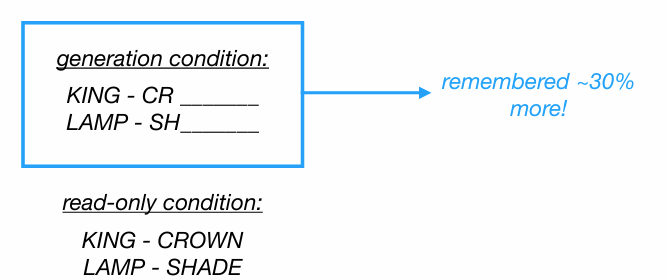
how to improve encoding (STM→LTM) GENERATION
memory is better if you generate the material yourself
how to improve encoding (STM→LTM) ORGANIZATION
memory is better if the material is organized
• one word within a category could serve as a retrieval cue and prompt the memory for other words

how to improve encoding (STM→LTM) RETRIEVAL PRACTICE
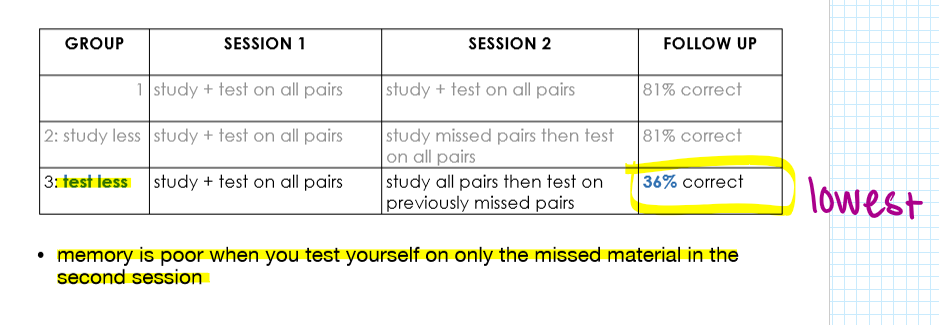
retrieval cues
memory is better when one stimulus prompts memory for other stimuli

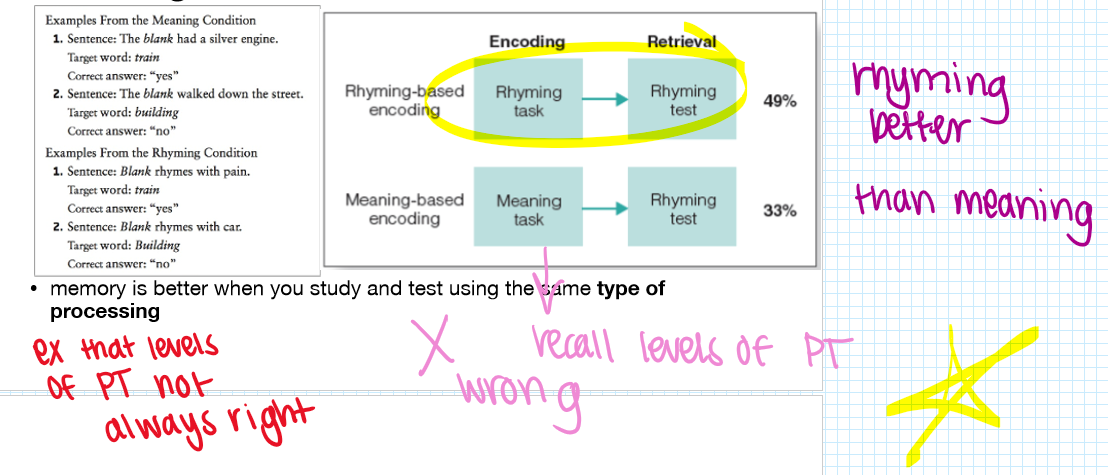
how to improve encoding (STM→LTM) MATCHING CONDITIONS
memory is better when we match the conditions at encoding at retrieval
1. encoding specificity CONTEXT
2. state-dependent learning MOOD
3. transfer appropriate processing TASK
Matching conditions: encoding specificity CONTEXT
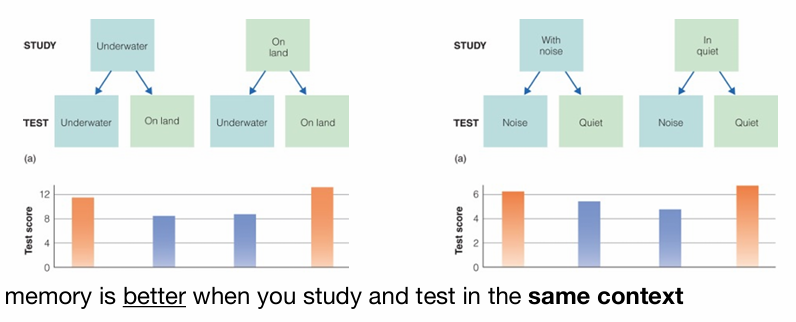
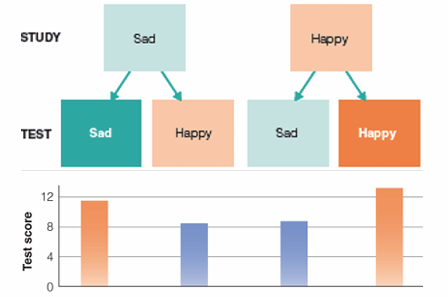
matching conditions: state-dependent learning MOOD
• memory is better when you study and test in the same mood
matching conditions: transfer appropriate processing TASK
memory is better if the same type of processing is used during encoding and retrieval