CH12 LEC: INTRO TO OCHEM & ALKANES
1/144
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
All organic molecules contain one or more ___.
carbon atoms
Carbon is tetravalent - what does this mean?
each carbon atom forms 4 bonds
organic molecules mainly contain ___ bonds.
non-polar covalent
covalent bonds involve…
sharing of e- pairs b/t 2 atoms
when the electronegativity b/t 2 atoms is less than ___ the bond is non-polar covalent.
0.5
4 general properties of non-polar organic compounds: physical state:
mainly exists as gas or liquid
4 general properties of non-polar organic compounds: solubility:
insoluble or barely soluble in water, but soluble in non-polar solvents such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and chloroform (CHCl3).
very small molecules tend to be slightly more soluble
4 general properties of non-polar organic compounds: conductivity:
non-conductors b/c they have NO chargeable particles and do NOT ionize
4 general properties of non-polar organic compounds: boiling & melting points:
low boiling & melting points
organic molecules may contain some ___ bonds.
polar covalent
when electronegativity is ___, the bond is polar covalent.
0.5—1.9
what is the common force w/in polar and non-polar molecules?
London Dispersion Forces (LDFs)
define london dispersion forces
e- are constantly moving and sometimes they temporarily “bunch up” at one end of the molecule, creating temporary dipoles that induce a dipole in a neighboring molecule. the result is a weak attraction b/t molecules.
LDFs help molecules stick together — especially, non-polar and noble gases)
what is the internal force unique to polar molecules?
Dipole-Dipole Interactions
define dipole-dipole interactions
internal molecular force created due to polar characteristics — creates a permanent dpole w/in the molecule that results in strong attraction b/t neighboring molecules
polar molecules typically exhibit ___ melting points, boiling points, and water solubility in comparison to non-polar molecules of equivalent size.
elevated
Carbon can form ___ covalent bonds.
multiple
Multiple covalent bonds occur when 2 atoms share 2—3 e- pairs, creating a ___, ___ ___ connection b/t atoms.
stronger
more stable
Double bond
bond that shares 4 e-
triple bond shares how many e-
bond that shares 6 e-

organic molecules have specific ___.
3D shapes
the ___ and ___ of an organic molecule depends upon the type and number of bonds b/t 2 atoms
shape
bond angle
molecular model color code: hydrogen:
white
molecular model color code: carbon:
black
molecular model color code: oxygen:
red
molecular model color code: nitrogen:
blue
molecular model color code: phosphorus:
purple
molecular model color code: sulfur:
yellow
bond angle is measured b/t 2 atoms that share ___.
the same central atom
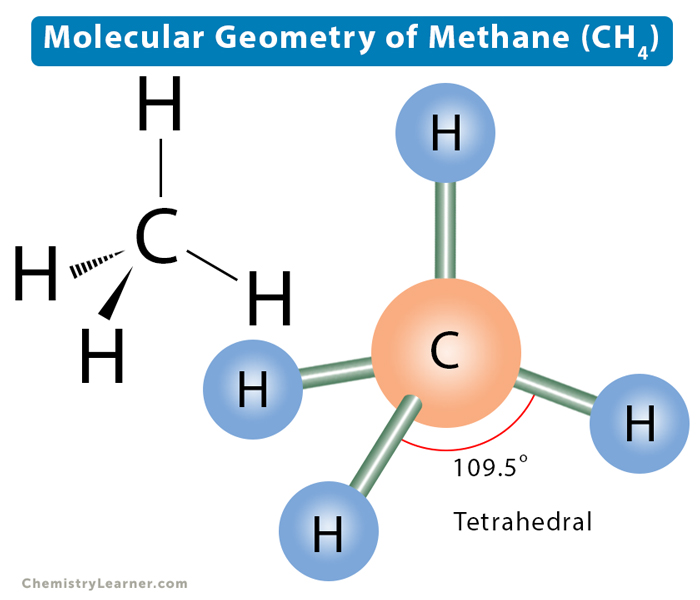
tetrahedral shape bond type and angle
single bond
109.5 degrees
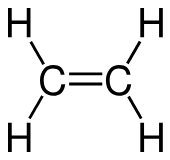
planar shape bond type and angle
double bond
120 degrees
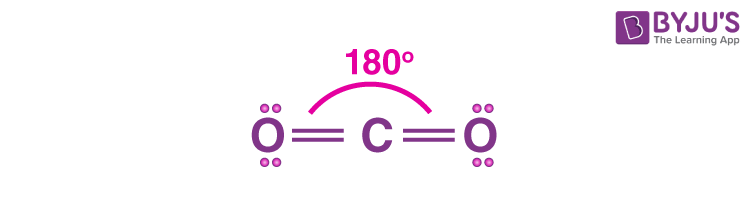
linear shape bond type and angle
triple bond
180 degrees
Organic molecules often contain some other ___.
atoms, in addition to C and H
may also contain N, O, S, P, and halides (F, Br, Cl, I)
what is the term for a group of atoms w/in a molecule that has a characteristic structure and chemical behavior?
functional group
a given functional group tends to undergo ___ in every molecule that contains
the same type of rxns
may have higher reactivity or ranking - larger size does not mean a higher ranking or reacivity
T/F: organic compounds are not classified into familial groups.
False; they are — there are 4 families.
how is the complexity of organic compounds primarily determined?
by the functional group is contains, not its overall size or complexity.
what are the 4 major groupings of functional family groups?
hydrocarbons
Carbon single bonded to electronegative atom
Carbonyl group
contains sulfur
hydrocarbons
alkane, alkene, alkyne, aromatics
contains only H and C
“An Easy Year’s Rest”.
Carbon single bonded to electronegative atom - which functional groups?
alkyl halide, alcohol, ether, amine
all single bonds
“Happy Aliens Enjoy Astronomy.”
carbonyls
aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, anhydride, ester, amide
carbon is seen double bonding to oxygen
“A Kind Cat Always Eats Apples.”
amide functional group has how many sub-structures?
3
contains sulfur grouping
thiol, disulfide, sulfide
the key is that is contains sulfur
“Thieves Discover Sulfur.”
hydrocarbons groupings
alkane, alkene, alkynes, and aromatic
alkane characteristics
saturated — all carbons are bonded to 4 groups and cannot add anymore hydrogens
contain only C-C and C-H single bonds
carbon backbone can be straight, branched chains, or cyclic/ring
which functional group is technically considered NOT a functional group and why
alkane
no readily reactive bonds
contains only C—C and H—C single bonds
serves as the backbone of organic compounds
alkene characteristic
bonds with at least one C—C double bond
alkyne characteristic
bones with at least one C—C triple bond
aromatic characteristics
contains a special ring structure known as aromatic ring, which is known for its unique stability
alkene definition
an unsaturated hydrocarbons w/ at least one Carbon double bond
alkyne definition
an unsaturated hydrocarbons w/ at least one Carbon triple bond
what does “unsaturated” mean?
means we can still add more hydrogens
we can turn double and triple bonds into single bonds (alkane)
Functional groups always have the ___ number label.
smallest
aromatic compounds definition
contain a special ring called an aromatic ring
includes single and double bonds called benzene rings
what are benzene rings known for?
their unique stability
What does “R-group” stand for?
rest of the molecule
what is the purpose of the R-group
abbrv. for structures of large molecules — especially when the interest/importance is placed on something other than the R-group — i.e., a functional group
When there are 2 R-groups present, how is the second one represented?
R’
alkyl halide general formula & definition
(—C—X)
contains 1 or more halogens (Fl, Cl, Br, I)
Alcohol general formula & definition
(—C—OH)
contains 1 or more hydroxyl groups (OH) bonded to a saturated carbon atom
Ether general formula & definition
(—C—O—C—)
contains an oxygen atom bound to 2 R-groups
Amines general formula & definition
(—C—N=) N can form 2 additional bonds
contains N bound to C by single bond
what else can an amine be bound to?
a cyclic compound or be a part of a ring structure
Thiol general formula & definition
(—C—SH)
—SH attached to a carbon
Disulfide general formula & definition
(C—S—S—C)
formed from 2 thiols
(—C—SH + HS—C— → —C—S—S—C)
what does the disulfide bond between 2 thiols connect?
2 distant regions or 2 molecules together
What happens when the oxidation of 2 thiols occurs?
an atom is lost from each of the 2 SH groups
removal of H atom (this is oxidation)
produce is called disulfide (bond b/t 2 S atoms)
carbonyl groups consists of…
C=O
what is the C in a carbonyl group called
carbonyl carbon
what is the O called in a carbonyl group
carbonyl oxygen
Aldehyde general formula & definition
carbonyl C bonded to 1—2 H atoms
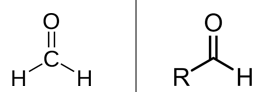
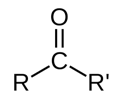
Ketones general formula & definition
carbonyl C bonded to 2 Cs (or R groups)
within aldehyde and ketone groups, carbonyl C forms bonds with H or C, which have ___ electronegativity.
lower
carboxylic acid general formula & definition
(—COOH)
the carbonyl C bonds to OH (hydroxyl)
ester general formula & definition
(—COOR’)
carbonyl C bonds to an O, which is, in turn, bonded to another C
amides general formula & definition
(—CON=) N can form 2 additional bonds
carbonyl C bonds to N
withing carboxylic acids, esters, and amides, the carbonyl C bonds with O or N, which have ___ electronegativity.
higher
In an alkane structural formula, the C atoms form a ___ with H bond to the remaining open bonding sites.
chain or backbone
Alkane general molecular formula
CnH2n+2
alkane condensed formula
no visible bonds, but each distinct structured group is written w/ subscript numbers to designate the multiple groups
w/in line structures, any element apart from the hydrocarbon portions are ___.
consistently depicted, along with the H atoms that form bonds w/ these elements.
Methane formula
CH4
Ethane formula
C2H6
Propane
C3H8
Butane formula
C4H10
Pentane formula
C5H12
Hexane formula
C6H14
Heptane
C7H16
Octane formula
C8H18
Nonane formula
C9H20
Decane formula
C10H22
isomer definition
molecules with same molecular formal but different arrangement / connectivity of those atoms
structural/constitutional isomers definition
when different arrangements of atoms (w/in a molecule) result in distinct physical and chemical properties
same formula, different structure, different connections
No isomeric forms for Alkanes w/ ___ Carbons b/c there is only ___ to arrange the atoms in each formula so that each C has 4 H.
1—3
one way
constitutional isomers are observed in alkanes that contain ___ C atoms.
4 or more
what is an atom or group that takes the place of a H atom in an organic molecule
a substituent
as the number of C ___, the potential for more constitutional isomers also ___.
increases
major differences b/t constitutional isomers of alkanes
connectivity of atoms
structure/shape
melting and boiling points
naming
what are the primary intermolecular forces w/in alkanes?
london dispersion forces (LDFs) (van der Waals or dispersion forces)
The strength of london dispersion forces depends upon what?
size and shape of molecules