Lecture 8: The Appendicular Skeleton Overview
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Appendicular Skeleton
126 bones facilitating movement and limb attachment.
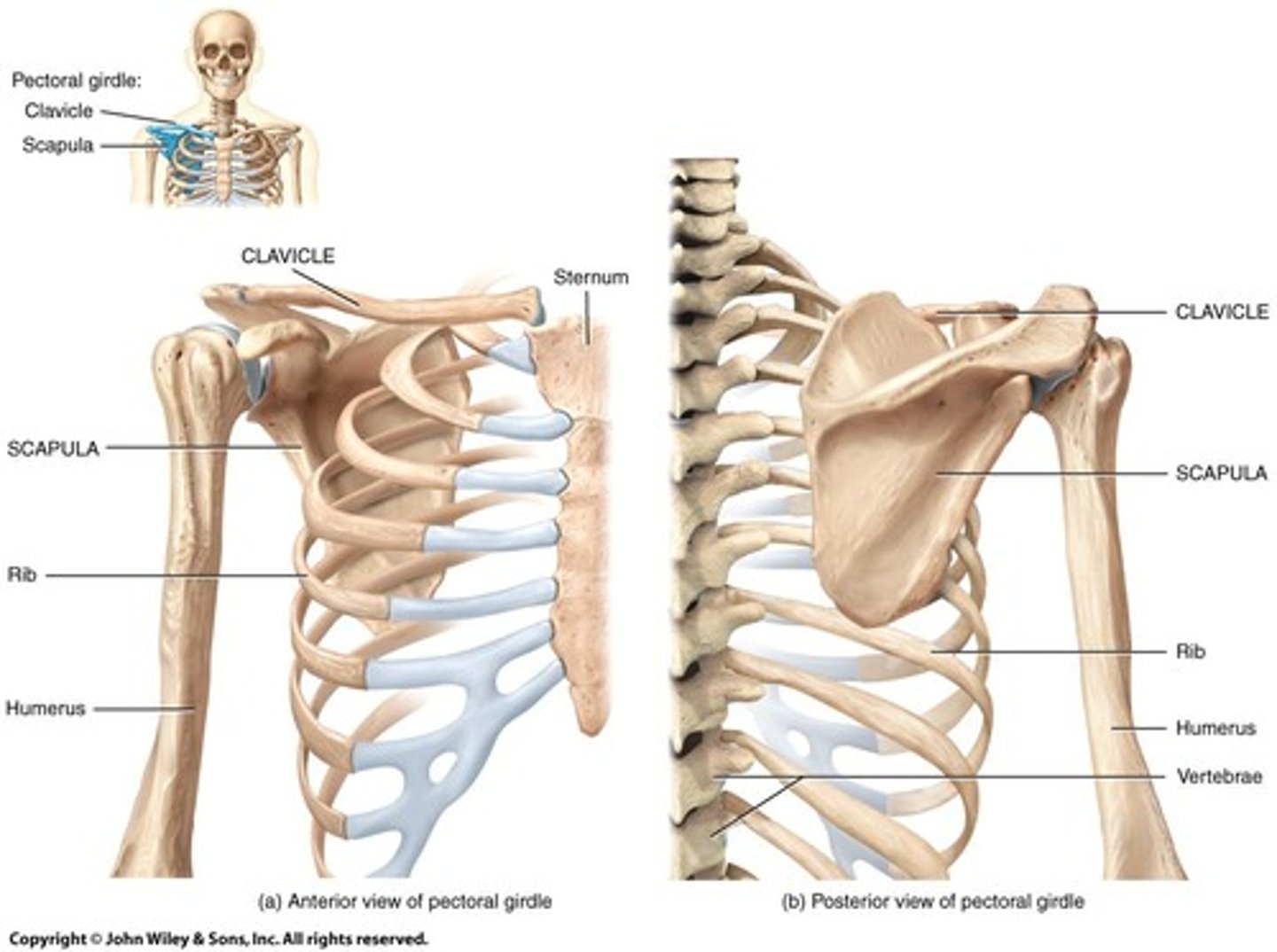
Pectoral Girdle
Superior girdle connecting upper limbs to axial skeleton.
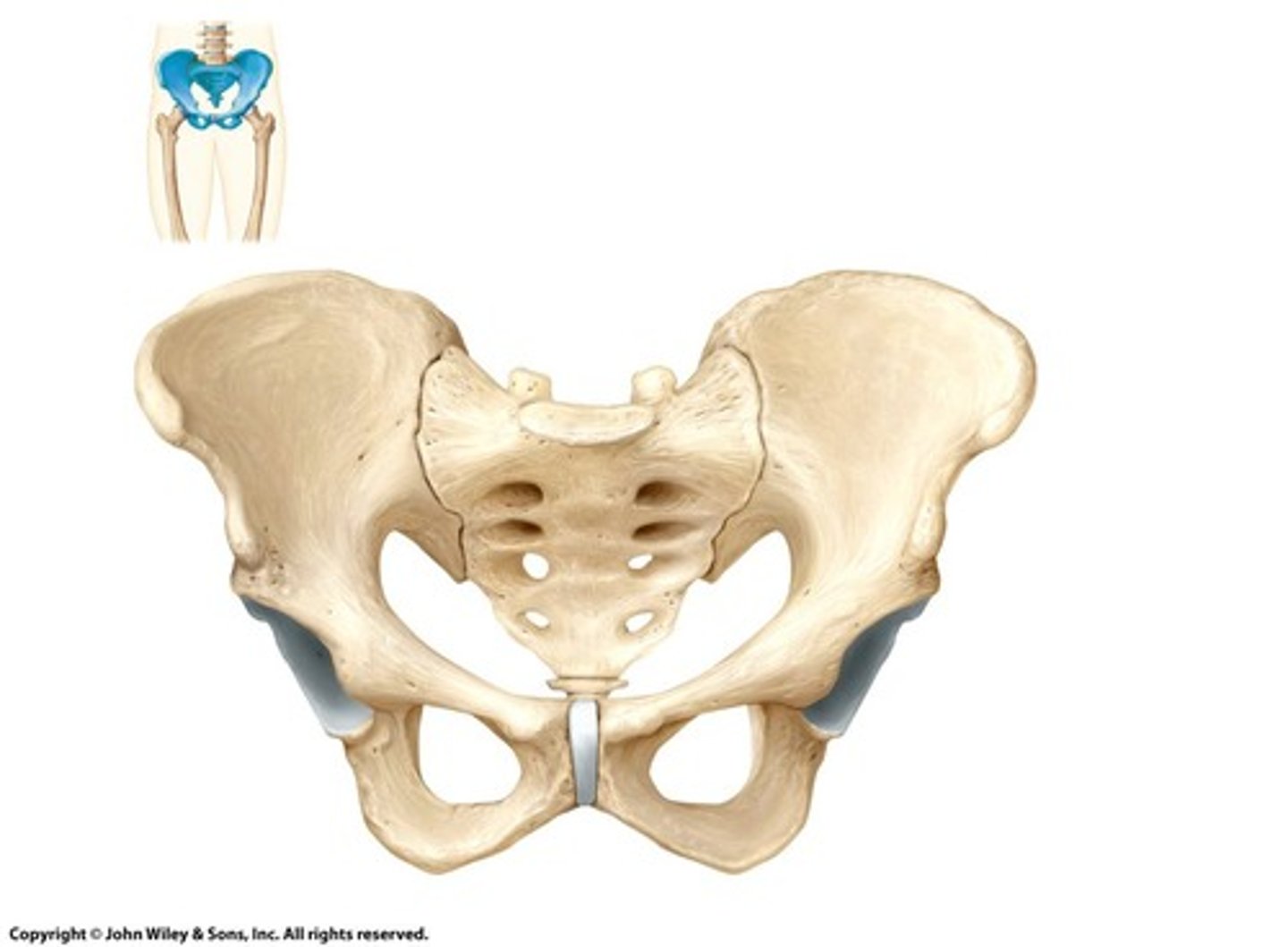
Pelvic Girdle
Inferior girdle connecting lower limbs to axial skeleton.
Humerus
Upper arm bone between shoulder and elbow.
Ulna
Forearm bone on the inner side of the arm.
Radius
Forearm bone on the outer side of the arm.
Carpals
Proximal bones of the hand, forming the wrist.
Metacarpals
Hand bones between carpals and phalanges.
Phalanges
Distal bones of the fingers.
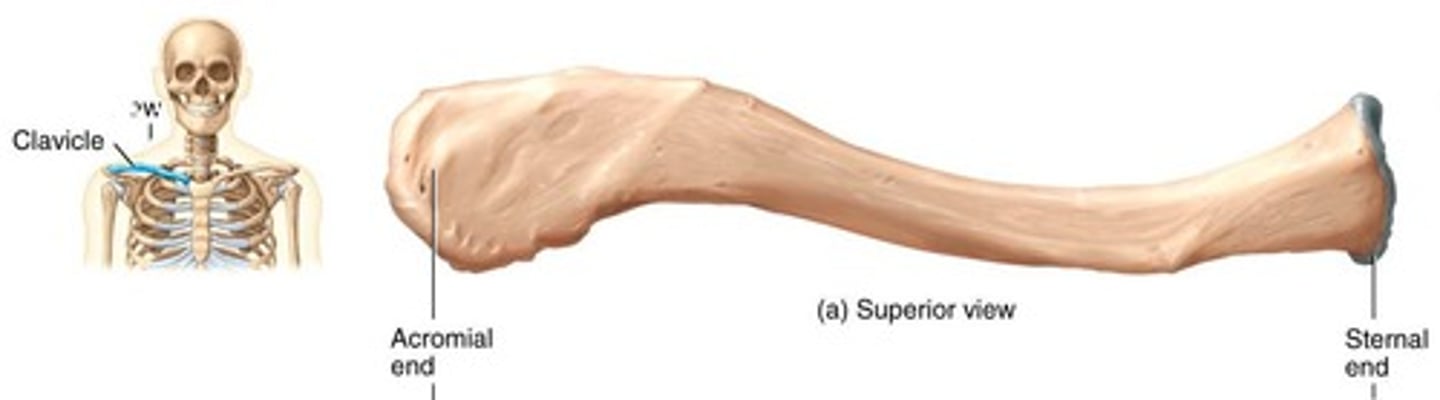
Clavicle
S-shaped bone connecting sternum and scapula.
Scapula
Shoulder blade, does not articulate with spine.
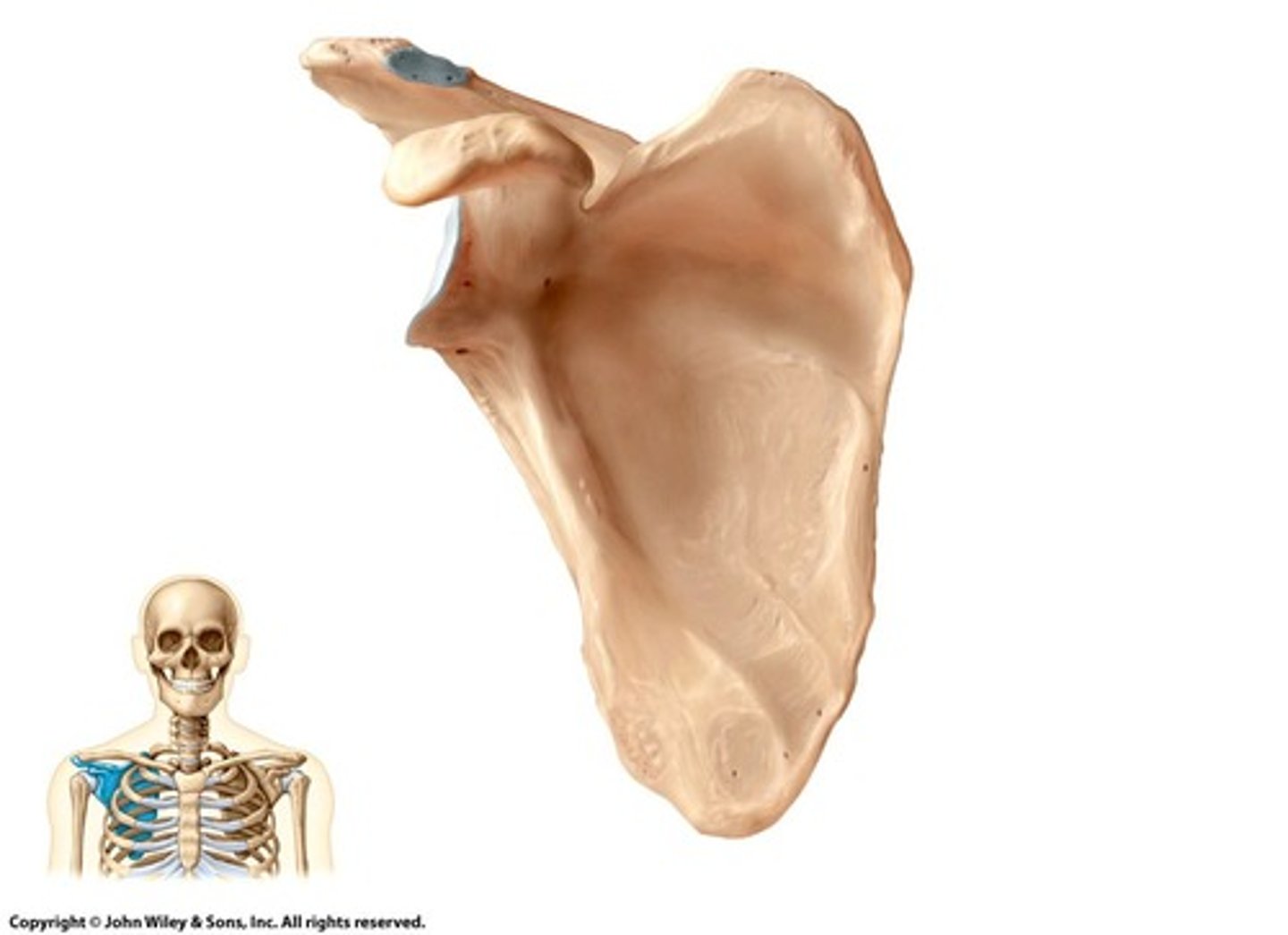
Glenoid Cavity
Ball joint region for humerus articulation.
Acromion
Scapula surface articulating with the clavicle.
Coracoid Process
Scapula marking for muscle attachment and humerus articulation.
Subscapular Fossa
Scapula area for muscle attachment in pectoral region.
Condyles
Depressions at bone ends facilitating articulation.
Epicondyles
Projections for ligament attachment at articulation sites.
Head
Bone projection facilitating articulation with depressions.
Tuberosity
Attachment site for tendons and ligaments.
Trochanters
Muscle attachment sites via tendons on bones.
Tubercle
Distinctive bone marking, may indicate muscle attachment.
Intertubercular Groove
Humerus groove for biceps brachii tendon attachment.
Major Groove
Pathway for blood vessels and nerves in limbs.
Condyles
Articulating regions at distal humerus ends.
Fossas
Depressions for blood vessels and nerves on humerus.
Greater Tubercle
Proximal attachment site for triceps muscle.
Olecranon Fossa
Depression for vessels and nerves at elbow joint.
Olecranon
Elbow bone projection on the ulna.
Radial Rotation
Movement of thumb from outside to inside body.
Radius
Lateral bone of the forearm in anatomic position.
Ulna
Medial bone of the forearm in anatomic position.
Bony Elbow
Olecranon process of the ulna.
Radial Tuberosity
Attachment site for biceps muscle on radius.
Coronoid Process
Proximal articulating region of the ulna.
Interosseous Membrane
Connective tissue between radius and ulna.
Styloid Process
Projection at the distal end of the radius.
Carpus
Wrist composed of 8 carpal bones.
Metacarpals
Five bones forming the palm of the hand.
Phalanges
Fourteen bones forming the fingers.
Proximal Phalanx
First phalanx in each finger except thumb.
Middle Phalanx
Second phalanx in fingers II-V.
Distal Phalanx
Final phalanx in each finger.
Carpometacarpal Joints
Joints between carpal and metacarpal bones.
Metacarpophalangeal Joints
Joints between metacarpals and phalanges.
Interphalangeal Joints
Joints between phalanges in fingers.
1st Metacarpal
Lateral bone of the hand's base.
5th Metacarpal
Medial bone of the hand's base.
Gluteal Region
Area from pelvis to hip joint.
Thigh
Segment between hip and knee joint.
Leg
Segment between knee and ankle.
Foot
Distal part of the lower limb.
Sacroiliac Joint
Connects pelvic bone to sacrum.
Pelvic Girdle
Structure formed by paired hip bones.
Os Coxae
Hip bones composed of three fused bones.
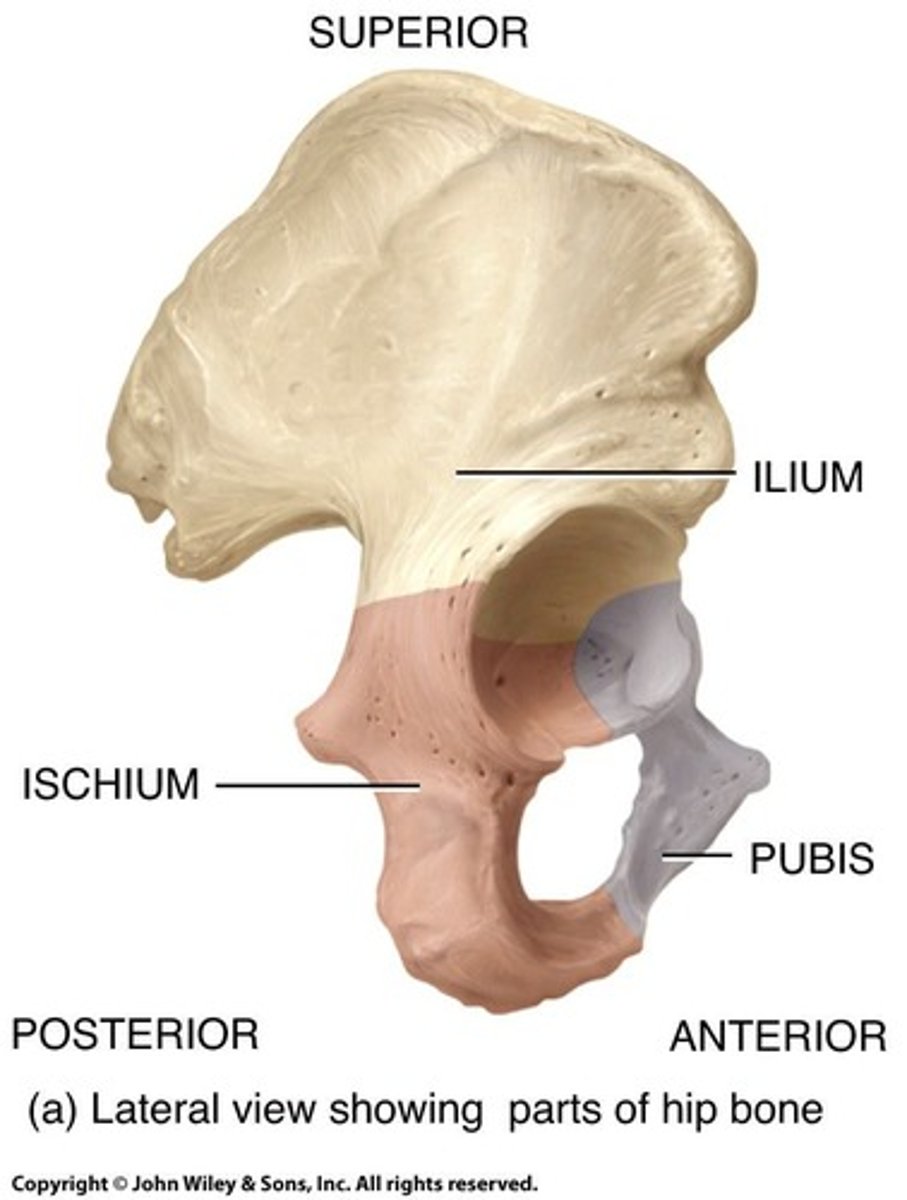
Ilium
Uppermost bone of the hip structure.
Ischium
Lower bone forming the hip structure.
Pubis
Anterior bone of the hip structure.
Iliac Crest
Top edge of the ilium bone.
Pelvic Brim
Line separating true and false pelvis.
False Pelvis
Wider area above pelvic brim.
True Pelvis
Bony cavity containing reproductive organs.
Pubic Symphysis
Cartilaginous joint between hip bones.
Male Pelvis
Larger, heavier, and more narrow than female.
Female Pelvis
Wider opening for childbirth assistance.
Pelvic Outlet
Inferior opening of the pelvic cavity.
Femur
Longest, heaviest bone in the body.
Acetabulum
Socket of hip bone for femur head.
Femoral Condyles
Articulate with tibia to form knee joint.
Patella
Knee cap; only named sesamoid bone.
Greater Trochanter
Large projection for muscle attachment on femur.
Lesser Trochanter
Smaller projection for muscle attachment on femur.
Neck of Femur
Connects femur head to diaphysis.
Distal Epicondyles
Projections for knee muscle attachment on femur.
Lateral Epicondyle
Outer projection above femoral condyles.
Medial Epicondyle
Inner projection above femoral condyles.
Tibia
Largest leg bone; weight-bearing.
Fibula
Smaller leg bone; non-weight bearing.
Condyles
Rounded ends of bones for articulation.
Talus
Ankle bone articulating with tibia and fibula.
Lateral Malleolus
Projection of fibula at ankle.
Medial Malleolus
Projection of tibia at ankle.
Tibial Tuberosity
Protrusion for patellar ligament attachment.
Calcaneus
Largest tarsal bone; forms heel.
Metatarsals
Long bones in the foot, five total.
Phalanges
Toe bones; three per toe except hallux.
Tarsal Bones
Seven bones forming the ankle.
Foot Arches
Support body weight; provide leverage.
Flatfeet
Condition where foot arches decrease.
MCL (Medial Collateral Ligament)
Connects femur to tibia; common injury site.
Interosseous Membrane
Connective tissue joining tibia and fibula.
Patellofemoral Joint
Joint between patella and femur; enhances leverage.