Biology B3 - Urinary system structure and function
1/39
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is the urinary system?
The urinary system is a vital organ system responsible for filtering blood, removing waste, produce urine and regulating fluid balance in the body
What is the urinary system also known as?
The renal system
What are the structures of the kidney?
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra
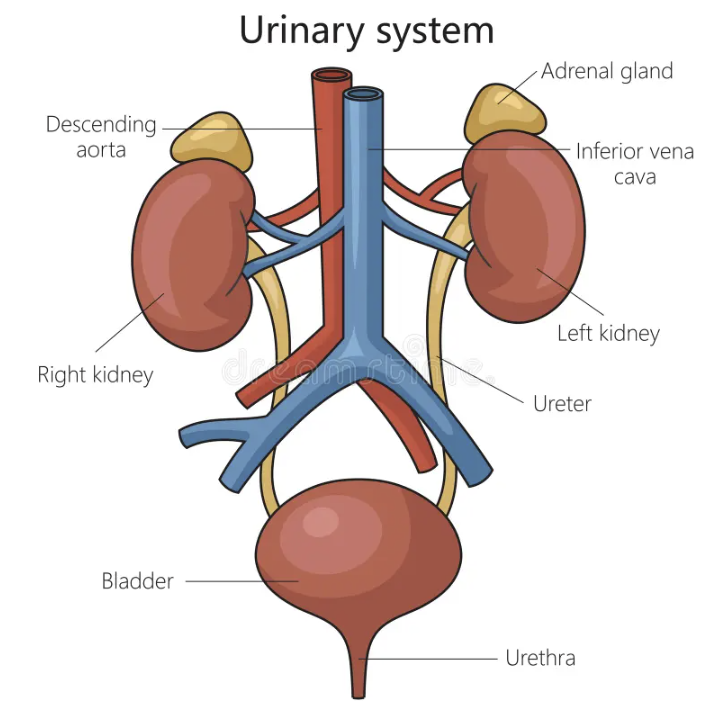
Where are the kidneys positioned?
Each side of the spine at the back of the abdominal cavity, just below the waist
What is osmoregulation?
The control of water and salt levels in the body which prevents problems with osmosis
What are the ureters?
Two narrow tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The ureters use muscular contractions to move urine downward
What is the bladder?
A muscular sac that stores urine from the kidneys until it is ready to be expelled from the body. The urine enters the bladder through the ureter and urine leaves the bladder by the urethra
What is the renal artery?
Renal arteries deliver oxygenated blood supply to the cells in each kidney
What is the renal vein?
Once the blood has been processed in the renal arteries, it leaves the kidney via the renal veins and is transported in the inferior vena cava back to the heart
What is the kidney?
The kidney filters waste products from the blood before turning it into urine
What are 3 regions that the kidney consist?
Surrounded by a strong capsule and consists of the cortex, medulla and in the centre the renal pelvis
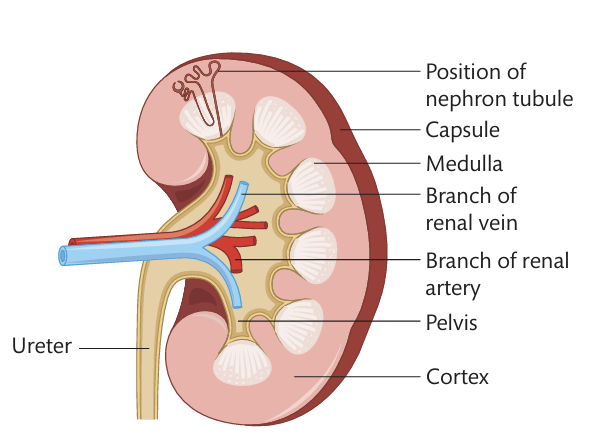
Where does the renal pelvis lead to?
The ureter
What is a kidney nephron?
The functional unit of the kidney. Urine is produced here.
What do the nephrons make up?
Nephrons are microscopic structures that make up the bulk of the kidney
How many nephrons does approximately each kidney have?
One million nephrons and each is close to many blood capillaries
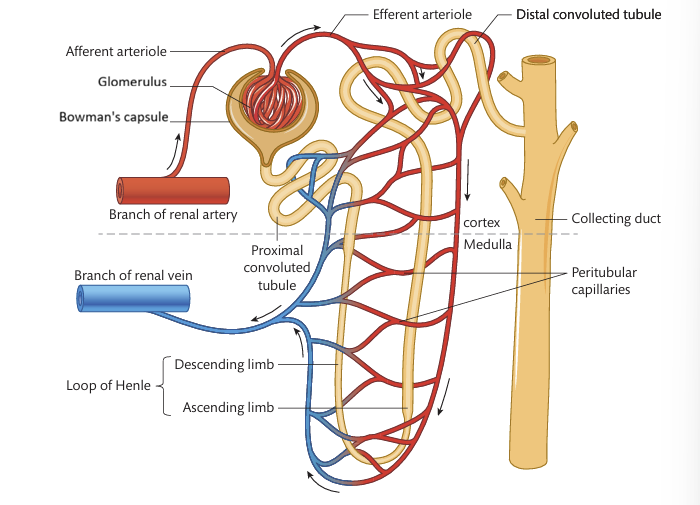
Where do each nephron start?
In the cortex of the kidney
The blood capillaries from the renal artery form a knot that is known as?
The glomerulus
The glomerulus sits inside a cup-shaped structure called?
The Bowman’s capsule
What is ultrfiltration?
The process whereby fluid from the blood is pushed into the Bowman’s capsule so that the process of selective reabsorption can take place as the fluid flows along the nephron
What happens to the substances that the body needs to conserve?
They are reabsorbed back into the blood capillaries and anything not reabsorbed ends up as urine to be expelled from the body
How many parts is the nephron divided into?
4 parts
What are the parts that the nephron is divided into?
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Loop of Henle
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
Collecting duct
Where does the glomerulus receives blood from?
The afferent arteriole
And where does the blood leave through?
The efferent arteriole
Which arterioles is wider?
The afferent arteriole are wider than the efferent arterioles
What does this difference in diameter cause?
Increases the pressure in the blood capillaries of the glomerulus and pushes fluid out of the capillaries and into the Bowman’s capsule where there is a lower pressure
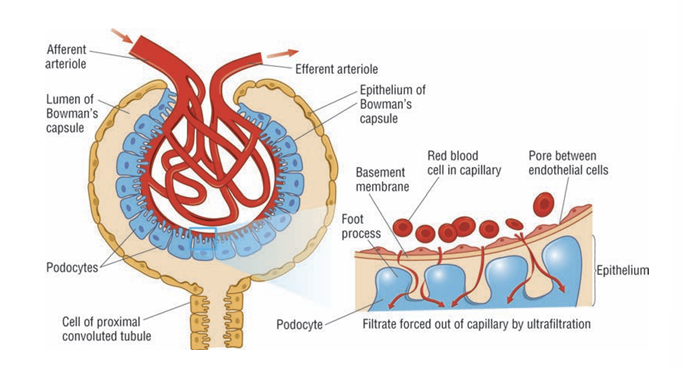
What does the fluid pushed out of the blood capillaries contain?
Water, amino acids, glucose, urea, and inorganic ions e.g. sodium, chloride and potassium
Why are blood cells and proteins left in the capillary?
They are too large to pass through the small gaps in the capillary walls
What does this mean?
The water potential in the blood capillaries is very low after ultrafiltratio
Why is this important?
To help reabsorb water later in the process
What are afferent arterioles?
A group of blood vessels that supply the nephrons in many excretory systems
What does water potential mean?
A measure of the ability of water molecules to move freely in solution
How many layers must the fluid pass to get into the Bowman’s capsule?
Endothelium of the blood capillary
Basement membrane of Bowman’s capsule
Epithelial cells of Bowman’s capsule
What is the endothelium of the blood capillary?
Small gaps in between the cells that line the blood capillary so that blood plasma and the substances dissolved in it can pass through
What is the basement membrane of Bowman’s capsule?
Consists of a very this network of collagen fibres and glycoproteins. It acts as a filter to prevent the movement of larger substances from the blood capillary into the Bowman’s capsule
What is the epithelium cells of Bowman’s capsule?
Cells that are celled podocytes and have many finger-like protections called foot processes to ensure there are gaps between the cells. This enables the fluid from the capillary to pass between the cells into the Bowman’s capsule
What happens as the fluid moves along the nephron?
All the glucose and amino acids, and some salts and water that have been pushed out of the blood capillaries are reabsorbed back into the blood
What percentage of the filtrate is reabsorbed and where?
85% of the filtrate is reabsorbed into the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Which structures form the folds on the PCT cell surface membrane?
Microvilli
What do these microvilli increase?
Surface area