Chest Semiotics Past Papers
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is the Levine scale used for?
a. Pain
b. Heart murmurs
c. Heart sounds
d. Respiratory distress
b. Heart murmurs
When is mitral stenosis best heard?
a. Left decubitus position
b. Bent forward
c. With the diaphragm of the stethoscope
d. With the patient standing
a. Left decubitus position
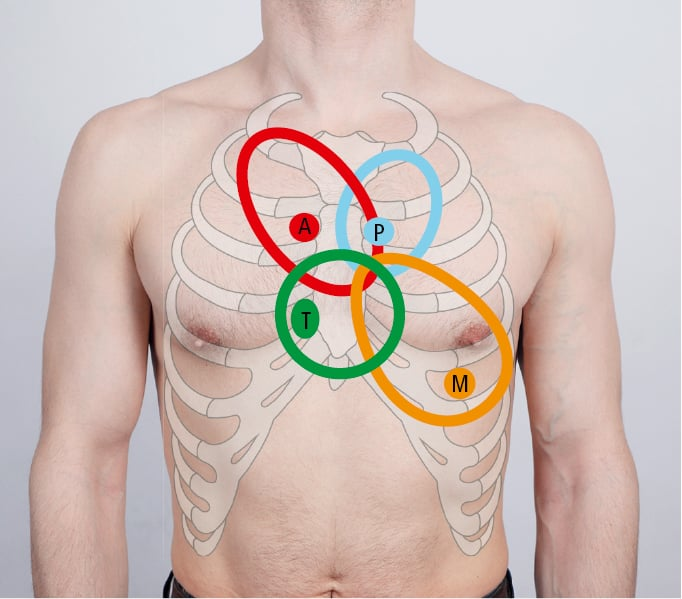
The aortic area is at the level of:
a. Apex of the heart
b. Lower left sternal border
c. 2nd left intercostal space
d. 2nd right intercostal space
d. 2nd right intercostal space
It is a normal breath sound:
a. Bronchial breathing
b. Wheezes
c. Pleural rubs
d. Crackles
a. Bronchial breathing
In lobar pneumonia:
a. Crackles are never heard
b. Resonant notes at percussion are typical
c. Transmitted voice sounds cannot be heard
d. Hypophonetic notes can be heard at percussion
d. Hypophonetic notes can be heard at percussion
Wheezes are typical of:
a. Pneumothorax
b. Pleural effusion
c. Asthma
d. None of the others are correct
c. Asthma
A murmur from mitral regurgitation:
a. Can be better heard on the pulmonic area
b. Is located in diastole
c. Is located in systole
d. The shape is usually crescendo-decrescendo
c. Is located in systole
With indirect percussion:
a. The clinician using a stethoscope discerns differences in sounds created by the plexor finger
b. The plexor (i.e. tapping) finger strikes against the patient’s body
c. The plexor finger strikes a pleximeter which is typically the middle finger of the non-dominant hand placed against the patient’s body
d. None of the above
c. The plexor finger strikes a pleximeter which is typically the middle finger of the non-dominant hand placed against the patient’s body
The crackles are:
a. Sounds originating from the upper respiratory system
b. Pleural sounds
c. Can be heard only using the bell of the stethoscope
d. Lung adventitious sounds
d. Lung adventitious sounds
Tactile vocal fremitus:
a. Can be detected by placing the ulnar aspect of both hands against the side of the chest
b. Requires the patient to speak in a low tone
c. Is absent in normal lungs
d. Is better detected with the fingertips
a. Can be detected by placing the ulnar aspect of both hands against the side of the chest
Mitral stenosis:
a. Associated with a systolic murmur
b. Best heard with the diaphragm
c. Usually limited to the apex
d. Characterized by a fixed split S2
c. Usually limited to the apex
Semeiotics of pneumothorax is characterized by:
a. Shifted mediastinum
b. Hyperresonant percussion notes
c. No sounds at auscultation
d. Decreased tactile fremitus
c. No sounds at auscultation
A characteristic feature of asthma:
a. Reversible airflow obstruction and airways hyperactivity
b. Fixed bronchial obstruction
c. Pleural thickening
d. Decreased lung compliance
a. Reversible airflow obstruction and airways hyperactivity
What is the wrong statement about S4 and S3 sounds?
a. Can be heard during systole
b. S4 is associated with atrial contraction
c. S3 can occur with heart failure
d. Both are low-pitched sounds
a. Can be heard during systole
What does an elevated jugular venous pressure typically indicate?
a. Hypovolemia
b. Right-sided heart failure
c. Pulmonary embolism
d. Peripheral artery disease
b. Right-sided heart failure
The JVP is best assessed with the patient positioned at:
a. 30 to 45 degrees
b. Flat, lying completely supine
c. Sitting upright at 90 degrees
d. Prone
a. 30 to 45 degrees
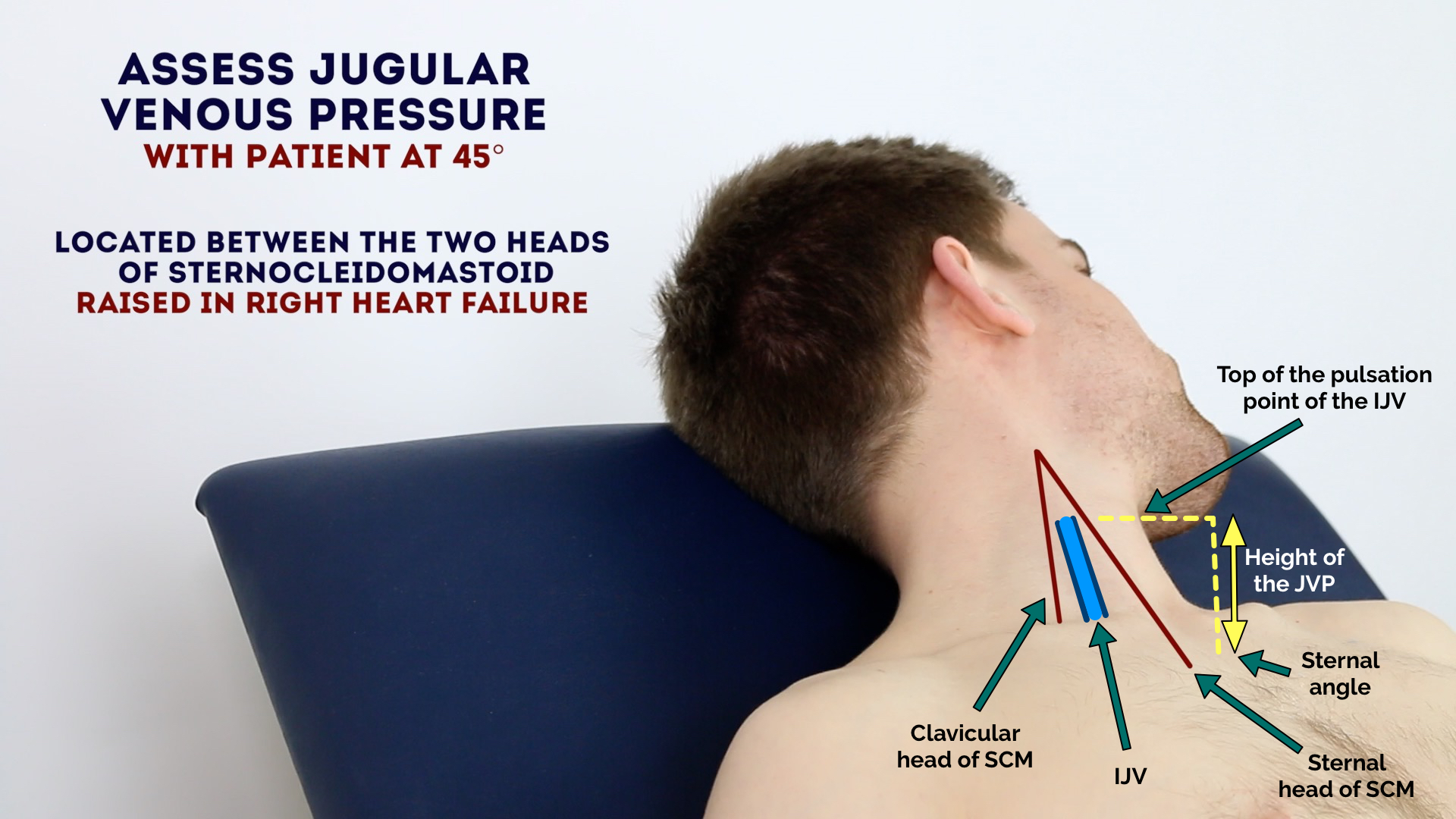
Which of the following is NOT true about the JVP?
a. It reflects right atrial pressure
b. It is elevated in conditions like tricuspid stenosis
c. It is directly palpable
d. It decreases during inspiration
c. It is directly palpable
Crackles are most commonly associated with:
a. Pneumothorax
b. Pulmonary edema
c. Asthma
d. Pleural effusion
b. Pulmonary edema
Which of the following statements about crackles is TRUE?
a. Crackles are heard over the pleura
b. Crackles are high-pitched, continuous sounds
c. Crackles can be fine or coarse
d. Crackles disappear after coughing
c. Crackles can be fine or coarse
Fine crackles are typically associated with:
a. Interstitial lung diseases
b. Chronic bronchitis
c. Lobar pneumonia
d. Pleural effusion
a. Interstitial lung diseases
Respiratory Distress Syndrome is commonly seen in:
a. Adults with asthma
b. Premature neonates
c. Children with viral pneumonia
d. Patients with pneumothorax
b. Premature neonates
The primary cause of neonatal RDS is:
a. Hypovolemia
b. Lung infection
c. Deficiency of surfactant
d. Congenital lung malformation
c. Deficiency of surfactant
Which of the following is a key feature of Respiratory Distress Syndrome?
a. Hyperinflated lungs on imaging
b. Ground-glass appearance on X-ray
c. Tracheal deviation
d. Pleural effusion
b. Ground-glass appearance on X-ray
Tactile vocal fremitus is increased in:
a. Pleural effusion
b. Consolidation
c. Pneumothorax
d. Emphysema
b. Consolidation
A decrease in vocal fremitus is most commonly seen in:
a. Pleural effusion
b. Lobar pneumonia
c. Pulmonary edema
d. Bronchitis
a. Pleural effusion
A murmur from mitral regurgitation:
a. The shape is usually crescendo-decrescendo
b. The sound is high-pitched
c. Is best heard at the upper sternal border
d. Radiates to the left axilla
d. Radiates to the left axilla
Clubbing of the fingers is caused by:
a. Interstitial lung disease
b. Asthma
c. Pneumonia
d. Bronchitis
a. Interstitial lung disease
In physical examination, the:
a. Palmar surface of the fingers is used for palpation
b. Diaphragm of the stethoscope is used to hear only for the high-frequency sounds
c. Bell of the stethoscope is used to hear both low and high-frequency sounds
d. Both diaphragm and bell can detect only low-frequency sounds
a. Palmar surface of the fingers is used for palpation
Characteristics of dyspnea include:
a. Use of accessory muscles for breathing
b. Sensation of inadequate breathing when exerting
c. Audible wheezing with every breath
d. Decreased respiratory rate
b. Sensation of inadequate breathing when exerting
The internal jugular vein pressure is an indicator of:
a. Pulmonary hypertension
b. Pericardial effusion
c. Aortic stenosis
d. Left-sided heart failure
a. Pulmonary hypertension
Semiotics of pneumothorax include:
a. Decreased tactile fremitus
b. Decreased breath sounds and hyper-resonance
c. Dullness to percussion
d. Both a and b
c. Both a and b